Unit 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
1
New cards
Threats to soil
\-erosion
\-pollution
\-over-cultivating (compaction)
\-global warming
\-salinization
\-urban sprawl
\-pollution
\-over-cultivating (compaction)
\-global warming
\-salinization
\-urban sprawl
2
New cards
Soil
\-final product of specific pedogenic processes active at a specific site over time
\-unconsolidated mixture of mineral and inorganic material
\-more or less loose
\-unconsolidated mixture of mineral and inorganic material
\-more or less loose
3
New cards
Soil Mineral Components
sand, silt, clay
4
New cards
Soil Organic components
\-dead plants and animals
\-SOM, OM, Humus
\-SOM, OM, Humus
5
New cards
pedosphere
\-found near earth surface
\-interacts with atmosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere
\-interacts with atmosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere
6
New cards
5 Plant Growth factors Supplied by soil
1. Water
2. Air
3. Nutrients
4. Physical Support
5. Heat
7
New cards
Main Chemical Components of Soil
\-Carbonate ion
\-Calcium Carbonate
\-Magnesium Carbonate
\-Calcium Carbonate
\-Magnesium Carbonate
8
New cards
carbonate minerals
\-includes calcium, magnesium carbonates or lime
\-most common carbonate material is Calcium carbonate
\-presence verified by usage of 10% HCl
\-most common carbonate material is Calcium carbonate
\-presence verified by usage of 10% HCl
9
New cards
soil profile
\-vertical section formed by distinct layers known as horizons
\-consists of a, b, and a thin slice of c for horizons
\-consists of a, b, and a thin slice of c for horizons
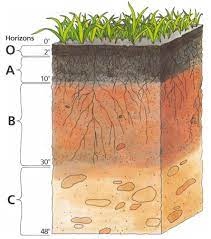
10
New cards
Solum
\-consists of a and b horizons
11
New cards
Parent Material (PM)
\-fragmented bedrock or superficial deposit
\-relatively thick in western Canada (1m to 30m thick)
\-rocks and sediments in which soils are formed
\-two types, residual and transported
\-relatively thick in western Canada (1m to 30m thick)
\-rocks and sediments in which soils are formed
\-two types, residual and transported
12
New cards
soil horizon
\-horizontal and parallel to soil surface
\-properties differ from layers above and beneath
\-Each soil type has a unique horizon sequence
\-differentiated by OM content, Carbonate minerals, pH, soluble salts, fertility, roots
\-properties differ from layers above and beneath
\-Each soil type has a unique horizon sequence
\-differentiated by OM content, Carbonate minerals, pH, soluble salts, fertility, roots
13
New cards
Master (Major) Mineral Horizons
A, B, C
14
New cards
A horizon
\-found near soil surface
\-often maximum accumulation of OM
\-site of material removal (^^elluviation^^)
\-often maximum accumulation of OM
\-site of material removal (^^elluviation^^)
15
New cards
B Horizon
\-development of soil structure
\-color change
\-deposition of material occurs here (^^illuviation^^)
\-color change
\-deposition of material occurs here (^^illuviation^^)
16
New cards
C horizon
\-negligible change from PM
\-usually no structure development
\-usually no structure development
17
New cards
Topsoil
\-uppermost soil zone
\-enriched with OM/humus (active zone)
\-most fertile soil zone
\-enriched with OM/humus (active zone)
\-most fertile soil zone
18
New cards
subsoil
\-lower part of active soil profile
\-mostly b plus upper part of c horizon
\-less active than topsoil, plant roots are still able to access water and some nutrients
\-important for internal drainage and water percolation
\-mostly b plus upper part of c horizon
\-less active than topsoil, plant roots are still able to access water and some nutrients
\-important for internal drainage and water percolation
19
New cards
Soil Suffixes Common
h, p, m, k, t, e
20
New cards
h suffix
\-enriched with OM/ humus
21
New cards
p suffix
\-horizon that has been disturbed by mans activities such as logging, habitation, and cultivation
22
New cards
m suffix
\-change in color, or structure, or both compared to c horizon
23
New cards
k suffix
\-presence of carbonate minerals
\-fizz when treated with 10% HCl
\-alkaline pH
\-fizz when treated with 10% HCl
\-alkaline pH
24
New cards
2 Soil Formation processes
1. Destructive processes
ex. rock weathering, organic residues, decomposition
2. Synthetic (constructive) processes
ex. formation of clay and humus
25
New cards
soils as an open system
\-additions to (inputs)
ex. energy, water, plants and animals, deposition, weathering
\-removals from (losses)
ex. energy, evaporation, erosion, leaching
\-vertical transfers
\-transformations
ex. energy, water, plants and animals, deposition, weathering
\-removals from (losses)
ex. energy, evaporation, erosion, leaching
\-vertical transfers
\-transformations
26
New cards
leaching (loss)
\-removal of ions in solution (nutrients, salts dissolved in water) (washed out) below root zone
27
New cards
enrichment (addition)
\-addition of material to soil body
\-addition of OM
\-addition of OM
28
New cards
Eluviation (translocation, loss)
\-removal via downward transport of tiny soil particles
29
New cards
e suffix
\-signifies eluviation, which is removal of soil particles
30
New cards
illuviation (translocation, addition)
\-deposition of tiny soil particles removed from upper horizon
31
New cards
decalcification (transformation)
\-acid reaction that remove carbonates from one or more horizons
32
New cards
calcification (translocation, addition)
\-deposition of carbonate transported down from an upper horizon
33
New cards
salinization (translocation, addition)
\-accumulation of soluble salts
34
New cards
residual PM
\-bedrock weathers in place, loose weathered products become a soil in spot
35
New cards
transported PM
\-more common PM
\-major influence of glaciers
\-glaciers melting transported loos mineral material
\-major influence of glaciers
\-glaciers melting transported loos mineral material
36
New cards
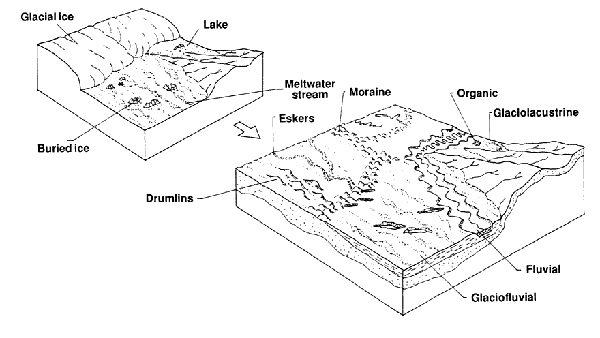
Classes of Transported PM
1. Glacial till (or morainal(
2. Glacio-fluvial
3. Glacio-lacustrine
4. Eolian
5. Colluvial
37
New cards
Glacial Till PM
\-deposited by glacial ice
\-contains limestone, carbonate minerals, marine shale, and other sedimentary rocks
\-variable mix of sand, silt, and clay
\-most common transported PM in Prairies
\-angular rocks present
\-contains limestone, carbonate minerals, marine shale, and other sedimentary rocks
\-variable mix of sand, silt, and clay
\-most common transported PM in Prairies
\-angular rocks present
38
New cards
Glacial Till Soil characteristics
\-slightly to extremely rocky
\-majority are loamy textured
\-wave-like topography
\-often hummocky> nonlinear tops and depressions
\-rolling> linear top and depressions
\-undulating> gentle slops
\-majority are loamy textured
\-wave-like topography
\-often hummocky> nonlinear tops and depressions
\-rolling> linear top and depressions
\-undulating> gentle slops
39
New cards
Glacio-Fluvial PM
\-deposited by moving melt-water within drainage channels
\-___ gravel-deposited by rapid moving water and formed by sand, grave land, and other coarse fragments (outwash)
\-___ sand- deposited by slower moving water formed by sand ranges from coarse sand to very fine sand
\-___ gravel-deposited by rapid moving water and formed by sand, grave land, and other coarse fragments (outwash)
\-___ sand- deposited by slower moving water formed by sand ranges from coarse sand to very fine sand
40
New cards
Glacio-fluvial soil characteristics
\-high in sand content (sandy/coarse texture group)
\-silt high with some clay content
\-poor moisture retention therefore susceptible to drought and wind erosion
\-good drainage and aeration
\-high leaching potential
\-topography- lower slops, winding
\-silt high with some clay content
\-poor moisture retention therefore susceptible to drought and wind erosion
\-good drainage and aeration
\-high leaching potential
\-topography- lower slops, winding
41
New cards
Glacio-Lacustrine PM
\-deposited by stagnant melt-water collected in drainage basins (glacial lakes)
\-high in clay with lots of silt (clay/fine textured)
\-very few to no coarse fragments
\-high in clay with lots of silt (clay/fine textured)
\-very few to no coarse fragments
42
New cards
Glacio-Lacustrine Soil Characteristics
\-high in clay content
\-few to no stones
\-often level/ flat topography
\-hold high amounts of water
\-most productive soils for annual crops
\-susceptible to compaction
\-poor drainage/aeration
\-few to no stones
\-often level/ flat topography
\-hold high amounts of water
\-most productive soils for annual crops
\-susceptible to compaction
\-poor drainage/aeration
43
New cards
Eolian (or Aeolian) PM
\-after glaciers melted wind deposits were utilized
\-deposited by wind (highly sorted)
\-dominated by sand size particles (most commonly) or silt particles (known as loess)
\-form active or inactive dunes
\-deposited by wind (highly sorted)
\-dominated by sand size particles (most commonly) or silt particles (known as loess)
\-form active or inactive dunes
44
New cards
Eolian Soil Characteristics
\-Silt, very fine sand, fine sand, and medium sand
\-little to no clay present
\-no coarse fragments therefore highly susceptible to wind erosion
\-lower productivity and fragile ecosystem
\-little to no clay present
\-no coarse fragments therefore highly susceptible to wind erosion
\-lower productivity and fragile ecosystem
45
New cards
Colluvium PM
\-Deposited by gravity (unsorted PM)
\-found in coulee bottoms, bases of hills, and in mountainous areas
\-may bury existing soils
\-material deposited before gravity induced movement
\-found in coulee bottoms, bases of hills, and in mountainous areas
\-may bury existing soils
\-material deposited before gravity induced movement
46
New cards
Colluvium Soil Characteristics
\-”young” stage of soil development
\-may be associated with buried soil horizons (Ahb)
\-Not stable, and not widely distributed
\-may be associated with buried soil horizons (Ahb)
\-Not stable, and not widely distributed
47
New cards
soil properties directly affected by PM
1. texture
2. pH
3. Fertility
4. Salinity
5. Topography (landform)
48
New cards
Texture from PM
\-Coarse-grained PM> produces sandy soils
\-Fine-grained PM> produces clayey soils
\-characteristics affect porosity, water retention, drainage, leaching, compaction, erosion, fertility
\-Fine-grained PM> produces clayey soils
\-characteristics affect porosity, water retention, drainage, leaching, compaction, erosion, fertility
49
New cards
Water-holding capacity
ability of soil to store water against gravity
50
New cards
pH from PM
\-Alkaline is most prominent because of amounts of naturally present finely ground limestone (free-lime)
\-Free-lime present in the form of Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and lesser amounts in Magnesium carbonate (MgCO3)
\-Free-lime present in the form of Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and lesser amounts in Magnesium carbonate (MgCO3)
51
New cards
fertility by PM (prairie specific)
\-due to high amounts of free-lime, Ca and Mg fertilizers are hardly ever needed
\-K maintenance is often kept due to amount taken in by the soil.
\-PM affects all plant essential nutrients EXCEPT for Nitrogen
\-K maintenance is often kept due to amount taken in by the soil.
\-PM affects all plant essential nutrients EXCEPT for Nitrogen
52
New cards
salinity by pm
\-PM high in salt content (ex. marine shale) is a direct source this characteristic
\-not all PM have soluble salts, but where they occur this can develop
\-not all PM have soluble salts, but where they occur this can develop
53
New cards
topography by PM
\-different PM causes change in landform
\-affects runoff and drainage/aeration
\-steepness of slope influences potential for water erosion
\-affects runoff and drainage/aeration
\-steepness of slope influences potential for water erosion
54
New cards
climate and soil
\-MOST influential factor
\-controls chemical, physical, and biological processes
\-determines kind and amount of vegetation
2 major components are:
1. temperature
2. moisture
\-controls chemical, physical, and biological processes
\-determines kind and amount of vegetation
2 major components are:
1. temperature
2. moisture
55
New cards
temperature affects
\-increase causes the rate of soil formation to increase
\-soils in warmer climates usually develop deeper profiles
\-soils in warmer climates usually develop deeper profiles
56
New cards
moisture affects
\-semi-arid conditions result in a slower rate of soil formation
\-dry soil profiles not as deep as in humid regions
\-affects kind and amount of vegetative cover (SOM accumulation)
\-dry soil profiles not as deep as in humid regions
\-affects kind and amount of vegetative cover (SOM accumulation)
57
New cards
western canada soil
\-precipitation slightly increases, temp. decreases, SOM of Ah horizon increases from brown to black soil zones
58
New cards
organisms influence
\-SOM accumulation in the grassland
\-Soil structure porosity
\-pH> ex. forested soils are generally more acidic
\-fertility> grassland are more fertile
\-nutrient cycling> grassland or forested
\-Soil structure porosity
\-pH> ex. forested soils are generally more acidic
\-fertility> grassland are more fertile
\-nutrient cycling> grassland or forested
59
New cards
topography parts
\-elevation> vertical distance
\-slope> angle which any part of the earths surface make with a horizontal surface
\-aspect> direction of the slope surface relative to the points of the compass (S, N, W, or E)
\-slope> angle which any part of the earths surface make with a horizontal surface
\-aspect> direction of the slope surface relative to the points of the compass (S, N, W, or E)
60
New cards
topography affects on soil development
\-differential erosion and moisture content because of differences in elevation slope
\-modify the effects of macroclimate of a site specific basis, creating a microclimate
\-shoulder slopes have thinner profiles
\-lower slopes have thicker profiles as it receives soil material from upper slopes
\-modify the effects of macroclimate of a site specific basis, creating a microclimate
\-shoulder slopes have thinner profiles
\-lower slopes have thicker profiles as it receives soil material from upper slopes
61
New cards
aspect of slope
\-affects temperature and rate of evapotranspiration which regulates moisture content and affects soil development
62
New cards
groundwater affects
\-groundwater travels and it can potentially transport Na+ and/or soluble salts
63
New cards
time affects
\-degree of weathering
\-presence of carbonates can indicate young soil
\-presence of carbonates can indicate young soil
64
New cards
man affects
\-increasingly modified to suit mankind needs
\-regular addition of manure over time in western europe has produced a thick a horizon
\-sea draining
\-regular addition of manure over time in western europe has produced a thick a horizon
\-sea draining