Risk Estimates
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Risk
Often expressed as the probability or likelihood that an event will occur
(BEIR) VII
Biological effects of Ionizing Radiations International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) 103
Committee reports such as ____ and ____ state risk from radiation exposure as either absolute risk or relative risk.
probability or likelihood
Risk Often expressed as the ____ or ____ that an event will occur
relative risk
absolute risk
There are two models used to assess the risk of stochastic effects from radiation exposure: ____ and _____
Relative Risk
multiplicative risk model
Relative Risk
Computed by comparing the number of persons in the exposed population showing a given stochastic effect with the number in an unexposed population who show the same stochastic effect.
1 to 10
Relative risk rates range from
Relative Risk
rates range from 1 to 10, with 1 representing no risk at all
1
Relative Risk rates range from 1 to 10, with ___ representing no risk at all
expressing risk
The relative and absolute risk models are most often used for
relative & absolute risk
The ___ and ____ models are most often used for expressing risk
BEIR Committee
which is associated with the National Academy of Sciences, used the relative risk model
Committee on the Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation
BEIR Committee
relative risk model
The BEIR Committee (Committee on the Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation), which is associated with the National Academy of Sciences, used the
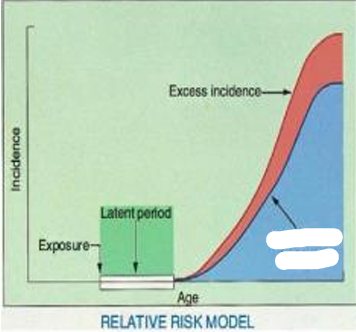
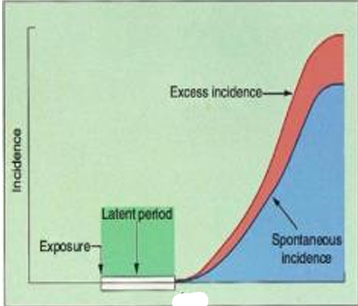
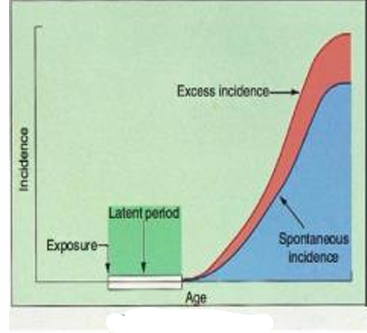
Incidence
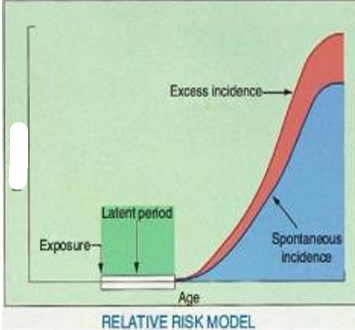
Exposure
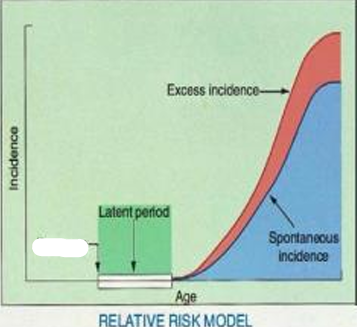
Latent Period
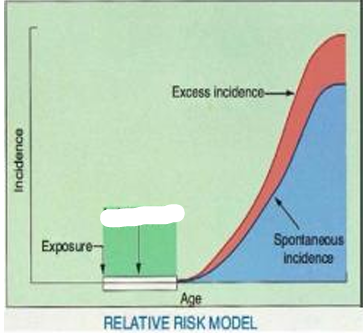
Excess Incidence
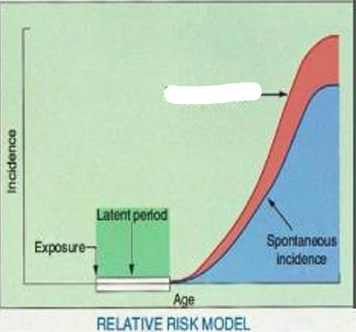
Spontaneous Incidence
Age
Relative Risk Model
this model predicts that the number of excess cancers will increase as the natural incidence of cancer increases with advancing age in a population
2.5
Relative Risk
A study of radiation-induced leukemia (cancer of blood-forming cells in bone marrow) was performed after diagnostic levels of radiation. Four hundred cases were observed in 150, 000 people irradiated. The normal incidence of leukemia is 120 cases per 100,000. What is the relative risk of radiation-induced leukemia?
5.08
Relative Risk
In Hiroshima, 61 leukemia deaths were observed as compared with the expected incidence of 12
2.85
Relative Risk
In Nagasaki, 20 leukemia deaths were observed as compared with the expected incidence of 7.
Excess Relative Risk
Equal to the relative risk minus 1
relative risk minus 1
Excess Relative Risk Equal to the ____
Excess Relative Risk
Determined by subtracting one from the relative risk calculated, e.g., if the relative risk is 1.5, the ____ would be 0.5
0.015 or 1.5%
Excess Relative Risk
Consider a population with a natural absolute risk for incidence of a disease of 20,000 cases. After this population is exposed to ionizing radiation, there are 20,300 disease cases observed.
Absolute Risk
additive risk model
Absolute Risk
predicts that a of specific number of excess cancers will occur as a result exposure.
Absolute Risk
states risk in terms of number of cases/106 persons/rad/year
number of cases/106 persons/rad/year
Absolute Risk states risk in terms of ___
Absolute Risk
assumes a linear dose-response relationship.
linear dose-response relationship
Absolute Risk assumes a
0.9
Absolute Risk
Absolute risk for radiation-induced breast cancer is presumed to be 6 cases/106 persons/rad/year at a 15-year at risk period. If 10, 000 women receive 1 rad during mammography, what would be the total number of cancers expected to be produced?
3.6
Absolute Risk
Absolute risk for radiation-induced breast cancer is presumed to be 12 cases/106 persons/rad/year at a 30-year at risk period. If 10, 000 women receive 1 rad during mammography, what would be the total number of cancers expected to be produced?
Excess risk
observed cases - expected cases
5 cases
EXCESS RISK
If 52 cases of a disease are observed in a population exposed to 200 rad and 47 were expected, the excess is?
~12.9
EXCESS RISK
Problem: In a population of 2,000 radiologists, 13 cases of skin cancer were detected. The incidence for the general population is 0.5/100,000. How many excess skin cancers were produced in the radiologist population?
EXCESS ABSOLUTE RISK (EAR)
or excess attributable risk
EXCESS ABSOLUTE RISK (EAR)
Equal to the rate of disease in exposed population minus the rate of disease in unexposed population
excess attributable risk
EXCESS ABSOLUTE RISK (EAR) or ____
EAR per unit dose
Difference between two absolute risk and is commonly used in radiation epidemiology expressed as the ____
radiation epidemiology
Difference between two absolute risk and is commonly used in ____ expressed as the EAR per unit dose.
two absolute risk
Difference between ____ and is commonly used in radiation epidemiology expressed as the EAR per unit dose.
300/100,000 or 300 in 100,000
EXCESS ABSOLUTE RISK (EAR) Problem: Consider a population with a natural absolute risk for incidence of a disease of 20,000 cases in every 100,000 individuals. After this population is exposed to ionizing radiation, there are 20,300 disease cases observed
Absolute Risk Model
This model predicts that a specific number of excess cancers will occur as a result of exposure