Natural Disasters
1/260
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GEO118
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
261 Terms
Which of the following is NOT an example of a natural hazard?
Smoking and/or drug use
Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and landslides are examples of
Geological/Geophysical Hazards
How many fatalities resulted from the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens in Washington, USA?
57
The majority of the more than 19,000 deaths from the 2011 magnitude 9 Japan were caused by
The subsequent tsunami
What was the deadliest disaster mentioned in the lecture video?
The 1931 flood of the Yangtze River in China
Why isn’t the asteroid impact that caused the extinction of the dinosaurs considered a ‘natural disaster’
Because it didn’t have any impact on humans and society
What are considered meteorological hazards?
Thunderstorms, Blizzards, Hurricanes
In 2010, the eruption of the Icelandic volcano Eyjafjallajökull caused a 7-day shutdown of aviation over much of Europe, with widespread economic impacts costing over 1 billion dollars. Additionally, thick ash deposits had a negative impact on the nearby farming community by making it difficult to grow crops and raise livestock.
True
Only explosive volcanic eruptions can cause natural disasters
False; both effusive and explosive eruptions can lead to natural disasters.
Which is NOT a requirement for a natural hazardous event to be considered a natural disaster, according to the UN?
The event causes at least 1,000 human casualties
A regional flood is an example of
A slow-onset disaster
A disease outbreak among displaced survivors of an earthquake living in an overcrowded refugee camp is an example of
Tertiary Disaster
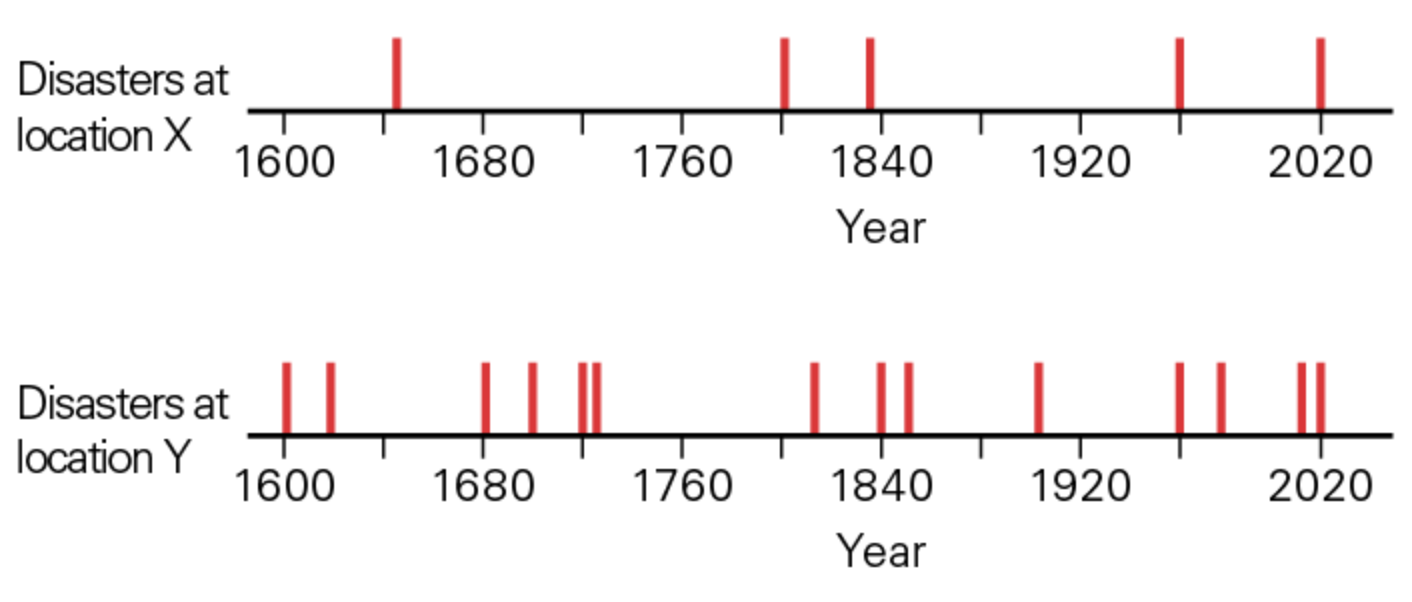
The figure below shows historical records of category 3+ hurricanes that have struck locations X (top) and location Y (bottom). What location has the greater Annual Probability (AP) of experiencing a category 3+ hurrican?
Location Y
From the question above, the recurrence interval (RI) for a category 3+ hurricane at location X is approximately 84 years. What is the annual probability (AP) in percent of a category 3+ hurricane at this location?
1.19 (1/RI → 1/84 = 0.0119 so, AP (%) = 0.0119 × 100 = 1.19)
From historical data, a volcano’s eruption recurrence interval (RI) has been calculated to be 200 years. If the last time it erupted was 1992, when will it erupt next?
2192 ( Last eruption year + RI) - 1992 + 200 + 2192
Hazard
The annual probability of a phenomenon that has the potential to harm people and/or property
Exposure
The potential for casualties, economic loss, or social disruption, due to proximity to a natural hazard
Vulnerability
A community’s ability to withstand the negative effects of a natural hazard
Risk
The total danger a community faces
Which of the following could be an example of a ‘stealth disaster’ ?
A community depleting its fresh water supply by over-pumping groundwater at a faster rate than it is replenished
The category of a hurricane (i.e., on the Saffir-Simpson scale) is the most important factor determining the extent of damage caused
False
What was the deadliest earthquake in the US history?
The 1906 San Francisco California earthquake (magnitude 7.9)
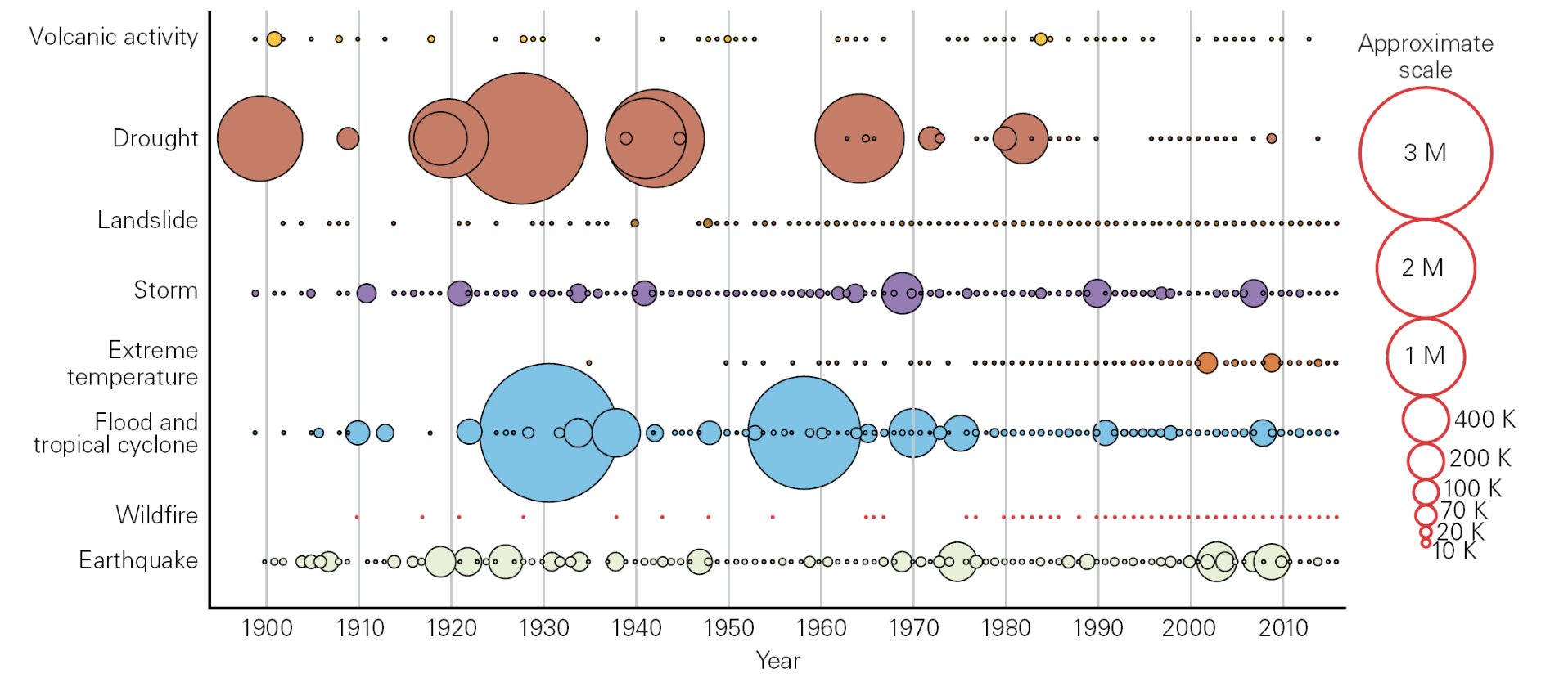
The graph below shows global deaths due to natural disasters since 1900. What categories of natural disasters generally cause the most fatalities?
Meteorological, climatological, and hydrological
How might climate change effect disaster risk?
By causing sea level to rise and increasing flood risk
By increasing the strength of hurricanes
By increasing the likelihood of droughts, heatwaves, and wildfires
Examples of steps a community might take towards disaster-risk reduction
Build disaster-resilient infrastructure that conforms with modern building codes
Develop warning systems and safety protocols for the event of a natural disaster
Develop evacuation plans and provide shelters to displaced people
Factors that may lead to poor communities facing a higher exposure and vulnerability to the negative consequences of a natural disasters
Lack of resources to build disaster-resistant buildings
Land may be cheaper in areas that are more prone to natural hazards
Poor communities have less funding for emergency response and personnel
Which stage of a severe natural disaster usually lasts the longest?
The restoration age
Home insurance policies typically cover costs related to flood damage
False
Which major natural disaster caused a large shift in how US property insurance companies issue policies?
Hurrican Andrew in 1992
If a tornado caused severe damage in the state of Illinois, which steps might the Governor take to help with disaster response and recovery?
Declare a ‘State of Emergency’
Mobilize the Illinois National Guard
All natural hazards have observable precursors
False
The purpose of a hazard potential map is to
show areas that have a higher probability of natural disasters occurring
What does ut mean if the National Weather Service has issued a tornado warning for your area?
A tornado has been sighted or indicated by radar observations
What effect does the magnetic field have on earth?
It prevents charged particles emitted by the Sun as solar wind from reaching the surface of the Earth
The two most abundant gases comprising the atmosphere of the Earth are…
nitrogen and oxygen
The difference between bathymetry and topography is that…
topography describes the shape of the land surface; bathymetry is the shape of the seafloor
What is the distribution of surface water on the Earth?
97% occurs as salty water in the oceans, and 3% occurs as freshwater on land surface and groundwater in the subsurface
What defines a “mineral” geologically?
homogenous composition crystalline solids

Rock or Mineral?
Mineral

The bluffs at the Papakolea Beach on Hawaii are made up of olivine grains eroded from nearby lava flows. What type of rocks are the bluffs seen in the photo below?
Sedimentary
The biosphere realm of the Earth incorporates all living organisms. Where is life found on Earth?
On the surface, in bodies of water, in the atmosphere, and in the shallow subsurface
Oxygen in the atmosphere exists because
It accumulated as a byproduct of photosynthesis from early primitive organisms
What is the difference between Climatology and Meteorology?
Climatology is the study of long-term weather patterns and Meteorology studies short rapid changes in weather
We know that the outer core is a liquid because shear waves do not travel through the outer core
True
Seismic velocity discontinuities are caused by…
changes in the material composition, such as a change from a continental composition to a mantle composition
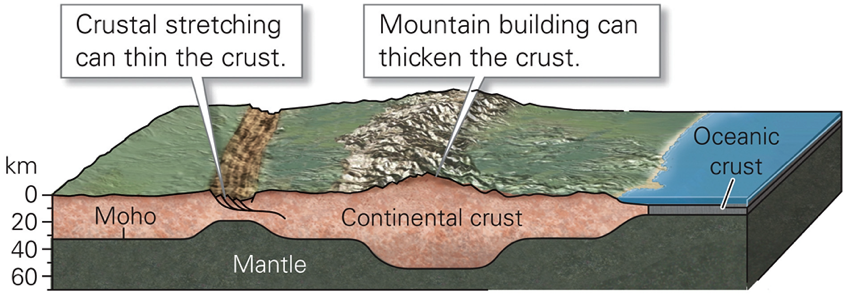
A model of the Earth’s crust in the figure below illustrates a boundary between the crust and the underlying upper mantle lithosphere. This boundary is called Moho. How was it discovered?
It was discovered that seismic waves refracted along this surface.
The difference in the continental crust versus the oceanic crust is that..
Oceanic crust is thinner and denser than the continental crust
(fill in the blank) encompasses rock that is relatively ridged and can bend and break and is made up of the crust and mantle, whereas (fill in the blank) consists of mantle rock that is hot enough to undergo plastic flow
lithosphere
asthenosphere
The earth’s mantle consists mostly of a silica-poor igneous rock called (gabbro, granite, basalt, or peridotite)
peridotite
The earth’s mantle is mostly (liquid or solid)
solid
The core, which is the densest portion of the Earth, is subdivided into an outer liquid and inner solid zone, Calculations suggest the composition is dominated by
iron
Which type of plate boundary produces new oceanic crust?
divergent boundaries
What observations contributed to development of the theory of plate tectonics?
Sonar mapping of the seafloor
Earthquake epicenters
The shapes of the continents
The fossil record
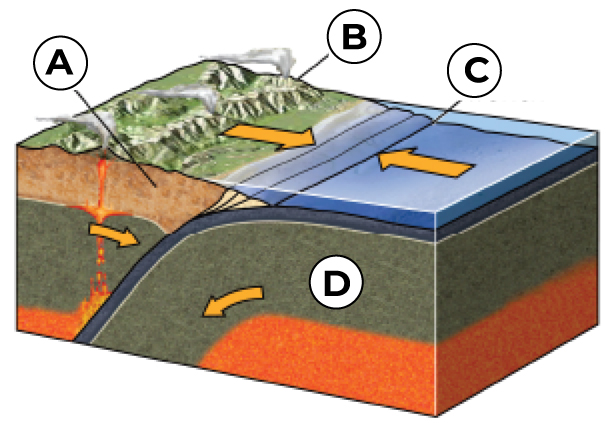
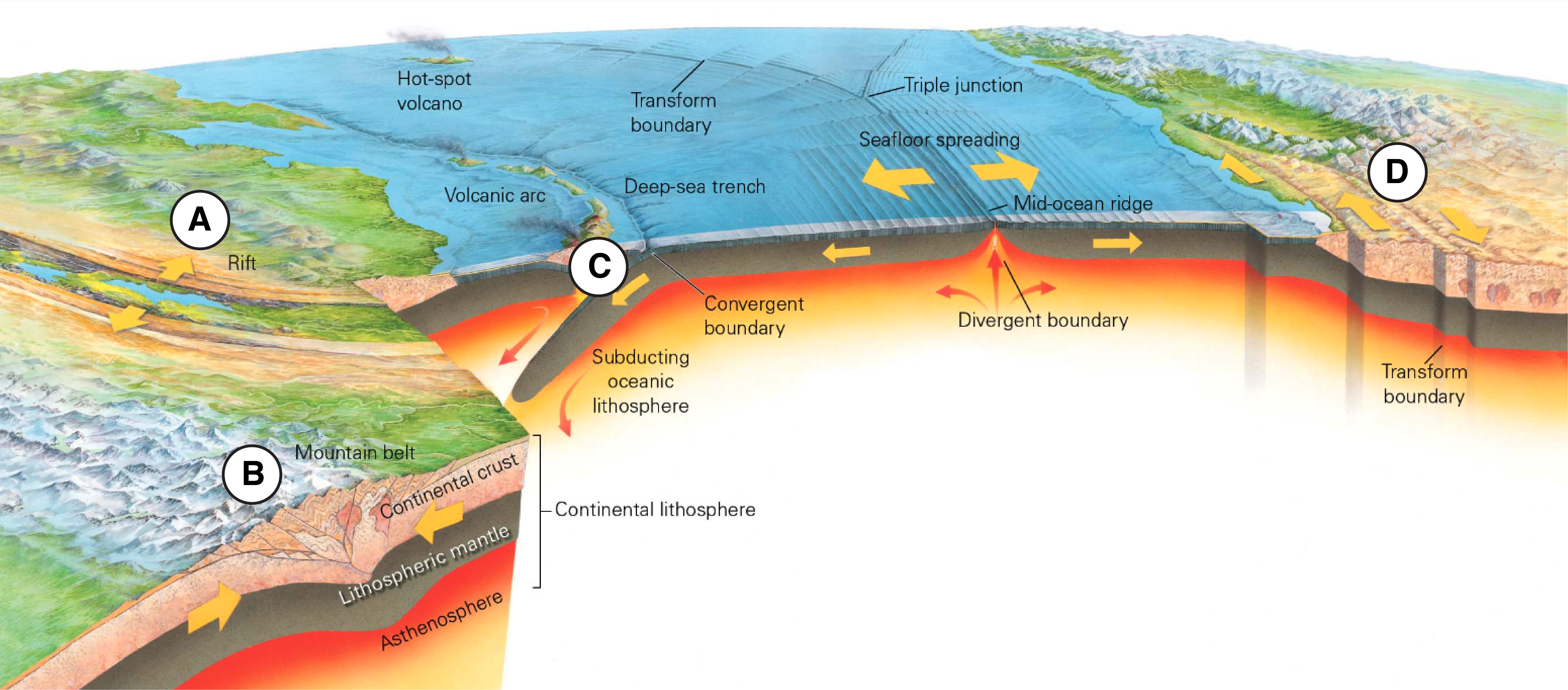
What is A?
Volcanic Arc
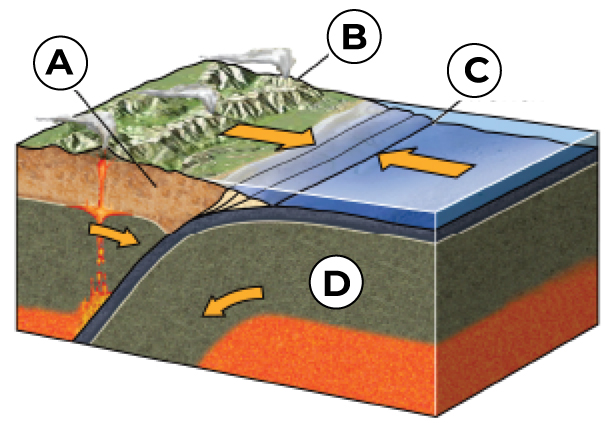
What is B?
Overriding Plate
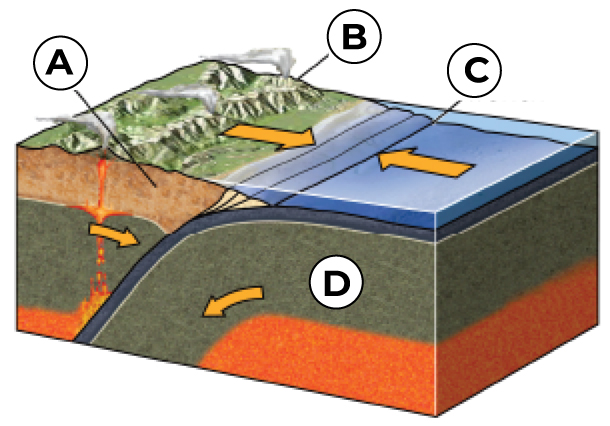
What is C?
Trench
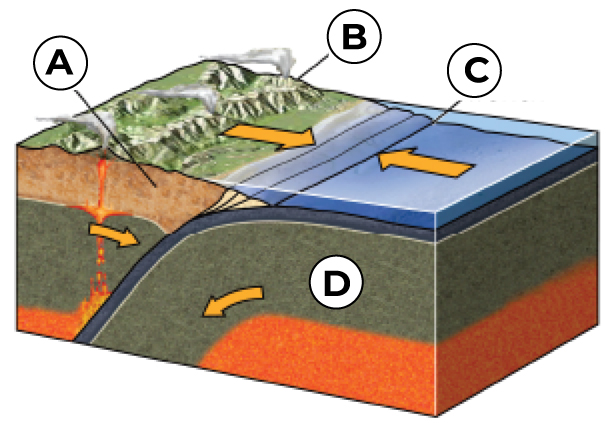
What is D?
Down going Plate (the subducting oceanic plate)
Mountains can be built by which of the following tectonic events?
Subduction at convergent boundaries
Continental collision at convergent boundaries
Match the plate boundary to the dominant plate tectonic stress or force being applied: Convergent plate boundary
Compressional stresses
Match the plate boundary to the dominant plate tectonic stress or force being applied: Divergent plate boundary
Tensional stresses
Match the plate boundary to the dominant plate tectonic stress or force being applied: Transform boundary
Shear stresses
Brittle deformation
where rocks crack and break (typically low pressue and low temperature).
Plastic deformation
where rocks change shape without breaking (typically high pressure and high temperature).
Geologic structures
visible features that develop into rock due to deformation
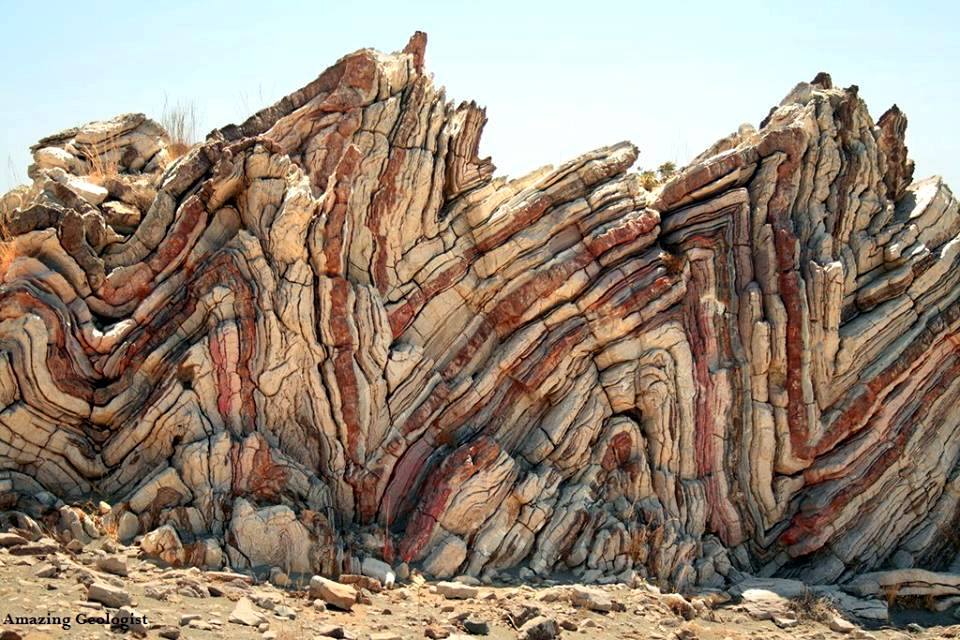

The following image depicts what type of geological structure?
folded beds
James Hutton is credited with developing the principle of uniformitarianism, which states that..
natural physical processes operating in the past are very similar to those operating today
An application of the principle of uniformitarianism related to hazard prediction is that..
principle may be useful to understand where natural hazards may be likely in the future
The earth forms in our solar system (years)
4.56 billion years
Plate tectonics begins
3 billion years
Land plants appear
470 million years
A permanent Ocean exists on Earth
3.9 billion years
Single-cell life appears
3.5 billion years
The rock cycle describes..
the evolutional relationship between different types of rocks

The pictures of ripples below illustrate what geological principle?
uniformitarianism
When geologist first began to explore geologic time, they were able determine only the relative ages of geologic features, meaning the age of one feature with respect to another. What would be an example of how relative ages might be used:
using the fossils that are present in sediments to determine the age of the formation
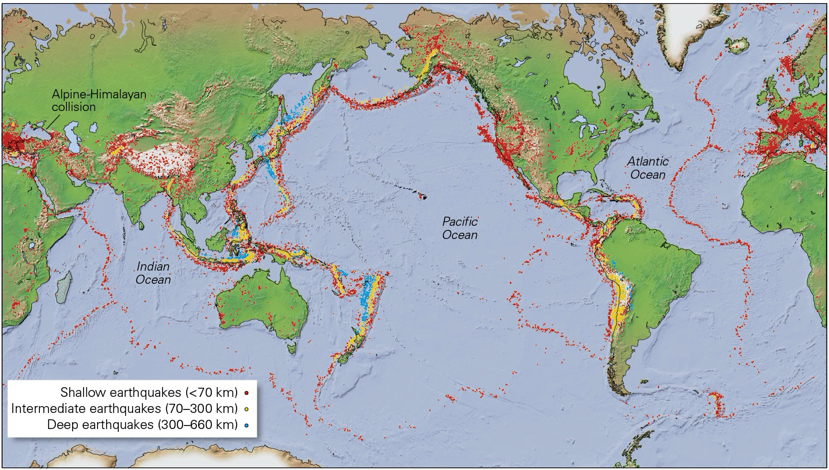
What does this map of global seismicity reveal about earthquakes?
That most earthquakes occur near plate boundaries
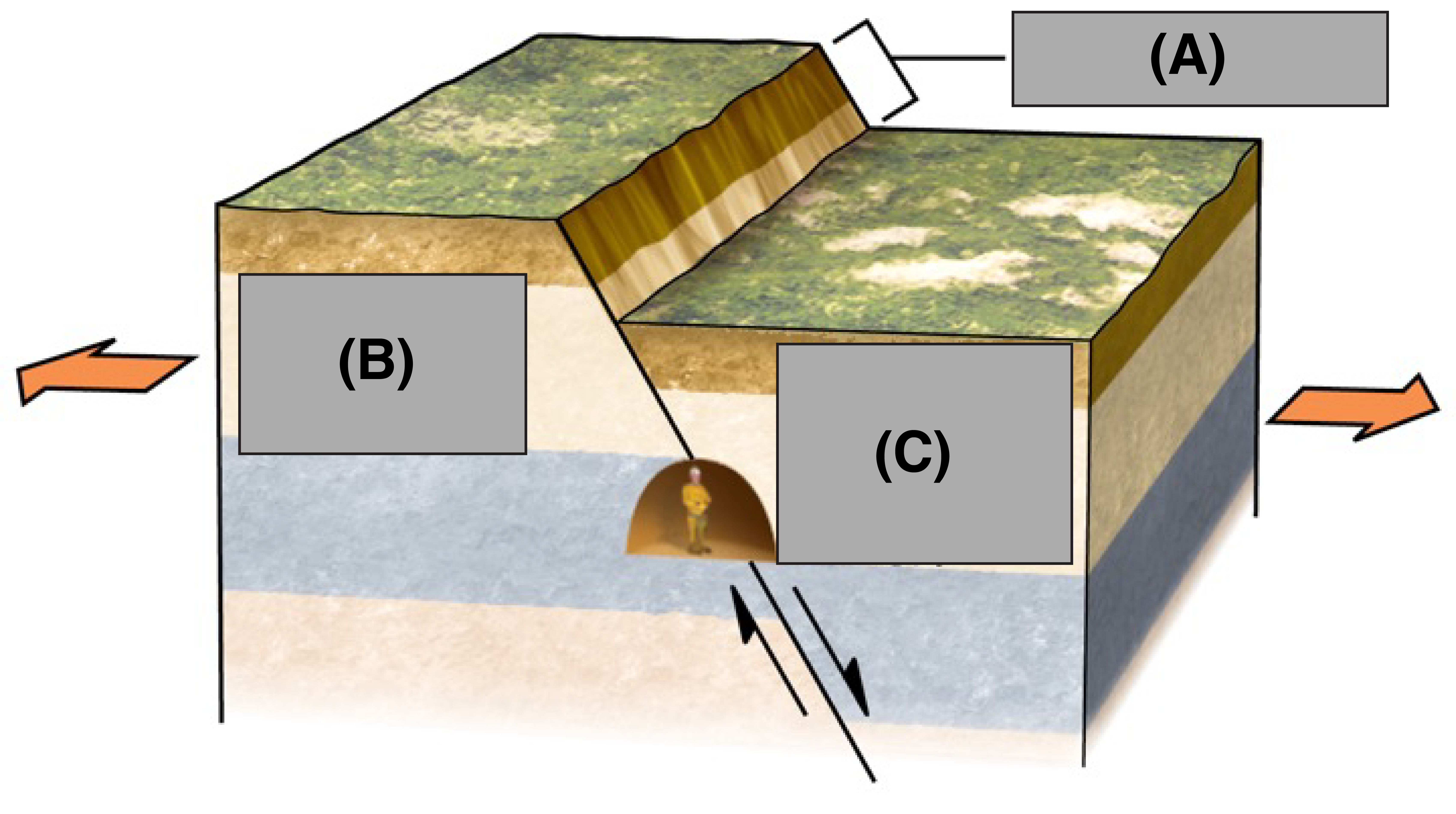
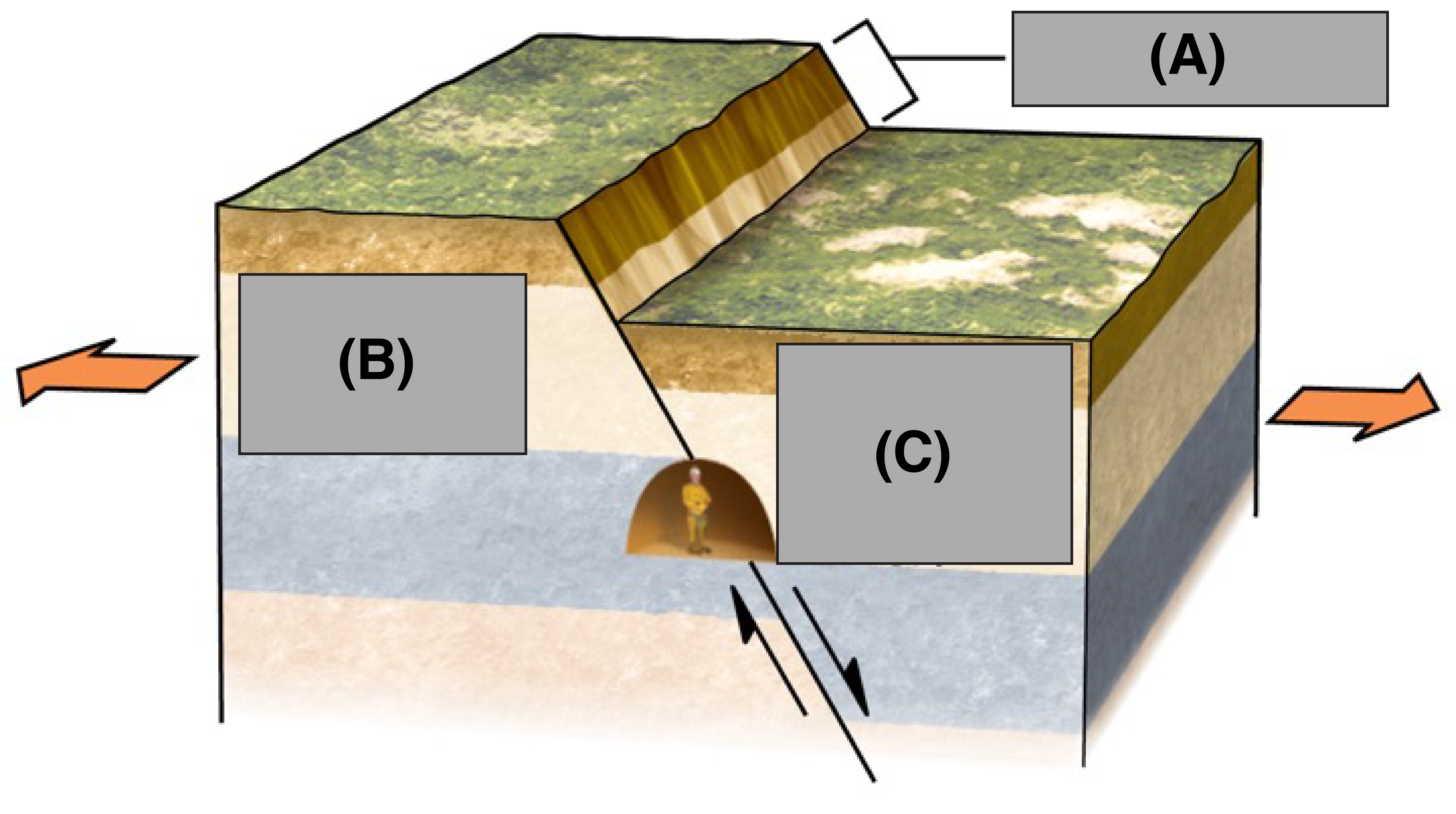
What is A?
Fault Scarp
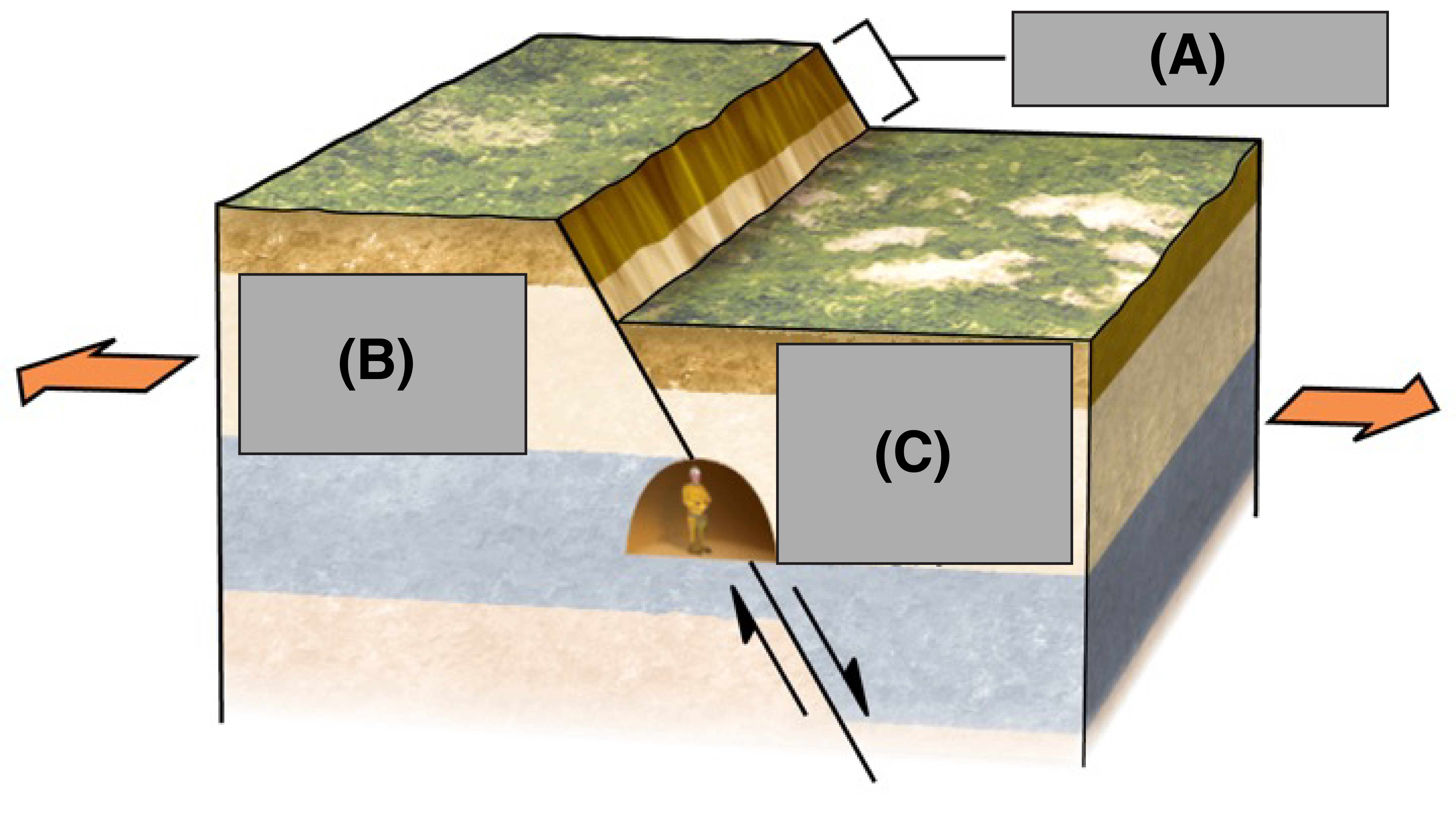
What is B?
Foot Wall
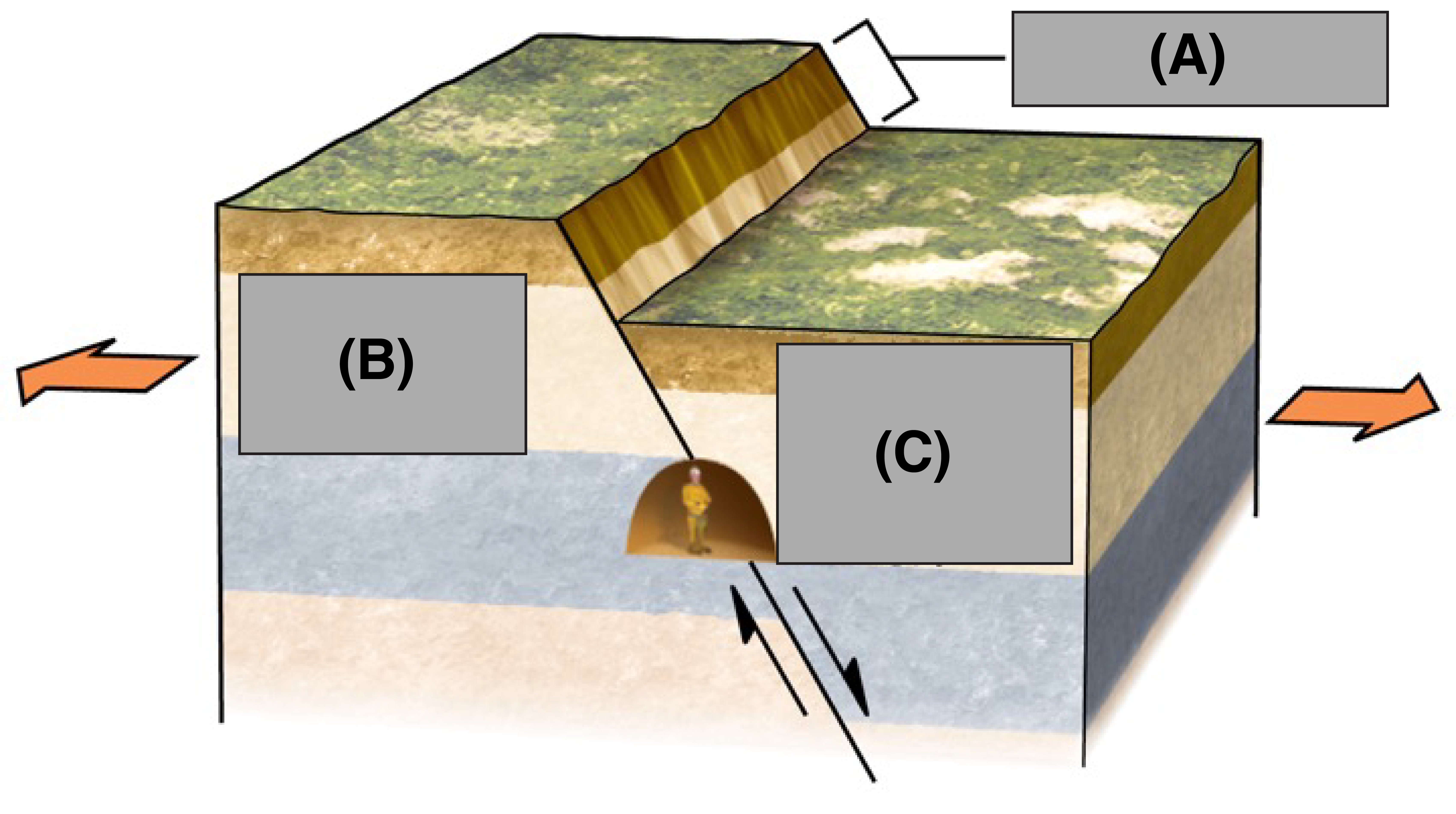
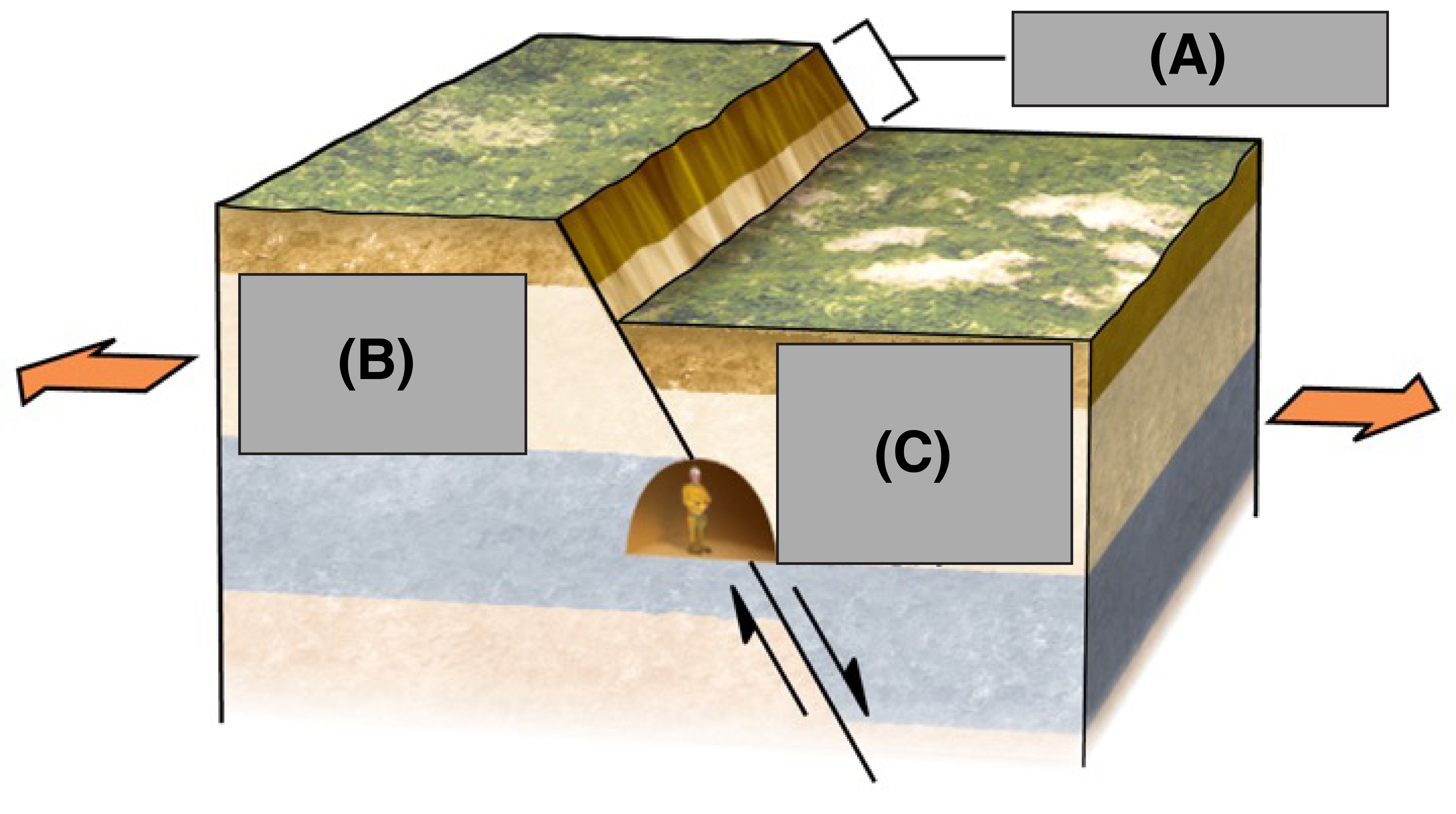
What is C?
Hanging Wall
What type of fault is shown here?
A normal fault
What earthquake scale is based on the intensity of ground shaking estimated using assessments of earthquake damage and reports of the amount of shaking felt by people?
The Modified Mercalli Intensity scale
What seismic observation is the most useful observation for determining the distance to an earthquake’s epicenter?
The difference in travel times of the S wave and P wave (i.e., the S-P time)
What are foreshocks?
Small earthquakes preceding a main shock
What is NOT true about mechanical seismographs?
The seismograph only works if the pen can’t move relative to the frame
The diagram below shows a variety of different tectonic environments on Earth. Match each of the labeled regions with the type of faulting that you would expect to occur in that tectonic environment. What is A?
(Rift) Normal faulting
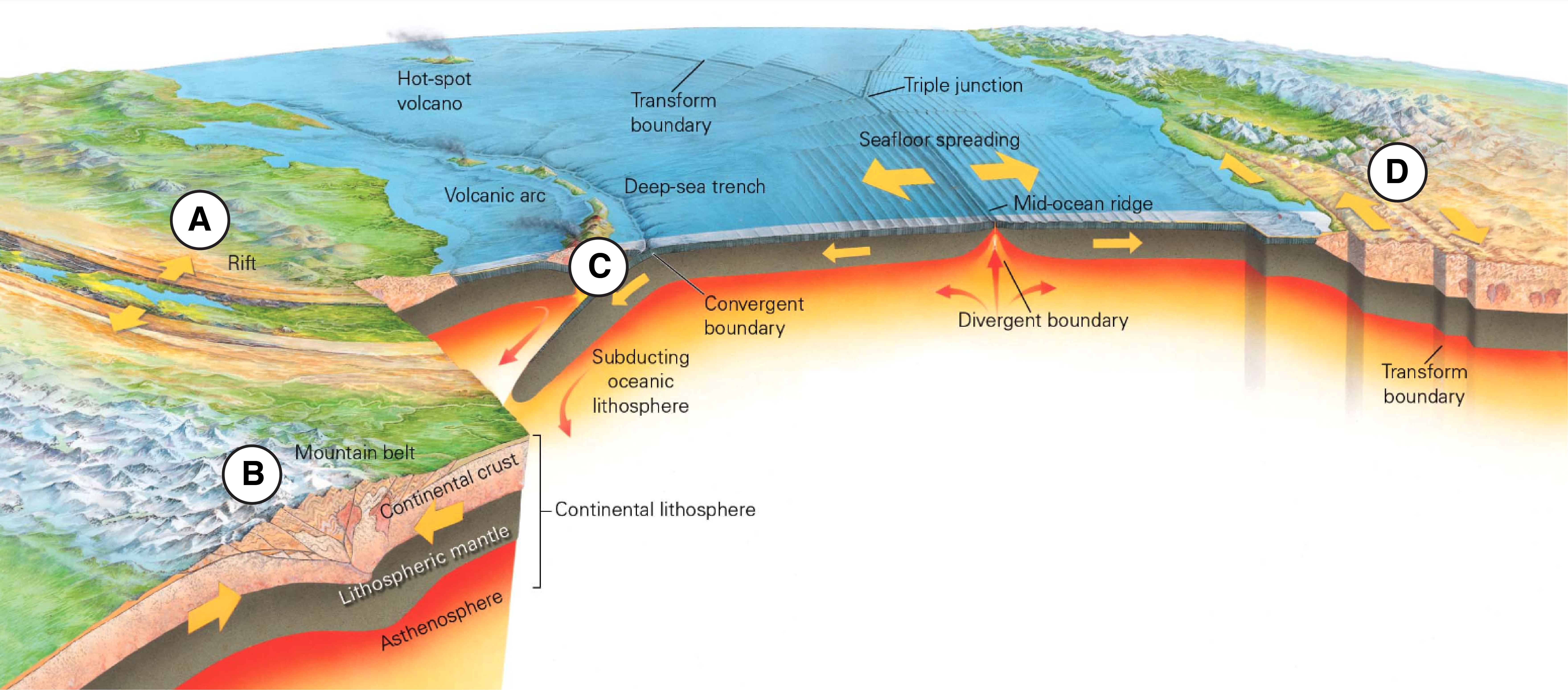
The diagram below shows a variety of different tectonic environments on Earth. Match each of the labeled regions with the type of faulting that you would expect to occur in that tectonic environment. What is B?
(Mountain belt/Continental collision) Reverse Faulting
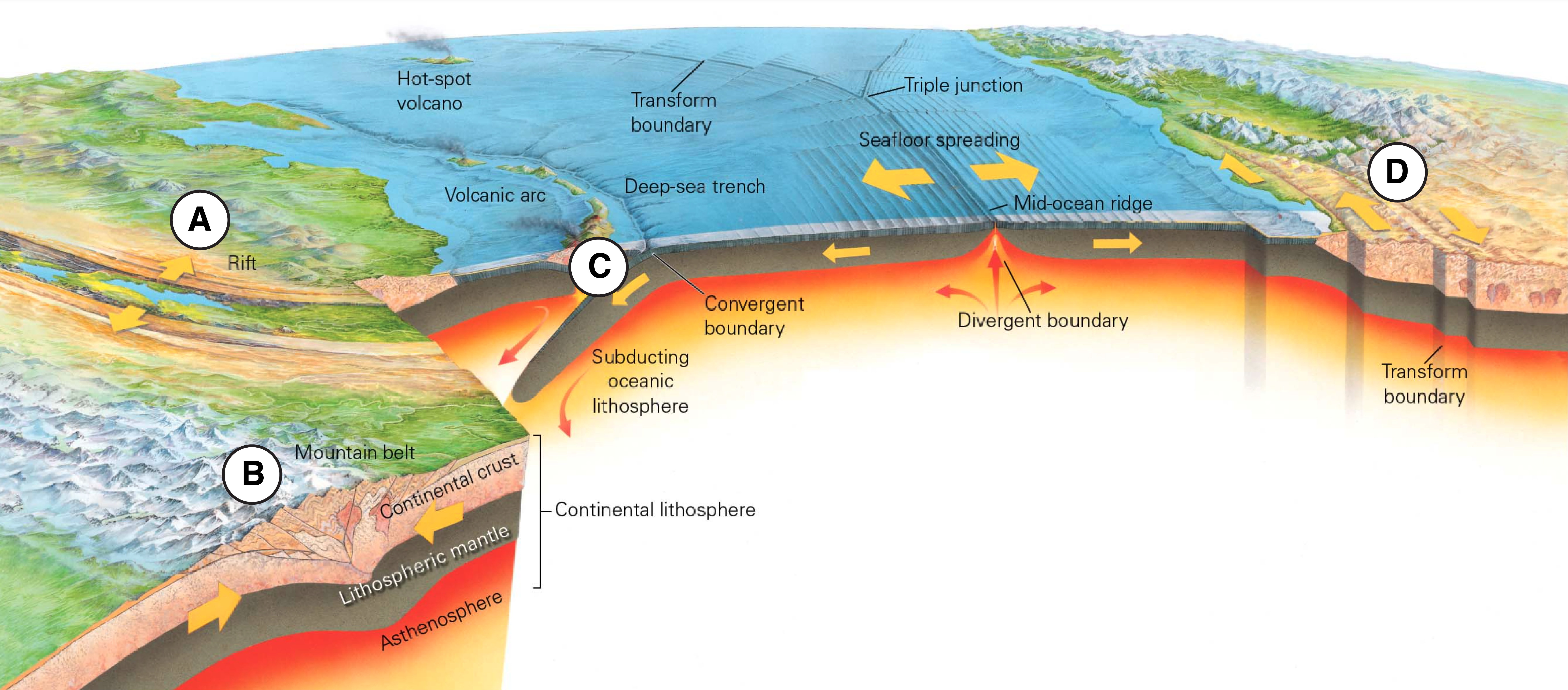
The diagram below shows a variety of different tectonic environments on Earth. Match each of the labeled regions with the type of faulting that you would expect to occur in that tectonic environment. What is C?
(Subduction zone/ Convergent boundary) Reverse Faulting
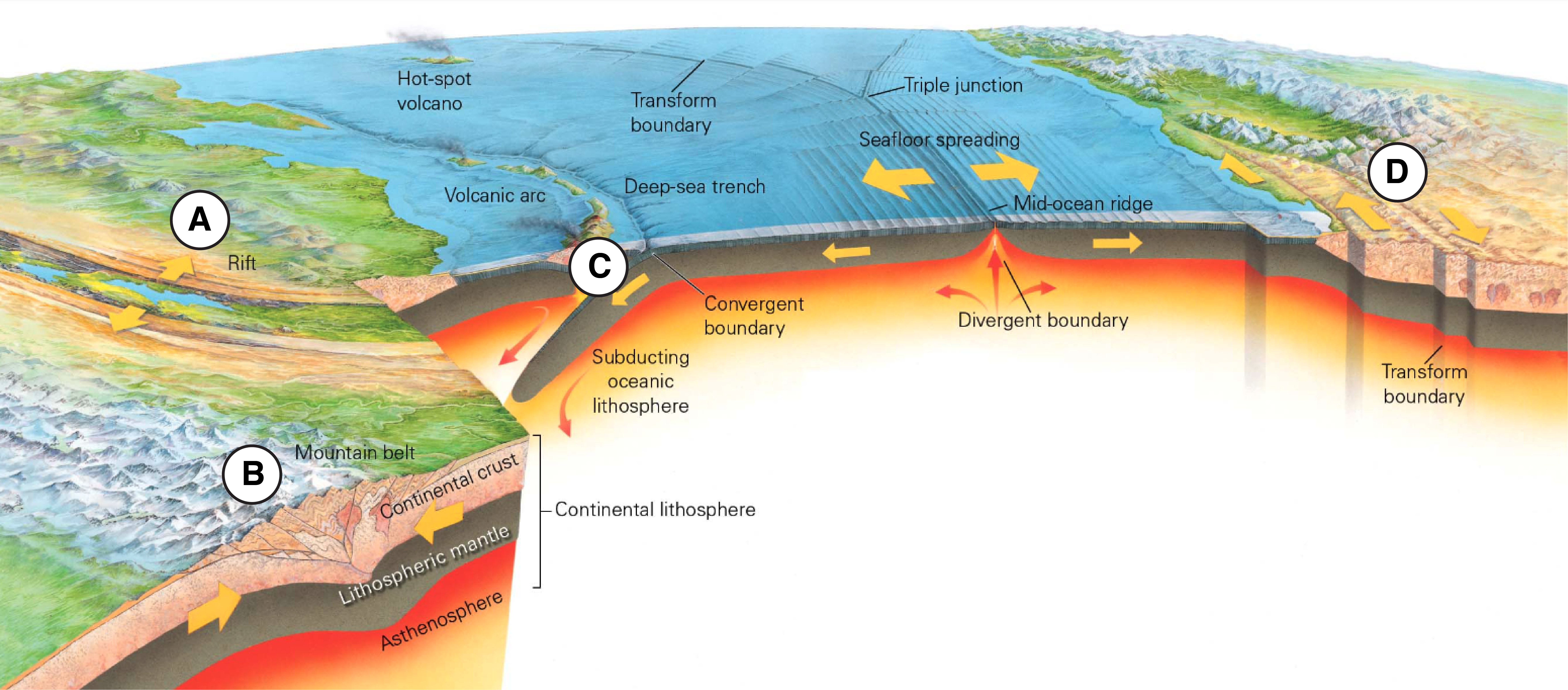
The diagram below shows a variety of different tectonic environments on Earth. Match each of the labeled regions with the type of faulting that you would expect to occur in that tectonic environment. What is D?
(Transform boundary) Strike-Slip faulting
How much energy does a Mw 8 earthquake release than a Mw 6 earthquake?
1000 times more
The point on the Earth’s surface above the location where earthquake slip begins is known as the
Epicenter
Seattle Washington is located in a large sedimentary basin called the Seattle Basin. What is true about how the subsurface geology affects the threat that Seattle faces from earthquake ground shaking?
Seattle faces an increased threat from ground shaking due to basin amplification
Why would a city official in an earthquake-prone area pass a zoning regulation that prohibits construction in a reclaimed area of land that is primarily filled with sand or wet sediment?
To prevent buildings from tipping over due to liquefaction
Earthquake early warning systems provide public alerts that a nearby fault is about the rupture.
False
What actions might you take to prepare for an earthquake or decrease the chance that you get hurt during an earthquake?
Install fire extinguishers
Know how to shut off gas and electricity
Secure heavy objects (e.g. bookshelves) to the wall
During an earthquake, take cover below a sturdy table to prevent objects falling on you
What is true about intraplate earthquakes?
Intraplate earthquakes often occur on ancient, reactivated fault systems
The last major earthquake disaster in the San Francisco Bay area was the 1989 Mw 6.9 Loma Prieta earthquake, which killed 63 people and caused over $5 billion dollars in damage. If a similar earthquake were to strike southern California, what types of dangers might be expected?
Landslides
Collapse of buildings/bridges
Liquefaction
A ‘resonance disaster’ (i.e. damage caused by amplification of building movement) is more likely if
the predominant of ground motion matches the resonant period of the building
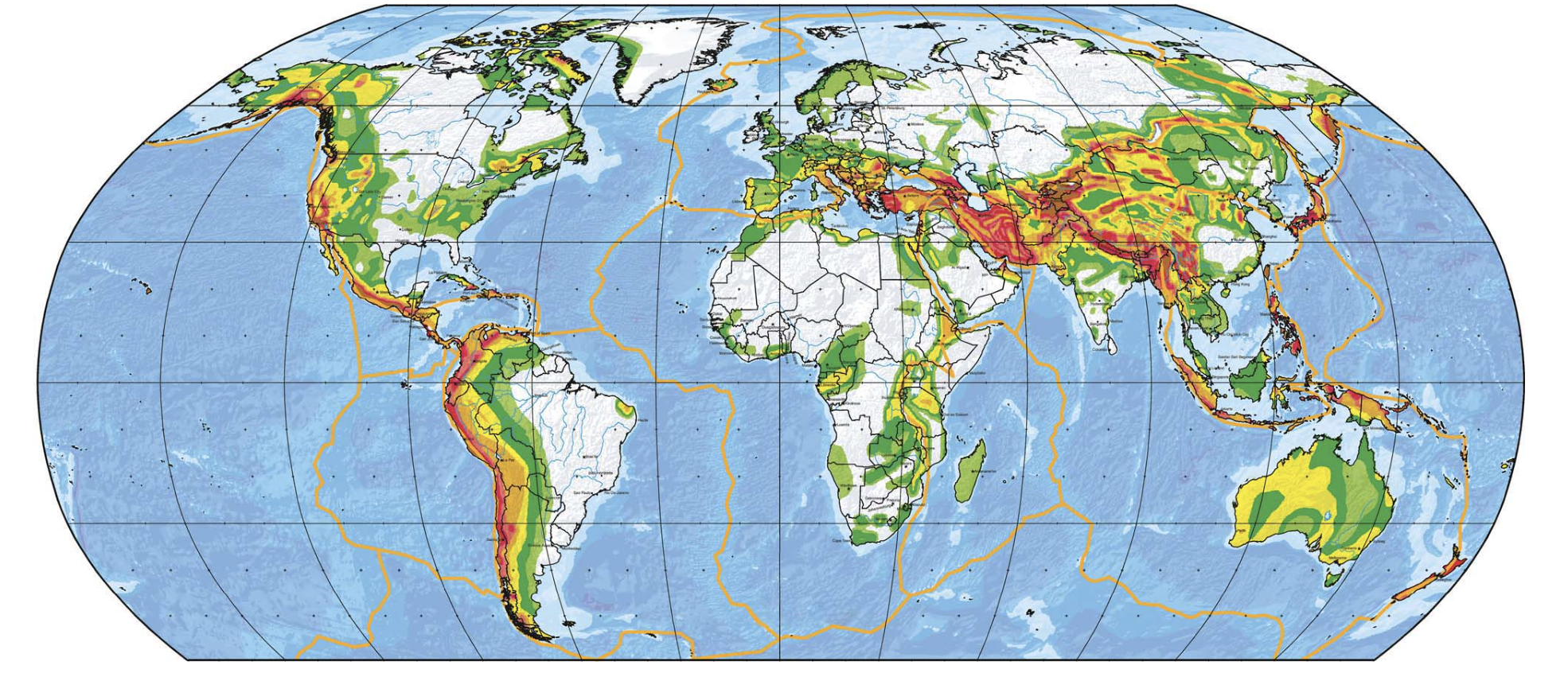
The map below shows the global seismic hazard map, where red colors indicate the regions most likely to experience strong ground shaking from an earthquake. According to this map, which type of plate boundaries are typically associated with the greatest seismic hazard?
Convergent plate boundaries
What approaches have earthquake engineers used to try to design earthquake resilient buildings?
Installing motion dampers to decrease swaying
Reinforcing the building with internal or external braces to make it more resistant to shear
Isolating the base of the building from the substrate (e.g. with springs or rubber rings)