L2: Architecture of the nucleus 2
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chromosomes and organisation of the nucleus
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
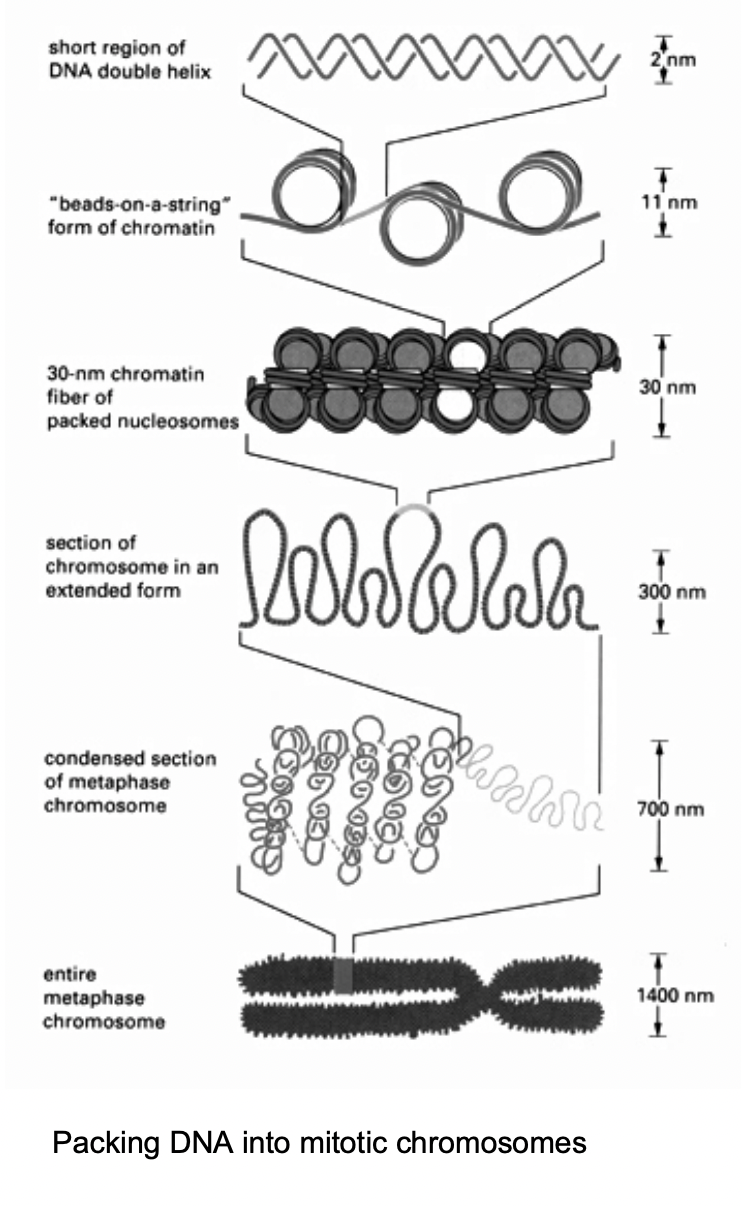
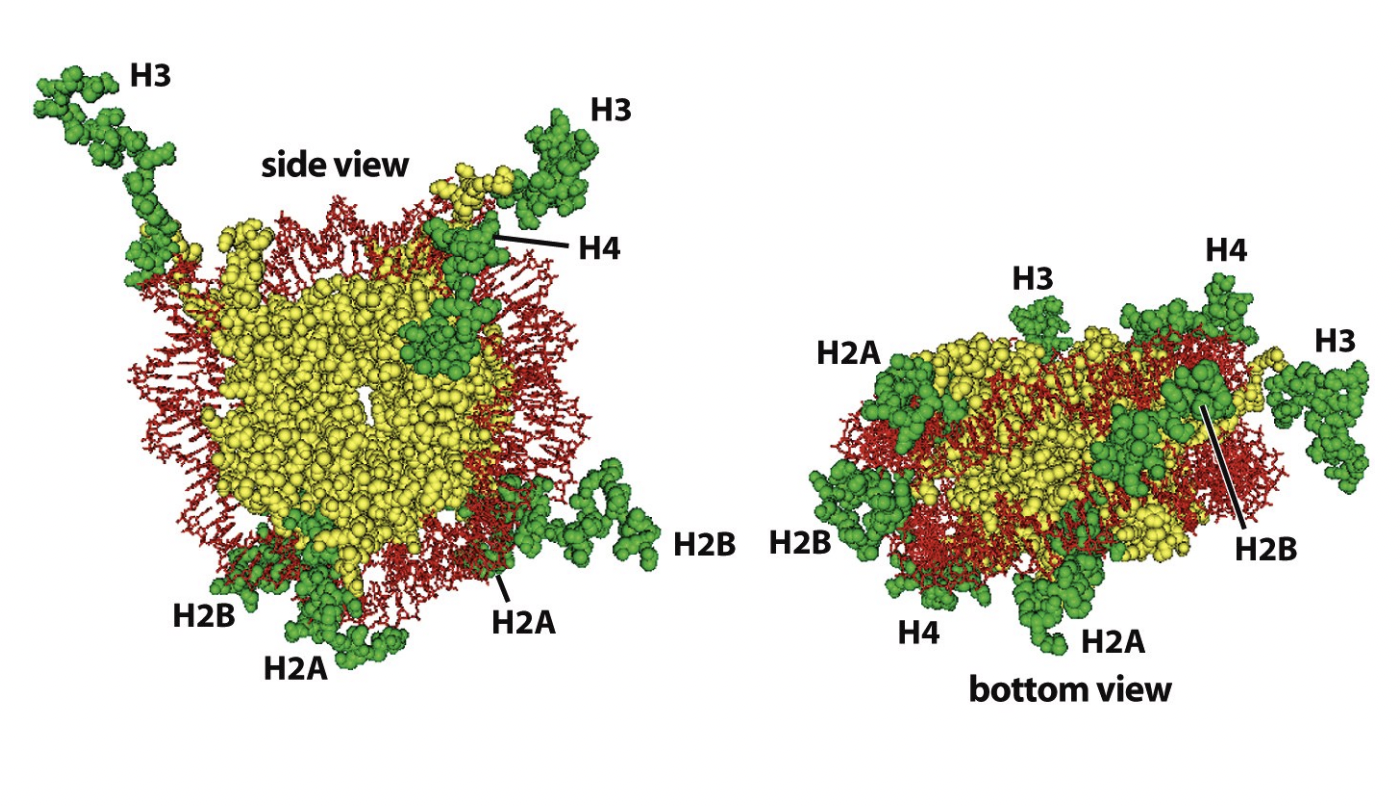
The nucleosome subunites of chromatin allow for
hierarchies of folding chromatin fibres
For gene expression of replication
dynamic accessibility of certain regions of DNA in the chromatin has to be provided
When is the most condensed state of chromatin found
during metaphase of mitosis
→ chromosomes
Key principles of higher-order packing
loop formation
attachment of chromatin fibres
→ to an underlying scaffold or matric strucutre
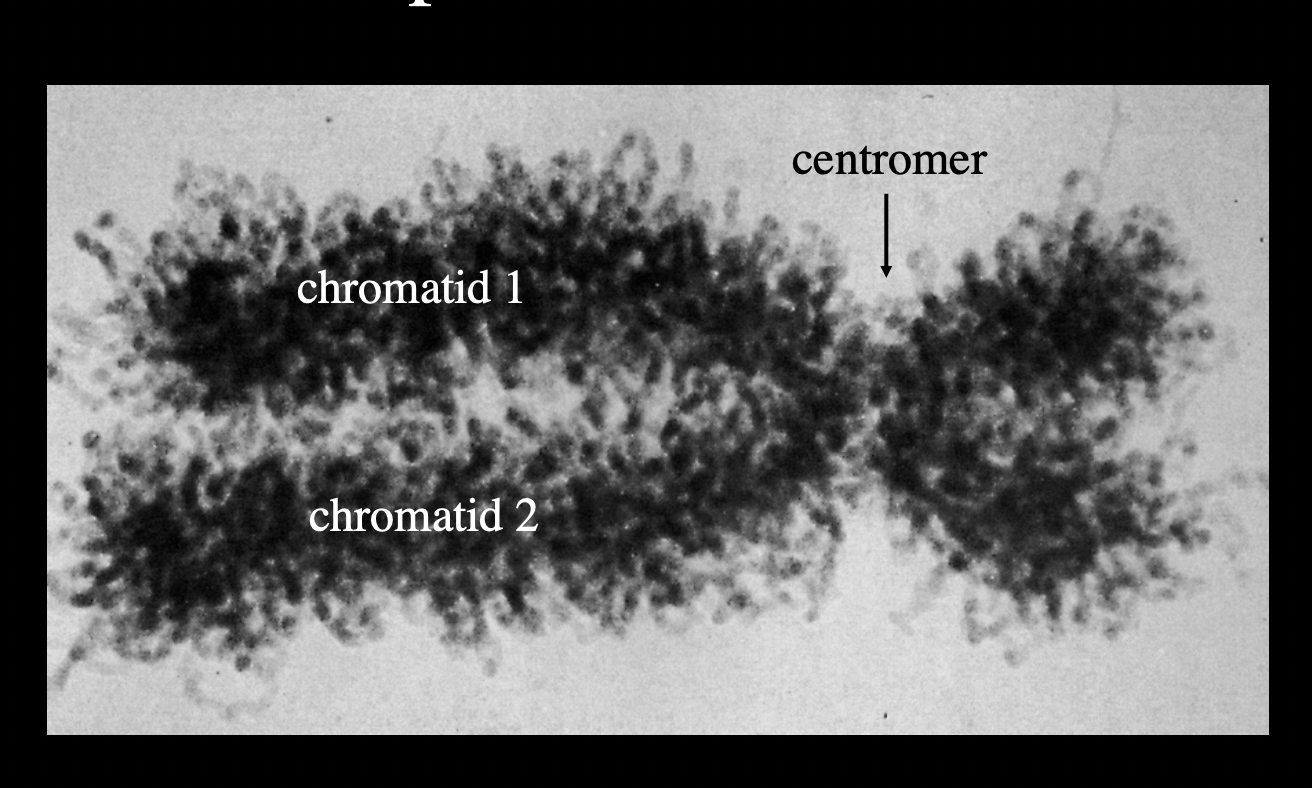
Note: this shows the chromosome in interphase→ the most condensed phase needed for mitosis
In normal conditions: DNA is more lose and jus exists in its territory
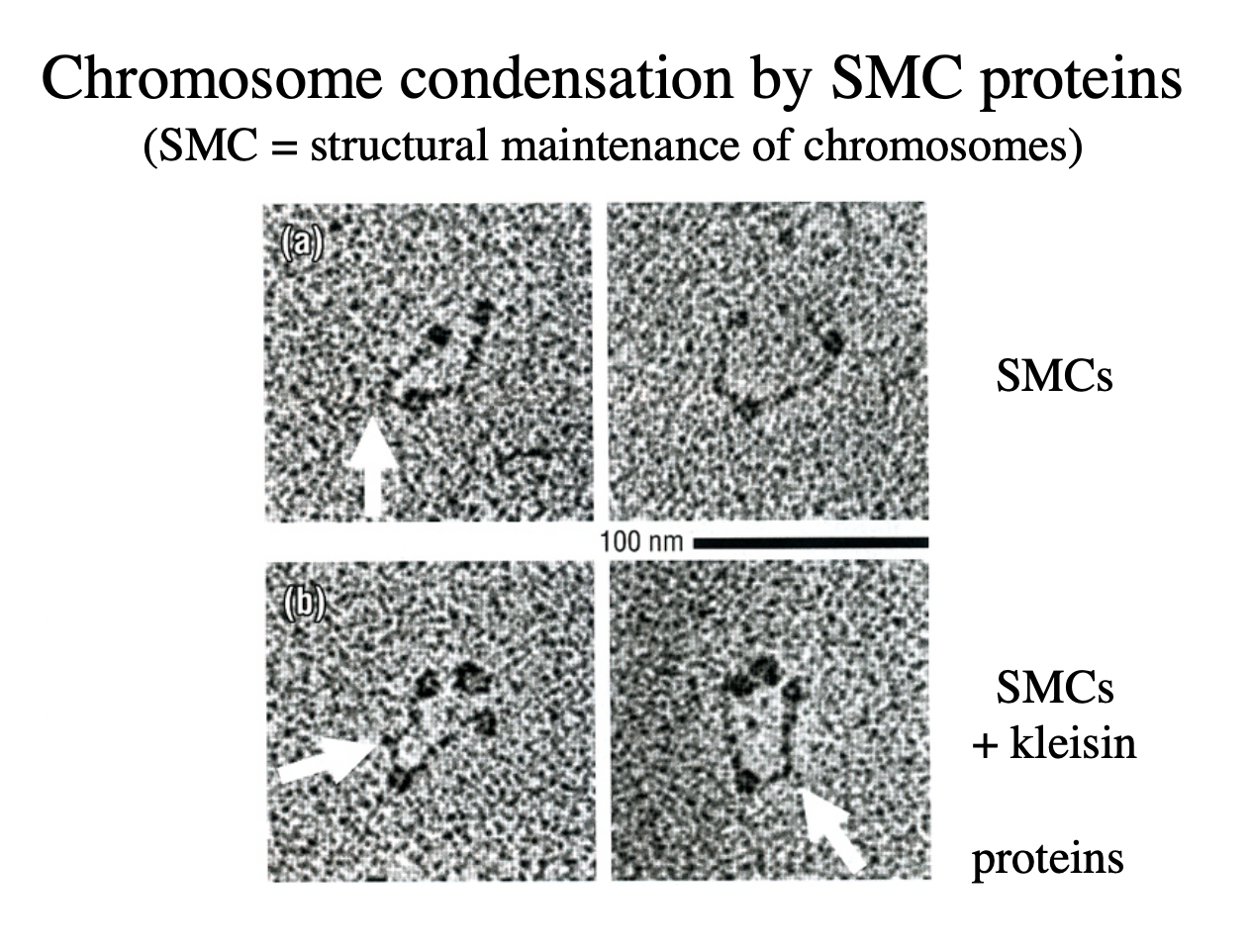
How is chromatin condensation mediated
condensins
large proteins
‘strucutural maintenance of chromosomes’ proteins (SMCs)
HOw was this experimentally found out
mutagenesis
continue with all proteins
until find the proteins that are needed for the condensation
RESULT:
SMCs→ unclosed loop thing
Kleisin→ ‘to glue’ closes the loop together
How does this work?
Complexes of SMC2 and SMC4
with kleisin proteins (CAPs)
clamp chromatin fibres
→ Condensation mediated!
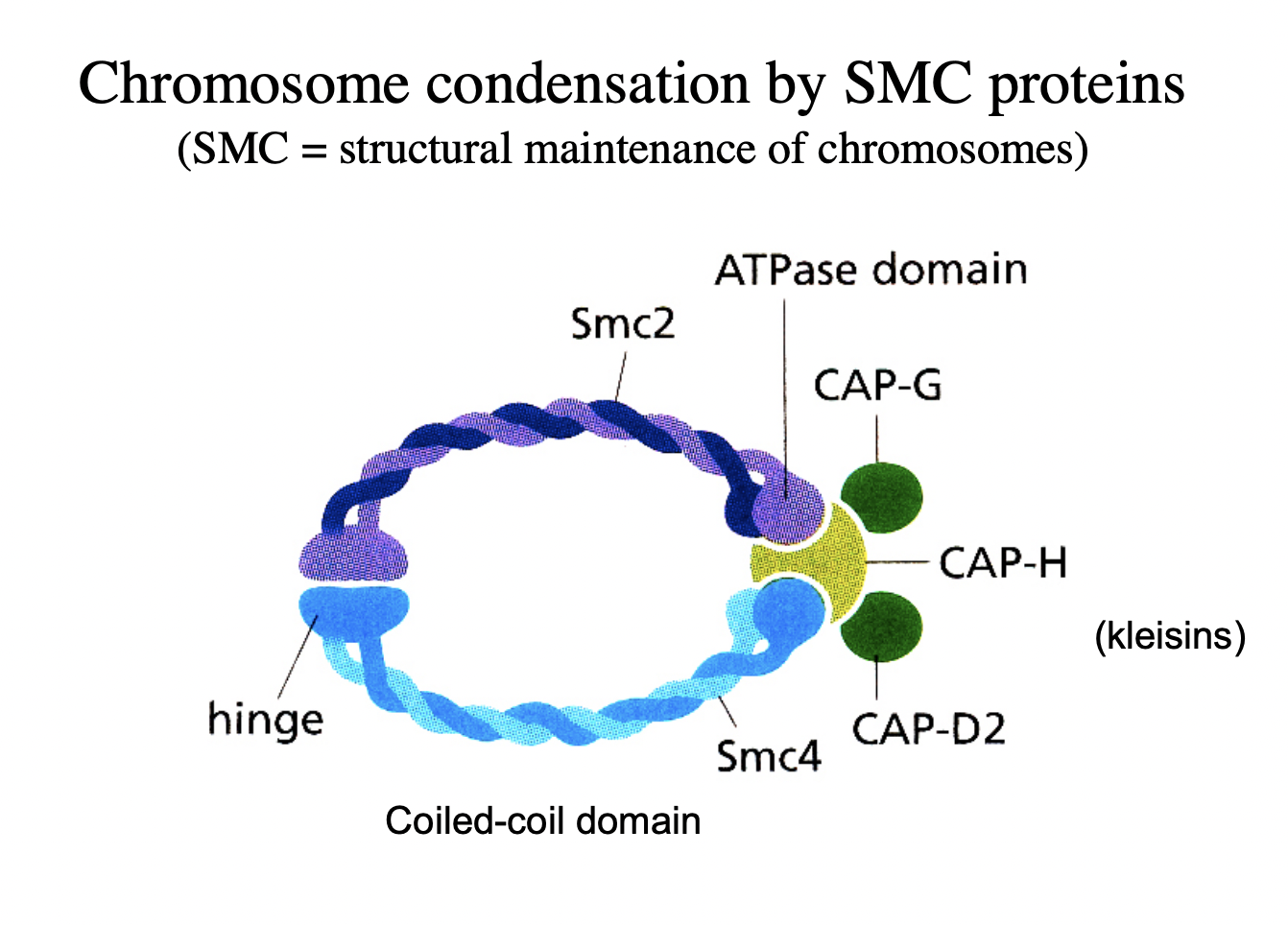
Visualisation of chromosome condensation by SMC proteins: condensin
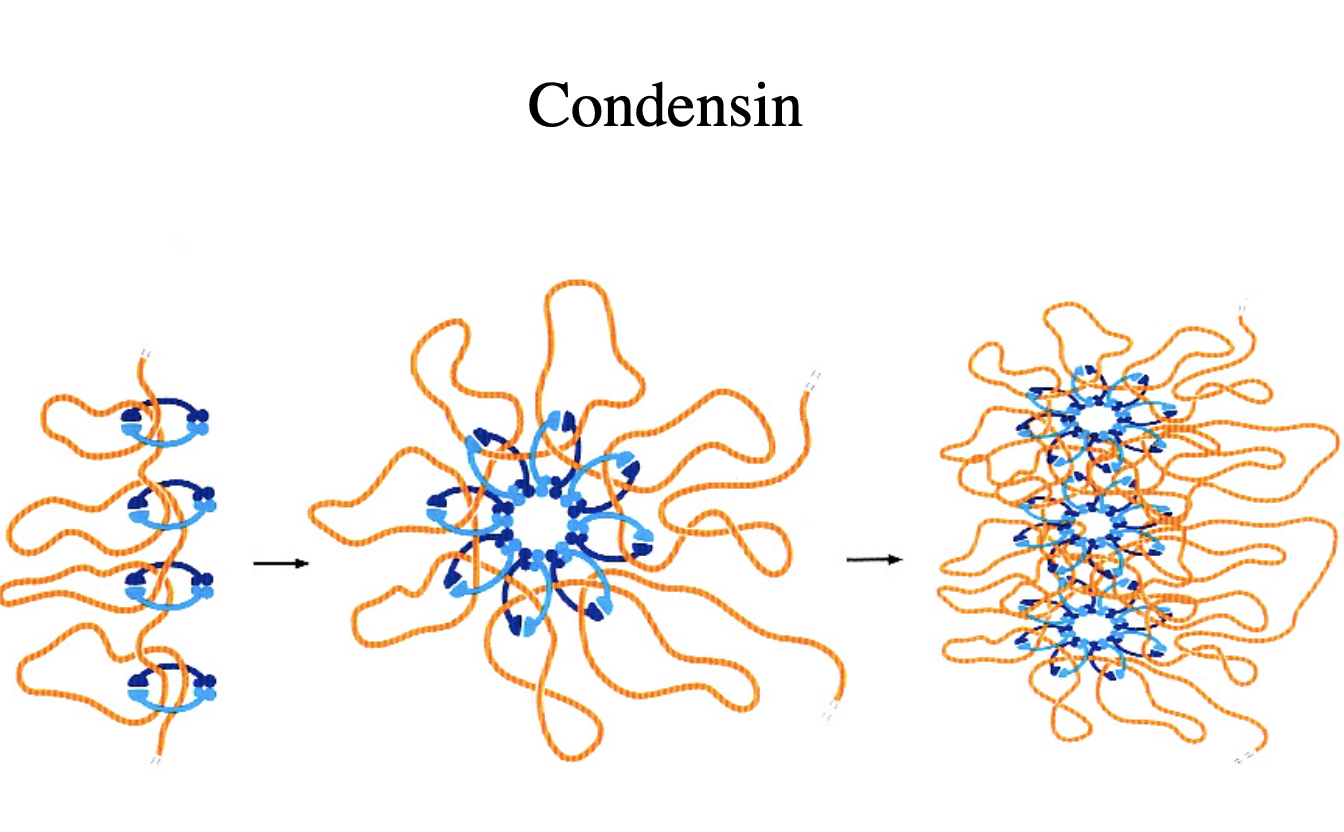
But you don’t walays want it to be condensed
need phosphate? to break the kleisins
so can de-condense after replication
Nuclear matrix
when the crhomosomal DNA
from underlying residual protein strucuture
is liberated
HOw is this made?
depleteing entire interphase nuclei or mitotic chromosomes
from histones
e.g by detergents and high salt
The DNA in this nuclear matrix is attached in…
loops of -60kbp
to the residual matrix or scafforld
→ big fibres come out of uncerlying structure→ some more condesned than others
This DNA that is attached is called…
MAR
matrix-associated regions
or
SAR
scafford-associated regions
But how to experimentally show that there iis a scaffold?
Dissociate metaphase chromosome DNA from scaffold
Functional identification of DNA sequences that attach loops to chromosomal matric/scaffold
Dissociated metaphase chromosome
shows evidence that there is a scaffold
but not completely confirms how the scaffold works
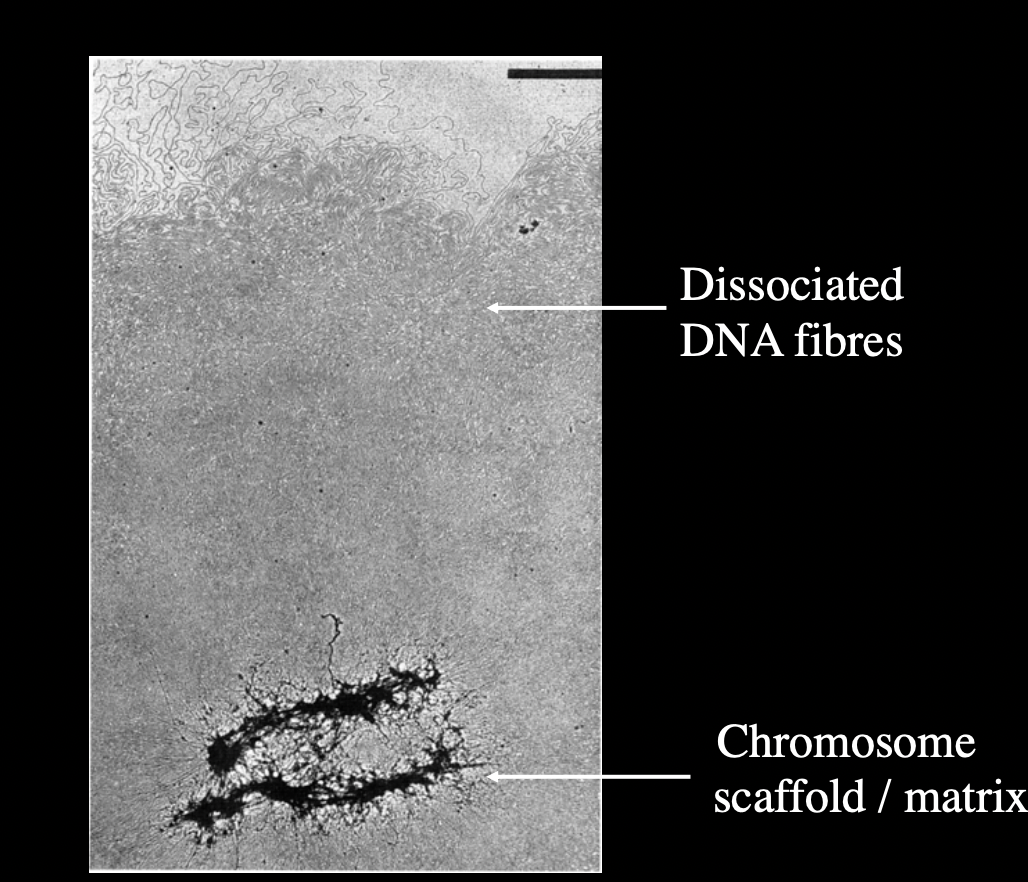
Functional identification of DNA sequences that attach loops to chromosomal matric/scaffold: i.e finding out which parts of the DNA are ‘sticky’ for the scaffold to attach to (The MARs)
Adding nuclease to the MAR an SAR
can isolate the DNA loops
wash away the proteins
degrade all DNA with DNAase
label
ass DNA
extract and sequence the DNA
see if they are the same region all the time?
Might have to check this!
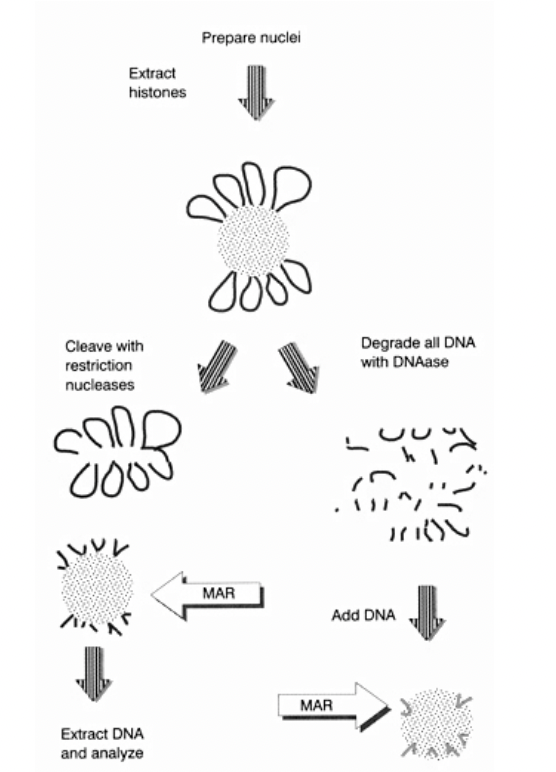
First way to do experiment: conceptual stickiness (right handside)
DNA on the scaffold (which is made of proetins, laminins etc
DNAase→ degrades DNA off→ into fragments
Now add random small fragments of DNA
See what sticks
THEREFORE:
Can see which parts of DNA have ability to stick to scaffold
but
Ignores the context of continuous long strand and loops
OVERALL: just conceptual
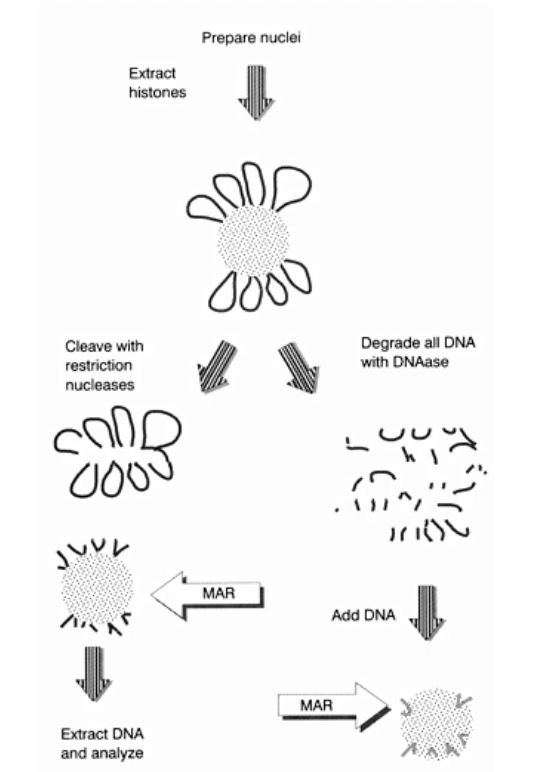
Second way to do experiment: conceptual stickiness (left handside)
DNA on scaffold
Cleave with resistriction nucleases
cuts at certain points (almost like shaving the histone ball)
Extrat this DNA
anaylse
THEREFORE:
we have taken off the DNA off the scaffold and sequenced
so show what is actually on the scaffold
Features of MARs found out from these experiments
very A/T rich
contain weak consensus sites for DNA topoisomerase II
Not specific: BUT some regions are more sticky than others
more stoacastic distribution
taking into account the loop and tension
to see which parts will be more likely to stick
What does this suggest about DNA topoisomerase II?
Might be involved in:
controlling coiling of (topologically closed) DNA loops of the matrix
Other features of the nuclear matrix or scafford?
consistuents are ill-defined but…
SAF-A
Scaffold attachment factor A
directly bind to SAR elements
How can principle chromones arcitecture in interphase be visualised?
in special cases
light microscopy
Example of this?
Lampbrush chromosomes of newt oocytes
highlight essential features of interphase chromatin organisation
Features of amphibian oocyte chromosomes
condensed for several months
in early meiotic prophase
very active in transcription→ desnsely packed nascent RNP particles coat the loops
non condensed parts are actively transcipbed and condesned are not
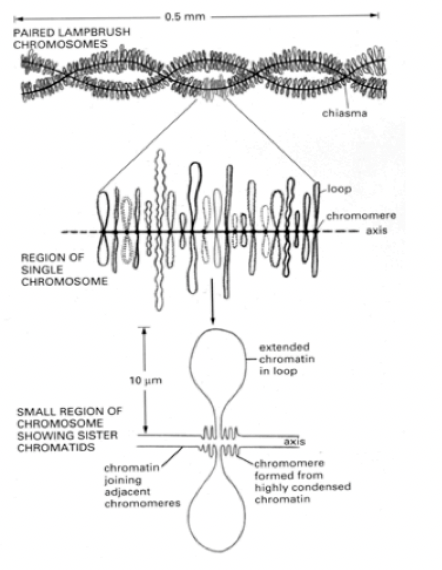
What is helpful about the RNP particles coating the loops
allows them to be seen in the light microscope
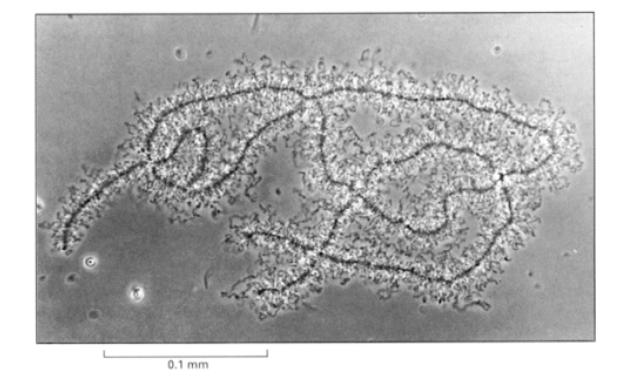
But how do we know the loops are chromatin?
use a floresecent histone
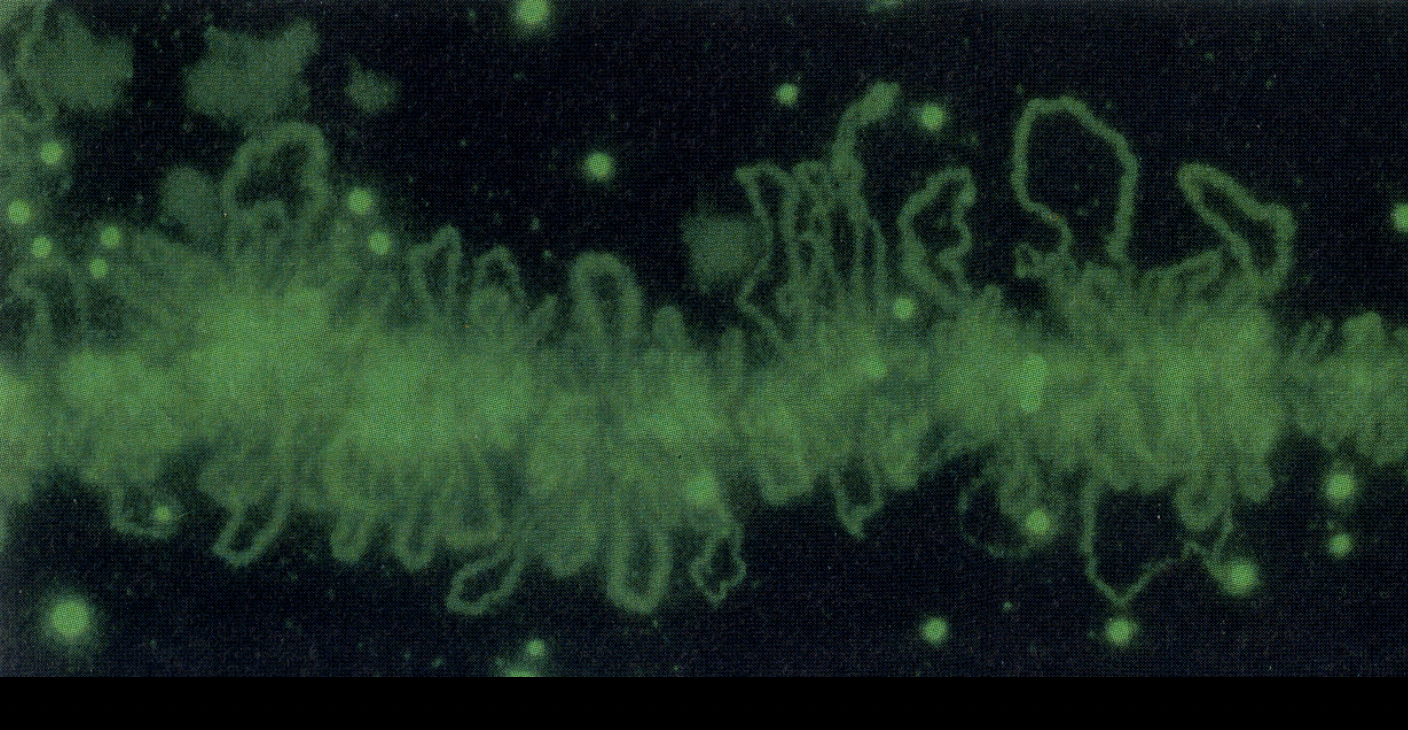
What does hybridisation of DNA probes to chromosomes preparations confirm?
organisation is strictly sequence specific
individual decondensed loops can correspond to particular active genes
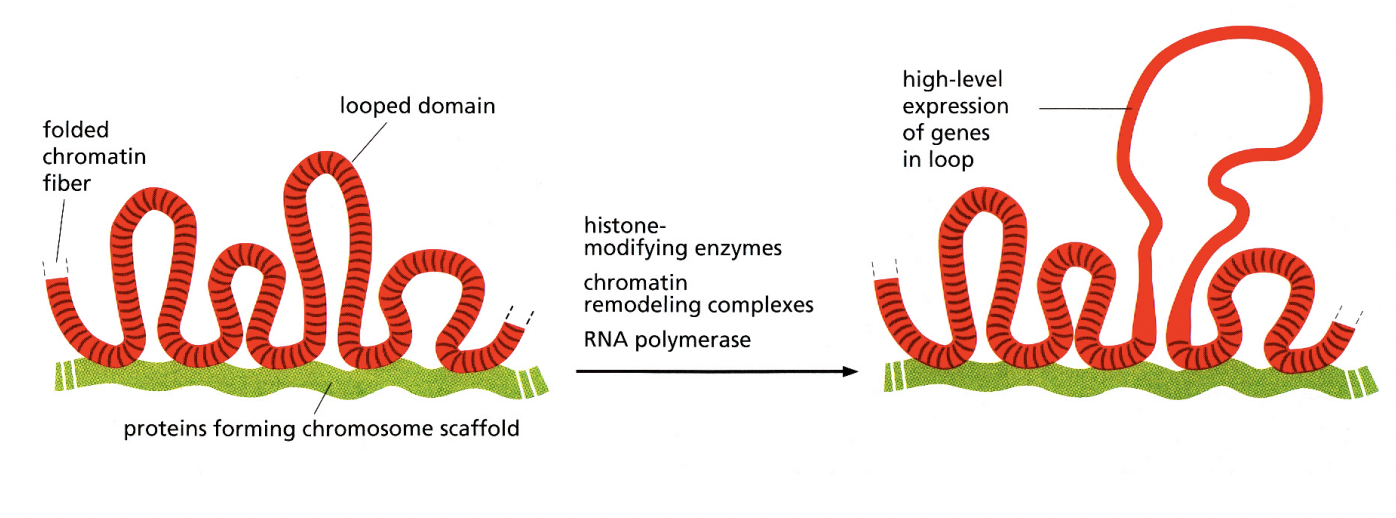
Can transmission EM help differentiat individual chromosomes in interphase nuclei
no
What is seen in the TEM instead?
densely packed heterochromatin
(no active genes)
(relatively) decondensed euchromatin
(active genes present) (lighter in colour)
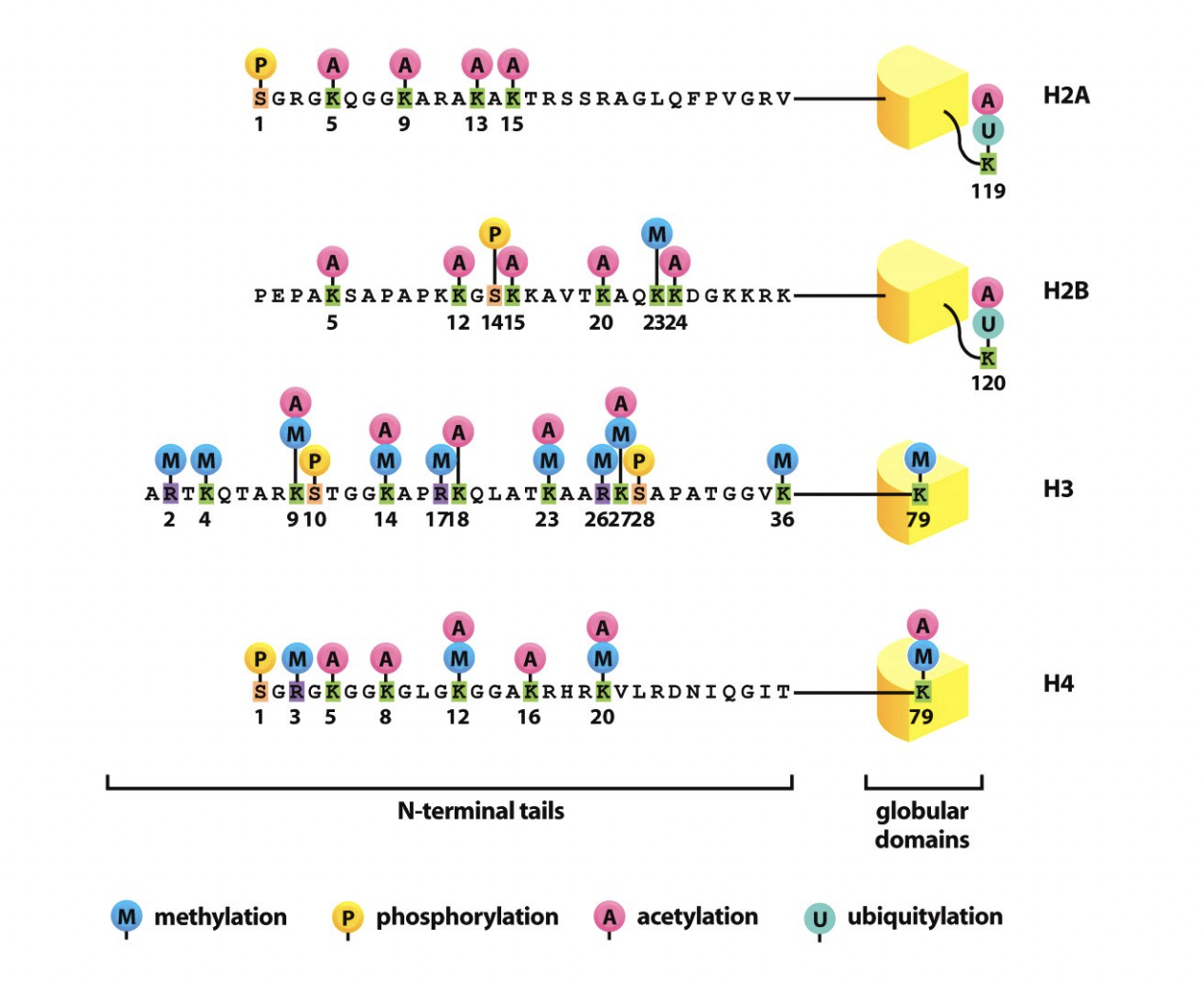
What is involved in the formation of euchromatin and heterochromatin: histone code
Post-translational modifications of histone tails
produce altered binding surfaces
for effector proteins
→ influence chromatin strucuture
Example of these modifiations → SILENCE
HIstone H3:
methylated at lysine residue 9 (H3K9me)
bound by the HP1 heterochromatin protein
this HP1 itself brings with it other proteins
→ Act to SILENCE the DNA
Example of these modifiations → ACTIVATION H3 example
Histone H3
acteylation on lysine (H3K9)
brings chromatin remodelling enzymes
open the chromatin strucutre
enable access of the transcription machinery
→ ACTIVATED

But how do we experimentally know this?
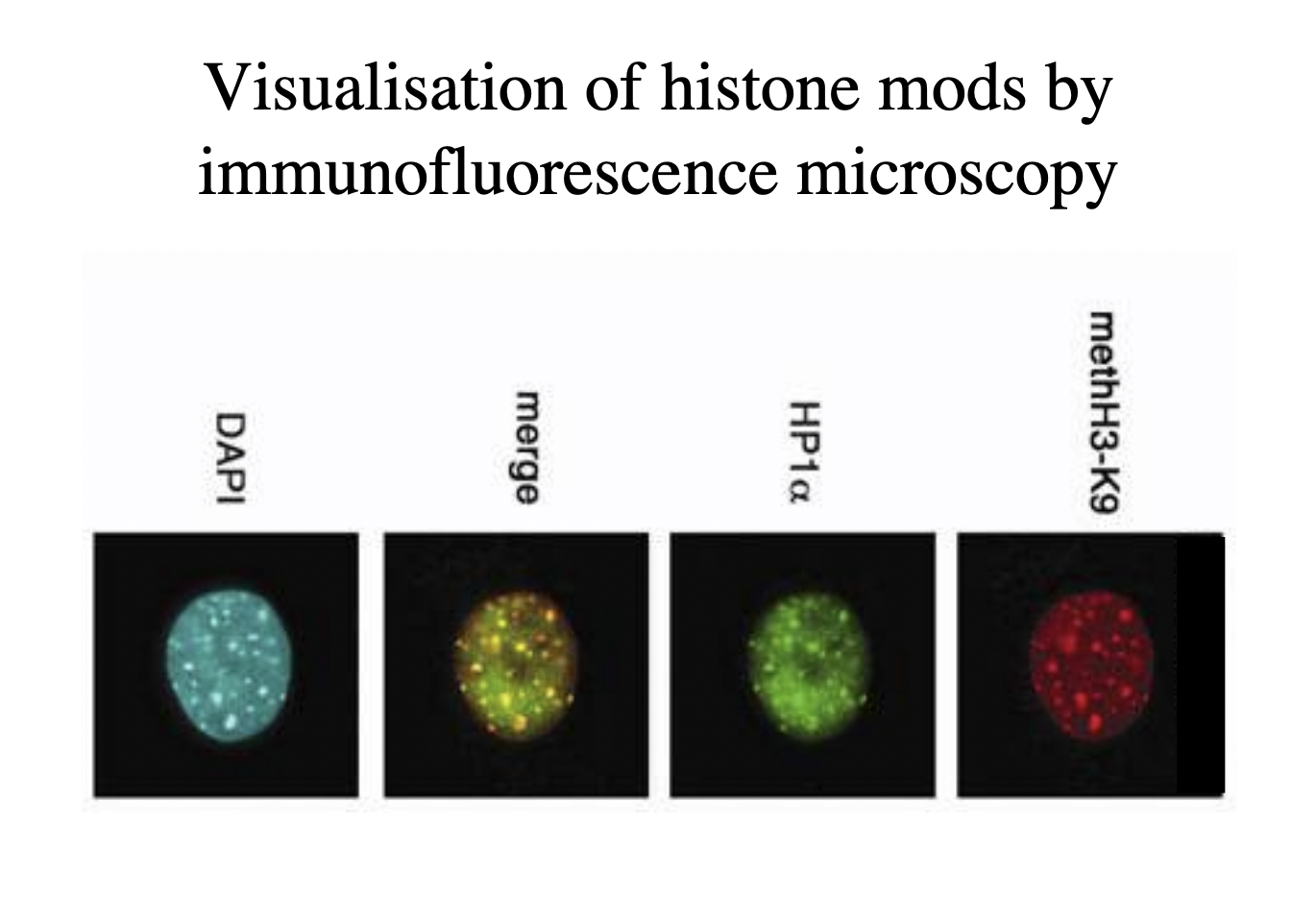
Visualisation of histone modes by immunofloresence microscopy
antibodies
How this works: finding out if methylation is associated with heterochromatin
Label nucleus with methH3-K9 antibody → red
Label with antibody for heterochromatin
Merge to see yellow colour if they are in the same place
Double check with DAPI that there is more DNA (e.g the unlabbeled euchromatin)
What have hybridisation experiments help show about chromosomes
Experiements with whole nucleus preparations
with probes specific for individual chromosomes
→ chromosome painting
RESULT:
evidence for concept that individual chromsomes occupy discrete territories
within the interphase nucleus
however
Locations of individual chromosomes and individual genetic loci within the nucleus are dynamic
But how do we visualise indivisual chromsomes to find their territoires
need DNA sequence
abel part of it that is spcific to the chromosome
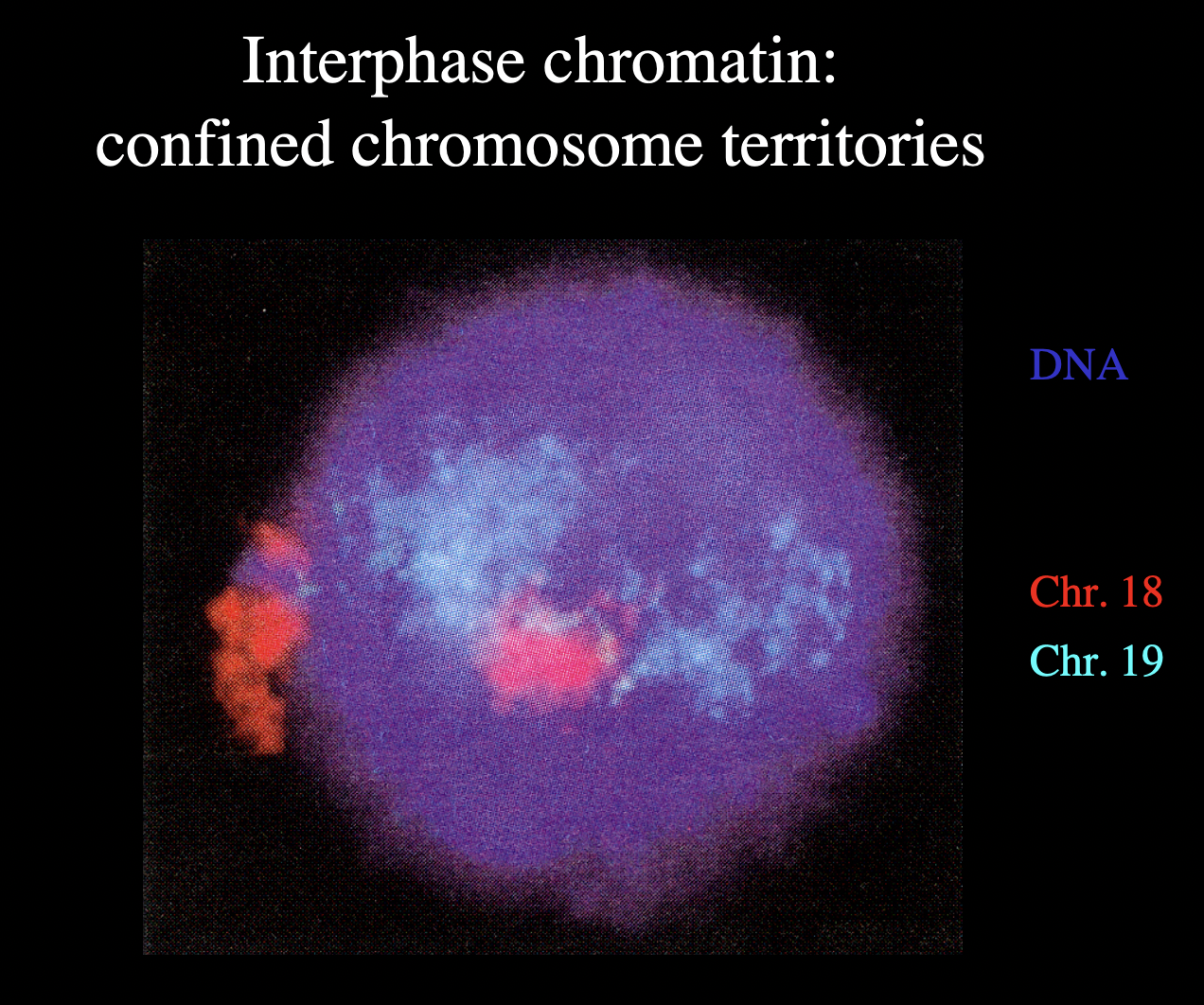
Map of the chromosome territores
→ bt can these move around? Are they dynamic?
note that HeLa cells are not like this→ once mutated, cancer cells lose their territorial organisation
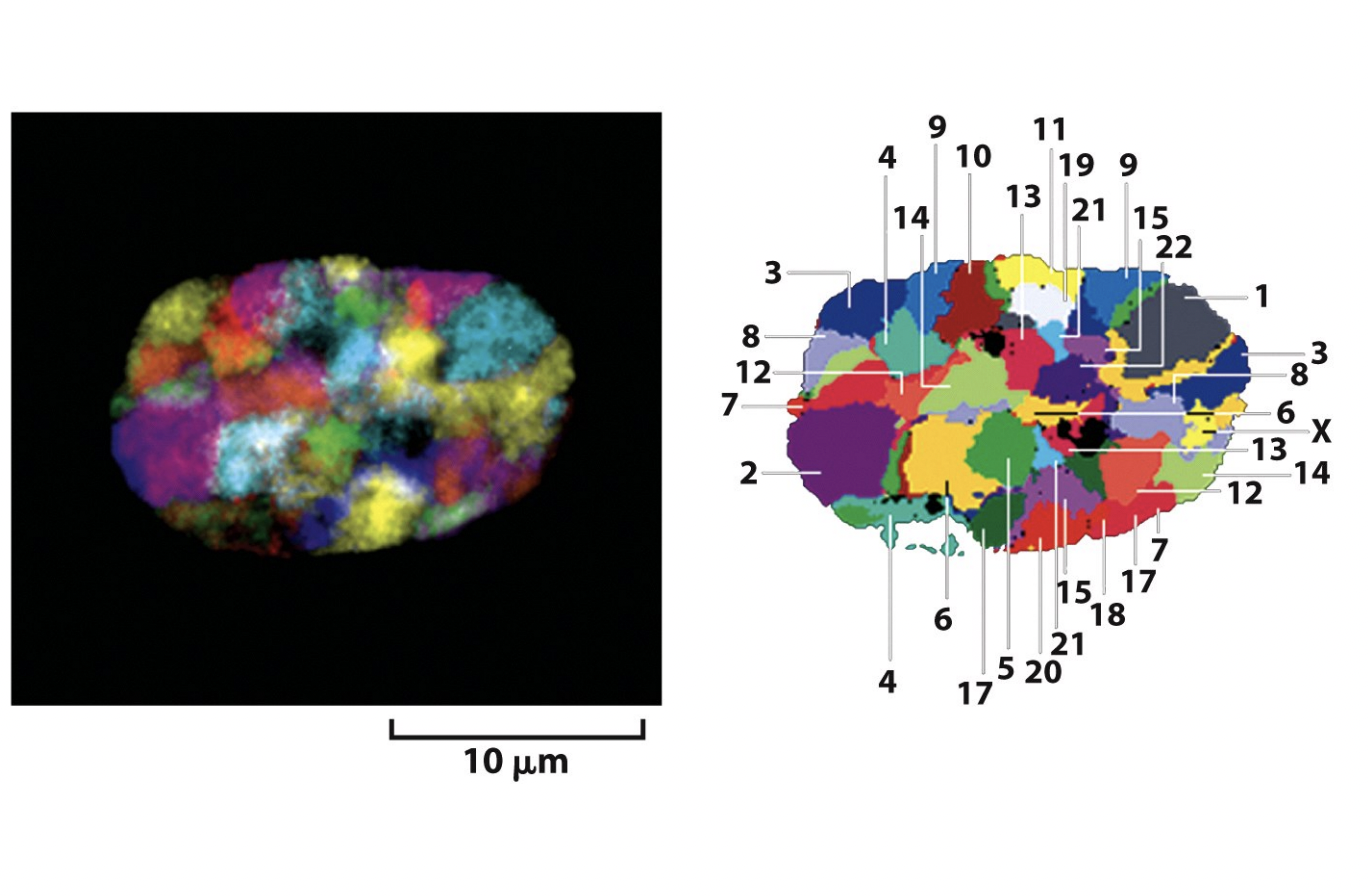
How to find synamic behaviour of chromosome
tag over time:
RESULT:
dynamic
but does stay in rrough territory
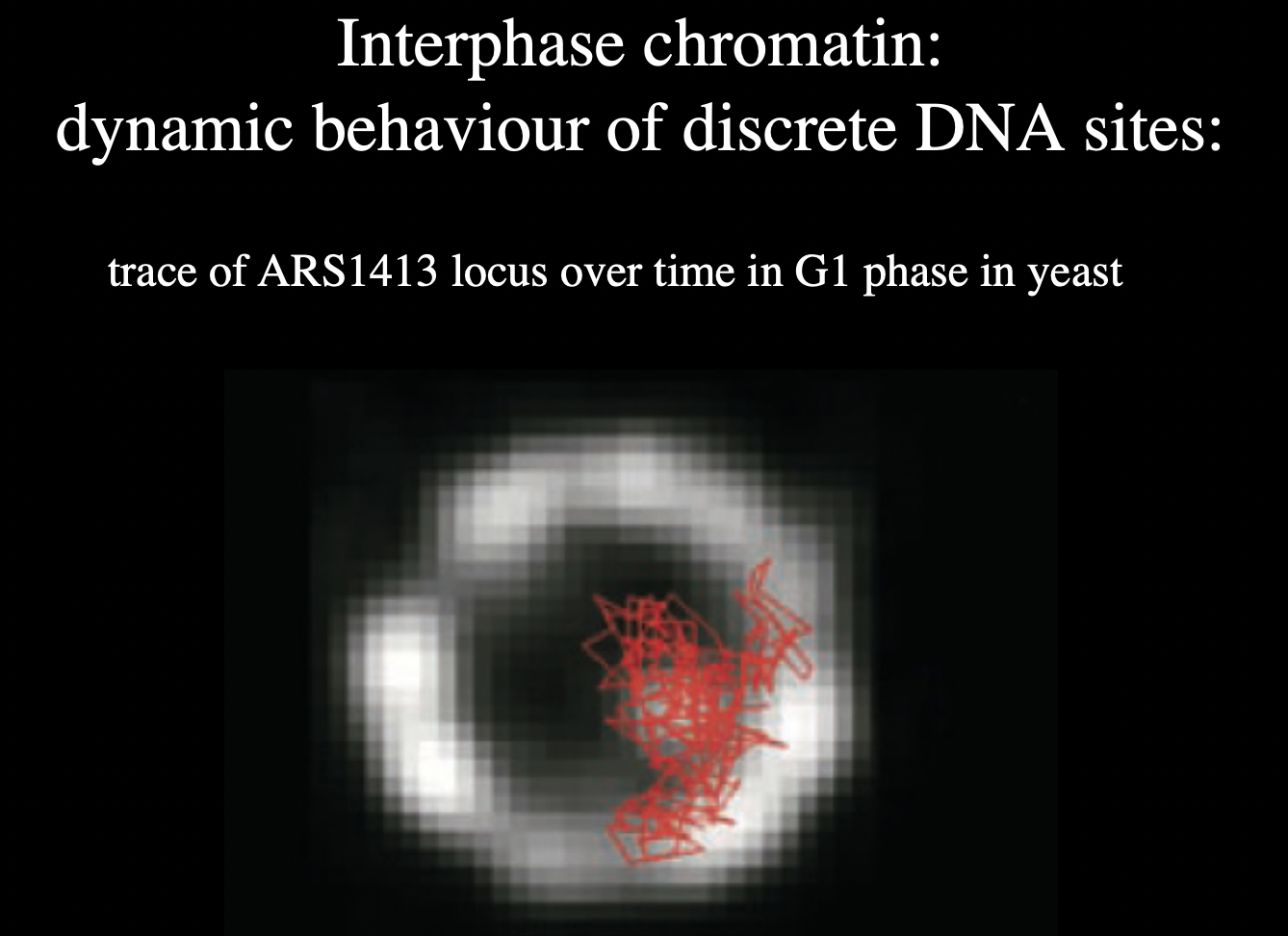
Next question to ask about the territories
Which parts of the DNA touch eachother
within and between the territories
(within same chromosome or between different chromosomes)
HOw do we find this out
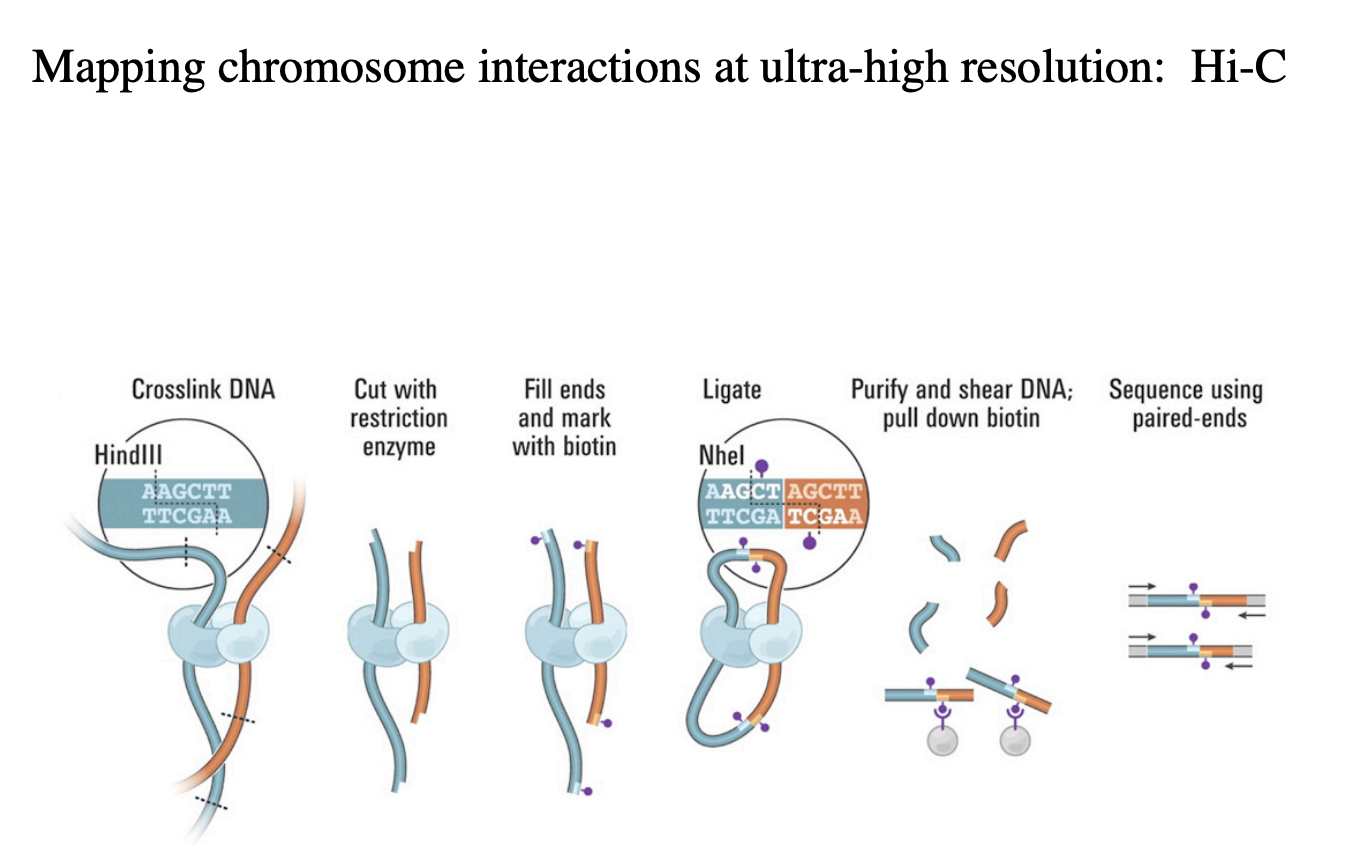
Hi-C→ high throughput DNA sequencing
What has high throughput DNA sequencing techniques enabled us? (Hi-C)
Enabled the mapping of 3D DNA-DNA interactions
within the nucleus
What is this technique called?
Hi-C
→ High-resolution Chromosome conformation capture
Principles of this technique?
Cross link the DNA→ this will stick together anything that is close to eachother
Cut crosslink of DNA with restriction enzyme
sticky ends
fill with biotin mark
ligation of proximal DNA segments
purify and shear DNA→ pull down biotin (around 100bp long)
sequence of these junctions, using paired ends
Bulk experiment: get a better understanding of the loops of DNA→ looking at ALL the different interactions and closeness of all chromosomes in the genome at once
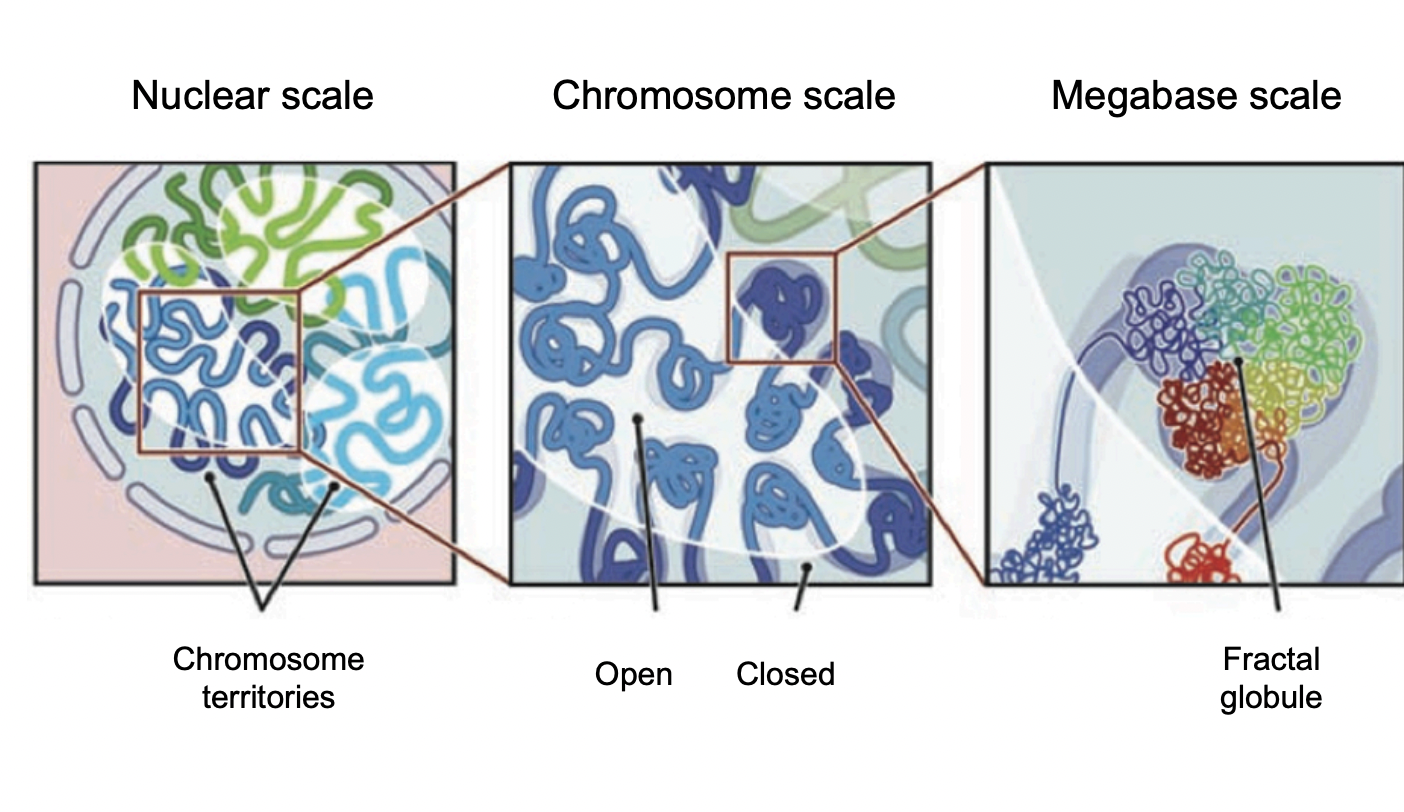
Results of this e.g interactions within the Chr 14
show zones of high interction topologically associated domains (TADs)
I think the shape of this graph is trivial and is a coincidence that it is kinda a straight line

Evidence obtained by Hi-C has been used for
modelling interactions within chromosome territories
at chromosomal resolution
dynamic spatial segregation of chromatin fibres
into open and closed domains at megabase resolution
really good to get an almost gene level view of what genes could influence eachtoother due to the proximity of their terrioties
Many Interphase activites have been shown to occur where?
at discrete subnucleuar sites, or foci
NOT: dispersed or in solution
Nuclear compartmentalisation
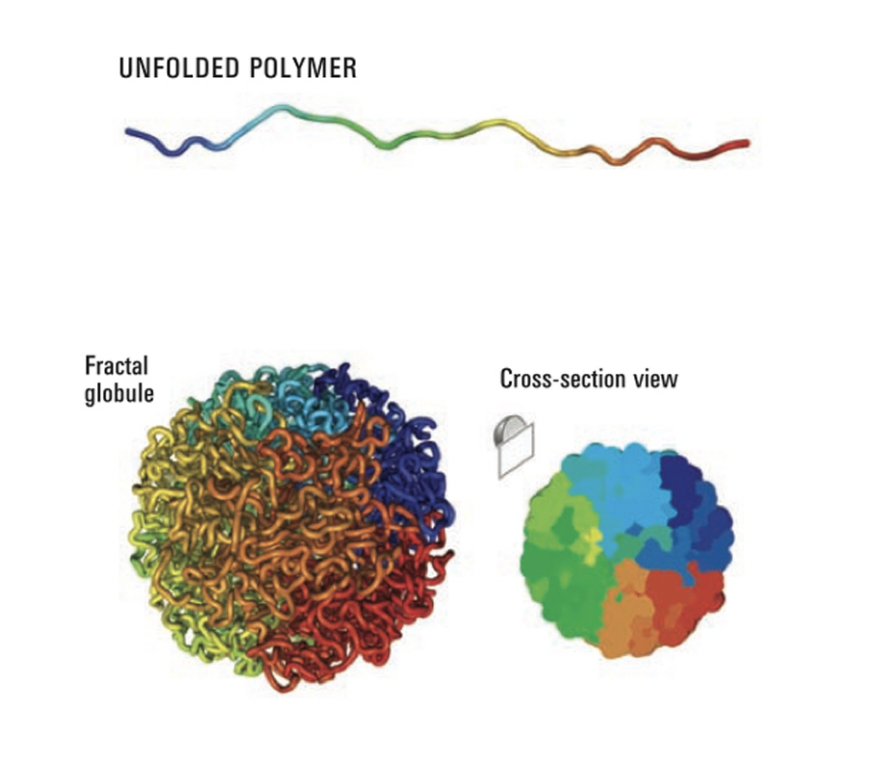
Next question to ask
Are there specific places for:
DNA replication foci
transciption foci
nucleoli
or are they just in random places
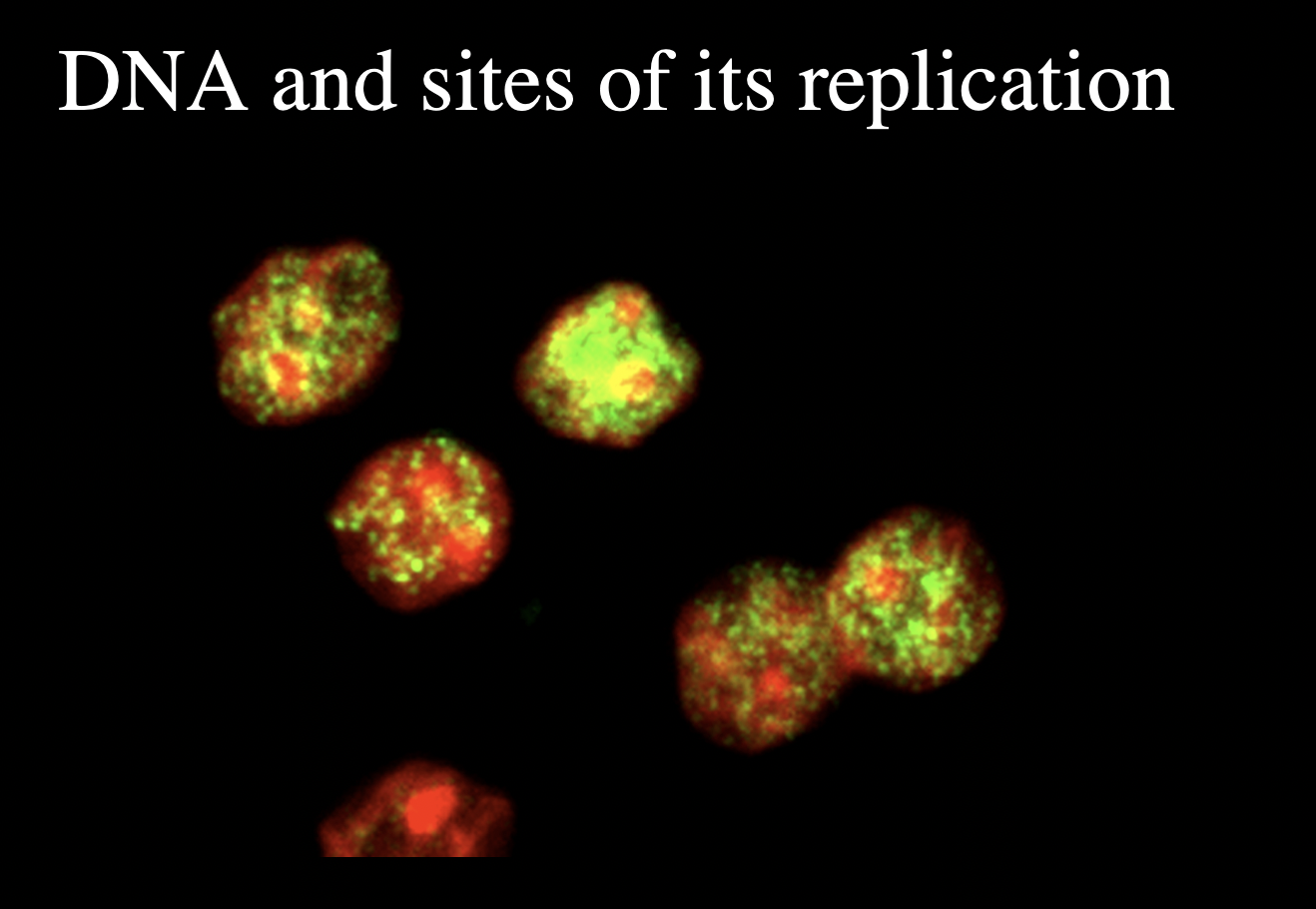
How to find this out
tag with fluorescent
green= sites of replication
red=nuclear DNA

Examples of this nuclear compartmentalisation
clusters of DNA replication forks (replication foci)
clusters of RNA synthesis and processing machinery (transciption foci)
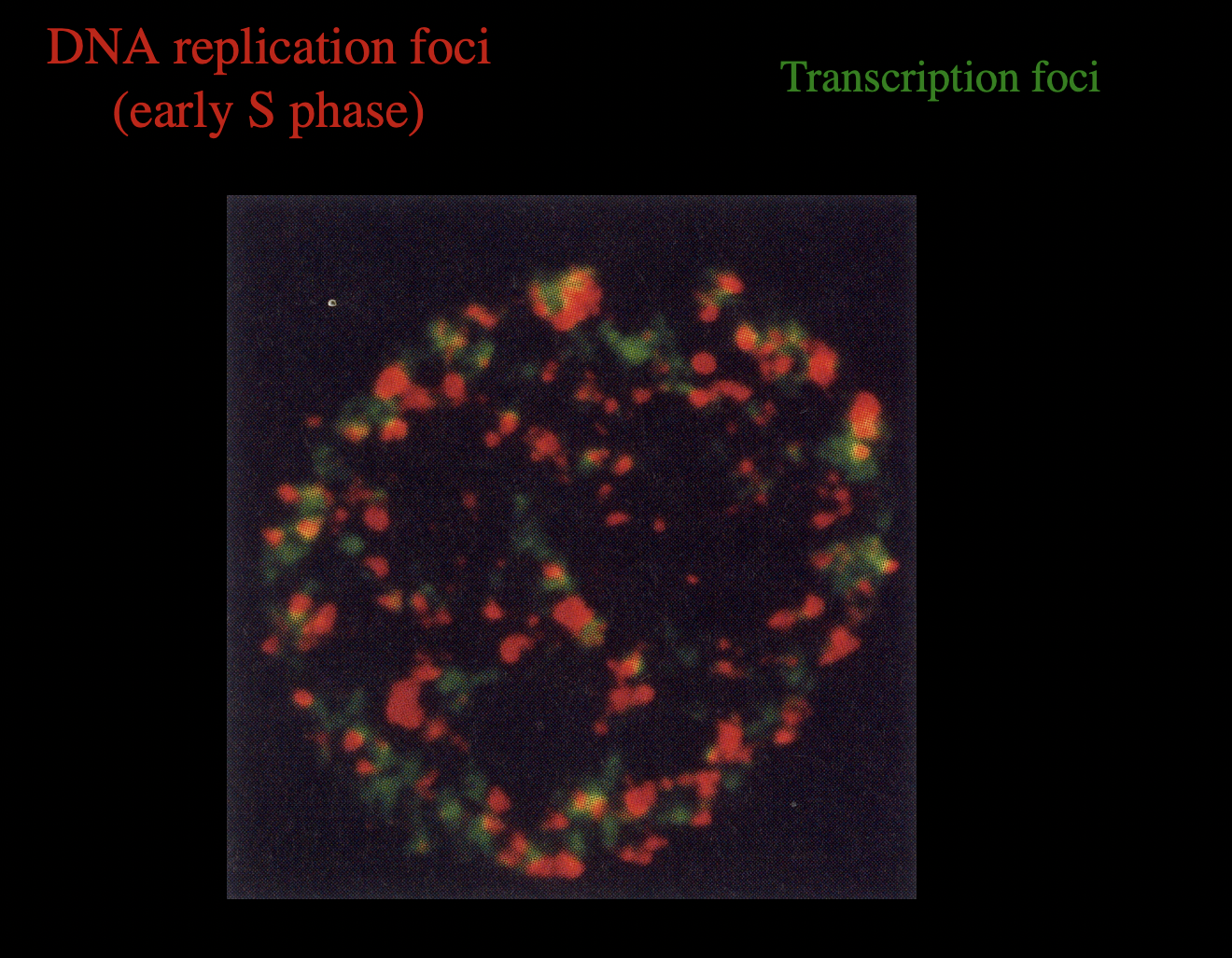
Features of the intracellular locations and patterns of these foci?
highly dynamic
seem to be associated with the nuclear matrix
Tagging the parts of DNA which are replicating also gives infor for the timing of replication during interphase:
EARLY: euchromatin
LATE: heterochromatin

DNA replication foci and trasciption foci
WHat is the nucleolus
large subnuclear compartment
separated from the rest of the nucleus
by region of condensed heterochromatin
How are nucleoli dynamic
Early G1: separately made from each chromsome territory
aggregate mid G1
finaally one nucleous late G1/S phasse

What happens with in the nucleolus
rDNA is transciptbed by RNA polymerase 1
generatres pre rRNA
these RNAs are processed to generate mature rRNAs
assembled with imported ribosomal proteins
to generate ribosome subunits
THEN exported out of the nucleus
complete ribosomes are assembled in the cytoplasm
What surrounds the chromatin in interphase nucleus
nuclear envelope (the nuclear frontier
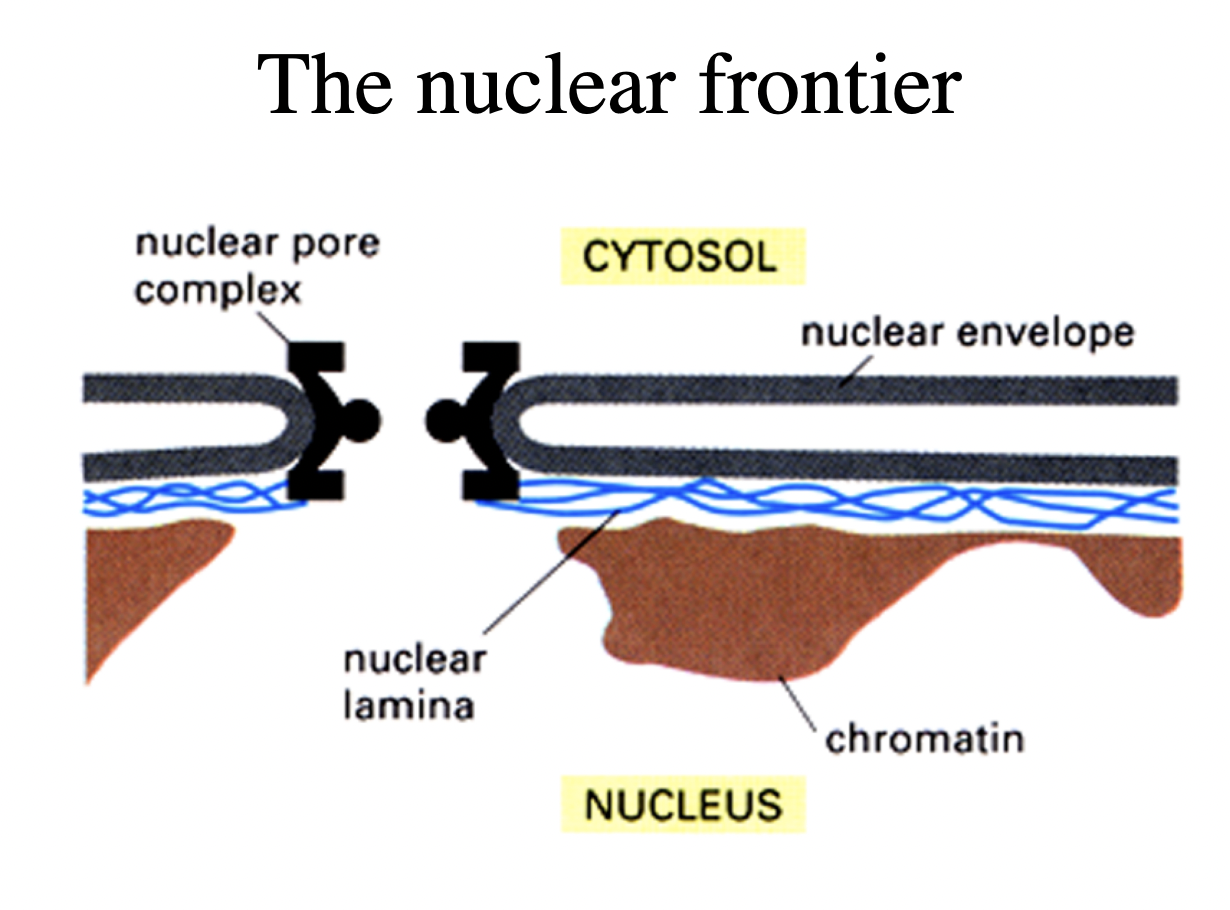
What does the nuclear envelope consist of
2 membranes
underlying lamina
2 dimensional meshworkd made of a spcieal kind of intermediate filament proteins
lamina itself is used to help repair DNA after damage e.g UV light
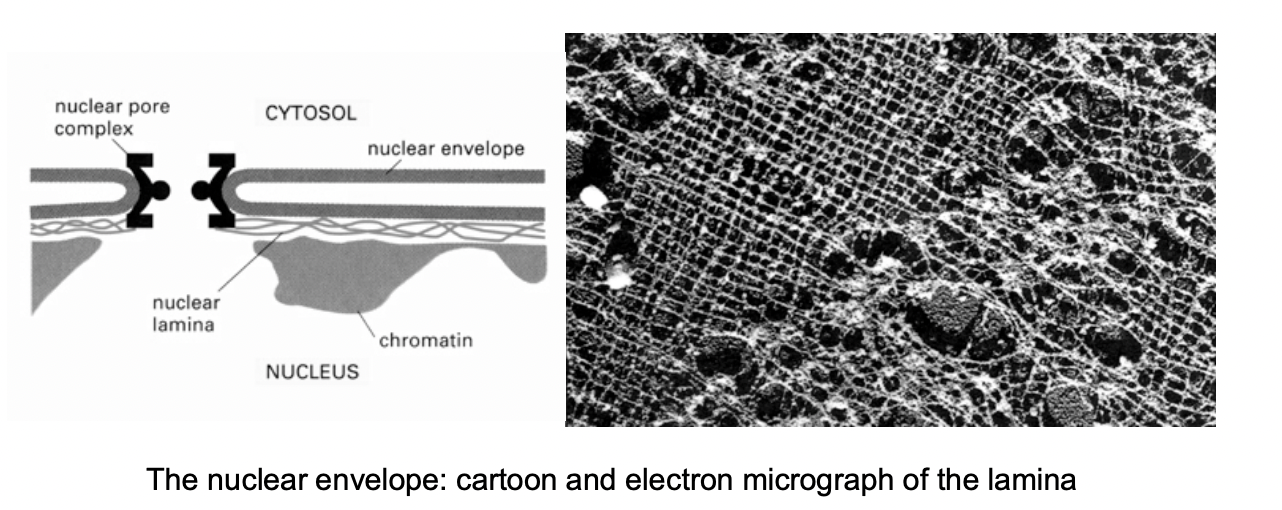
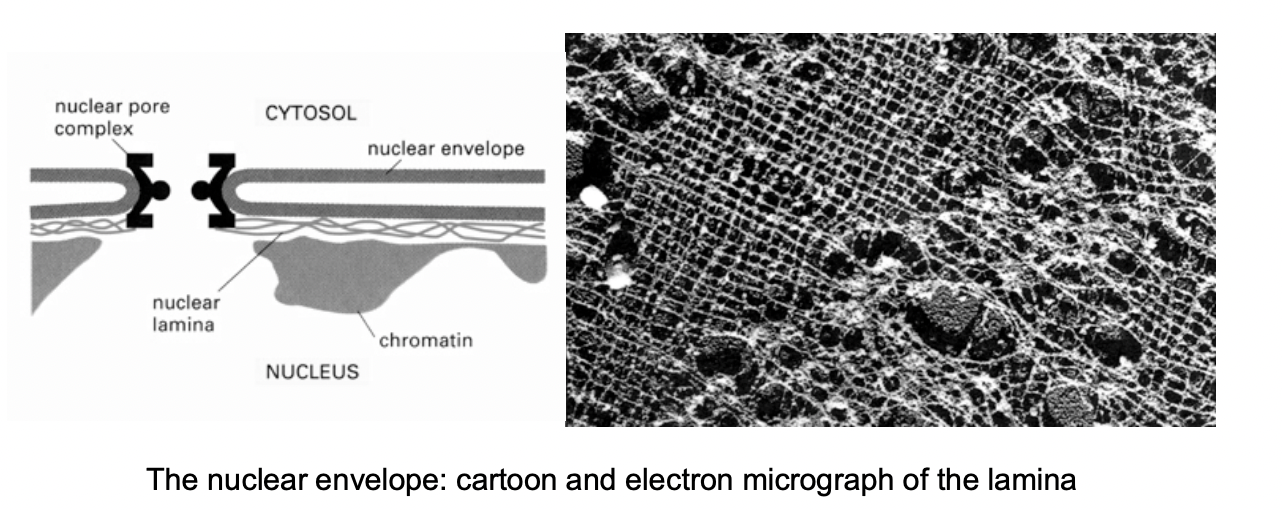
What are these special kinds of proteins
Lamins
A B and C
cross linked protein fibres
solid stuff the keep chromatin in
the membrane is only like a bubble
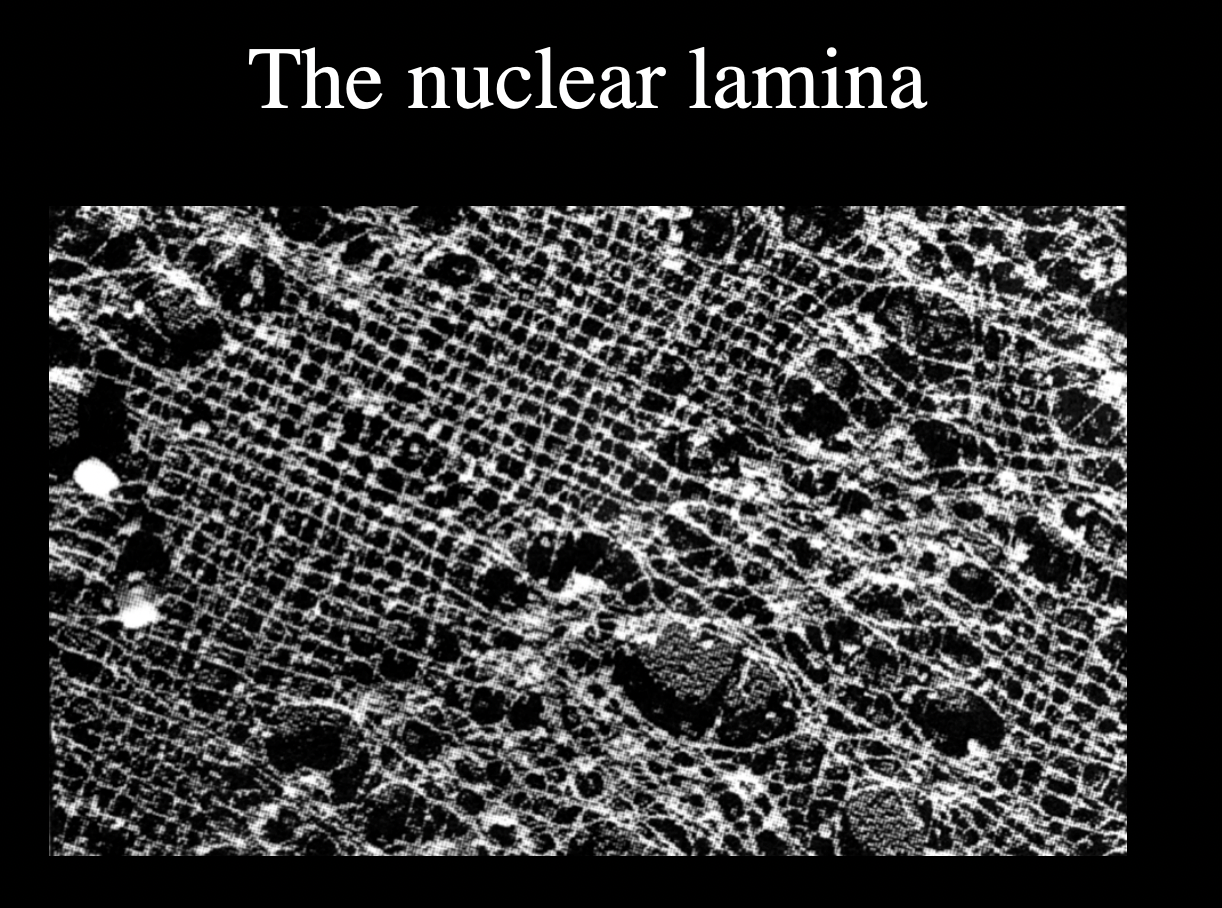
HOw does the nucleaur envelope interact with the nucleus
Direct contact to
chromatin
inner nuclear membrane
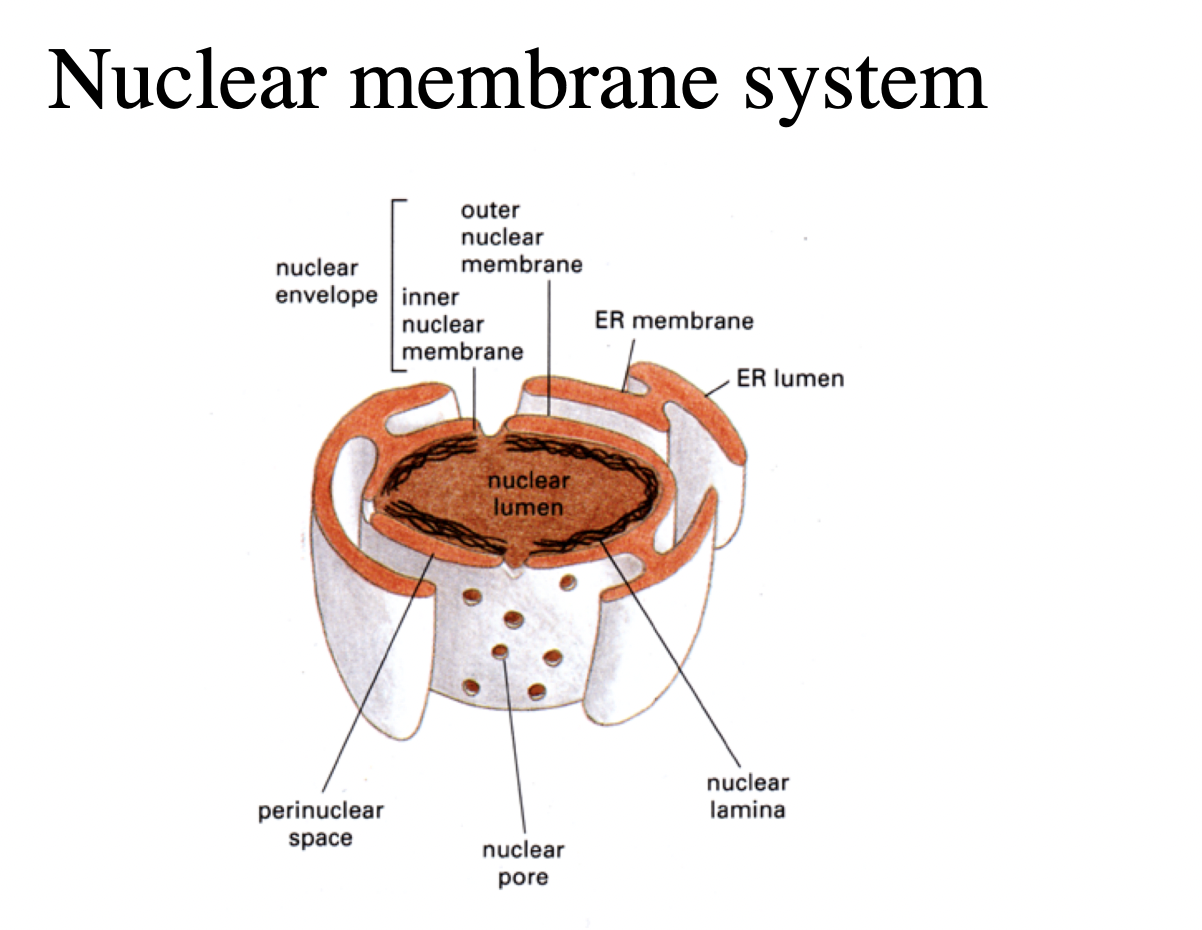
How do lamin fibres contribute to architecture of nuclear matrix (as some evidence suggests)
Lamin fibres extend into the lumen of the nuclei
What does the inner membrane contain
receptors that bind the nuclear lamina
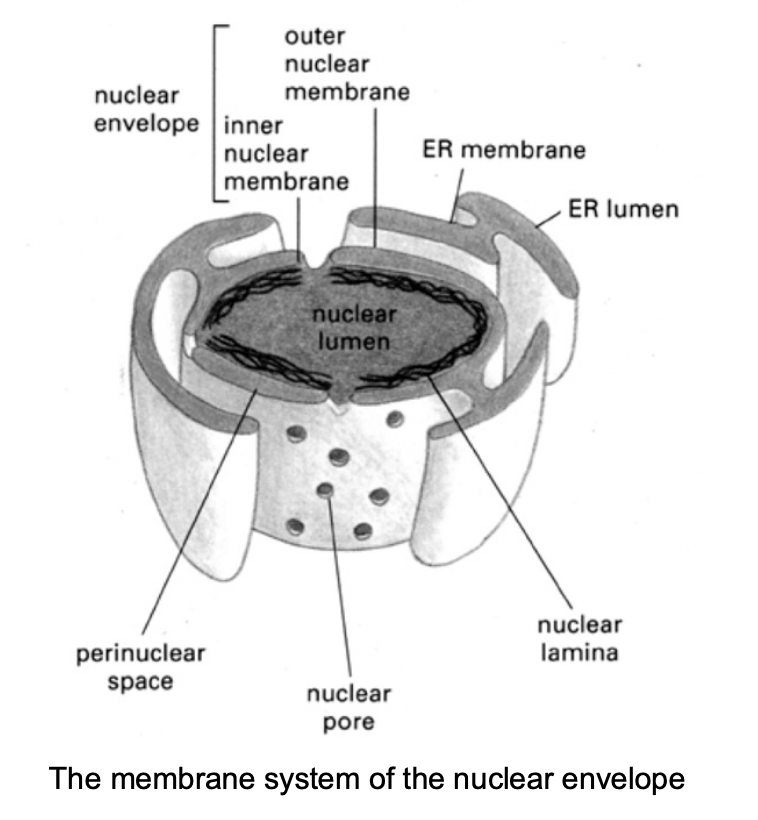
Features of the outermembrane
continuous with the rough endoplasmic reticulum
contains ribosomes
Both the inner nad outer membrane …
encapsulate the perinuclear space
which is continuous with the lumen of the ER
Both nuclear membranes are perforated by…
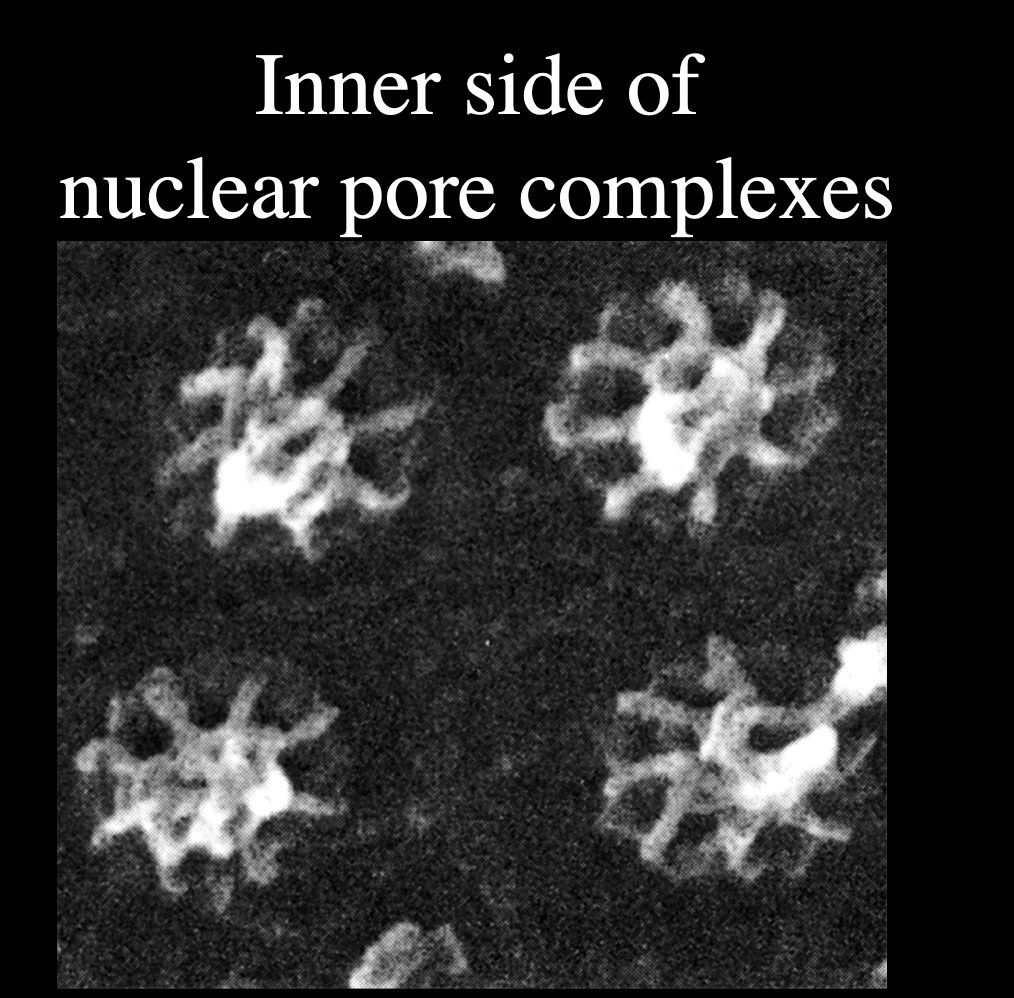
nuclear pore complexes
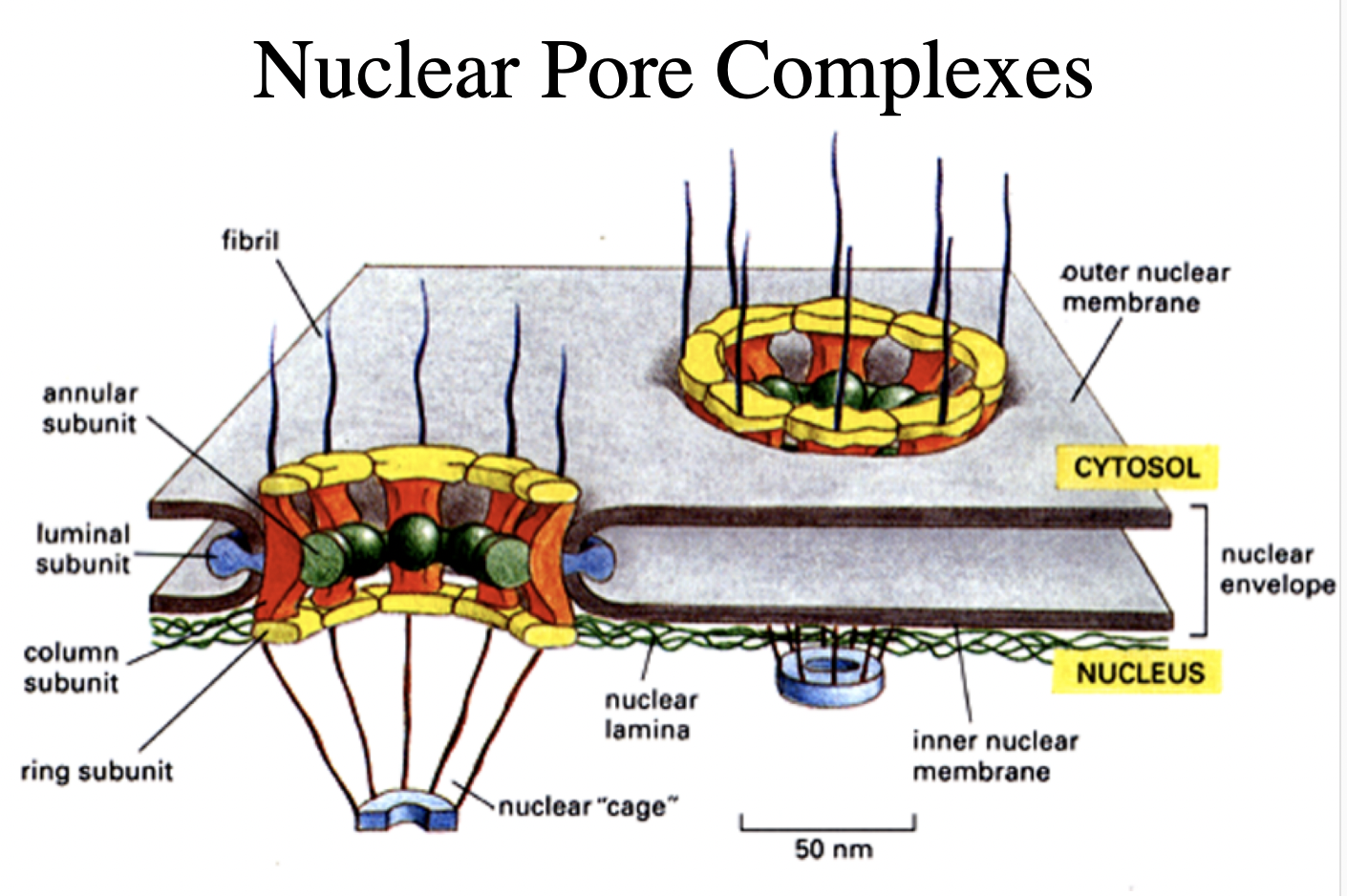
What are nuclear pore complexes
huge macromoleular complexes
aorund 150MDa
made of 50-100 different proteins
nucleoporins
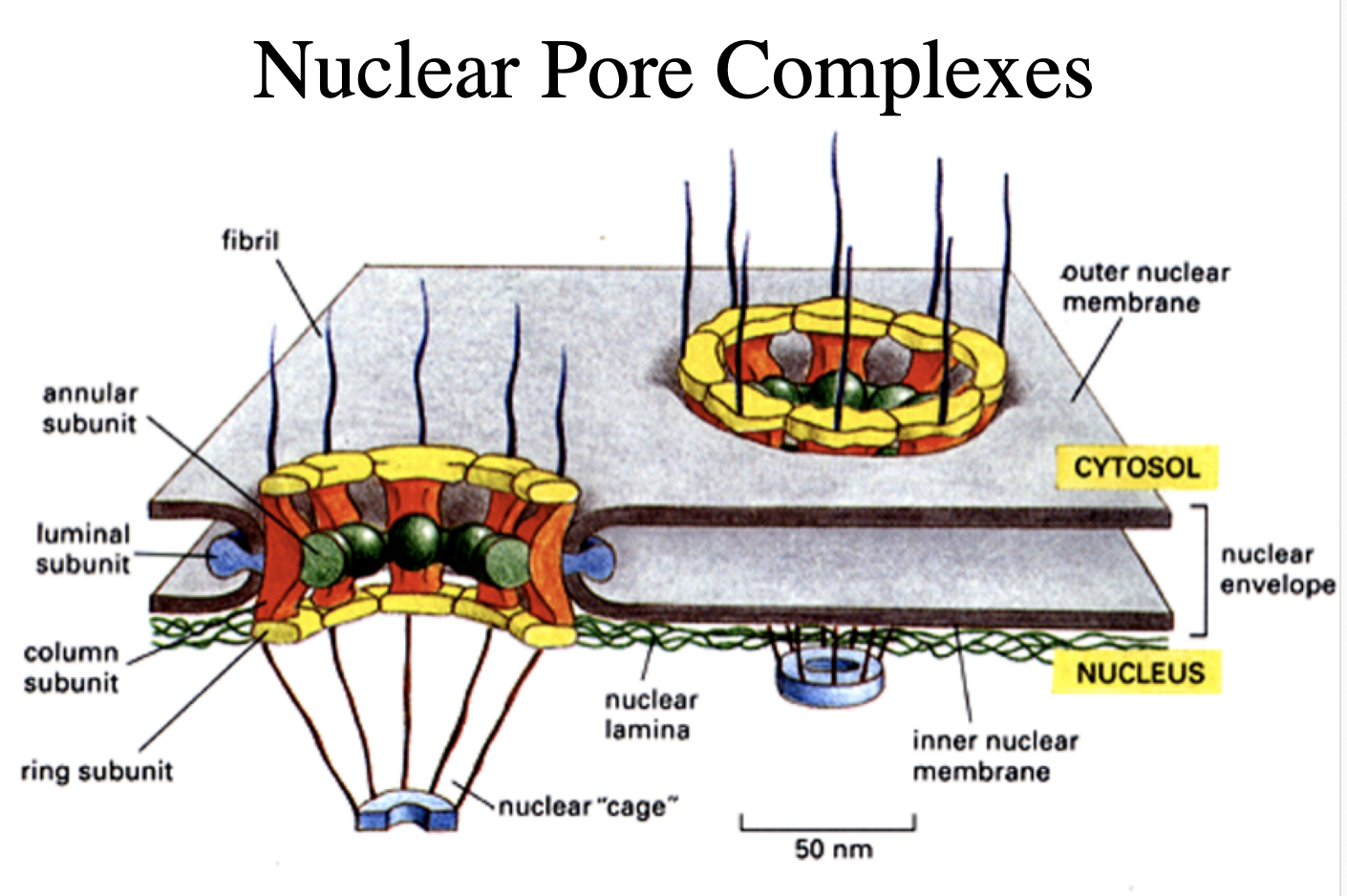
What do Nucleuar pore complexes form
aqueous channels across the nuclear envelope
allows diffusion of small molecules into and out of nucleus
But what is their main function?
regulated transport of mactomolecules
into and out of the nucleus