Topic 7 - Atomic, Nuclear, and Particle Physics
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Definitions for Topic 7 - Atomic, Nuclear, and Particle Physics: 7.1 - Discrete energy and radioactivity 7.2 - Nuclear reactions 7.3 - The structure of matter
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Energy level
Electrons can be in different orbits around the nucleus, these different orbits are called energy levels
Quantised

Radioactive decay
The process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy through radiation, the nucleus becomes more stable
Random and spontaneous

(Atomic) nucleus
The small, dense region at the center of an atom
Nucleon
A component of an atomic nucleus, so either a portion or a neutron
Nuclide
A species of an atom with a specific number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus
Isotope
Same element with the same number of protons, but a different number of neutrons
Background count
Naturally occurring radioactive decay is measured by a counter
Half-life
The time it takes for half of the parent nuclides in a sample to decay
Unified atomic mass unit
One-twelfth of the rest mass of an unbound, neutral carbon-12 atom in its nuclear and electronic ground state
1.661*10^-27 kg
Nuclear binding energy
The energy required to completely separate the nucleons of a nucleus
Quark confinement
That quarks do not exist on their own.
Always found in groups, within hadrons (two or three quarks)
Three quarks -> baryon; a quark and an antiquark -> meson
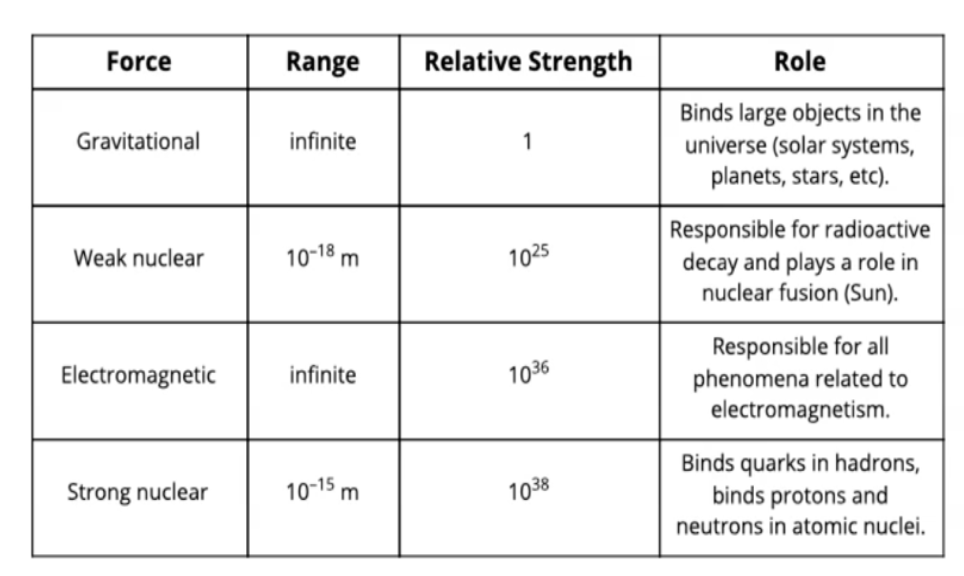
Strong nuclear force
Higgs boson
Predicted before it was observed, observed in 2012
Part of the Standard Model
Other particles gain mass by interacting with the Higgs field
No charge