Architecture History first Quiz Lecture one
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
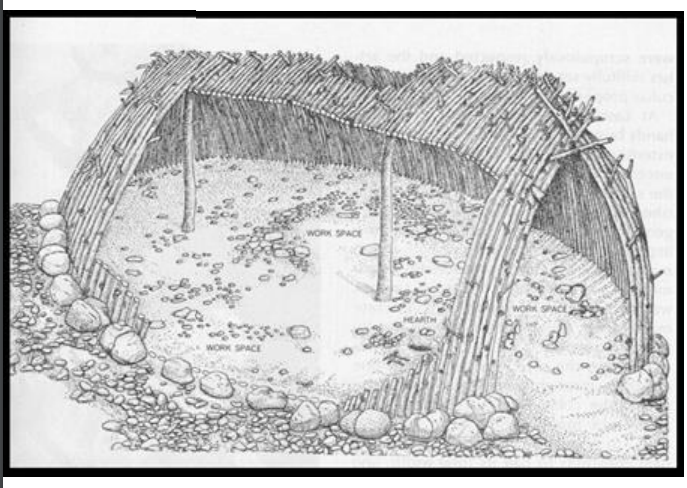
Terra Amata, 380,000 BCE or 230,000 BCE
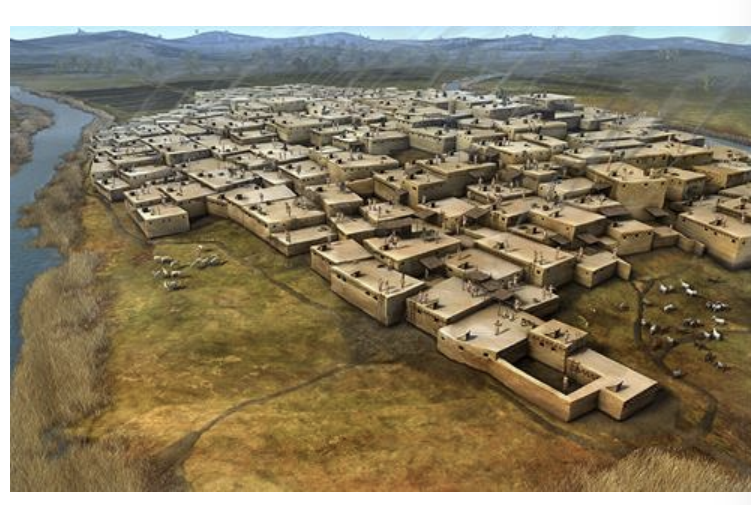

Çatalhöyük, ca. 7500 BCE - 5700 BCE
Paleolithic Era
period marked by the predominance of stone tools; circa 2.6 million years ago - 10,000 years ago; literally “old stone”
neolithic “revolution” era
period marked by transition from hunting and gathering societies to settlements and agriculture; still marked by the predominance of stone tools; circa 10,000 BCE - 3500 BCE; literally “new stone”
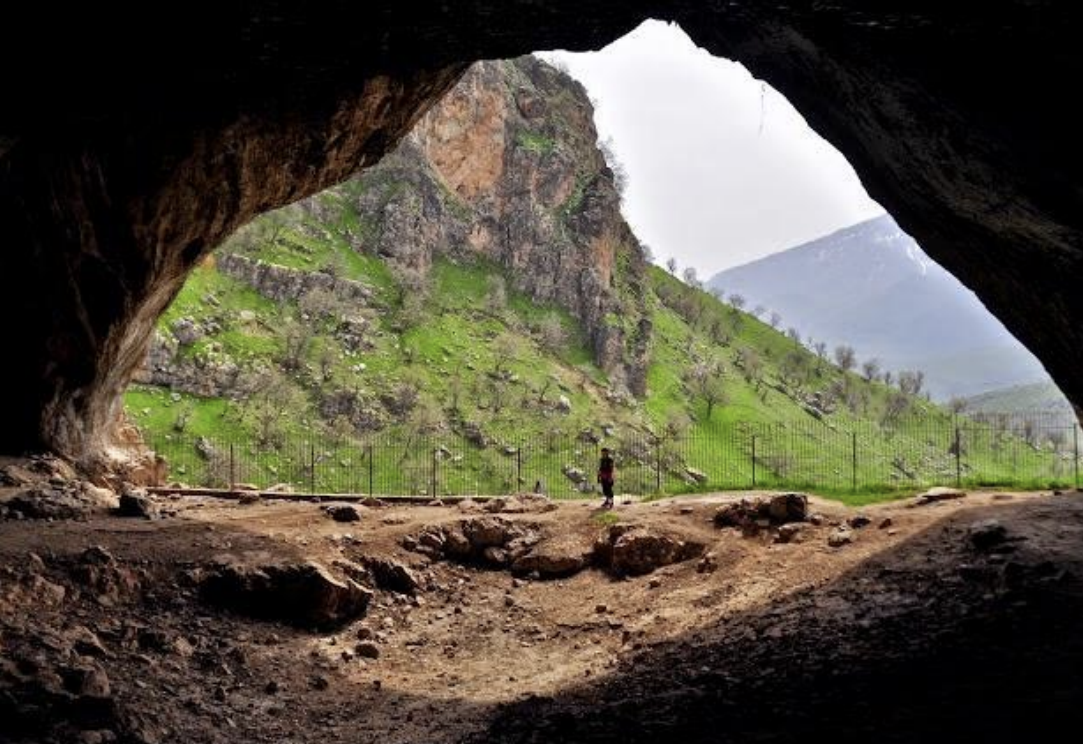

Shanidar Cave, Iraq, 65,000 BCE
Parietal Art
Is used to denote any prehistoric art found on cave walls. It embraces all types of cave painting, all forms of engraved rock art, or other petroglyphs, as well as any relief sculpture carved on walls, floors or ceilings.
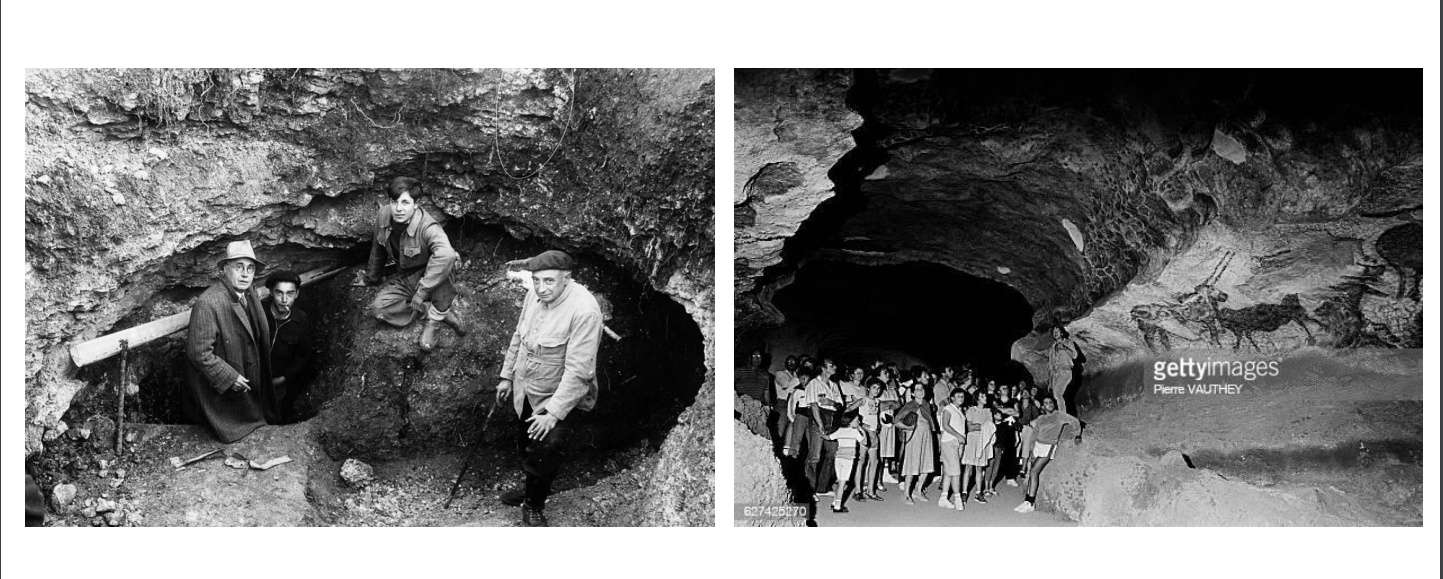

Lascaux Caves, Dordogne France, 17,000 BCE

What cave were these painted on
Lascaux Caves, Dordogne France, 17,000 BCE
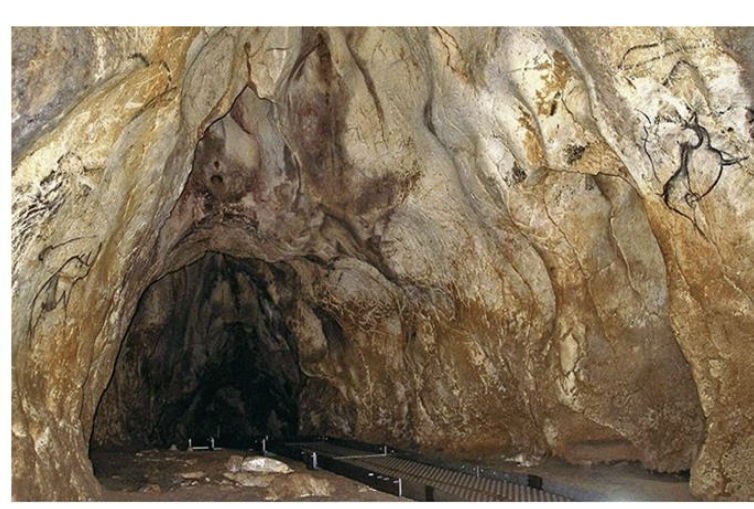

Chauvet Cave, ca. 35,000 BCE - 25,000, France
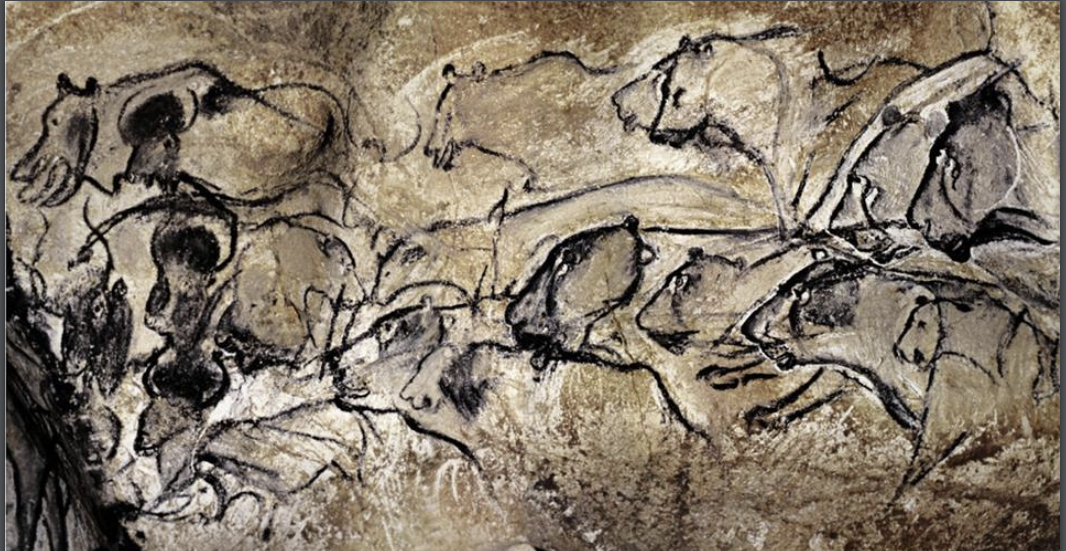

What cave were these painted on
Chauvet Cave, ca. 35,000 BCE - 25,000, France
megalith
large stone or boulder; literally ‘great stone’
Menhir
A tall upright stone of a kind erected in western Europe in the Neolithic period
Capstone
A single stone placed horizontally over burial chambers (without supports)
Dolmen
A megalithic tomb built with two or more upright stones capped by a flat stone.
Cromlechs
Neolithic stone circle formations
Cove
A Neolithic and Bronze Age megalith formation that is square or rectangular in plan and seem to have served as small enclosures within other henge, stone circle or avenue features. They consist of three or four orthostats placed together to give the impression of a box (stone is a square shape)
Henge
A particular type of earthwork of the Neolithic period, typically consisting of a roughly circular or oval-shaped bank with an internal ditch surrounding a central flat area of more than 20 m (66 ft)
Tumulus
Earth or stone mound raised over burial site or graves.
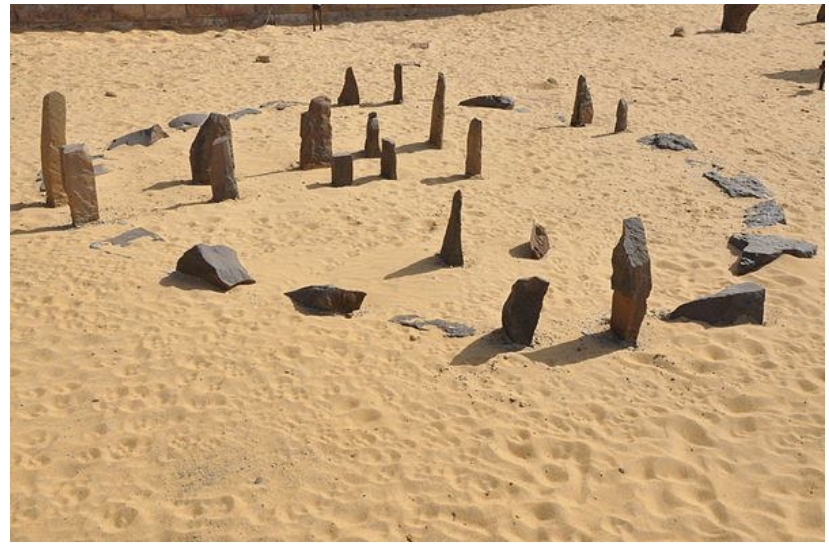

Reconstruction of Nabta Playa (South Egypt) 9000 BCE
Archaeoastronomy
Study of the role Of the sky in ancient cultures
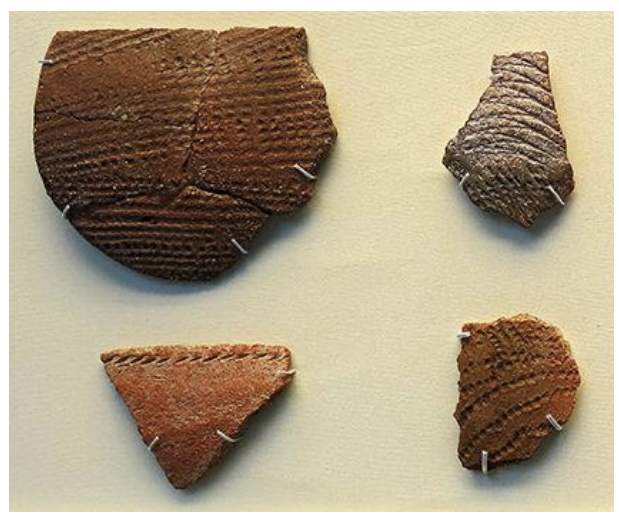

Fragments from Nabta Playa (South Egypt) ca. 9000BCE
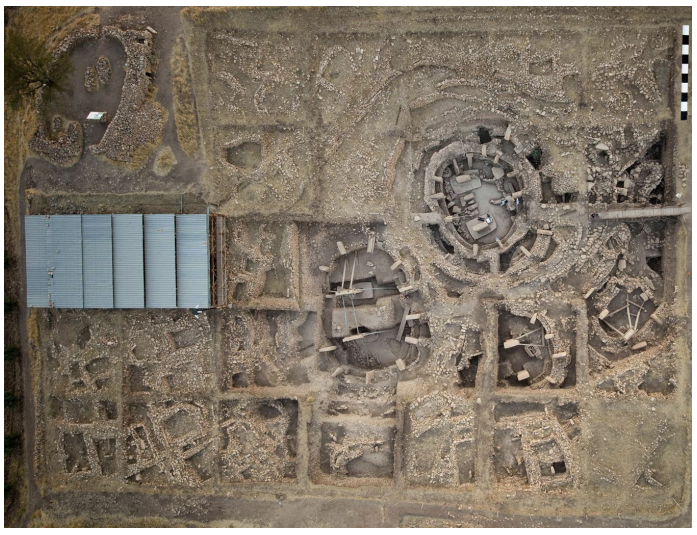

Göbekli Tepe (Girê Mirazan in Kurdish), ca. 9500 and 8000 BCE
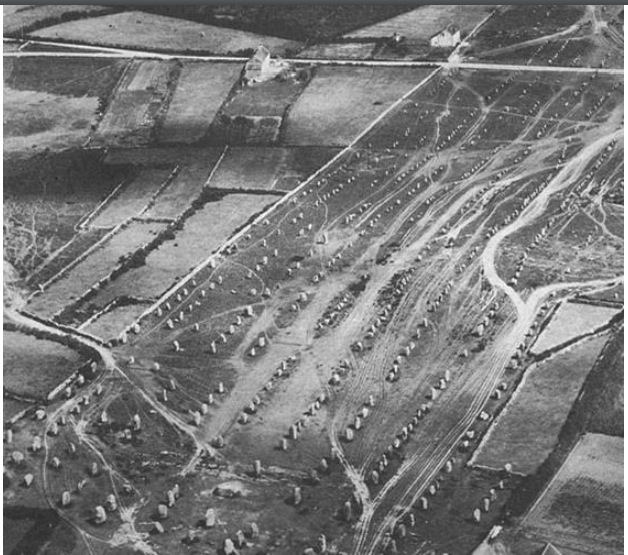

Carnac Stones, ca. 4500 BCE
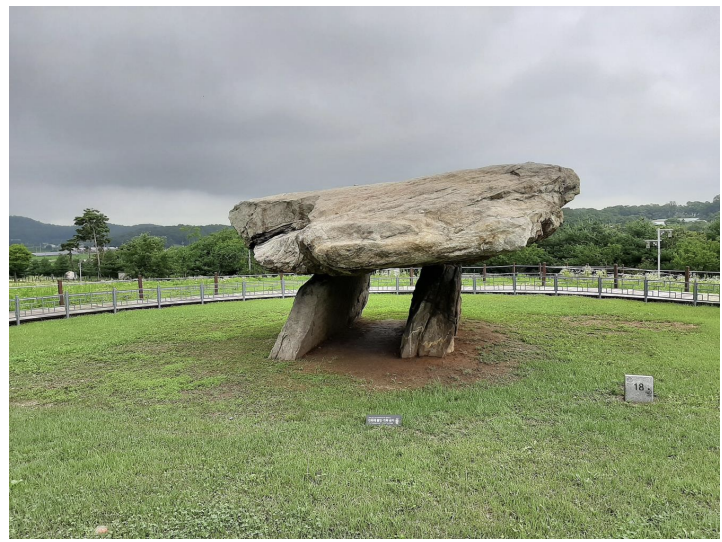

Korean Dolmen at Ganghwa Island (7000-3000 BCE)
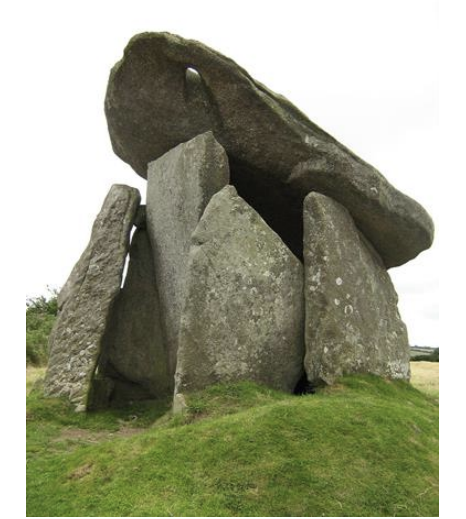

Trethevy Quoit, ca. 3700-3500 BCE
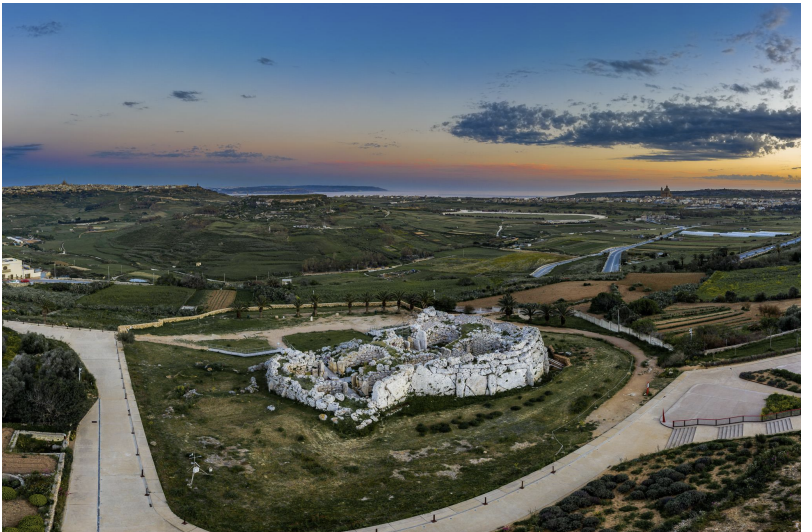

Ġgantija, Malta, 3600-2500 BCE
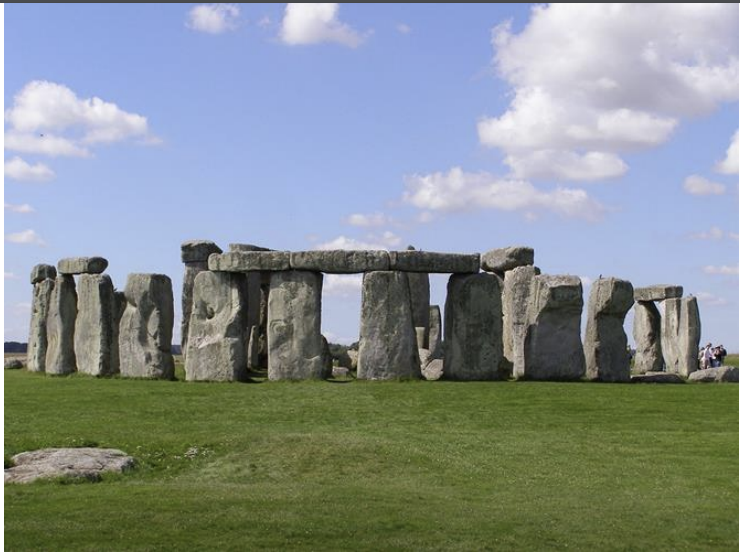

Stonehenge, ca. 2900-1400 BCE
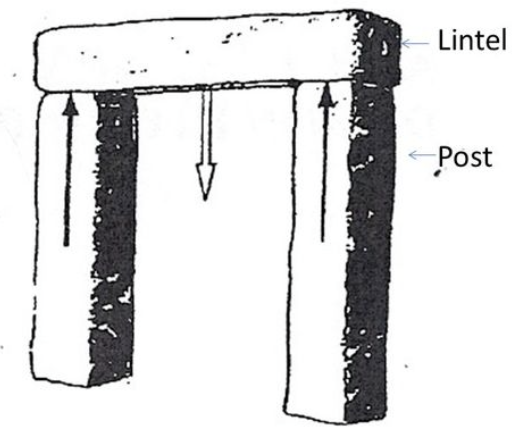
post-and-lintel construction
building system in which straight horizontal elements are supported by straight vertical elements

mortise and Tenon
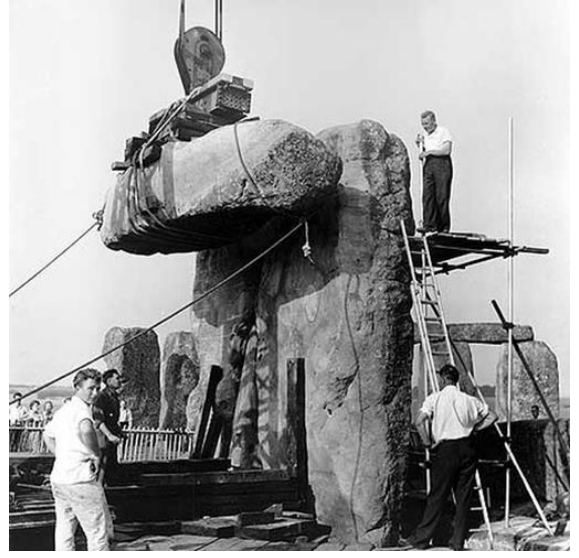

Stonehenge “Restoration,” 1958 CE
höyük
Neolithic mound
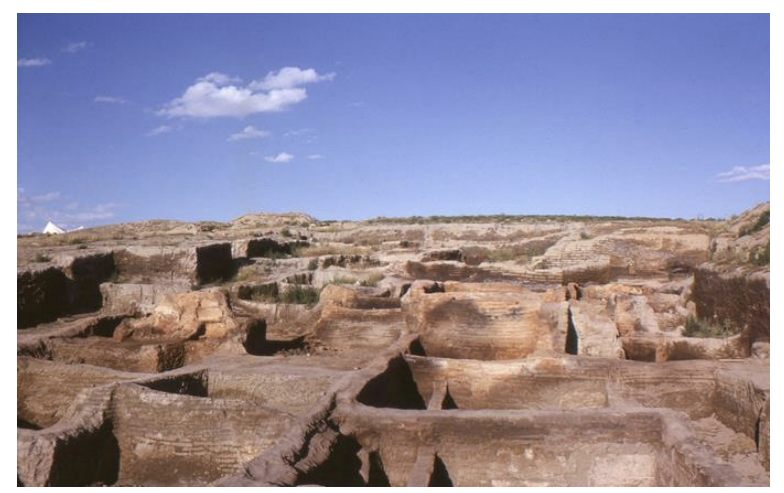

Çatalhöyük, ca. 7500 BCE - 5700 BCE
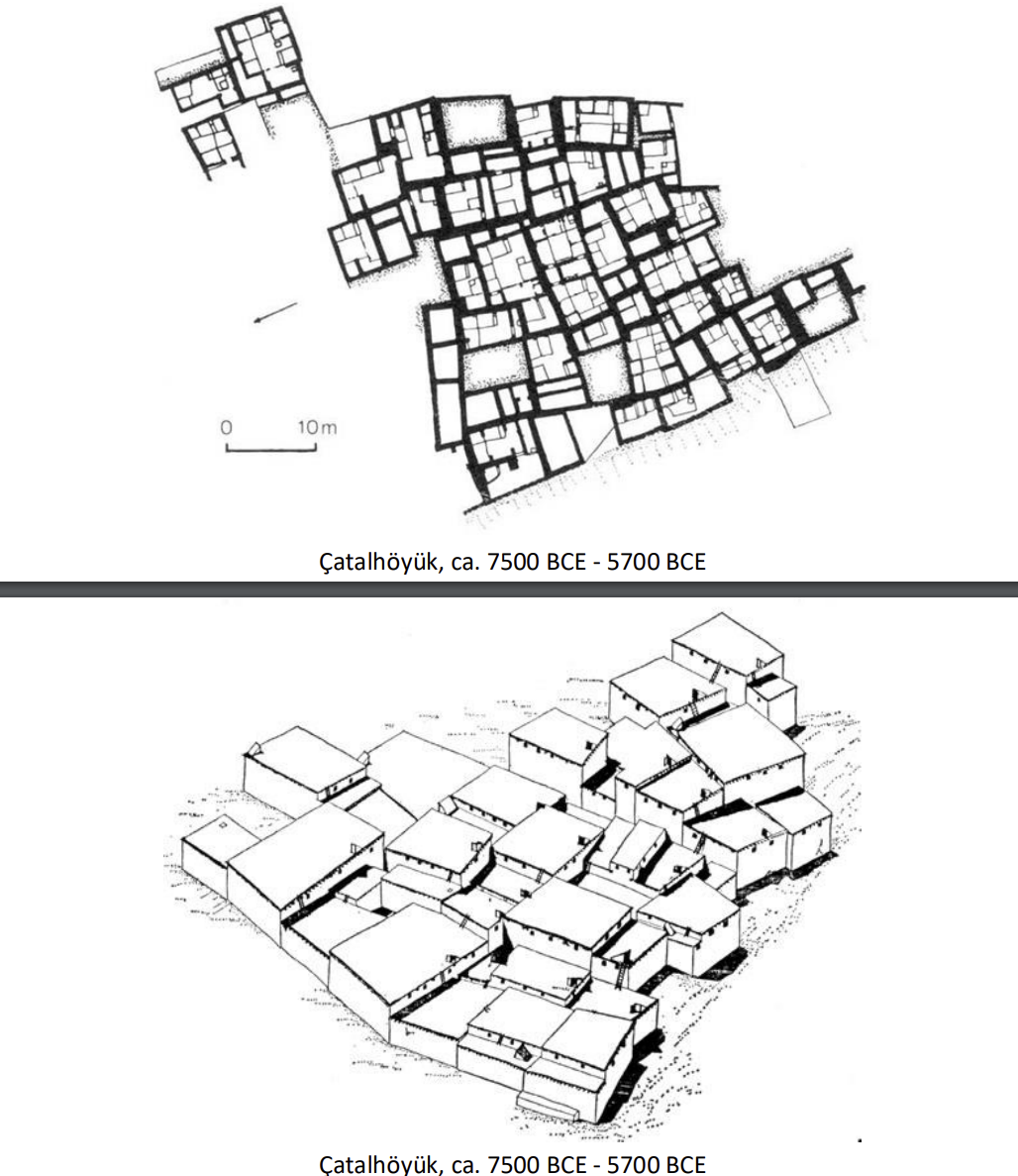
Catahoyuk
(7500–5700 BCE- it is a neolithic mound) 166 houses were discovered, with no streets, gaps, or courtyards. Built houses as they need it.

Seated Woman of Çatalhöyük, ca. 7500 BCE - 5700 BCE
