Chemistry 11 - Solutions and Acid-Base Reactions
1/155
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
156 Terms
What is an element?
An element is made of only one type of atom, such as hydrogen gas (H2) or aluminum foil (Al).

What is a compound?
A compound is made of two or more types of atoms, such as sodium chloride (NaCl) or water (H2O).
Define a solution.
A solution is a homogeneous mixture of substances composed of at least one solute and one solvent, where all components are uniformly mixed.
What is a solute?
A solute is a substance that is dissolved in a solvent, found in smaller amounts in solutions, such as oxygen in air or salt in saline solution.
What is a solvent?
A solvent is the medium in which a solute is dissolved, found in larger amounts in solutions, with water being called the universal solvent.
What happens to particles when a substance dissolves?
When a substance dissolves, its particles separate from each other and disperse into the solution.
What are nonelectrolytes?
Nonelectrolytes are molecular compounds like sugar that disperse electrically neutral particles throughout the solution.
What are electrolytes?
Electrolytes are ionic compounds that dissociate into electrically charged ions in solution, such as sodium chloride (NaCl).
How do water molecules interact with ions in a solution?
In water, positive ions are surrounded by the negative ends of water molecules, while negative ions are surrounded by the positive ends.
What occurs during the dissolution of a polar molecular compound in water?
The positive part of the polar molecule is surrounded by the negative ends of water molecules, and the negative part is surrounded by the positive ends.
What is the role of hydrogen bonds in the dissolution process?
During dissolution, some hydrogen bonds between water molecules are broken, and new ion-dipole attractions or hydrogen bonds are formed.
What is an aqueous solution?
An aqueous solution is one where water is the solvent, and it can be either colored or colorless.
What is an alloy?
An alloy is a solution of metals, such as brass or bronze.
What is the difference between a homogeneous mixture and a heterogeneous mixture?
A homogeneous mixture has a uniform composition throughout, while a heterogeneous mixture has a non-uniform composition.
Give an example of a heterogeneous mixture.
An example of a heterogeneous mixture is a salad or a mixture of sand and salt.
What is the significance of water being called the universal solvent?
Water is called the universal solvent because it can dissolve more substances than any other liquid, due to its polar nature.
What is the difference between a solute and a solvent in terms of quantity?
In a solution, the solute is present in smaller amounts, while the solvent is present in larger amounts.
What does it mean for a solution to be transparent?
A transparent solution allows light to pass through without significant scattering, making it clear.
What is the effect of temperature on the solubility of solids in liquids?
Generally, the solubility of solids in liquids increases with an increase in temperature.
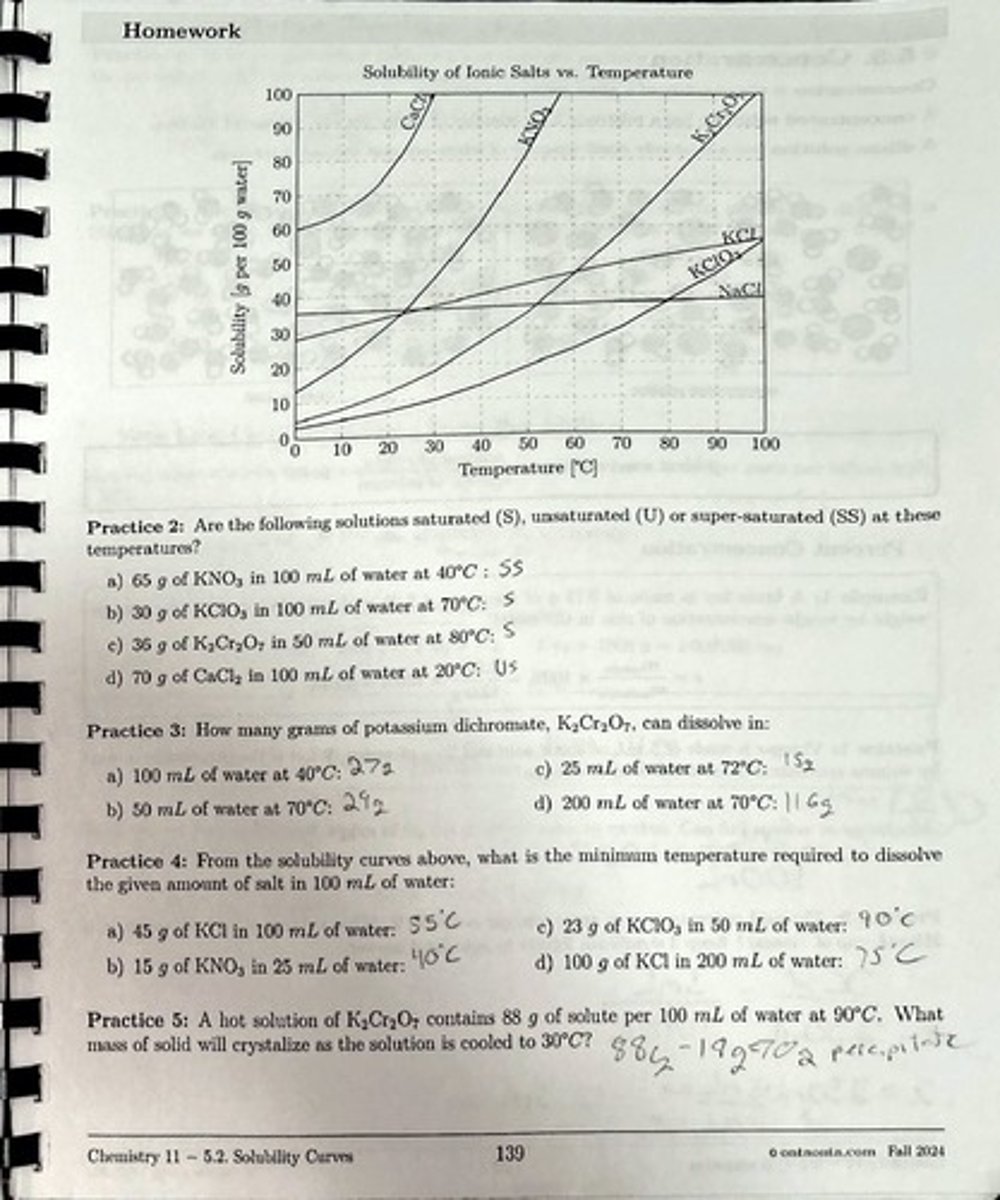
What is the difference between a saturated and unsaturated solution?
A saturated solution contains the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve at a given temperature, while an unsaturated solution can still dissolve more solute.
What is the role of ionic compounds in conducting electricity in solutions?
Ionic compounds dissociate into ions in solution, allowing the solution to conduct electricity.
What is a polar molecule?
A polar molecule has a partial positive charge on one end and a partial negative charge on the other, leading to dipole-dipole interactions.
What types of compounds are more soluble in water due to strong hydrogen bonds?
Compounds containing N-H, O-H, or F-H groups.
What is the definition of solubility?
The maximum amount of a solute that will dissolve in a certain amount of solution at a specified temperature.
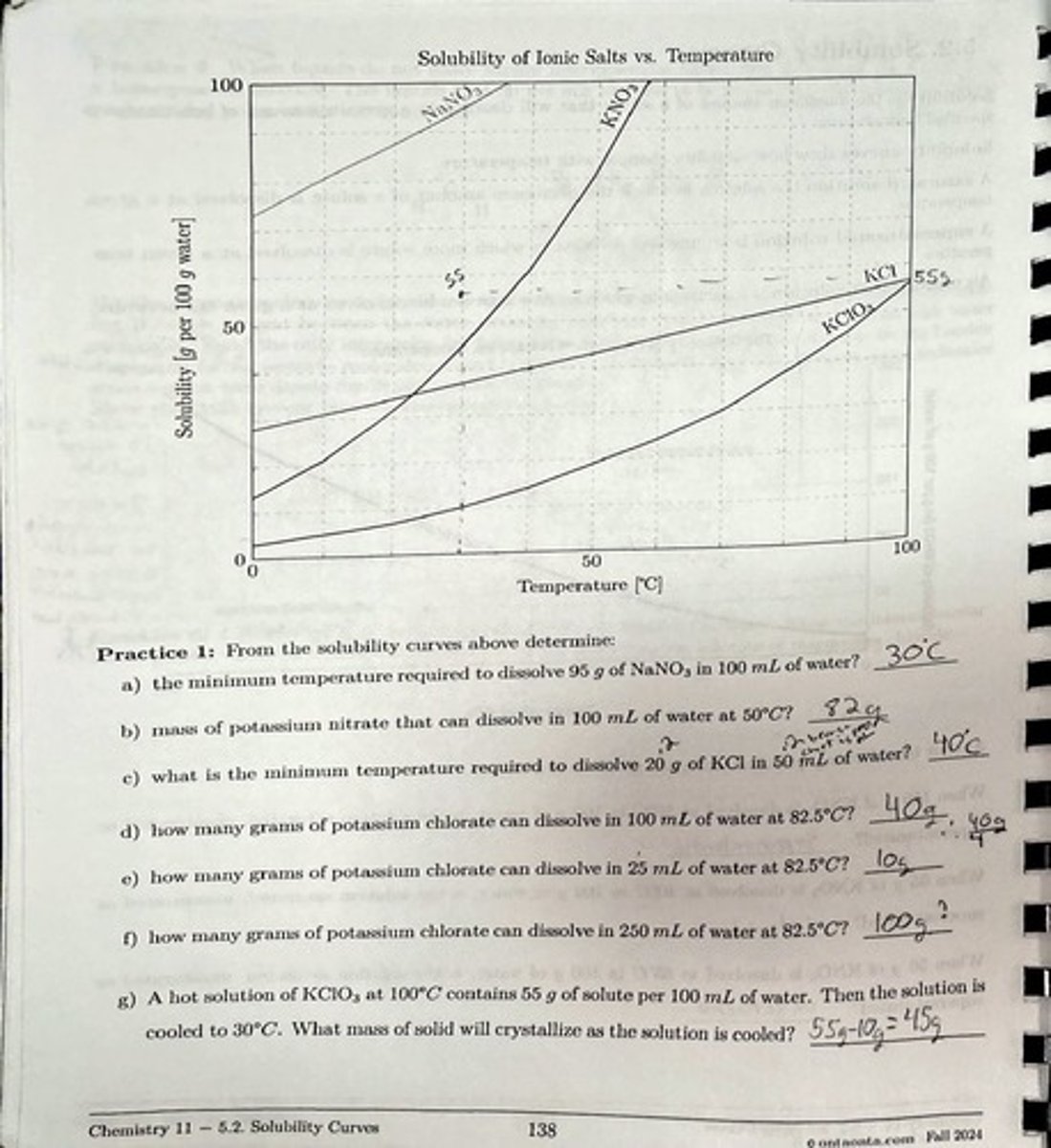
What is a saturated solution?
A solution in which the maximum amount of a solute is dissolved at a given temperature.
What is a supersaturated solution?
An unstable solution in which more solute is dissolved than is normally possible at a given temperature.
What is an unsaturated solution?
A solution in which more solute can be dissolved at a given temperature.
Which solute is soluble in water: NaCl, CH4, or MgCl2?
NaCl and MgCl2 are soluble in water.
Which solutes will dissolve in hexane (C6H14)?
CH4 and C5H12 are soluble in hexane.

What is the term for liquids that mix together to form a homogeneous mixture?
Miscible.
What is an example of two miscible liquids?
Ethanol and water.
What happens to the hydrogen bonds between water molecules when ethanol is mixed with water?
The existing hydrogen bonds between water molecules must be broken to form new hydrogen bonds with ethanol.
What is the reason that pentane and water are immiscible?
Pentane is nonpolar and cannot form dipole-dipole or hydrogen bonds with polar water.
What intermolecular forces are present between magnesium chloride ions and water molecules in an aqueous solution?
Ion-dipole interactions.
What is the significance of solubility curves?
They show how solubility changes with temperature.
What is the relationship between temperature and the solubility of potassium nitrate?
Solubility typically increases with temperature.
What is the definition of hydrogen bonding?
A strong type of dipole-dipole attraction between molecules that contain N-H, O-H, or F-H groups.
What must occur for two liquids to be miscible?
They must break existing intermolecular forces and form new ones.
What type of solution contains the maximum amount of solute dissolved at a specific temperature?
Saturated solution.
What type of solution can still dissolve more solute at a specific temperature?
Unsaturated solution.
What is the term for the forces that hold together nonpolar molecules?
London dispersion forces.
What is an example of a mixture that is not a solution?
Diamond.
What is the main reason for the difficulty in separating ethanol-water mixtures?
Their boiling points are very close to each other.
What happens to the intermolecular forces when two immiscible liquids are mixed?
They do not mix because their intermolecular forces are incompatible.
What is the role of energy in breaking intermolecular forces when mixing liquids?
Energy is required to separate the molecules from each other.
What is the solubility status of 150 g of KNO3 dissolved in 100 g of water at 50°C?
The solution is supersaturated.
What is the solubility status of 65 g of KNO3 dissolved in 100 g of water at 40°C?
The solution is saturated.
What is the solubility status of 50 g of KNO3 dissolved in 100 g of water at 65°C?
The solution is unsaturated.
What is the minimum temperature required to dissolve 95 g of NaNO3 in 100 mL of water?
The minimum temperature is above 50°C.
How many grams of potassium nitrate can dissolve in 100 mL of water at 50°C?
Approximately 40 g.
What is the minimum temperature required to dissolve 20 g of KCl in 50 mL of water?
The minimum temperature is approximately 60°C.
How many grams of potassium chlorate can dissolve in 100 mL of water at 82.5°C?
Approximately 70 g.
How many grams of potassium chlorate can dissolve in 25 mL of water at 82.5°C?
Approximately 17.5 g.
How many grams of potassium chlorate can dissolve in 250 mL of water at 82.5°C?
Approximately 175 g.
If a hot solution of KClO3 at 100°C contains 55 g of solute per 100 mL of water and is cooled to 30°C, what mass of solid will crystallize?
Approximately 30 g will crystallize.
What is the solubility status of 65 g of KNO3 in 100 mL of water at 40°C?
The solution is saturated.
What is the solubility status of 30 g of KClO3 in 100 mL of water at 70°C?
The solution is unsaturated.
What is the solubility status of 36 g of K2Cr2O7 in 50 mL of water at 80°C?
The solution is supersaturated.
What is the solubility status of 70 g of CaCl2 in 100 mL of water at 20°C?
The solution is unsaturated.
How many grams of potassium dichromate can dissolve in 100 mL of water at 40°C?
Approximately 25 g.
How many grams of potassium dichromate can dissolve in 50 mL of water at 70°C?
Approximately 35 g.
How many grams of potassium dichromate can dissolve in 200 mL of water at 70°C?
Approximately 140 g.
What is the minimum temperature required to dissolve 45 g of KCl in 100 mL of water?
The minimum temperature is approximately 60°C.
What is the minimum temperature required to dissolve 15 g of KNO3 in 25 mL of water?
The minimum temperature is approximately 70°C.
What is the minimum temperature required to dissolve 100 g of KCl in 200 mL of water?
The minimum temperature is approximately 80°C.
If a hot solution of K2Cr2O7 contains 88 g of solute per 100 mL of water at 90°C, what mass of solid will crystallize as the solution is cooled to 30°C?
Approximately 60 g will crystallize.
What is an electrolyte?
An electrolyte is a substance whose water solution conducts an electric current.
According to the Arrhenius definition, what is an acid?
An acid is a compound that ionizes in water to form hydrogen ions (H+).

What are the six strong acids?
The six strong acids are hydrochloric acid (HCl), hydrobromic acid (HBr), hydroiodic acid (HI), nitric acid (HNO3), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), and perchloric acid (HClO4).
What is a hydronium ion?
A hydronium ion is a hydrated hydrogen ion (proton), represented as H3O+(aq), formed by the attraction between a water molecule and a hydrogen ion (H+) from an acid.
What is an amphiprotic compound?
An amphiprotic compound is a substance capable of acting as an acid or a base in different chemical reactions, with water (H2O) being the most common example.
Give an example of an amphiprotic substance and its reactions.
H2SO4 can act as an acid: H2SO4 ⇌ HSO4- + H+ and as a base: HCO3- + H2CO3 ⇌ H2CO3 + SO4^2-.
What is the significance of conjugate acid-base pairs?
Conjugate acid-base pairs consist of two species that transform into each other by the gain or loss of a proton.
In the reaction HF + H2O → F- + H3O+, identify the acid and the base.
HF is the acid and H2O is the base.
What happens in the reaction HSO4- + H2O?
HSO4- acts as an acid and donates a proton to H2O, forming H2O and SO4^2-.
Why is HCl a stronger electrolyte than acetic acid (HCH3COO)?
HCl ionizes completely in solution, while acetic acid only partially ionizes, making HCl a stronger electrolyte.
What is the ionization percentage of strong acids in solution?
Strong acids ionize completely (100%) in solution.
What is the ionization percentage of weak acids in solution?
Weak acids ionize less than 50% in solution.
How does acid strength change down a group in the periodic table?
Acid strength increases down a group due to the weakening of the H-X bond as the size of the element X increases.
What is the relationship between the strength of an acid and the H-X bond?
As the H-X bond gets weaker, the strength of the acid increases because acids are proton donors.
What is the formula for benzoic acid?
The formula for benzoic acid is C6H5COOH.
In the reaction of benzoic acid with water, what are the products?
The products are C6H5COO- and H3O+.
What is the role of hydrogen sulfate ions in an aqueous solution?
Hydrogen sulfate ions can act as an acid, donating a proton to water.
What is the conjugate base of sulfuric acid (H2SO4)?
The conjugate base of sulfuric acid is HSO4-.
What is the conjugate acid of hydrogen phosphate (HPO4^2-)?
The conjugate acid of hydrogen phosphate is H2PO4-.
What is the significance of the reaction HS04 + H2O?
This reaction illustrates the amphiprotic nature of water and the ability of HSO4- to act as an acid.
What is the product of the reaction H2SO4 + H2O?
The products are H3O+ and HSO4-.
What is the ionization behavior of sulfuric acid?
Sulfuric acid ionizes completely to form HSO4- and H+, but its second proton ionizes partially.
What does the term 'strong acid' imply about its ionization in water?
A strong acid implies that it ionizes completely in water, resulting in a high concentration of H+ ions.
What is the trend in strength of oxyacids with respect to the number of oxygen atoms?
The strength of oxyacids increases with the increasing number of oxygen atoms: HClO < HClO2 < HClO3 < HClO4.
What are the common properties of acids?
1. Taste: sour when dissolved in water. 2. Touch: produce a stinging feeling, especially strong acids. 3. Corrosive: can corrode substances they contact. 4. Reactivity: react aggressively with most metals. 5. Electrical conductivity: strong acids are good electrolytes due to hydrogen ions.
What defines a strong base?
A strong base is an ionic hydroxide that dissociates completely in water to produce hydroxide ions (OH-).
List the nine strong bases.
1. Lithium hydroxide (LiOH) 2. Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) 3. Potassium hydroxide (KOH) 4. Rubidium hydroxide (RbOH) 5. Cesium hydroxide (CsOH) 6. Magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2) 7. Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) 8. Strontium hydroxide (Sr(OH)2) 9. Barium hydroxide (Ba(OH)2).
What are the properties of bases?
1. Taste: bitter. 2. Touch: soapy. 3. Corrosive: exercise safety. 4. Reactivity: react with acids to form salts. 5. Electrical conductivity: strong bases are good electrolytes due to hydroxide ions. 6. Turns litmus blue. 7. Turns phenolphthalein pink. 8. Changes bromothymol blue from yellow to blue.
What is the definition of an acid?
An acid is a compound that donates hydrogen ions (H+) and acts as a proton donor.
What is the definition of a base?
A base is a compound that accepts hydrogen ions (H+) from an acid and acts as a proton acceptor.
What is the pH scale used for?
The pH scale is used to measure the acidity of a solution, indicating whether it is acidic, neutral, or basic.
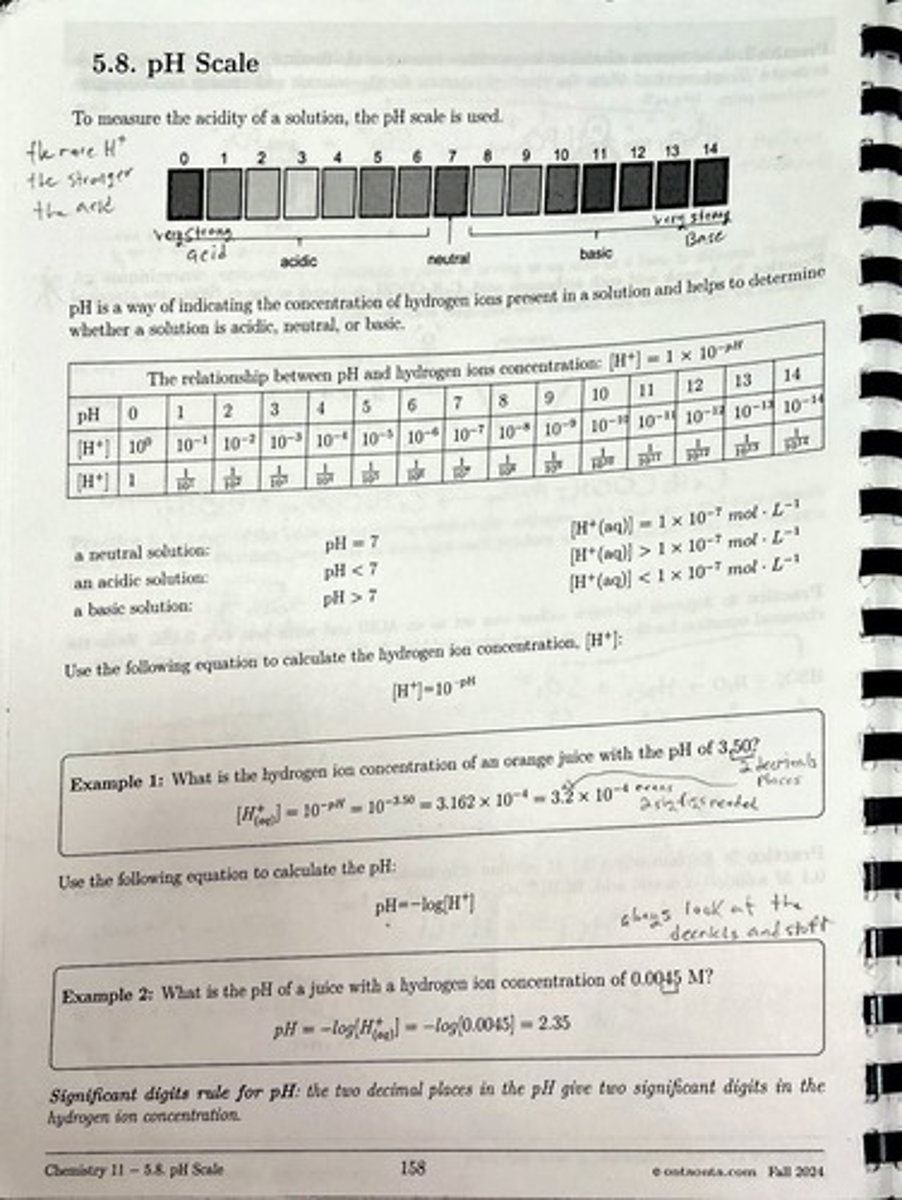
How is pH related to hydrogen ion concentration?
pH is calculated using the formula: [H+] = 10^-pH.
What is the pH of a neutral solution?
A neutral solution has a pH of 7.
What indicates an acidic solution in terms of pH?
An acidic solution has a pH less than 7.