AP World Unit 5 (Revolutions)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:09 AM on 11/10/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
1
New cards
Empiricism
The idea that knowledge and understanding comes from your senses and experience, through observation and experimentation.

2
New cards
Social Contract
The view that peoples' moral and/or political obligations are dependent upon a contract or agreement among them to form the society in which they live.

3
New cards
Popular Sovereignty
The idea that the government gets its power and authority from the will of the people. (the people rule)

4
New cards
Scientific Method
A process for knowledge understanding that involves hypothesis, experimentation, and observation.
5
New cards
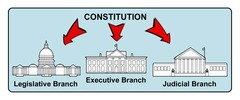
Montesquieu (1689-1755)
French political philosopher who advocated the separation of executive and legislative and judicial powers (1689-1755)
6
New cards
Thomas Hobbes (1588-1679)
English philosopher who believed that people are naturally selfish and without the social contract with the government, there would be complete anarchy.

7
New cards
Adam Smith (1723-1790)
Scottish economist who wrote the Wealth of Nations a precursor to modern Capitalism. He spoke of the laissez-faire and the "invisible hand."

8
New cards
Voltaire (1694-1778)
French philosopher who argued for the rights of freedom of speech and religion and criticized intolerance and oppression?

9
New cards
John Locke (1632-1704)
English philosopher who insisted that governments are formed to protect natural rights. He also stated that people are not naturally bad and that they are like a blank slate (tabula rasa) when born.

10
New cards
Abolitionism movement
Movement to end slavery

11
New cards
Women's Suffrage
the right of women to vote

12
New cards
Self-determination
Concept that ethnicities have the right to govern themselves

13
New cards
Liberty, Equality, Fraternity
Slogan of the French Revolution

14
New cards
"Let them eat cake"
saying attributed to Marie Antoinette that showed insensitivity to the unfortunate

15
New cards
Life, Liberty, and the Pursuit of Happiness
the 3 Unalienable Rights that were listed in the Declaration that all humans receive from birth

16
New cards
"damn sugar, damn coffee, damn colonies"
attributed to Napoleon Bonaparte after the French lost the Haitian Revolution.
17
New cards
Jamaica Letter
Written by Simone Bolivar, in this letter he argues that liberty should come to Latin America but before true freedom can be experienced, there should be a period of transition in which a dictator should rule.

18
New cards
Reign of Terror (1793-1794)
Ten-month period of brutal repression when some 40,000 individuals were executed as enemies of the French Revolution.

19
New cards
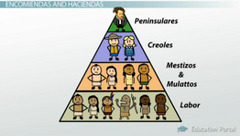
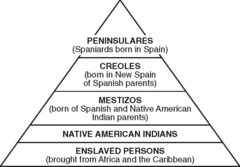
Peninsulares
Spanish-born, came to Latin America; ruled, highest social class.
20
New cards
Creoles
Descendants of Spanish-born but born in Latin America; resented inferior social, political, economic status.
21
New cards
Mestizos
A person of mixed Native American and European ancestry

22
New cards
Mulattos
Persons of mixed European and African ancestry

23
New cards
indigenous
native to a certain area

24
New cards
Nationalism
A strong feeling of pride in and devotion to one's country

25
New cards
American Revolution (1775-1783)
This political revolution began with the Declaration of Independence in 1776 where American colonists sought to balance the power between government and the people and protect the rights of citizens in a democracy.

26
New cards
French Revolution (1789)
Reacting to the oppressive aristocracy, the French middle and lower classes overthrew the king and asserted power for themselves in a violent and bloody revolution. This uprising was inspired by America's independence from England and the Enlightenment ideas.

27
New cards
Bastille
fortress in Paris used as a prison; French Revolution began when Parisians stormed it in 1789

28
New cards
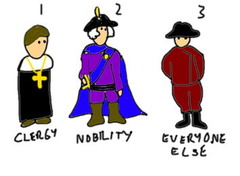
Estates General
An assembly of representatives from all three of the estates, or social classes, in France. (nobility, clergy, commoners)
29
New cards
Tennis Court Oath (1789)
Oath taken by representatives of the Third Estate in June 1789, in which they pledged to form a National Assembly and write a constitution limiting the powers of the king.

30
New cards
Haitian Revolution
The only successful slave revolt in history; it was led by Toussaint L'Ouverture.

31
New cards
Simon Bolivar (1783-1830)
was a Venezuelan military and political leader who played an instrumental role in the establishment of Venezuela, Ecuador, Bolivia, Peru and Colombia as sovereign states, independent of Spanish rule.

32
New cards
George Washington
1st President of the United States; commander-in-chief of the Continental Army during the American Revolution (1732-1799)

33
New cards
Manuela Saenz
Mistress of Simon Bolivar. female freedom fighter S. AM

34
New cards
Louis XVI and Marie Antoinette
queen and king during the French Revolution, Marie was Austrian (French hate Austrians) lived a spoiled, lavish lifestyle when the rest of France was starving

35
New cards
Creole Revolutions
Wave of political change across Spanish/Portuguese controlled Latin America. Influenced by the Enlightenment, it was caused by class antagonism and frustrations caused by mercantilism
36
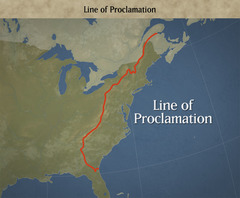
New cards
Proclamation of 1763
An order in which Britain prohibited its American colonists from settling west of the Appalachian Mountains.
37
New cards
No taxation without representation
Colonists did not want to be taxed if they did not have a representative in Britain's Parliament.
38
New cards
Industrial Age
Led to the increased mechanization of production
Not only were ideas reshaping societies during this era, but new technologies were also very influential and led to drastic changes in society and economics.
Not only were ideas reshaping societies during this era, but new technologies were also very influential and led to drastic changes in society and economics.

39
New cards
cottage industry
Manufacturing based in homes rather than in a factory, commonly found before the Industrial Revolution.

40
New cards
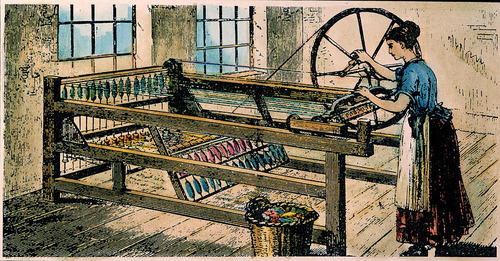
Spinning Jenny (James Hargreaves)
A machine that could spin several threads at once
41
New cards
Water Frame, 1769
a spinning machine that could be powered by water

42
New cards
division of labor
Division of work into a number of separate tasks to be performed by different workers

43
New cards
moving assembly line
method of production in which workers stay in one place as products edge along a moving belt

44
New cards
Britain's Industrial Advantages
1. Improved agricultural production & urbanization, 2. Resources from colonies and capital, 3. Legal protection of private property, 4. Lots of waterways & located on the Atlantic, 5. Strong navy, 6. Geographical distribution of coal, iron, & timber
45
New cards
Sepoy Mutiny
The revolt against the British by many different groups across India 1857 but led particularly by some of the disgruntled Indian soldiers working for the British. It caused the British government to take over more direct control of India from the British East India Company.

46
New cards
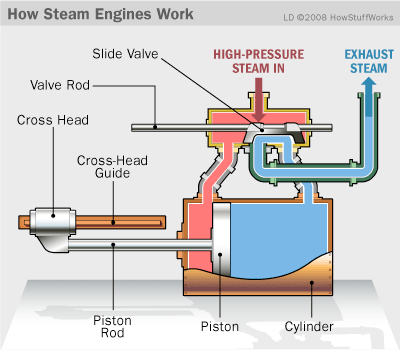
Steam Engine
A machine that turns the energy released by burning fuel into motion. Thomas Newcomen built the first crude but workable steam engine in 1712. James Watt vastly improved his device in the 1760s and 1770s. Steam power was then applied to machinery.
47
New cards
steamship
ship moved by engines that work by the action of steam under pressure. Robert Fulton is credited with inventing the first successful steamship.

48
New cards
Coaling Stations
these were refueling stations used by navies' coal-powered steamships. The need for these was one of the driving forces behind the establishment of European and American bases/colonies around the globe.
49
New cards
coal
a combustible black or dark brown rock consisting mainly of carbonized plant matter, found mainly in underground deposits and widely used as fuel.

50
New cards
coke
a refined form of coal that made it possible to use larger iron producing furnaces
51
New cards
steel
A form of iron that is both durable and flexible. It was first mass-produced in the 1860s and quickly became the most widely used metal in construction, machinery, and railroad equipment.

52
New cards
Bessemer Process
A way to manufacture steel quickly and cheaply by blasting hot air through melted iron to quickly remove impurities.

53
New cards
kerosene
a light fuel oil obtained by distilling petroleum, used especially in jet engines and domestic heaters and lamps and as a cleaning solvent.

54
New cards
electricity
A form of energy used in telegraphy from the 1840s on and for lighting, industrial motors, and railroads beginning in the 1880s.

55
New cards
Edison and Tesla
These two men and rival engineers worked on direct and alternating currents for electric power

56
New cards
Samuel Morse and the telegraph
Communication inventor whose early invention greatly aided communication during the Civil War era. "What hath God wrought?"

57
New cards
Alexander Graham Bell (1876)
Invented the telephone. "Come here Watson. I want you."

58
New cards
Gugliemo Marconi
Italian inventor credited with the invention of the radio

59
New cards
Entrepreneur
A person who organizes, manages, and takes on the risks of a business.

60
New cards
capital
money for investment

61
New cards
Transcontinental Railroad
Completed in 1869 at Promontory, Utah, it linked the eastern railroad system with California's railroad system, revolutionizing transportation in the west
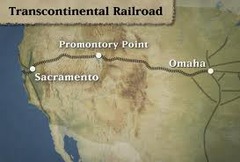
62
New cards
Ottoman Empire
Major Islamic state that dominated the Middle East, the Balkans, and North Africa at its height of power. The empire fell by the end of WWI.
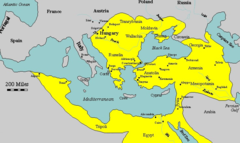
63
New cards
Mamluks
Under the Islamic system of military slavery, Turkic military slaves who formed an important part of the armed forces of the Abbasid Caliphate of the ninth and tenth centuries. Mamluks eventually founded their own state, ruling Egypt and Syria (1250-1517). They famously held off the Mongols as they tried to advance into Egypt.

64
New cards
Muhammad Ali
Not a modern nationalist, but this leader of Egypt is seen as the father of modern Egypt and made modernizing reforms in the military, economic and cultural spheres during the 19th century.
65
New cards
Meiji Restoration
In 1868, a Japanese state-sponsored industrialization and westernization effort that also involved the elimination of the Shogunate and power being handed over to the Japanese Emperor, who had previously existed as mere spiritual/symbolic figure.

66
New cards
Commodore Matthew Perry
Pressured the Japanese emperor to sign the Treaty of Kanagawa and open Japanese ports to trade. Helped institute the Meiji Restoration in Japan.

67
New cards
Charter Oath
A five point policy issued by Japan's Meiji emperor, which described Japan's plan for modernization calling for democracy, equality of class, rejection of outdated customs, and acceptance of foreign knowledge.

68
New cards
automatic loom
allowed clothes to be made at a faster rate and changed bobbins automatically without stopping.
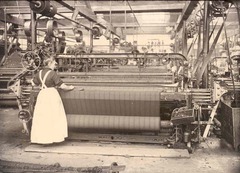
69
New cards
Zaibatsu
Large conglomerate corporations through which key elite families exerted a great deal of political and economic power in Imperial Japan. By WWII, four of them controlled most of the economy of Japan.

70
New cards
Corporation
A business owned by stockholders who share in its profits but are not personally responsible for its debts

71
New cards
stock holder
person who owns a share or shares of stock in a corporation

72
New cards
stock market
A general term used to describe all transactions involving the buying and selling of stock shares issued by a company.

73
New cards
Monopoly/Trust
Complete control of a product or business by one person or group

74
New cards
Cecil Rhodes
British entrepreneur (founder of De Beers Diamonds) and politician involved in the expansion of the British Empire from South Africa into Central Africa. The colonies of Southern Rhodesia (now Zimbabwe) and Northern Rhodesia (now Zambia) were named after him. (p. 736)

75
New cards
Transnational Corporation
A company that conducts research, operates factories, and sells products in many countries, not just where its headquarters or shareholders are located.

76
New cards
Unilever Corporation
a British and Dutch company that focused on household products, most notably soap products.

77
New cards
Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation
a prominent bank established and based in Hong Kong since 1865 when Hong Kong was a colony of the British Empire.

78
New cards
Consumerism
the buying and selling of various goods and products
79
New cards
Urbanization
Movement of people from rural areas to cities

80
New cards
Socialism
A system in which society, usually in the form of the government, owns and controls the means of production.

81
New cards
Communism
a political theory derived from Karl Marx, advocating class war and leading to a society in which all property is publicly owned and each person works and is paid according to their abilities and needs.

82
New cards
Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels
Wrote the Communist Manifesto

83
New cards
Communist Manifesto (1848)
A book written by Karl Marx. It suggested that there would be a social revolution in which the proletariat (working class) would overthrow the bourgeoisie (middle class factory owners) and then set up a classless, socialist community. This book was the blueprint for communist governments around the world.

84
New cards
Means of Production
the tools, factories, land, and investment capital used to produce wealth

85
New cards
John Stuart Mill (1806-1873)
1. English Utilitarian and essayist best known for writing "On Liberty" and "The Subjection of Women"
2. Advocated women's rights and endorsed universal suffrage
2. Advocated women's rights and endorsed universal suffrage

86
New cards
Utilitarianism
idea that the goal of society should be to bring about the greatest happiness for the greatest number of people

87
New cards
labor union
An organization of workers that tries to improve working conditions, wages, and benefits for its members

88
New cards
Proletariat
Marx's term for the exploited class, the mass of workers who do not own the means of production

89
New cards
Bourgeoisie
the upper & middle class, including merchants, industrialists, and professional people, who own/control the means of production

90
New cards
Bushido
the code of honor and morals developed by the Japanese samurai.

91
New cards
Genros
Former samurai who became advisors to the emperor during the Meiji Restoration

92
New cards
Mahmud II
19th Ottoman sultan who built a private, professional army; crushed the Janissaries and initiated reforms on Western precedents.

93
New cards
Tanzimat
'Restructuring' reforms by the nineteenth-century Ottoman rulers, intended to move civil law away from the control of religious elites and make the military and the bureaucracy more efficient.

94
New cards
Hatt-i Humayun
A far reaching Ottoman reform decree issued by Sultan Abdul-Mejid I in 1856. The decree created a national citizenship by taking away the political authority of the empire's religious leaders. It tried to remove cultural divisions by making people from all cultures and religions eligible to serve in the government.

95
New cards
Millet
separate legal courts within the Ottoman Empire set up by various religious groups throughout the empire.

96
New cards
Self-Strengthening Movement
A late nineteenth century movement in which the Chinese modernized their army and encouraged Western investment in factories and railways

97
New cards
Emperor Guangxu
in 1898, he implemented a series of reforms such as: westernized government, schools & military (Hundred Days of Reforms)

98
New cards
Hundred Days of Reform
Launched by young Chinese emperor. New laws were created that modernized civil service exams, streamline government, and encouraged new industry. Reforms also affected schools, the military and the bureaucracy. Conservatives rallied against these reforms and imprisoned the emperor.

99
New cards
Empress Cixi
Empress of China and mother of Emperor Guangxi. She put her son under house arrest, supported anti-foreign movements like the so-called Boxers, and resisted reforms of the Chinese government and armed forces.

100
New cards
Tenements
Poorly built, overcrowded housing where many immigrants lived
