Botany EXAM #1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CHPT 1-5
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
1
New cards
What is Botany?
scientific study of plants
2
New cards
What was the early atmosphere of earth like: aerobic or anaerobic?
anaerobic
3
New cards
What is Scientific Method? (4 Basic Tenets)
Development started before the 1400s
1\. Source of information
2\. Phenomena that can be studied
3\. Constancy and universality
4\. Based on skepticism
1\. Source of information
2\. Phenomena that can be studied
3\. Constancy and universality
4\. Based on skepticism
4
New cards
What are the major steps of the Scientific Method?
\
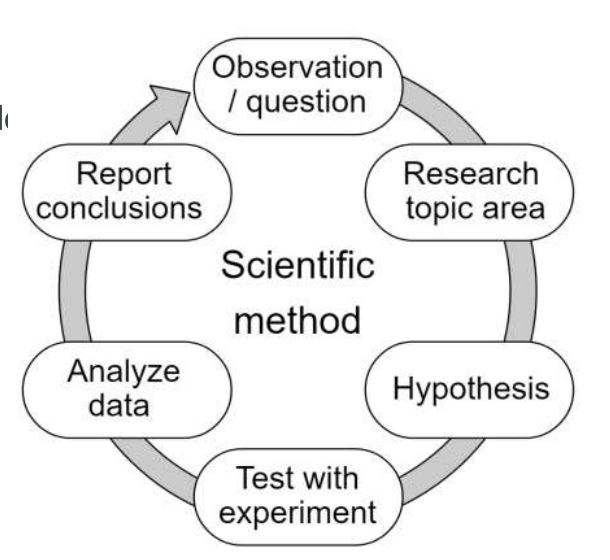
5
New cards
What is the structure of a hypothesis? (be able to Formulate One)
**must make predictions that can be tested.**
**▪ It must be consistent with further observations and experiments.**
**▪ It must be able to predict the results of future experiments.**
Format: IF THEN STATEMENT
**▪ It must be consistent with further observations and experiments.**
**▪ It must be able to predict the results of future experiments.**
Format: IF THEN STATEMENT
6
New cards
What is a Null Hypothesis? (be able to Formulate One)
is a hypothesis that has no statistical significance or based on observations of chance
7
New cards
What are the major characteristics of life?
Both Prokaryotic and Eukaryotes
5 Characteristics:
1. organized
2. energy
3. internal constancy
4. reproduction, growth, and development
5. evolution
5 Characteristics:
1. organized
2. energy
3. internal constancy
4. reproduction, growth, and development
5. evolution
8
New cards
What are Plant (and the Major Characteristics)?
not all biologists agree
Most have green leaves, stems, roots, and flowers, although there are exceptions
Most have green leaves, stems, roots, and flowers, although there are exceptions
9
New cards
What is Heterotrophy? What is Autotrophy? How are they different?
Heterotrophy- an organism that depends on other organisms for energy and nutrients
Autotrophy- an organism that produces their own energy and nutrient by using other sources of carbon (consists mainly of plants)
Autotrophy- an organism that produces their own energy and nutrient by using other sources of carbon (consists mainly of plants)
10
New cards
When are the major evolutionary steps in plants occur?
Plants reproduce and pass their genes/information to the next generation
This information can be changed through; mutation changes, natural selection (environment…)
This information can be changed through; mutation changes, natural selection (environment…)
11
New cards
What are the Major atmospheric components that are a direct result of photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the central metabolism (how plants acquire energy)
plants use Carbon Dioxide and Water to produce Carbohydrates and Oxygen as a secondary product.
plants use Carbon Dioxide and Water to produce Carbohydrates and Oxygen as a secondary product.
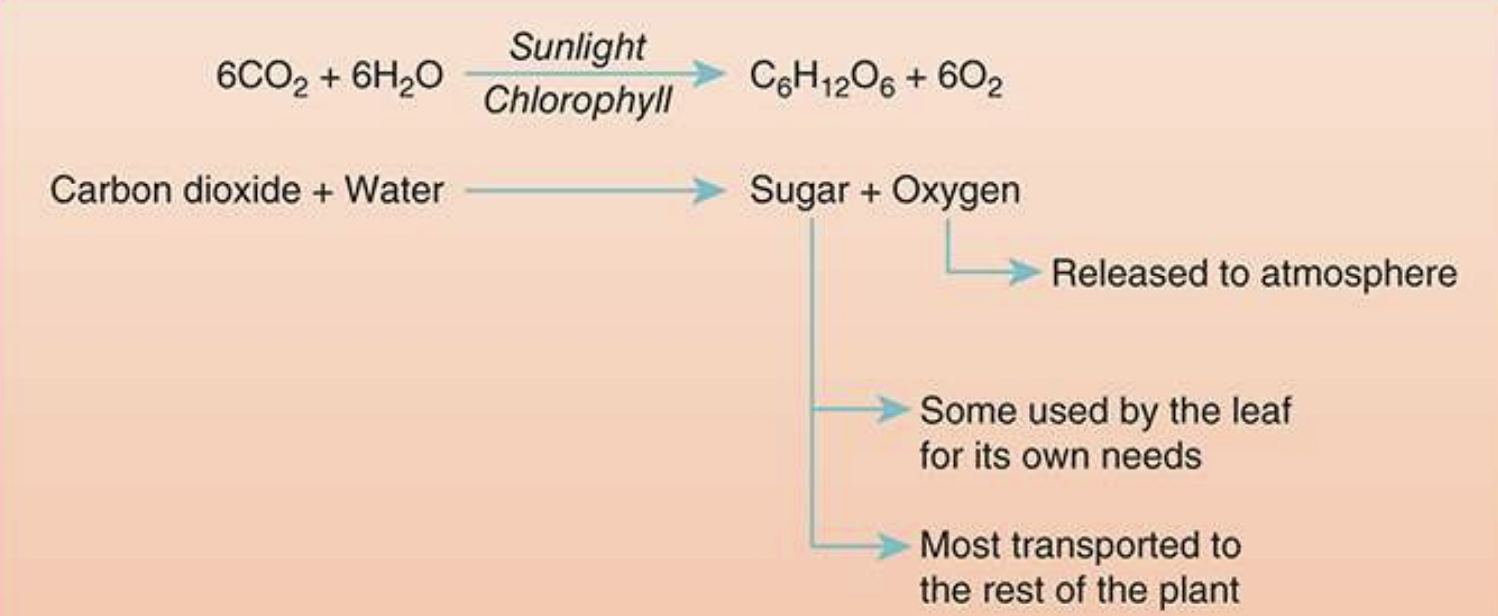
12
New cards
What are the Function of Pants that people use?
Oxygen
Shelter
Food
Clothes
…
Shelter
Food
Clothes
…
13
New cards
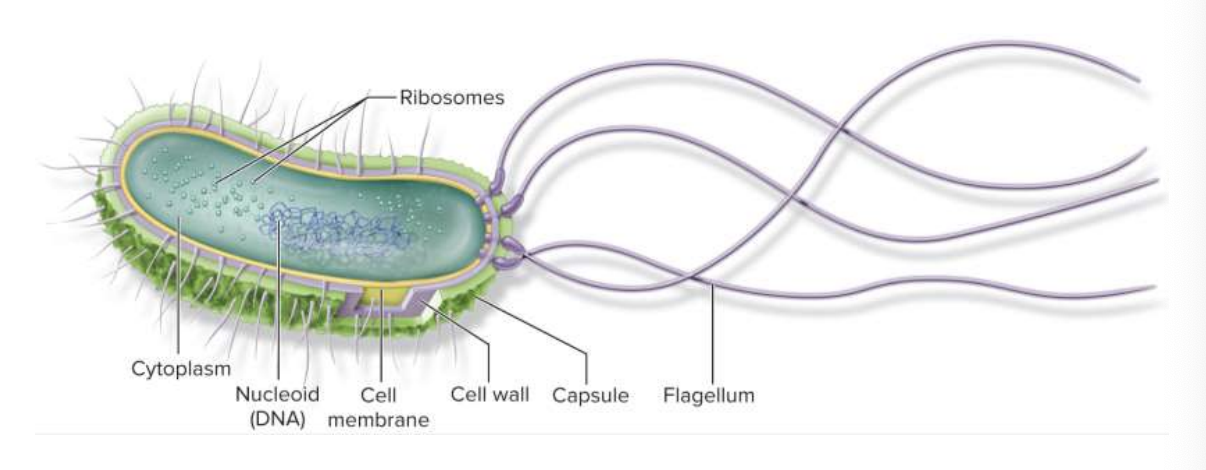
What is a Prokaryotes?
Simplest (ancient most) form of life. Ribosomes and DNA free float within the cell.
14
New cards
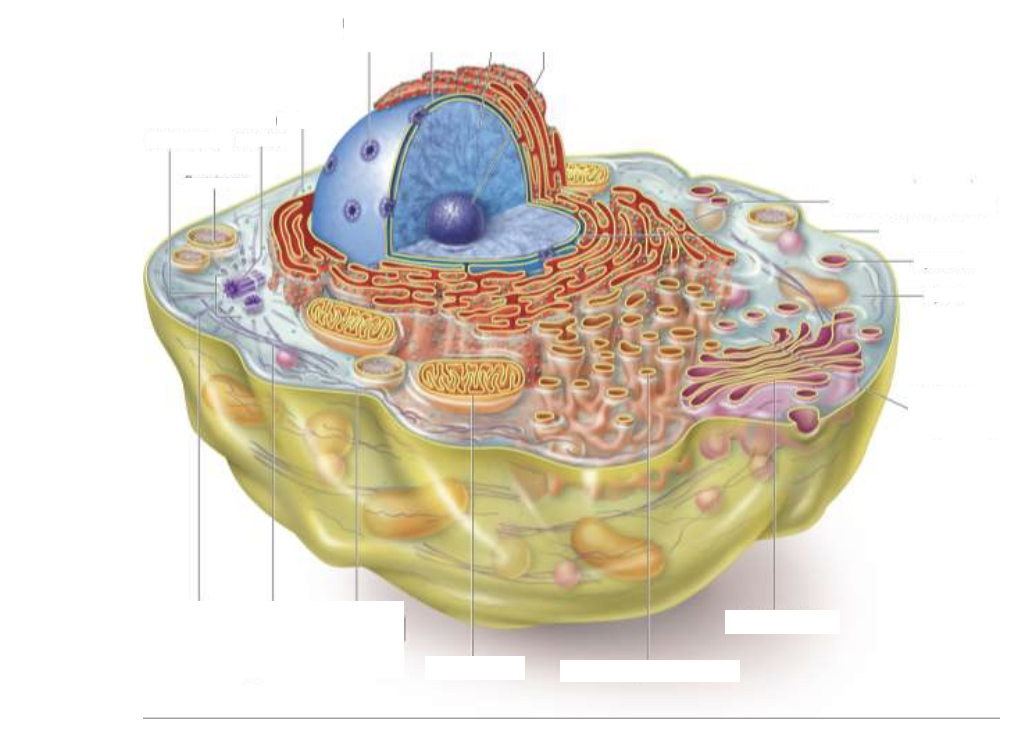
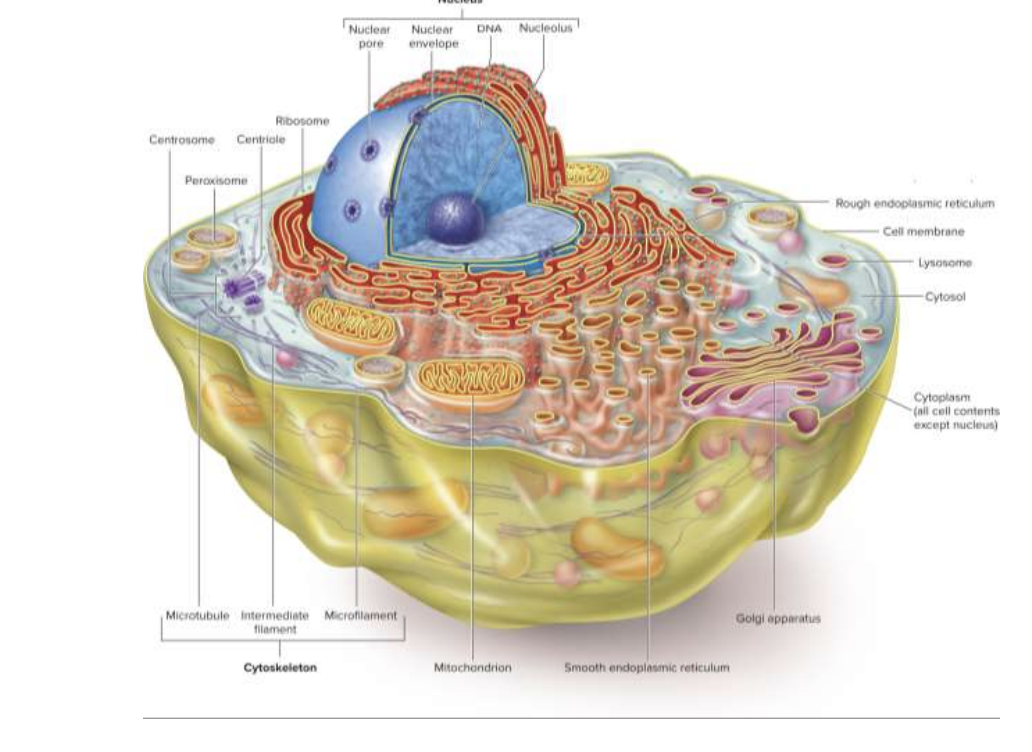
What is a Eukaryotes?
Evolved from Prokaryotes
Larger and more complex, with organelles
Larger and more complex, with organelles
15
New cards
How are Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes different?
Prokaryotes lack nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, found in Bacteria and Archaea
Eukaryotes possess a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, found in Plants, Animals, Fungi, and Protists
Eukaryotes possess a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, found in Plants, Animals, Fungi, and Protists
16
New cards
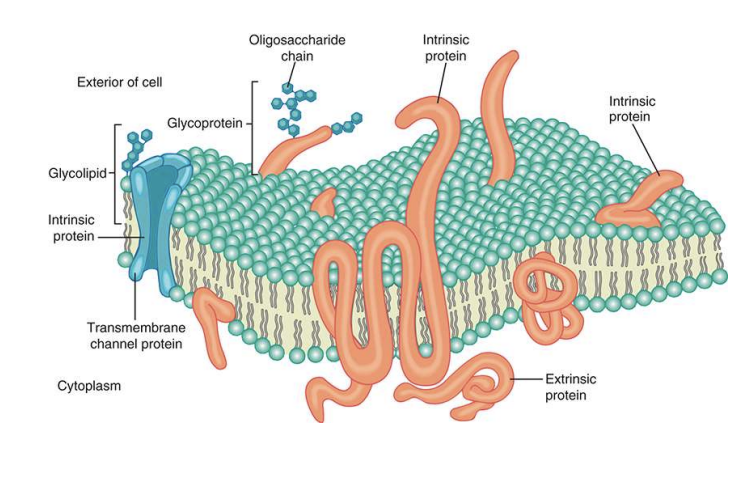
What are the components of the Cell Membrane? (what do each part do?)
Organelles involved in Protein Production, Protein Localization, and Cellular Digestion. The Cytoskeleton of the cell
Functions:
1. Forms a barrier between the cell and the outside world
2. Regulates passage of substances in and out of the cell; helps maintain homeostasis
composition:
* Composed of a Phospholipid Bilayer
* sugar molecules \[used for cell communication\]
* cholesterol \[mantains the right level of fluidity'\]
* proteins \[transports proteins, enzymes, recognition of proteins, adhesion of proteins, and protein receptors\]
* microfilament (cytoskeleton)
Functions:
1. Forms a barrier between the cell and the outside world
2. Regulates passage of substances in and out of the cell; helps maintain homeostasis
composition:
* Composed of a Phospholipid Bilayer
* sugar molecules \[used for cell communication\]
* cholesterol \[mantains the right level of fluidity'\]
* proteins \[transports proteins, enzymes, recognition of proteins, adhesion of proteins, and protein receptors\]
* microfilament (cytoskeleton)
![Organelles involved in Protein Production, Protein Localization, and Cellular Digestion. The Cytoskeleton of the cell
Functions:
1. Forms a barrier between the cell and the outside world
2. Regulates passage of substances in and out of the cell; helps maintain homeostasis
composition:
* Composed of a Phospholipid Bilayer
* sugar molecules \[used for cell communication\]
* cholesterol \[mantains the right level of fluidity'\]
* proteins \[transports proteins, enzymes, recognition of proteins, adhesion of proteins, and protein receptors\]
* microfilament (cytoskeleton)](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/bb9674cf72614e129bae8b2610ffa1eb.jpeg)
17
New cards
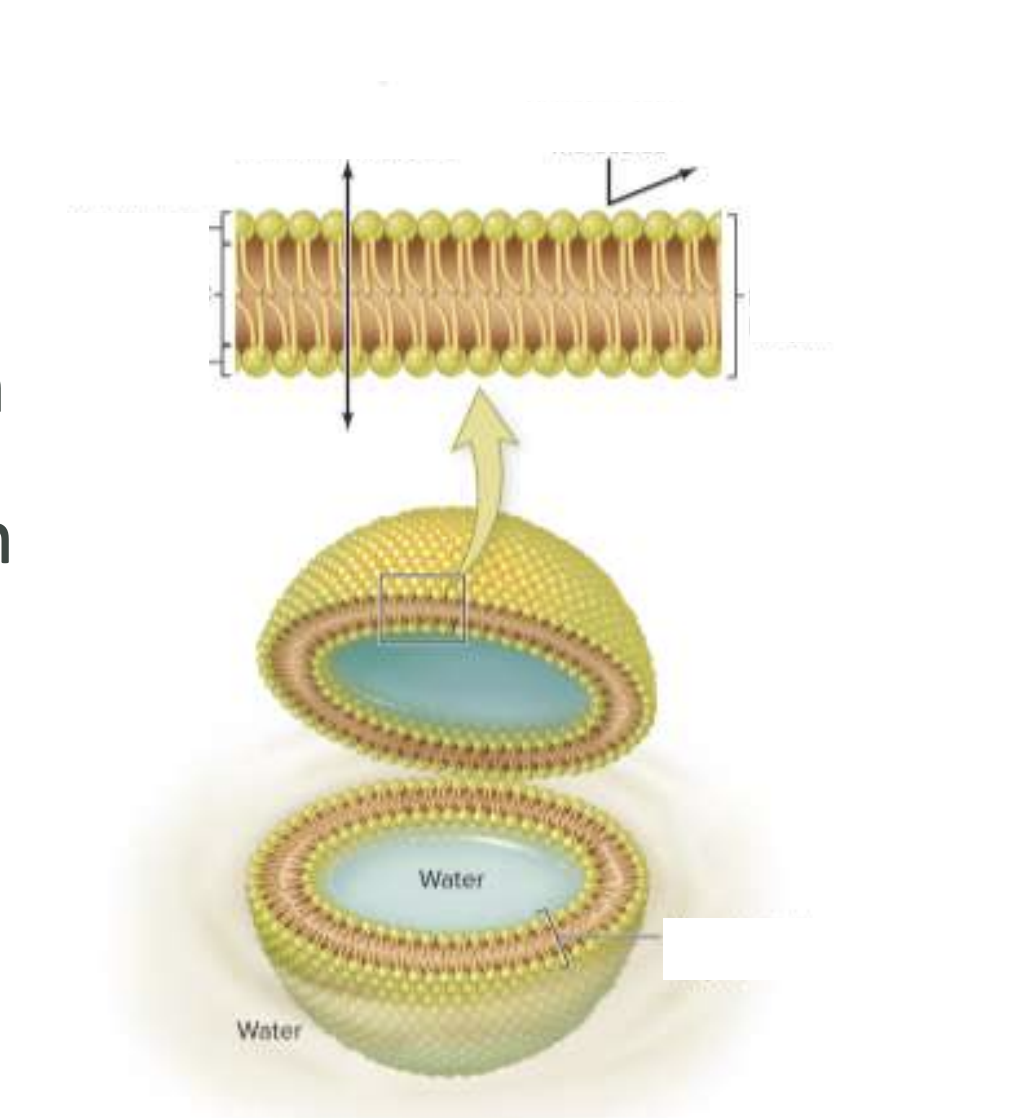
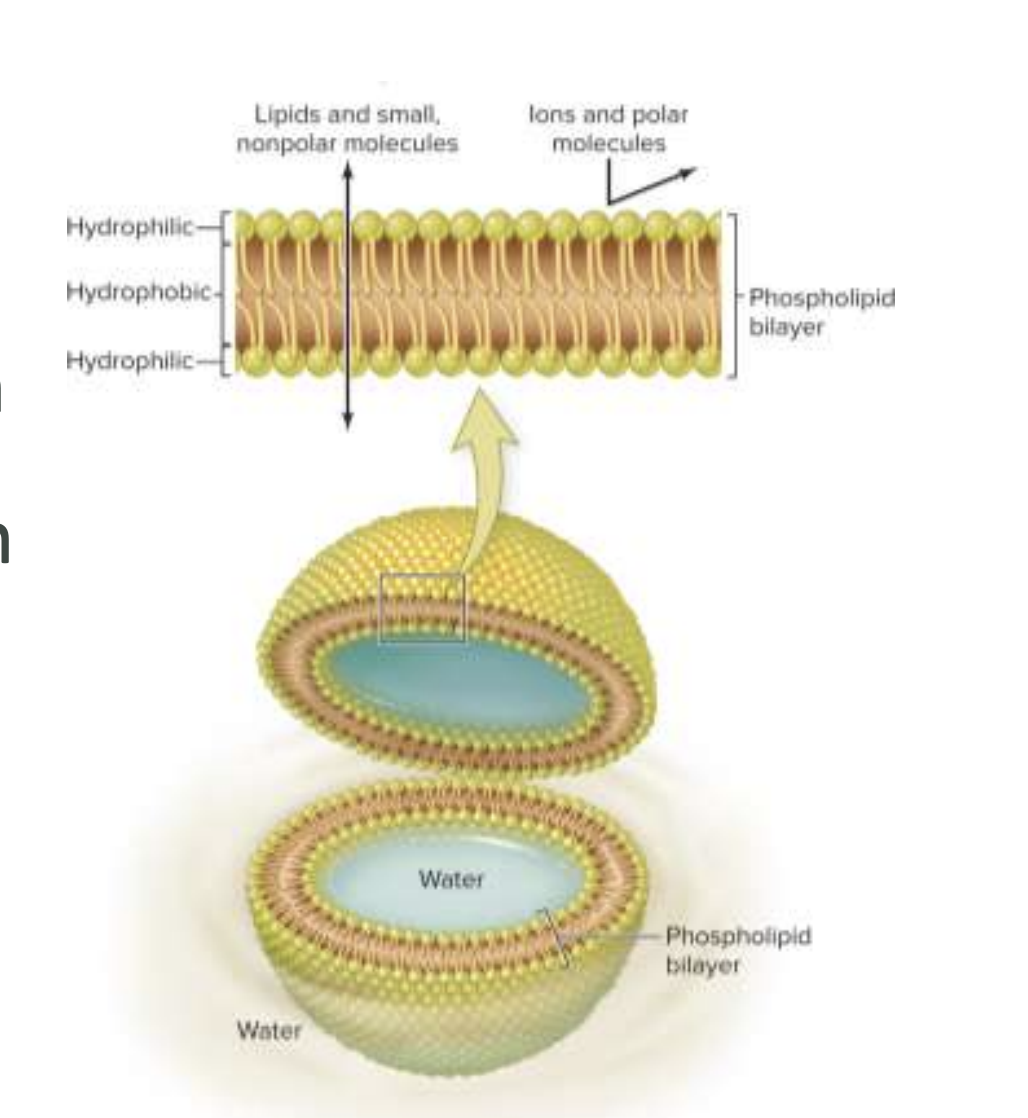
What is a Phospholipid Bilayer? (LABEL)
18
New cards
what are the parts of the Phospholipids? Hydrophilic or Hydrophobic?
Head= Hydrophilic
Tails= Hydrophobic
Tails= Hydrophobic
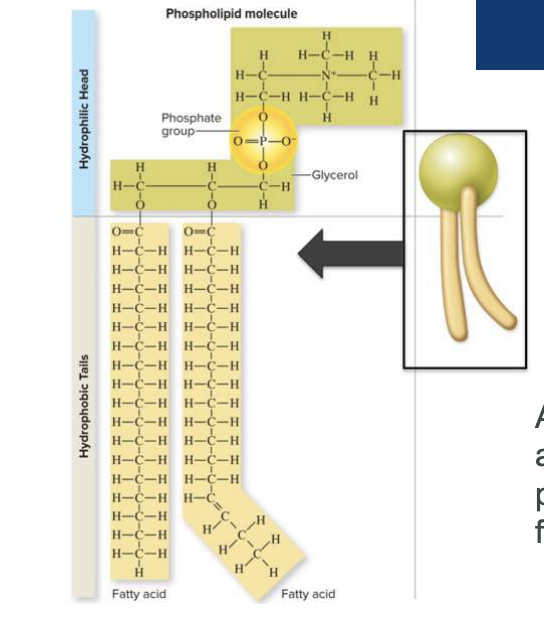
19
New cards
What are the “Jobs” of the Cell Membrane?
Growth (Membrane Fusion and Vesicle Formation)
Permeability
Dynamic
Transportation (Vesicles, Exocytosis, and Endocytosis)
Facilitated diffusion
Active Transport
Permeability
Dynamic
Transportation (Vesicles, Exocytosis, and Endocytosis)
Facilitated diffusion
Active Transport
20
New cards
What are the differences between Plant and Animal Cells?
Cell wall (plants) vs no cell wall (animals)
one big vacuole (plants) vs multiple Vacuoles (animals)
Plasmodesmata (plants) vs no Plasmodesmata (animals)
Photosynthesis (plants) vs no Photosynthesis (animals)
Chloroplasts (plants) vs Mitochondria (animals)
no Centrioles (plants) vs Centrioles (animals)
no Lysosomes (plants) vs Lysosomes (animals)
no Cilia/Flagella (plants) vs can have Cilia/Flagella (animals)
one big vacuole (plants) vs multiple Vacuoles (animals)
Plasmodesmata (plants) vs no Plasmodesmata (animals)
Photosynthesis (plants) vs no Photosynthesis (animals)
Chloroplasts (plants) vs Mitochondria (animals)
no Centrioles (plants) vs Centrioles (animals)
no Lysosomes (plants) vs Lysosomes (animals)
no Cilia/Flagella (plants) vs can have Cilia/Flagella (animals)
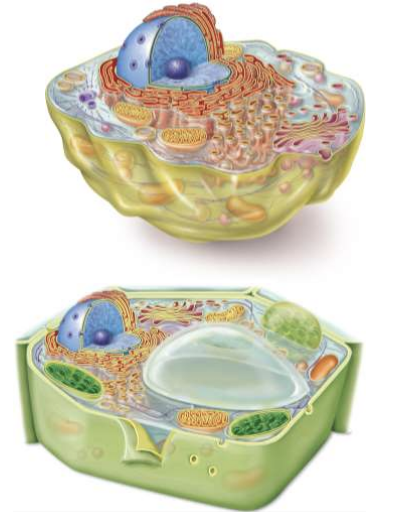
21
New cards
\
What is the Cell Theory?
What is the Cell Theory?
All living things are composed of one of more cell
cell is the most basic from of life
cell is the most basic from of life
22
New cards
What is the function of the Nucleus?
stores the organisms genetic information (DNA, Enzymes, Histones, Proteins, RNA, and Water)
surrounded by nuclear envelope (inner and outer membrane)
\
surrounded by nuclear envelope (inner and outer membrane)
\
23
New cards
What is the function of the Plasma Membrane?
selectively permeable that covers the protoplasm
(located inside of the cell walls)
(located inside of the cell walls)
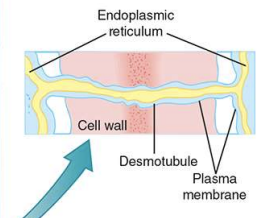
24
New cards
What is the function of the Mitochondria?
site of cellular respiration and ATP generation (powerhouse) in animal cells
double membrane: inside membrane folds to increase surface area
\
double membrane: inside membrane folds to increase surface area
\
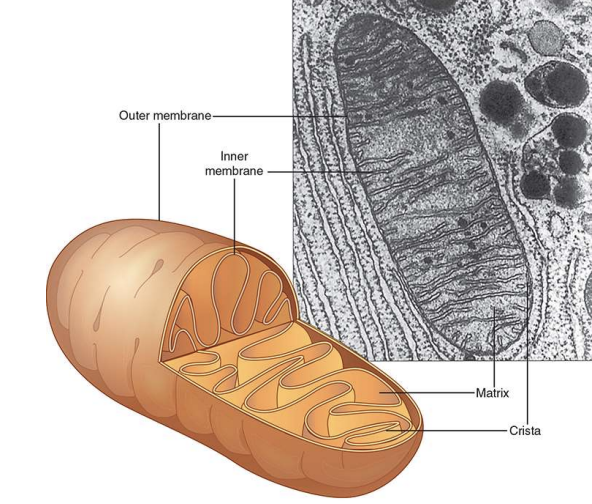
25
New cards
What is the function of the Chloroplast?
Responsible for photosynthesis
Contains Chlorophyll, stacks of Thylakoids/Grana, stroma (inner fluid)
Contains Chlorophyll, stacks of Thylakoids/Grana, stroma (inner fluid)
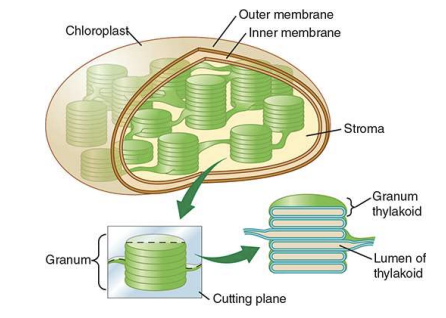
26
New cards
What is the function of the Vacuole?
single membrane
stores water, salt, crystals, starch, protein bodies, and other granules
used for cell enlargement
recycles monomers/impaired organelles by breaking them using digestive enzymes
stores water, salt, crystals, starch, protein bodies, and other granules
used for cell enlargement
recycles monomers/impaired organelles by breaking them using digestive enzymes
27
New cards
What is the function of the Endoplasmic Reticulum?
narrow tubes and sheets of membrane within the cytoplasm
manufactures and transports molecules
Rough (covered in Ribosomes)
Smooth (involved in lipid synthesis and membrane assembly)
manufactures and transports molecules
Rough (covered in Ribosomes)
Smooth (involved in lipid synthesis and membrane assembly)
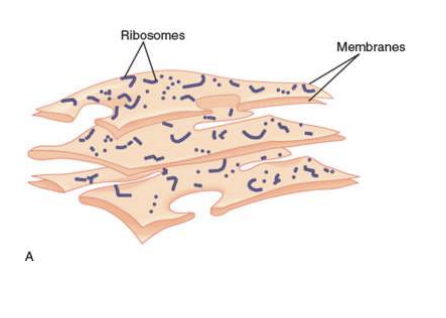
28
New cards
What is the function of the Golgi Apparatus?
sorts newly synthesized proteins and lipids, important for inner cell transportation, and secretion
29
New cards
What is the function of the Microtubules?
Structural elements of the cell that act as a cytoskeleton and separate chromatids during cell division
composed of two proteins
composed of two proteins
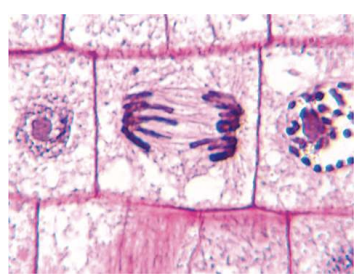
30
New cards
What is the function of the Flagella/Cillia?
microtubules that are used to move the cell
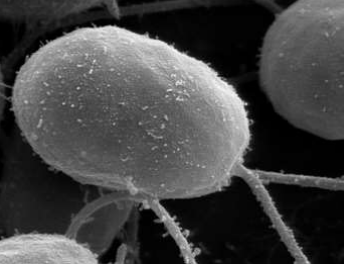
31
New cards
What is the function of the Cell Wall (Include the Major Layers)?
composed of cellulose and lignin
1. Primary cell wall
2. middle lamella
3. secondary cell wall
function:
* provide mechanical strength
* regulate volume
* prevent cell from bursting
* cell specialization
1. Primary cell wall
2. middle lamella
3. secondary cell wall
function:
* provide mechanical strength
* regulate volume
* prevent cell from bursting
* cell specialization
32
New cards
What is the function of the Plasmodesmata?
channels (to adjacent cells that pass through the cell wall) used to transport nutrients, biochemicals, plasma membrane, cytosol, or section of ER.
connect protoplast to create symplast
can be singular or in clusters called primary pit fields
connect protoplast to create symplast
can be singular or in clusters called primary pit fields
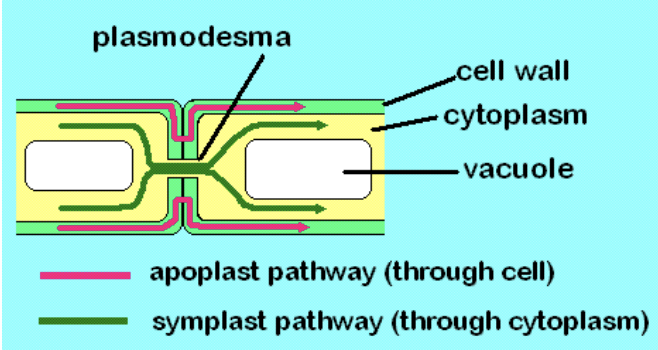
33
New cards
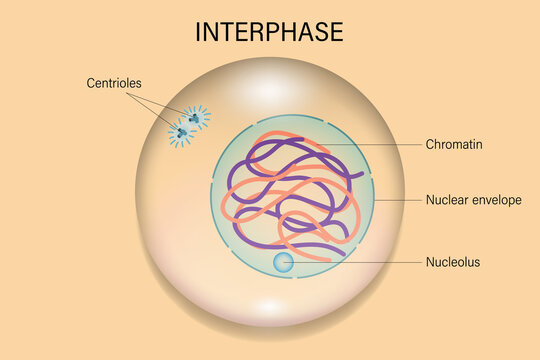
What happens in Interphase?
Growth phase consisting of: G1 phase, S phase, and G2 phase
resting period between cell division (longest stage)
resting period between cell division (longest stage)
34
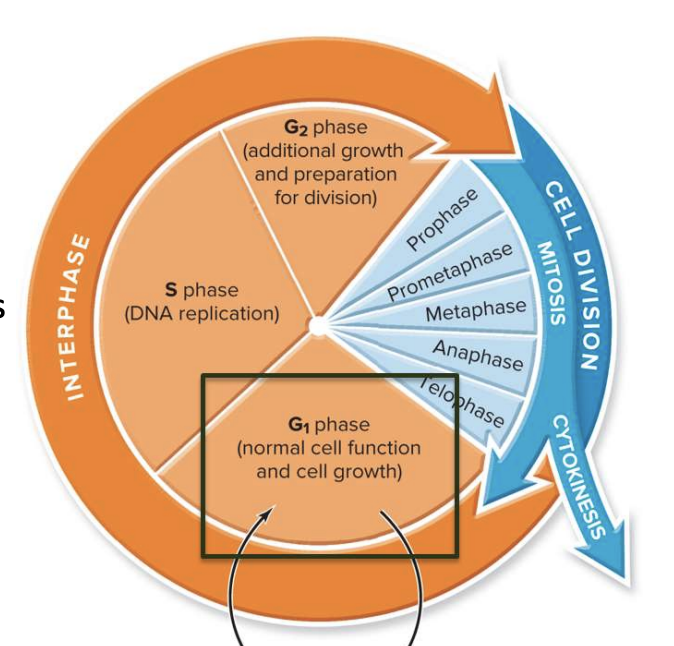
New cards
What happens in G1 phase?
Normal cell function and cell growth
* Protein synthesis
* normal metabolism
* nucleotides are synthesized
* longes part of cell cycle
* Protein synthesis
* normal metabolism
* nucleotides are synthesized
* longes part of cell cycle
35
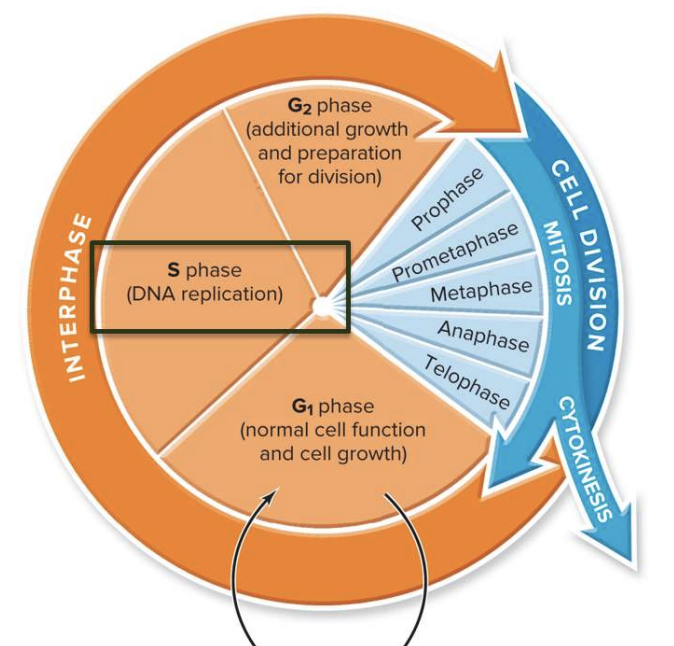
New cards
What happens in in S phase?
DNA Replication
* DNA wraps around histones
* DNA wraps around histones
36
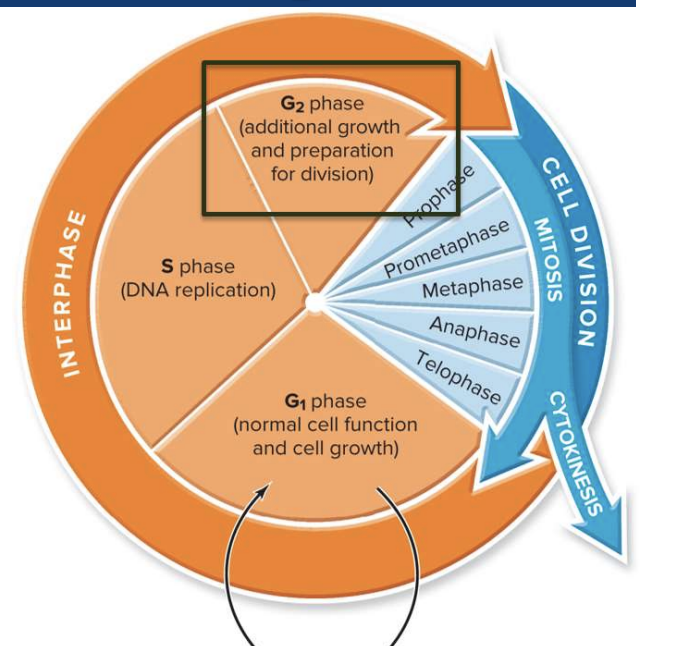
New cards
What happens in G2 phase?
Additional growth and preparation of division
* spindle microtubules are synthesized
* Proteins produced (proteins that break down nuclear envelope)
* spindle microtubules are synthesized
* Proteins produced (proteins that break down nuclear envelope)
37
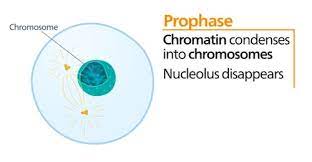
New cards
What happens in Prophase?
1. chromosomes condense
2. nucleolus becomes invisible
3. nuclear envelope breaks into vesicles
4. spindles (composed of microtubules)
5. spindle fibers move to opposite poles
38
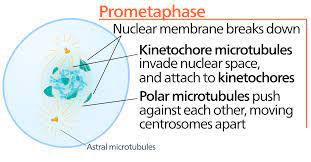
New cards
What happens in Prometaphase?
1. nuclear envelope breaks up
2. spindle fibers attach to kinetochores on chromosomes
39
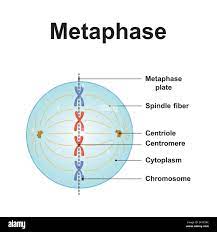
New cards
What happens in Metaphase?
1. chromosomes line up along equator
40
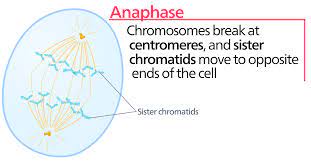
New cards
What happens in Anaphase?
1. centromeres split sister
2. chromatids separate
3. chromatids move to opposite poles
41
New cards
What happens in Telophase?
1. Nuclear envelope and nucleolus form on each pole
2. chromosomes uncondense
3. spindles disappear
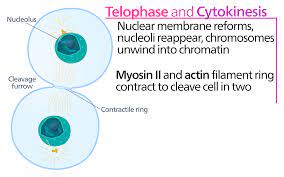
42
New cards
What are the steps of Cytokinesis? How does a new Cell Wall form?
division of the cytoplasm
1. cleavage furrow (phragmoplast)
2. cleavage deepens into a ring of proteins
3. membrane contracts
Dictyosome forms the cell membrane?
Phragmosome forms a new cell wall?
1. cleavage furrow (phragmoplast)
2. cleavage deepens into a ring of proteins
3. membrane contracts
Dictyosome forms the cell membrane?
Phragmosome forms a new cell wall?
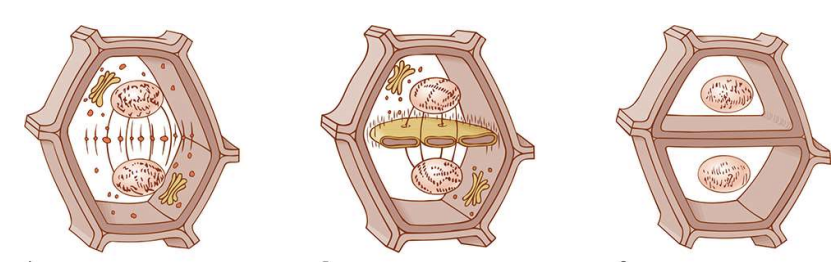
43
New cards
What are the products of Mitosis?
division for the growth of an organism
creates EXACT copies of the parent cell
2 Diploid cells
creates EXACT copies of the parent cell
2 Diploid cells
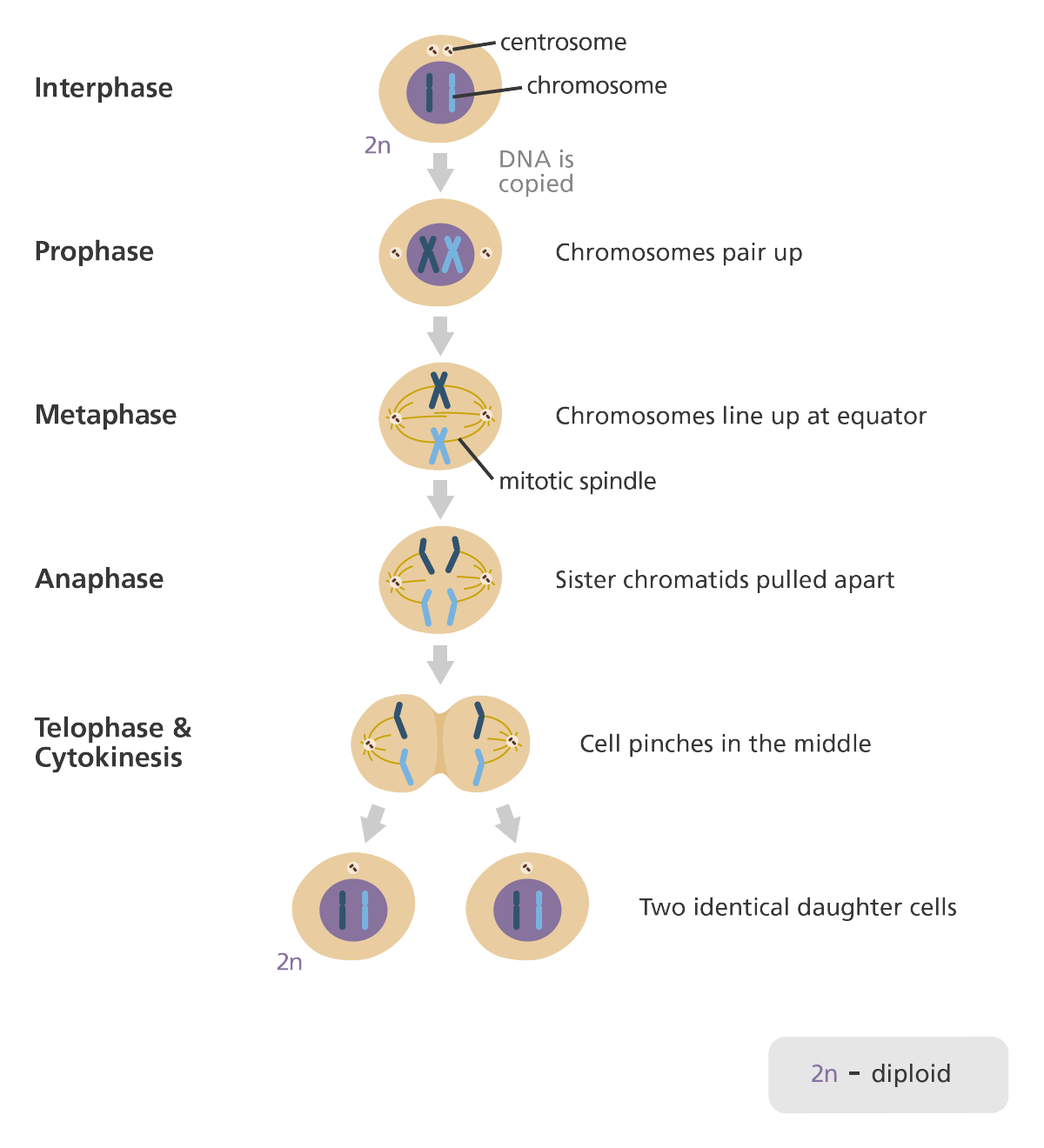
44
New cards
What are the products of Meiosis?
2 divisions that result in the production cells
4 Haploid cell/gametes (one chromatid)
4 Haploid cell/gametes (one chromatid)
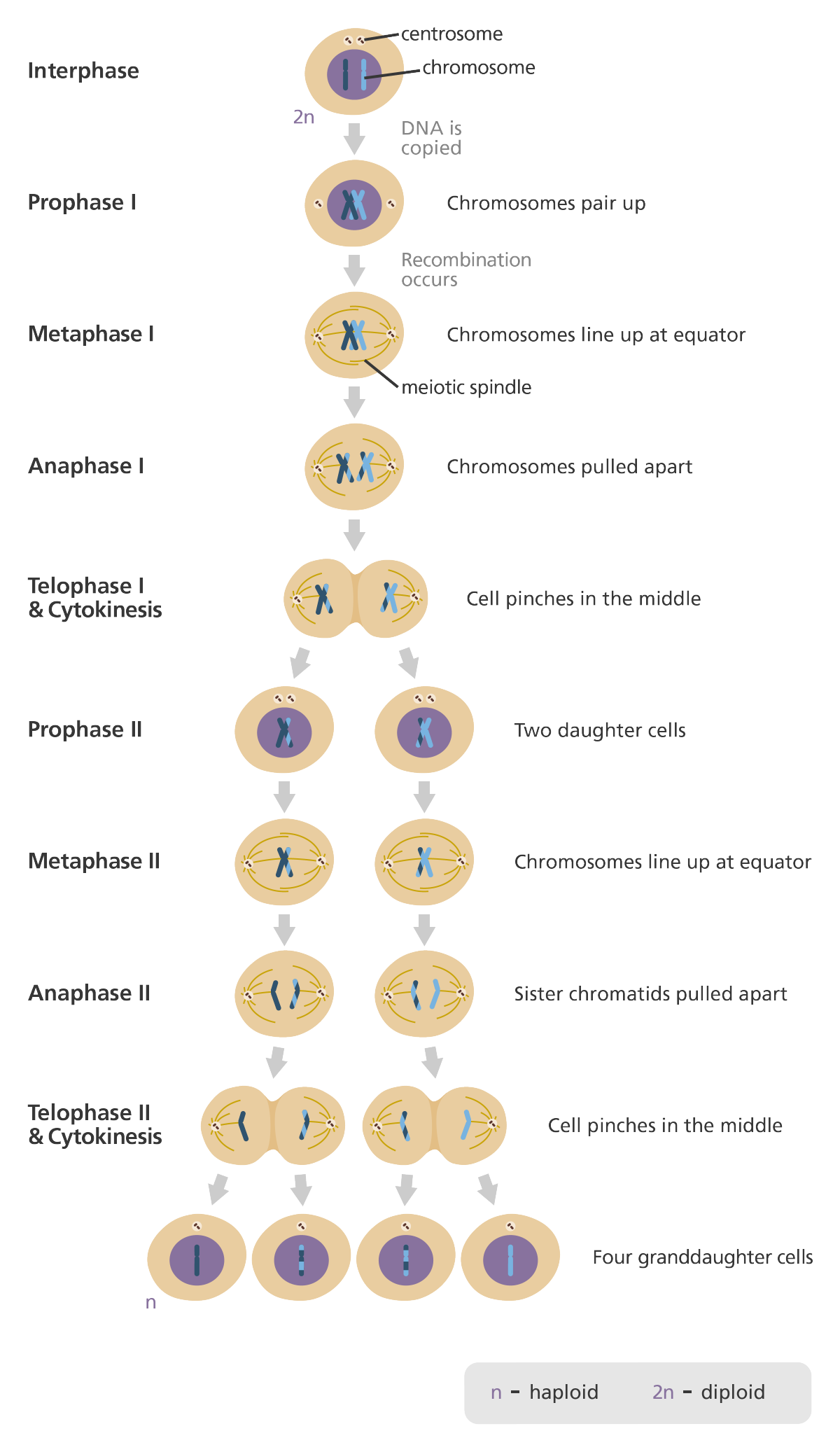
45
New cards
What is Crossing Over? When does occur in Meiosis?
occurs between maternal and paternal homologs
1. During prophase I (pachytene) of meiosis each paternal chromosome finds a pairs with a equivalent maternal chromosome
2. Breaks occur in similar sites of the chromatids
3. repair enzymes attach material pieces to paternal pieces
4. results in new chromatids
\
1. During prophase I (pachytene) of meiosis each paternal chromosome finds a pairs with a equivalent maternal chromosome
2. Breaks occur in similar sites of the chromatids
3. repair enzymes attach material pieces to paternal pieces
4. results in new chromatids
\
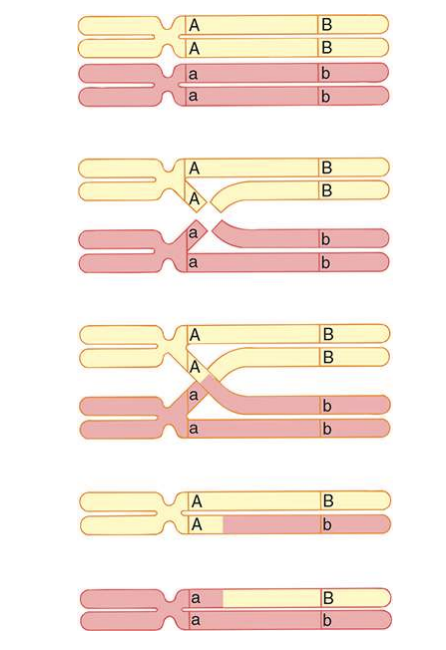
46
New cards
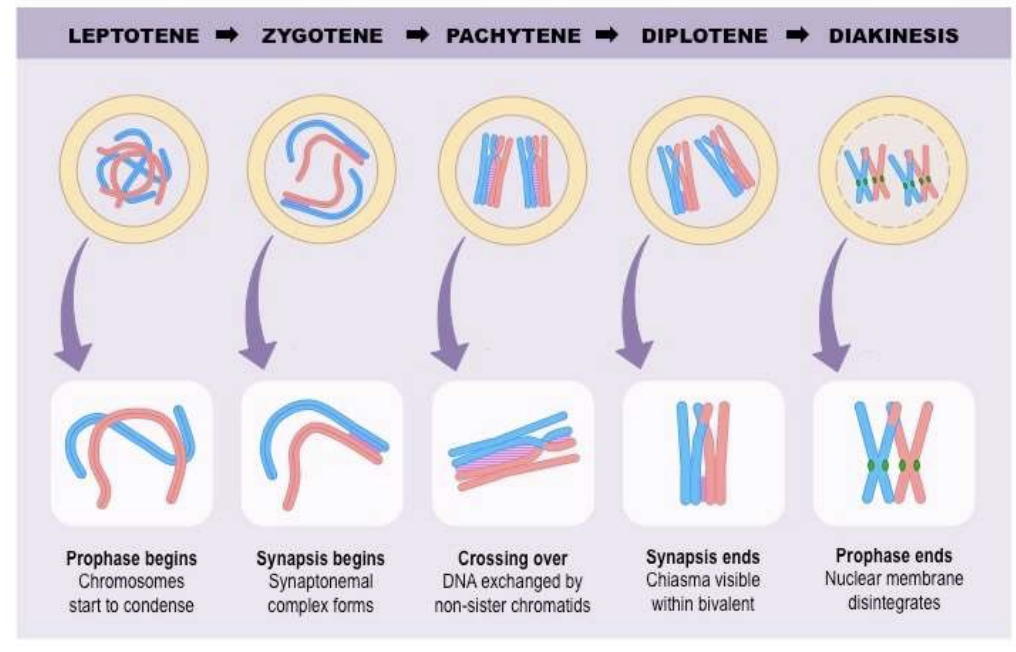
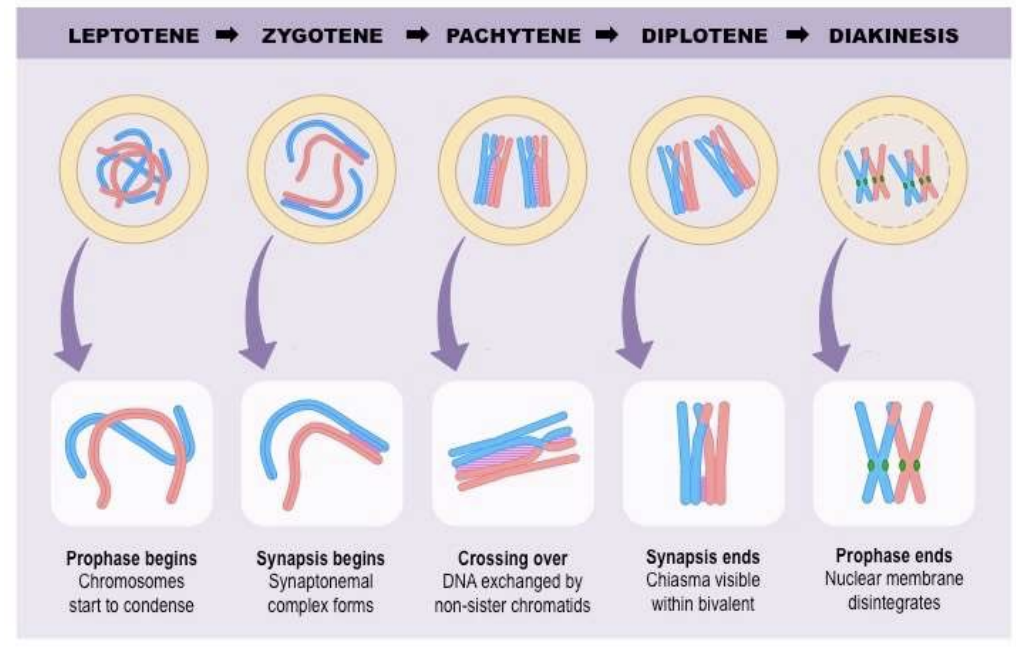
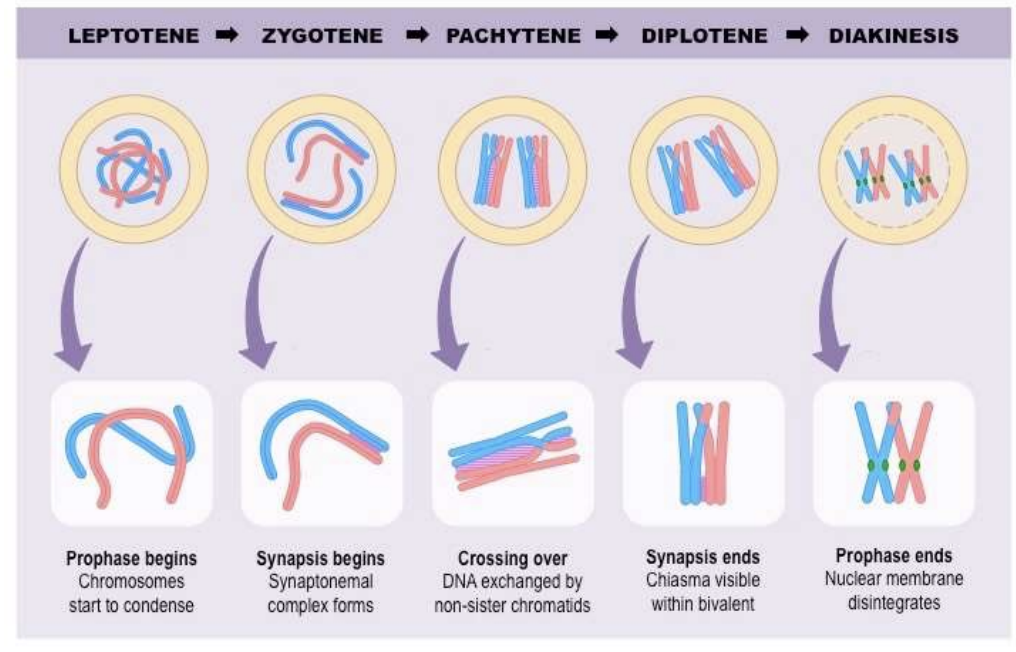
what are the stages of Prophase I?
Leptotene→ Zygotene→ Pachytene→ Diplotene→ Diakinesis
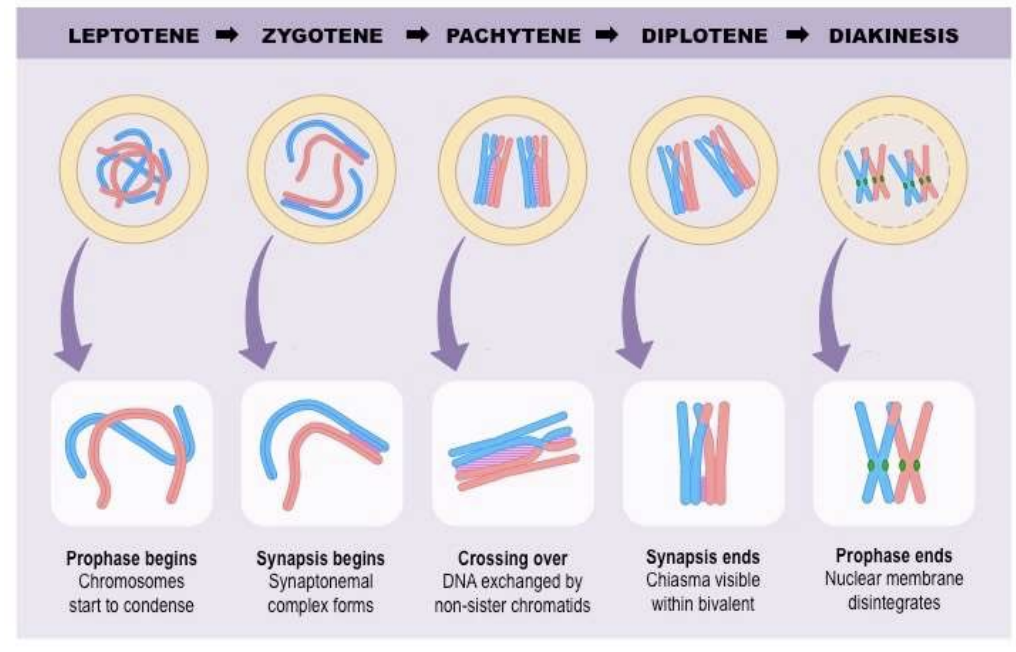
47
New cards
What is Leptotene?
the beginning of prophase I
chromosomes start to condense
chromosomes start to condense
48
New cards
What is Zygotene?
Synapsis begins
Synaptonemal complex forms
Synaptonemal complex forms
49
New cards
What is Pachytene?
Crossing-over
DNA exchange by non-sister chromatids
DNA exchange by non-sister chromatids
50
New cards
What is Diplotene?
Synapsis ends
Chiasma visible within bivalent
Chiasma visible within bivalent
51
New cards
What is Diakinesis?
Prophase I ends
Nuclear membrane disintegrates
Nuclear membrane disintegrates
52
New cards
When does the reductional division of meiosis happen?
during the formation of the gametes
53
New cards
How many nuclear divisions occur in meiosis?
2
54
New cards
When does crossing over and the division of maternal and paternal chromosomes occur? How do these both increase the genetic variability of the offspring?
Pachytene
Increases Genetic diversity variability in the offspring because it creates slightly different chromosomes from the originals.
Increases Genetic diversity variability in the offspring because it creates slightly different chromosomes from the originals.
55
New cards
What are the differences in the division of the chromosomes in meiosis compared to mitosis? How does this difference result in a reductional division?
mitosis= 2 diploid (2 identical cells)
meiosis= 4 haploid (crossing over occurs in meiosis + chromosomes reduced to half the normal number)
meiosis= 4 haploid (crossing over occurs in meiosis + chromosomes reduced to half the normal number)
56
New cards
What is Ethnobotany?
the scientific study of relationships between plants and people
57
New cards
When did humans start cultivating plants? Where was this?
Cultivation of food/plants began around 10,000 years ago
Crops were domesticated (agriculture) began around 9,000 years ago in the FERTILE CRESCENT
Crops were domesticated (agriculture) began around 9,000 years ago in the FERTILE CRESCENT
58
New cards
What are the three F’s of plant production?
?
59
New cards
What plants provide Carbohydrates?
Cereal Grains (small fruits of grasses/seeds)
Caryopses- grains, kernels, and seeds
wheat, Rice, Corn, Oats, Rye, and Barley
Caryopses- grains, kernels, and seeds
wheat, Rice, Corn, Oats, Rye, and Barley
60
New cards
What plants provide Oils, Vitamins, and Minerals?
Soybeans, Legumes, Oranges, Lemons, Limes, Grapefruit, Raspberries, Blackberries, Boysenberries, Strawberries, Peaches, Cherries, Apricots, Plums, and Almonds
61
New cards
What plants provide drugs?
Cola trees, Tobacco, and Marijuana
62
New cards
What plants provide Fibers, woods, and Chemicals?
Flax, Corchorus, Hemp, Conifers, Hardwood trees (dicot), Cotton, Pines, and Kenaf