Cell Surface Receptors and GPCR Signaling
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key vocabulary related to cell surface receptors and GPCR signaling based on lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
3 classes of cell surface receptors
Ionotropic receptors
Metabotropic receptors
Enzyme-couples receptor
Ion-channel-coupled receptors
Receptors that regulate ion flow across membranes, also known as ionotropic receptors.
G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs)
A large family of receptors that, upon activation by a ligand, trigger intracellular signaling cascades through G-proteins. (metabotropic)
Enzyme coupled receptors
are a class of membrane receptors that, when activated by a ligand, initiate signaling pathways inside the cell by activating associated enzymes, such as kinases.
GPCR signaling step 1
G protein activation is initiated when a ligand binds to the GPCR, causing a conformational change that activates a G protein by exchanging GDP for GTP.
GPCR signaling step 2
Downstream of GPCR: cAMP→PKA, PLC→Ca2+→CaMK that propagates the signal.
GPCR signaling step 3
Sensory transduction in various sensory systems, leading to cellular responses such as vision, taste, and smell.
GPCR signaling step 4
GPCR turn-off by negative feedback
GPCRs-ligand binding
Causes change in receptor conformation, which activates trimeric G proteins
Trimeric G proteins
peripheral membrane proteins that are consist of three subunits - α, and βγ subunits (therefore called as trimeric)
Trimeric G protein- α domain
binds to GDP or GTP and regulates downstream signaling.
Overall G protein activation- put on cheat sheet
1. Ligand binding to a G protein−linked receptor, the resulting change in receptor conformation
2. GPCR associates with G-protein and induces the release of G-protein bound GDP (acting as a GEF)
3. The Gα binds a GTP molecule and detaches from the complex
4. Either the Gα or the Gβγ initiates signal transduction, depending on the G protein
Adenylyl cyclase
An enzyme that converts ATP to cyclic AMP (cAMP), playing a key role in GPCR signaling.
activation of adenylyl cyclase
inactive until bound to activated by Gsα (by receptor-ligand-stimulated acquisition of GTP and release from Gsβγ)
cAMP
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate, a second messenger that activates protein kinase A (PKA).
Overall GPCR example-put in cheat sheet
GPCR → AMP→ cAMP → PKA → CREB → AMP response
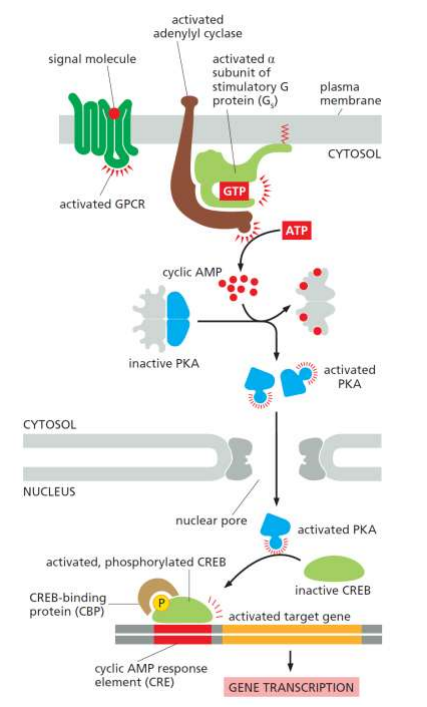
How long is G protein signaling active
Very short amount of time so they can respond to quick change situations
GPCR PKA pathway is an example of what
This negative feedback arrangement converts PKA response into a brief, local pulse of PKA activity
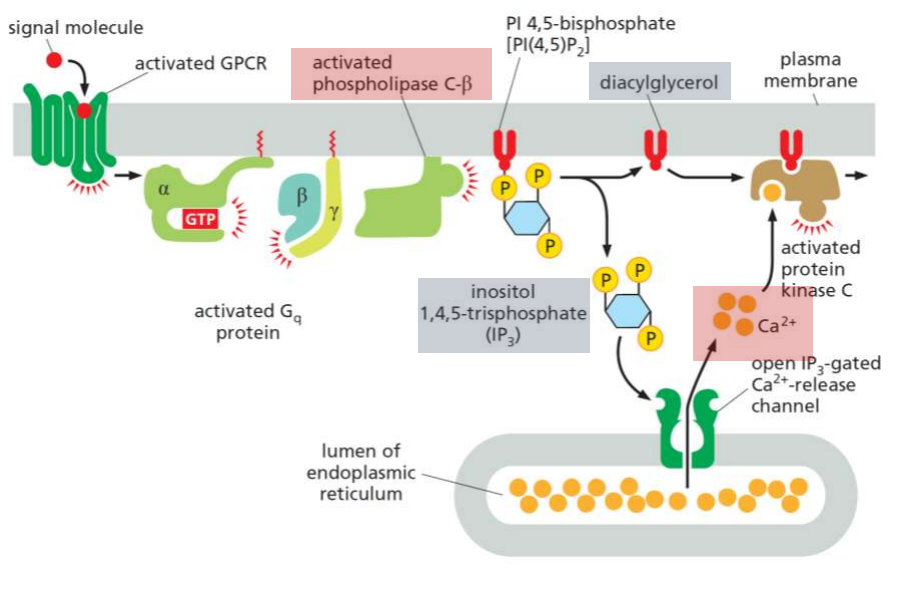
GPCR PKC pathway overview
GPCR – PLC – IP3 & DAG – PKC
Calmodulin
A calcium-binding messenger protein that mediates various cellular responses to calcium signals.
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinases (CaM-kinases)
are a family of enzymes that are activated by the binding of calcium-bound calmodulin, leading to phosphorylation of target proteins and mediating various cellular responses.
CaM-kinase II
acts as a molecular memory device that decodes Ca2+ oscillation frequency
CaM-kinase II activation
-Ca2+-calmodulin binding activates each subunit independently -
Once activated, each subunit can phosphorylate neighboring subunit only when that subunit has been activated as well (autophosphorylation)
Autophosphorylated CaM kinase II remains active even in the absence of Ca2+-calmodulin
-Until the phospho-group is removed by specific phosphatases
IP3 (Inositol trisphosphate)
A second messenger that triggers the release of calcium ions from the endoplasmic reticulum.
Phospholipase C (PLC)
An enzyme that hydrolyzes phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate to produce IP3 and diacylglycerol.
Importance of Ca2+
It has a low cytosol concentration so when channels open, it will rush into the cytosol rapidly to activate calcium responsive proteins
Calcium-induced calcium release (CICR)
A rapid increase in calcium ions can cause the ryanodine receptor channels to open, allowing calcium to enter the cytoplasm from the ER
CICR is what type of feedback
positive feedback mechanism.
Calcium oscillations
Wavelike motions of activation
Positive and negative feedback produce Ca2+ waves and oscillations.- Pathway cheat sheet
1.IP3 opens IP3 receptors on ER membrane
2.Increased local Ca2+ opens nearby IP3 and Ryanodine receptors by CICR → more Ca2+ (+ feedback)
3.Ca2+ release is propagated through ER membrane
4.High Ca2+ shuts down IP3 and Ryanodine receptors (- feedback)
5.Ca2+ pumps remove Ca2+
6.The decline in Ca2+ relieves – feedback on Ca2+ channels
7.Allowing cytosolic Ca2+ to rise again → Ca2+ wave and oscillation
Olfactory GPCR regulation
1. Odorants bind to GPCR
2. Adenylyl cyclase activation
3. cAMP increase
4. cAMP-gated cation channels
5. Na+ influx → depolarization
Vision GPCR regulation
1. Light (Photon) stimulates GPCR (Rhodopsin)
2. G protein (transducin) activation
3. Cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase activation
4. cGMP breakdown
5. The closure of cGMP-sensitive cation channel
6. Hyperpolarization
What is involved with enzyme coupled receptor signaling
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and downstream effectors
RTK activation
1. Ligand binding
2. Receptor dimerization/oligomerization
3. Activation of kinase domain
4. Autophosphorylation on the cytoplasmic domain
5. Converts a receptor into a signaling platform (scaffolding protein, induced proximity) → recruitment of signaling proteins onto phosphorylated tyrosines
6. Downstream signaling
What happens once RTK is activated
Activated RTK activates Ras-GEF which catalyzes GDP→ GTP exchange on Ras
Ras
Rat sarcoma a small GTPase involved in cell signaling pathways that regulate growth and differentiation.
What happens once Ras is activated
Raf → Mek → Erk map kinases linked by scaffolding protein
Overall RTK signaling pathway
RTK – Ras – MAP kinase and RTK – PI-3-kinase – AKT