Exam 1 Health Assesment
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Identify ways to connect and build trust
Open body language/position
Eye contact
Avoid distractions
Physical contact
Build trust
False assurance, Unwanted advice, Authority, Avoidance language, Distancing, Too much personal information, Professional jargon, Leading or biased questions, Talking too much, Interrupting, Asking “why?”
Subjective: Information supplied by patient or knowledgeable other
Objective: Information obtained by nurse directly by observation, physical examination, or measurement on patients, or from patient records, or through diagnostic studies
Identify the components of the health history (what content is placed in each section)
Biographical data
Reason for seeking care (Chief Complaint= CC)
Present health or history of present illness (HPI)
Health History
Health behaviors: preventive/ screening/ management of chronic conditions
Family history
Review of systems
Functional assessment
Developmental history for children
OLDCARTS
When documenting the CC (chief complaint)
make every attempt to quote the patient’s own words especially if it is descriptive, unusual, or unique.
Describe components of OLDCARTS
Onset
Location
Duration
Characteristics
Aggravating factors
Relieving Factors
Timing
Sequale/Severity
Describe considerations for non-English speaking patients
Always inform that a medical translator is available
Identify SDOH related to diet
Socioeconomic
Access to food (nutritious food)
Identify ways to discuss health behaviors without being judgmental
Respect them, and listen to concerns
Recognize cultural differences
Maintain positive body language
Adopt an attitude of acceptance, genuineness and empathy
Identify ways to assess pain
Subjective
"The fifth vital sign"
Severity
Numeric 0-10
Faces
Describe components of a general survey
Physical appearance
Body structure
Mobility
Behavior
Identify factors that influence vital signs
1. Age
2. Exercise
3. Stress
4. Race
5. Obesity
6. Sex
7. Medications
8. Diurnal variations
9. Disease process
Understand the 2 step process for taking a BP
1. Palpate brachial artery; with cuff deflated, center it about 1 inch above brachial artery and wrap it
2. Palpate brachial artery
3. Inflate cuff until artery pulsation obliterated and then 20 to 30 mm Hg beyond
4. Deflate cuff quickly and completely; wait 15 to 30 seconds before reinflating so blood trapped in veins can dissipate
List contraindications for taking a BP in a specific arm
The shoulder, arm, or hand (hip, knee, or ankle) is injured or diseased.
There is a cast or bulky dressing on any part of the limb.
The client has breast or axilla (or hip) surgery on that side.
The client has an intravenous infusion (IV site) or a blood transfusion running.
The client has an arteriovenous fistula graft (e.g., for renal dialysis)
Contractures of the arm or hand.
Arm or leg suspended in traction.
Pain with movement of the arm or leg.
Mastectomy → lymphedema
Identify rationale for checking a height/weight
monitors growth, used to calculate BMI, to calculate dosage for medication
Identify normal adult range for pulse, RR and BP
Pulse: 60-100 beats per minute
RR: 12-20 breaths per minute
BP: Under 120/80
Identify how to correctly take a pulse
Use the tip of the index and third fingers of your other hand to feel the pulse in your radial artery between your wrist bone and the tendon on the thumb side of your wrist.
Apply just enough pressure so you can feel each beat. Do not push too hard or you will block the blood flow.
List contraindications for taking a rectal temperature
Low WBC count or low platelet count
Describe steps for assessing orthostatic hypotension and why a patient might be at risk
Check lying down (rest 3-10 min), then standing (within 1-3 minutes)
Identify components of the exam (inspection and palpation)
First snapshot impression (how does this person look to me?)
Apparent Age
Level Of Consciousness
Facial Expressions
Affect
Posture/Gait
Speech
Grooming/dress
Signs of distress (cardiac, resp. pain, and anxiety)
Describe stages of pitting edema
0+ : no pitting edema (0 mm)
1+ : mild pitting edema; 2 mm depression disappears rapidly
2+ : moderate pitting edema; 4 mm depression disappears in 10-15 seconds
3+ : moderately severe edema; 6 mm depression that may last longer than 1 minute
4+ : severe pitting edema; 8 mm depression that can last more than 2 minutes
Identify worrisome changes in moles (ABCDE)
Asymmetry: not symmetrical
Borders: irregular
Color: variation
Diameter: > 6mm
Evolution: change (getting bigger)
Elevated
Firm to palpation: (no pain)
Growing: progressively over several weeks
Describe how to assess for jaundice and pallor
Look at color of skin; General pigmentation
Is it widespread or localized?
Is it normal for ethnicity? Are there bruises? Lesions?
Jaundice is yellowed skin
Pallor is pale skin
List factors that contribute to hair loss
nutrition, endocrine (hormones), genetics (e.g. male pattern baldness), medications (e.g. chemo), psychiatric (e.g alopecia (stress), trichotillomania)
Define clubbing and know why clubbing occurs
condition that causes the ends of the fingers or toes to enlarge and the nails to curve around the fingertips;
As a result of decreased tissue oxygenation/ perfusion such as with CHD, emphysema, bronchitis
Describe method for palpating for temperature of the skin
use back of hand; check symmetrically
Identify different characteristics/configuration of rashes (zoster, scabies)
Discrete: one lesion, or lesions that are separated
Grouped: lesions are clumped together
Confluent: lesions run together
Annular: ring-shaped (circular, lighter in the center)
Linear: a line
Zosteriform: follows dermatome pattern (band like)
Arciform: incomplete circle or arch
Reticular: lacy, net-like
Know definition of macule, papule, and pustule
Macule: flat, distinct, discolored area of skin
Papule: raised area of skin tissue that's less than 1 cm around
Pustule: a bulging patch of skin full of yellowish fluid called pus.
Difference between primary and secondary lesions>
Secondary lesions evolve from primary lesions or develop due to the patient's activities. Primary skin lesions develop as a direct result of the disease process.
List strategies to prevent skin cancer and eye damage from the sun
Sunscreen
Protective clothing
Avoid tanning beds
Annual skin checks
Self skin exams
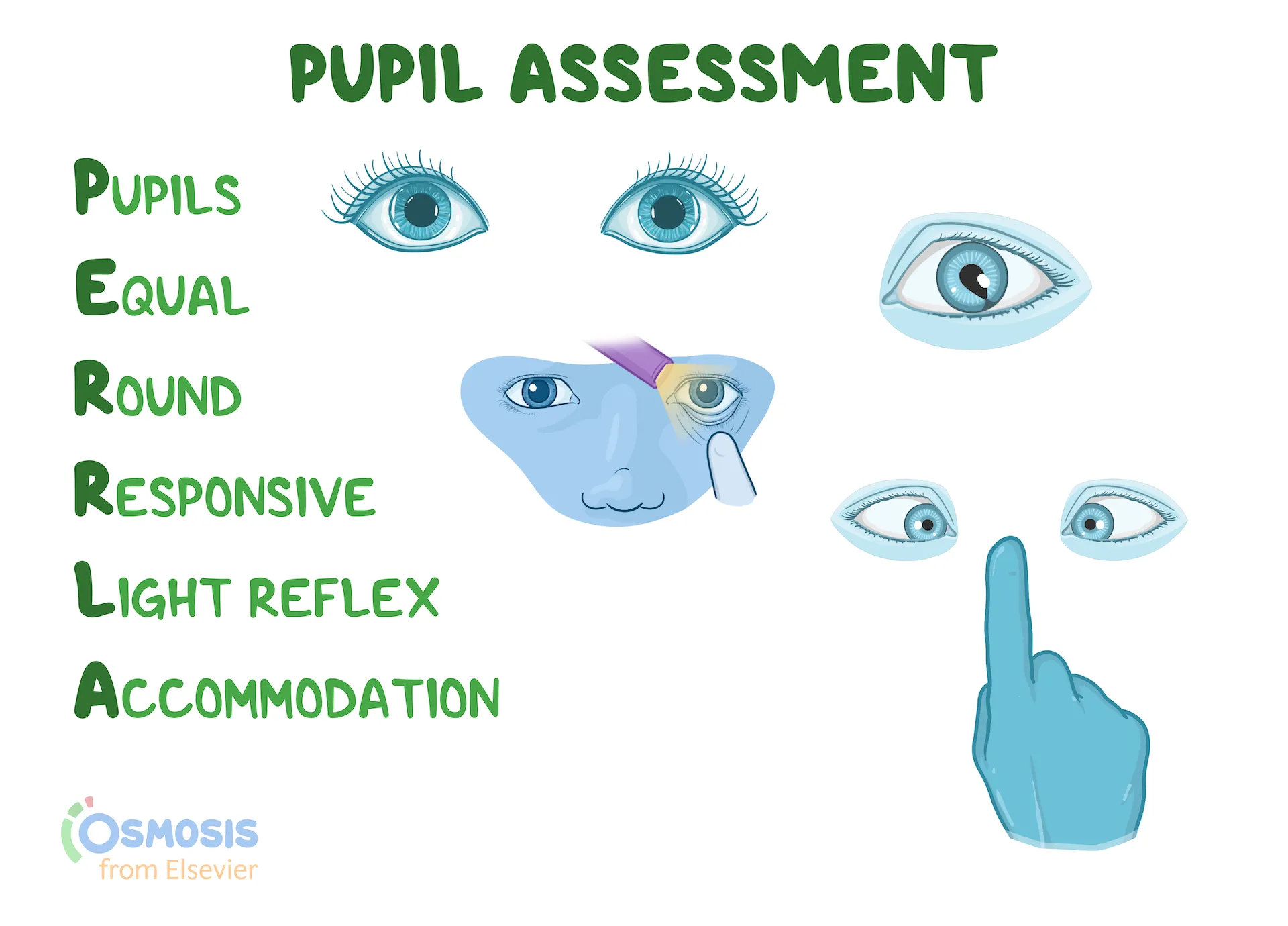
Understand the components of PERRLA
Pupils Equal Round Reactive to Light & Accommodation
List tests conducted to test coordination (finger to nose, rapid alt movement, gait)
Romberg test: eyes closed, arms at sides; slight swaying but no stumbling or falling
Observe gait: normal, tandem walk (heel to toe), heel walk, tip toes,
Rapid alternating movement: Palm of one hand on a flat surface; Flip hand repeatedly, so the palm side of hand moves from a downward-facing to an upward-facing position
Describe positive/negative results for the Babinski reflex
Negative: normal curling of the toes
Positive: abnormal fanning of the toes
(reflex disappears by age 2)
Identify grading scale for reflexes
0+ : No Reflexes
1+ : Diminished Reflexes
2+ : Normal Reflexes
3+ : Increased Reflexes
4+ : Hyperactive Reflexes
Identify grading scale for muscle strength testing
0+ Absent : contraction absent
1+ Trace : Slight contraction detected
2+ Weak: Movement with gravity eliminated
3+ Fair : Movement against gravity
4+ Good : Movement against gravity with some resistance
5+ Normal : Movement against gravity with full resistance
List signs of a stroke
Balance: loss of balance, headache, dizziness
Eyes: blurry vision
Face: facial drooping
Arm: arm or leg weakness
Speech: speech difficulty
Identify worrisome signs of a headache
Sudden onset (thunderclap)
Reporting worst headache ever
Projectile vomiting (on rising)
Stiff neck (associated fever)
Double vision
Recent head trauma
Changes with lying down
Describe process for assessing orientation
Ask “what is your name?”, “what is the date?”, “where are you currently”,“who is the president?”, “who is next to you?”
Differentiate between vertigo and dizziness
Dizziness generally describes a feeling of being off-balance. Vertigo describes a spinning, whirling, or tipping sensation
List expected findings when assessing the oral pharynx
Hard and soft palates are pink and smooth; Uvula is midline and rises symmetrically; Tonsils are pink, symmetrical, without lesions or exudate
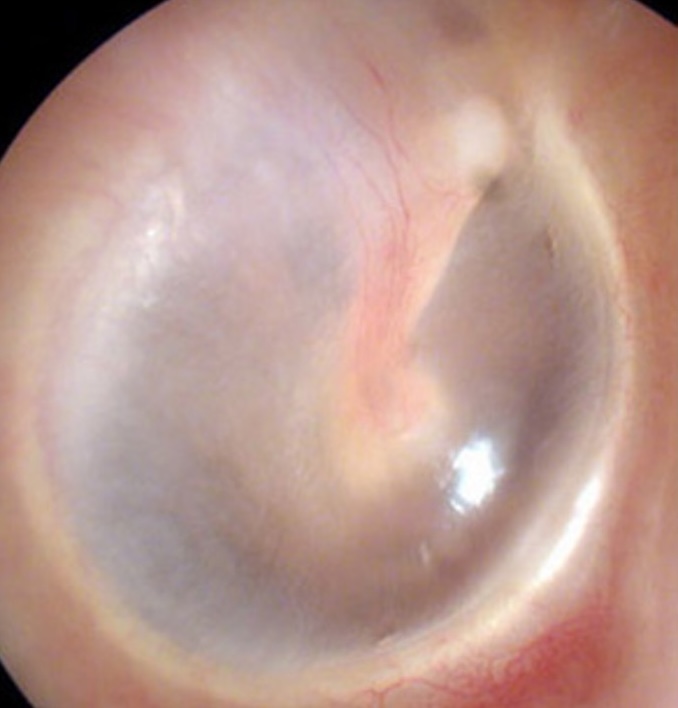
Identify expected findings when inspecting the tympanic membrane
A healthy tympanic membrane (eardrum) is pearly white or gray in color, but you can see through it.
Reflection
- Left: 7 o'clock
- Right: 5 o'clock

Identify ways to assess hearing
Whisper Test; Weber Test (above the head); Rinne Test (bone to air resonance)
The results are based on what you can see from 20 feet away compared to what someone with normal eyesight would see. It's why normal human eyesight is sometimes expressed as 20/20.
One eye at a time &
Then both eyes
With glasses (in lab)
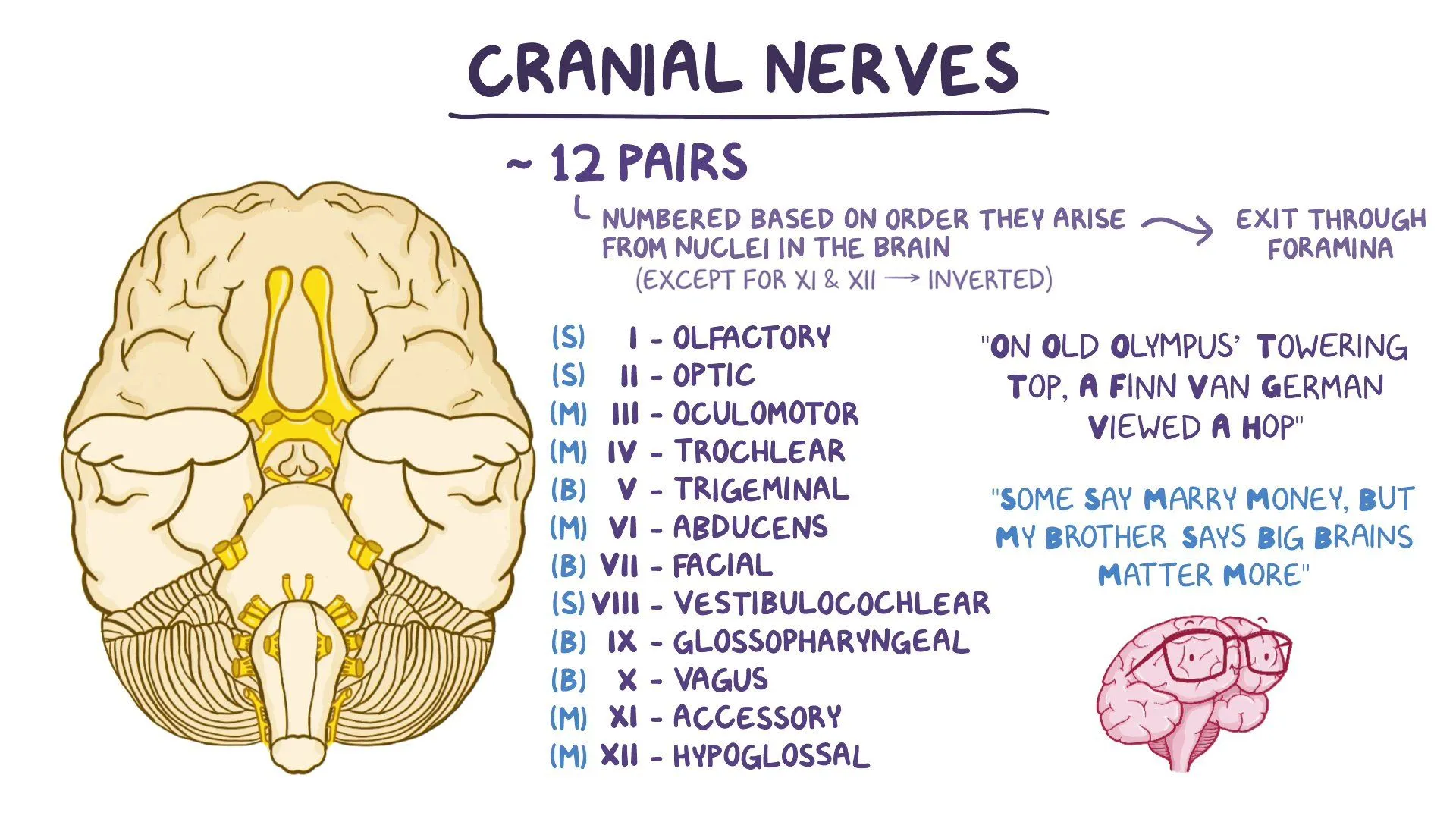
Describe functions of the cranial nerves
CN I (CN 1): olfactory nerve (smell)
CN II (CN 2): optic nerve (visual acuity, field)
CN III (CN 3): oculomotor (moves eye, pupil dilation)
CN IV (CN 4): trochlear nerve (moves eye down and in)
CN V (CN 5): trigeminal nerve (sensory functions of face, chewing)
CN VI (CN 6): abducens nerve (moves eye laterally)
CN VII (CN 7): facial nerve (controls facial expressions, salvation, taste)
CN VIII (CN 8): vestibulocochlear nerve (hearing, balance)
CN IX (CN 9): glossopharyngeal nerve (throat sensation, taste, swallowing)
CN X (CN 10): vagus nerve (movement, sensation, abdominal organs
CN XI (CN 11): accessory nerve (head, neck movement)
CN XII (CN 12): hypoglossal nerve (movement of tongue muscles)
Condition that causes involuntary, rhythmic eye movements
Identify signs and symptoms of respiratory distress
look for: tachypnea, cyanosis, pallor, accessory muscle use, shape of chest, body position, nasal flaring, pursed lips;
listen for: audible sounds of breathing (whistling or stridor, wheezing, grunting)
List the components of the respiratory exam (inspection)
Asymmetry or deformities in chest expansion and thorax
Abnormal muscle retraction of the intercostal spaces during inspiration (lower intercostal spaces)
Impaired respiratory movement on one or both sides or a unilateral lag (or delay)
Look for signs of respiratory distress
List the components of the respiratory exam (palpation)
Assess for areas of tenderness, bony abnormalities, or masses
Check chest expansion symmetrically (place your thumbs along each costal margin)
Palpate for tactile fremitus
List the components of the respiratory exam (percussion)
Short wrist movement
Percuss at interspaces
Patient sitting for posterior chest
Avoid bony scapulae
Side-to-side and top-to-bottom
use Ladder Pattern
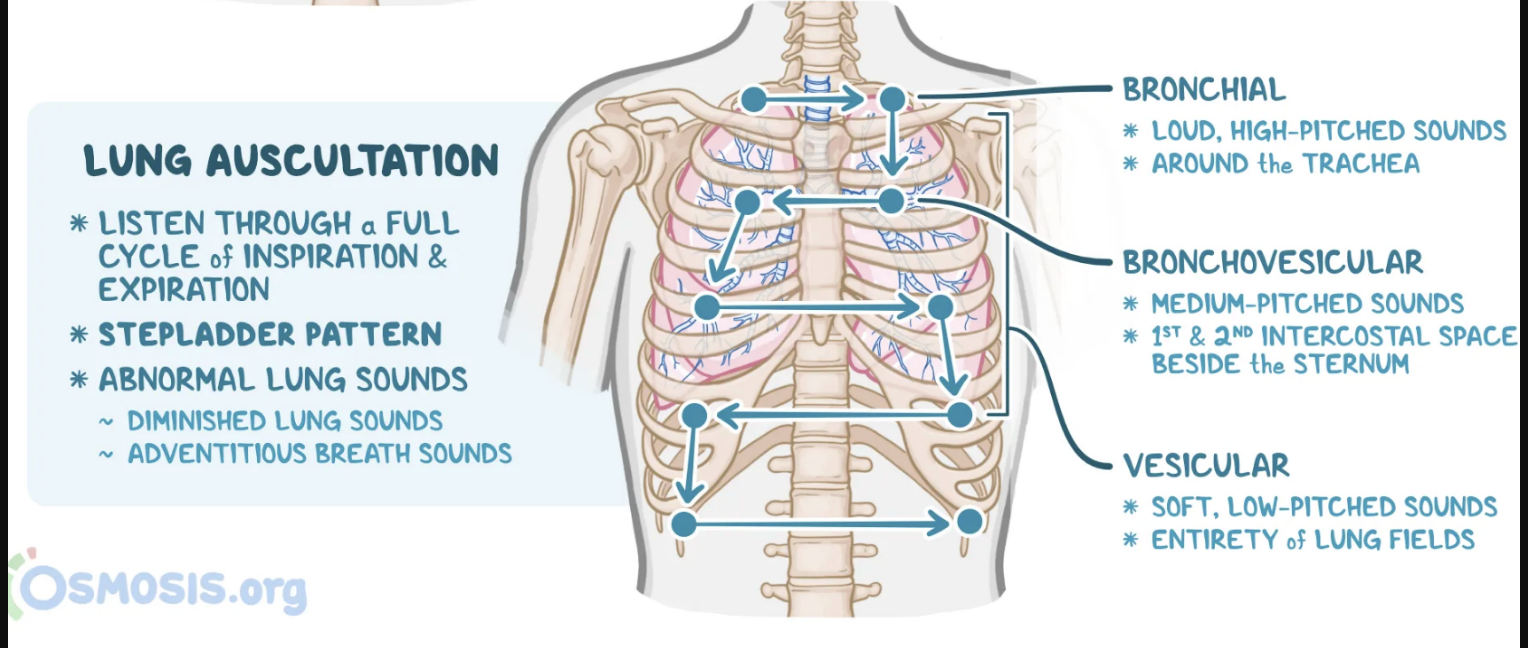
List the components of the respiratory exam (auscultation)
Listen to apices first; same sites as percussion
Identify expected sounds when percussing the lungs
Resonance – air within tissue, low pitch -Thorax
Flat – most dense tissue, high-pitch, no resonance - scapula
Dull – soft muffled thud, low-amplitude, no resonance (consolidated) (expected over heart, liver, and visceral areas)
Hyper resonance – ABNORMAL – large air pockets, lower-pitched booming sound
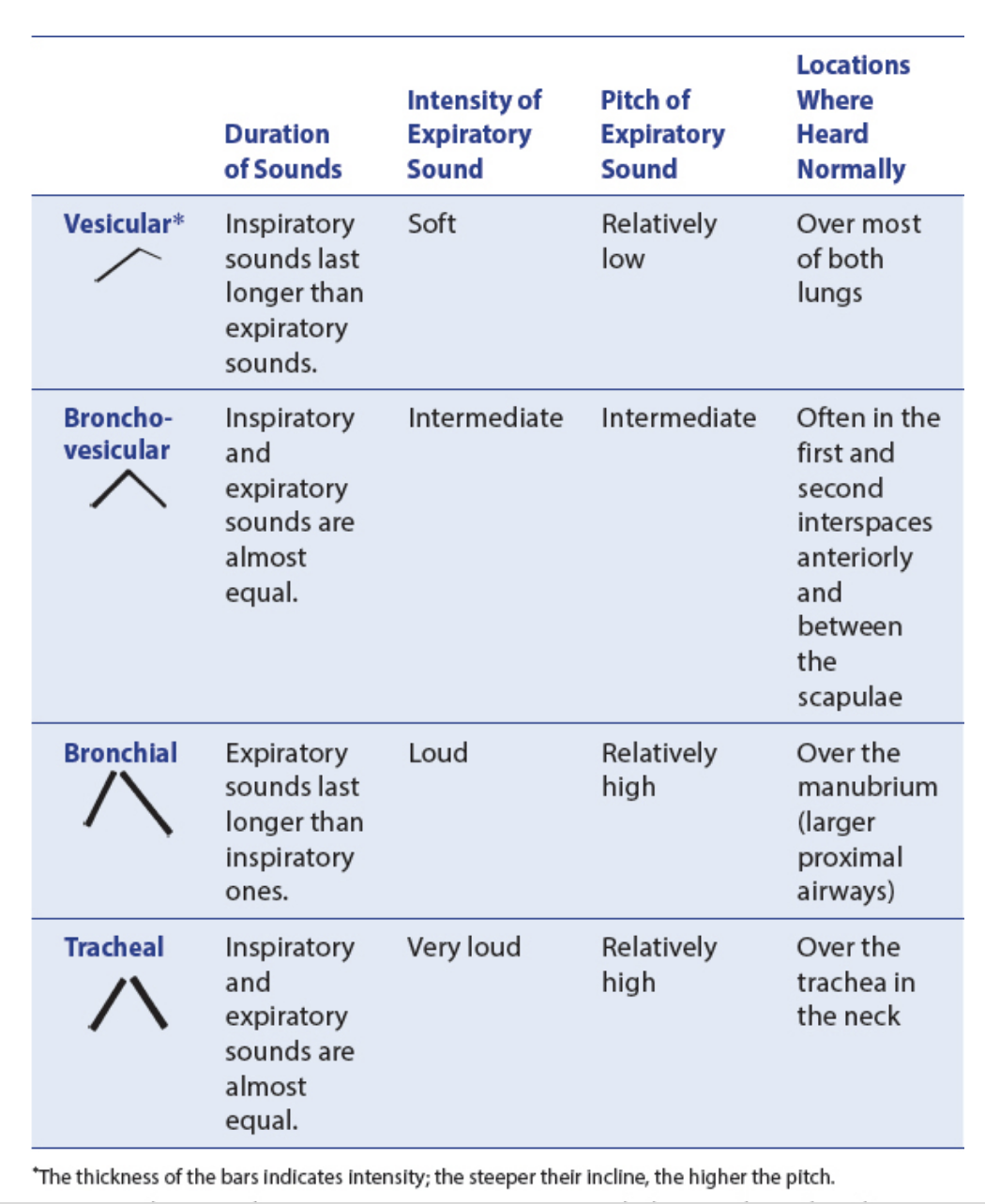
Identify sounds expected while auscultating the lungs
Tracheal – harsh, loud, high-pitched, over the trachea
Bronchial – loud, high-pitched, over the manubrium (Expiration louder and longer than Inspiration)
Bronchovesicular – mixture of bronchial and vesicular, between scapulae posteriorly and 1st/2nd intercostal spaces anteriorly
Vesicular – soft, low-pitched, over most lung fields (Inspiration much longer than Expiration)
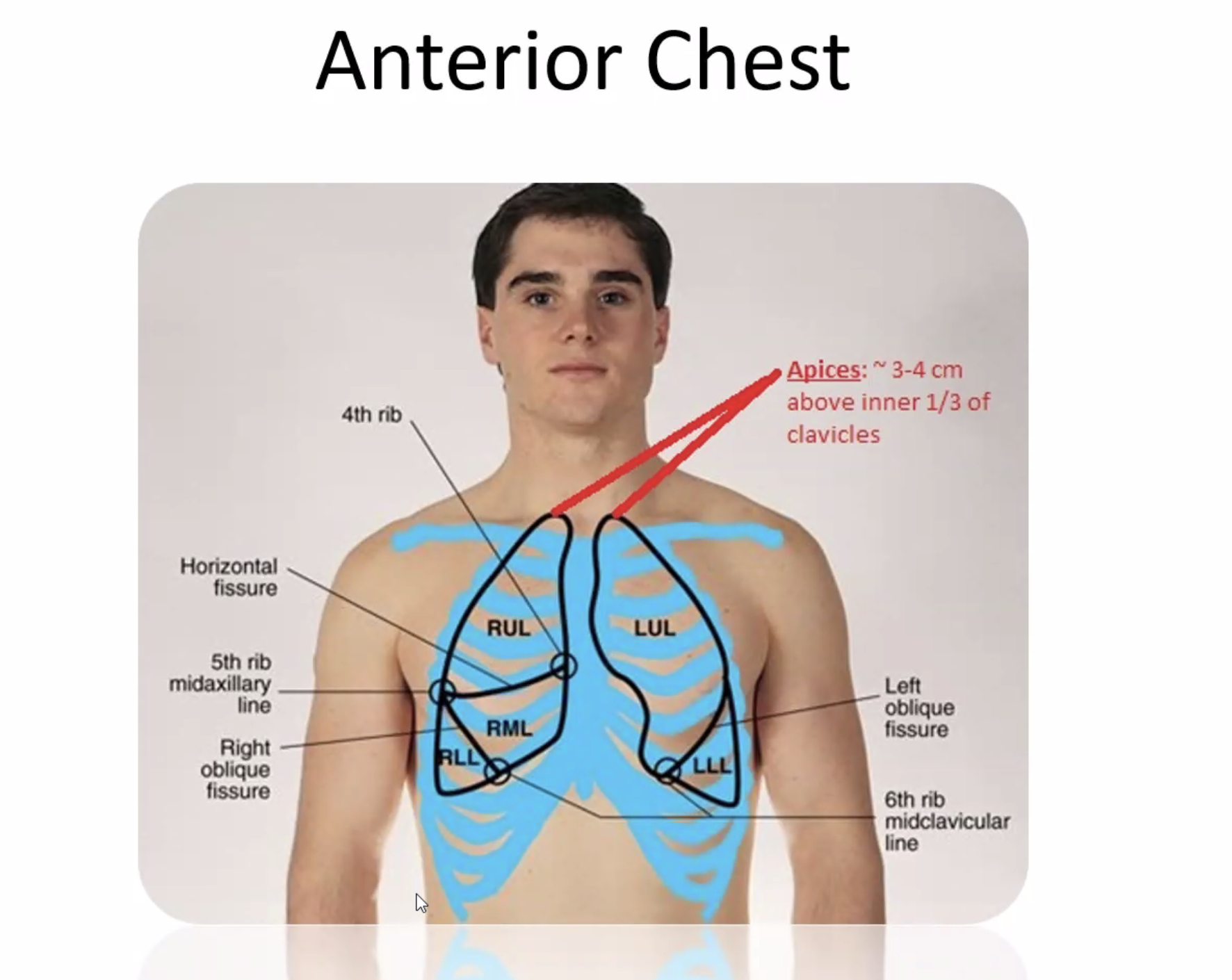
Understand lung anatomy (lobes, landmarks)
The left lung has no middle lobe
The anterior chest contains mostly upper and middle lobe with little lower lobe
The posterior chest contains almost all lower lobe
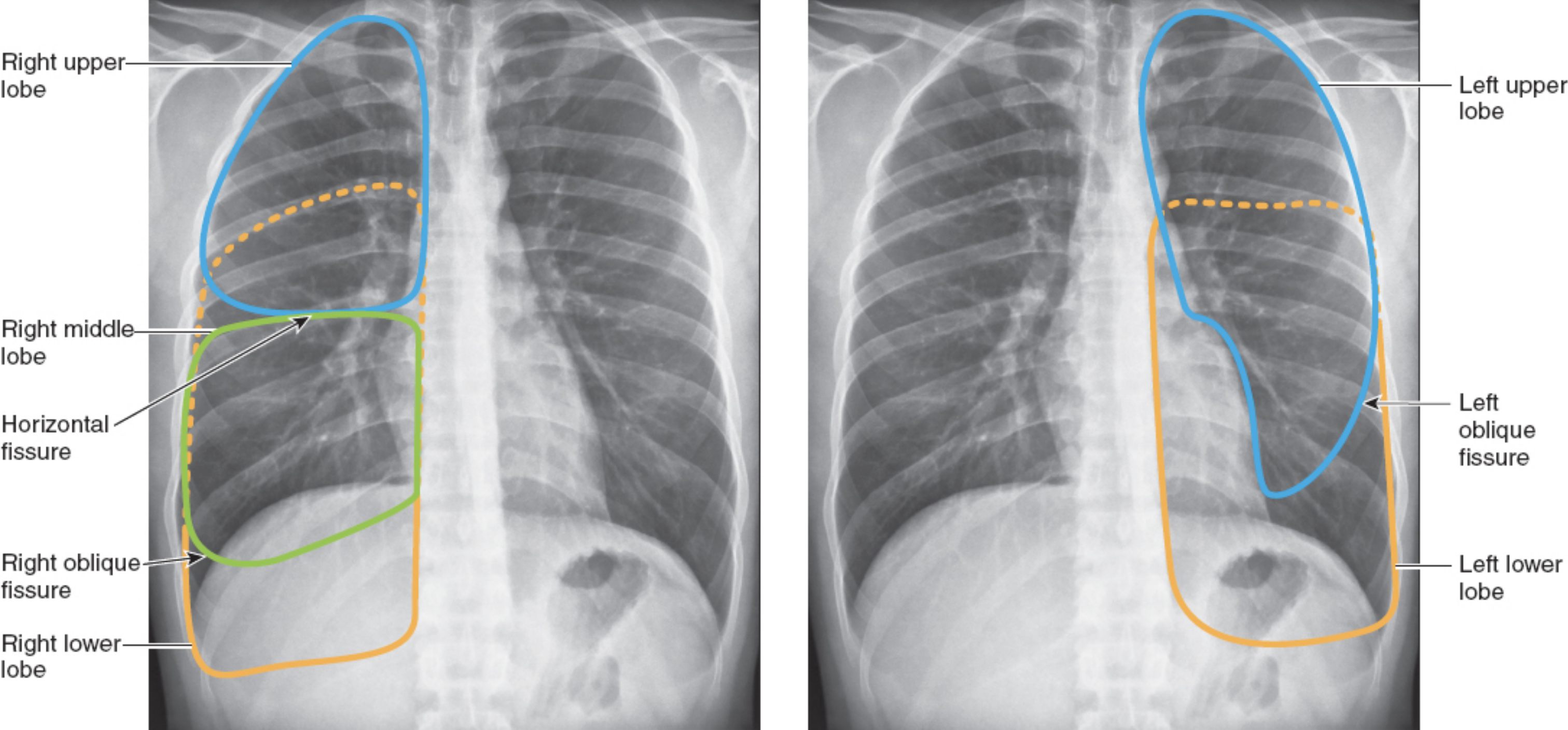
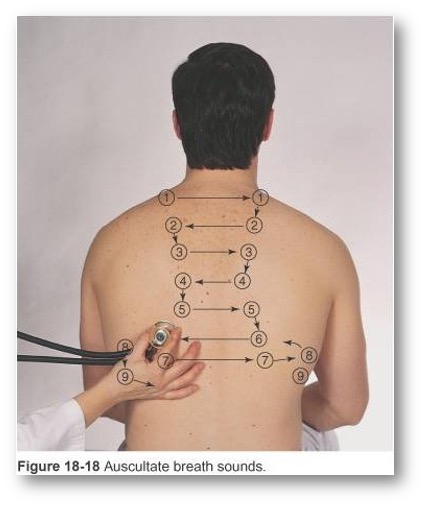
Identify points for auscultation
Use ladder pattern: moving from one side to the other and comparing symmetric areas of the lungs
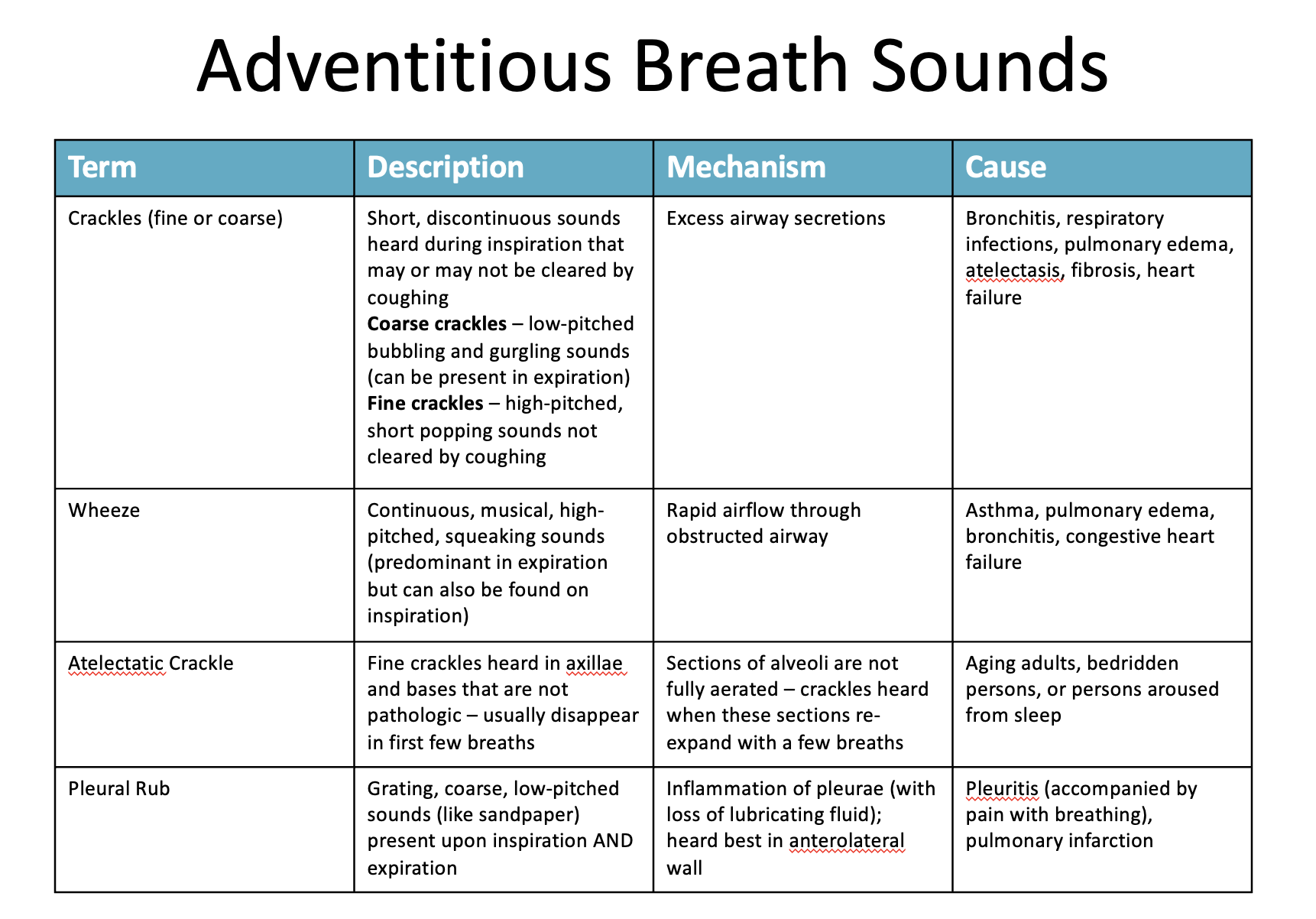
Identify different adventitious sounds
Crackles (or Rales)
Discontinuous
Intermittent, non-musical, and brief
like dots in time
Fine crackles
soft, high pitched, very brief
Coarse crackles
somewhat louder, lower in pitch, brief
Wheezes and Rhonchi
Continuous
Sinusoidal, musical, prolonged,
like dashes in time
Wheezes
relatively high-pitched, hissing or shrill quality
Rhonchi
relatively low-pitched, snoring quality
Stridor
Continuous
high frequency, high-pitched, musical,
Atelectatic Crackle
discontinuous
fine crackles
Relatively quiet, end-inspiratory,
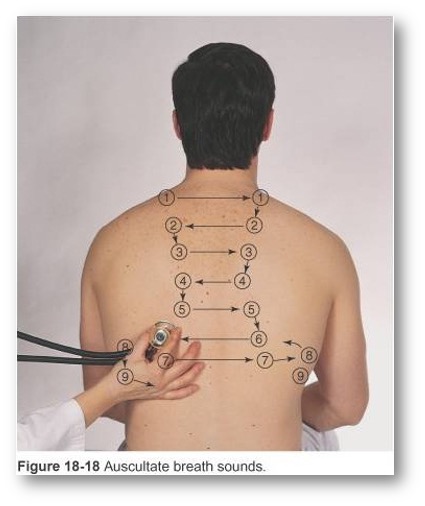
Describe proper technique for auscultation of the lungs
Listen through entire breath-cycle
Use ladder pattern (moving from one side to the other and comparing symmetric areas of the lungs)
NEVER listen through clothing
Put arms overhead for axillary areas
Identify nursing interventions to address atelectasis
Raise head of bed to at least 30 degrees
Use of incentive spirometer
Increase mobility
Encourage deep breathing
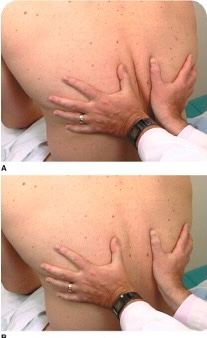
Identify different methods used in palpation for the respiratory exam (palpation, resp expansion and fremitus)
Using fingers, gently palpate the entire chest wall
Respiratory (or thorax) expansion: place your thumbs along the level of the 10th rib on both sides of the spine and lay your palms on the client's back, making a “W” with your hands. Ask your client to take a deep breath, and as they inhale, your thumbs should symmetrically spread apart
Tactile fremitus: ask the client to say “99” repeatedly while palpating both sides of their posterior chest