Benzene and aromatic compounds
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Define an arene
Aromatic hydrocarbons containing one or more benzene rings
Give some characteristics of benzene
A colourless, sweet smelling, highly flammable liquid
Classified as a carcinogen
Burns with smoky flame
What is benzene naturally found in?
Crude oil
Petrol
Cigarette smoke
Volcanoes and forest fires
What are some things benzene is used to produce?
Detergents
Explosives
Pharmaceuticals
Dyes
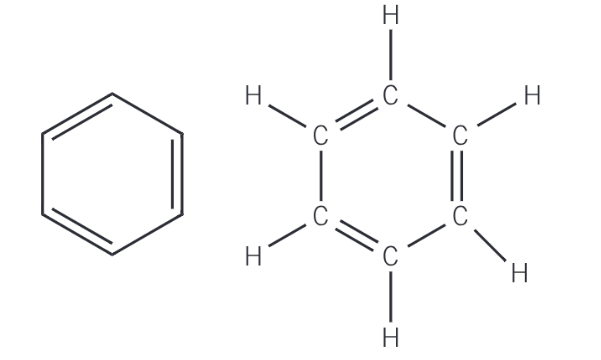
What was Kekulé’s proposed model of benzene?
Briefly state the 3 pieces of evidence which disproved Kekulé’s model
Benzene’s lack of reactivity
The lengths of the carbon-carbon bonds in benzene
Hydrogenation enthalpies
Explain how the benzene’s low reactivity disproved Kekulé’s model
Benzene cannot have any C=C bonds in its structure because:
Benzene does not decolourise bromine water
Benzene doesn’t take part in electrophilic addition reactions expected from the C=C
Explain how X-ray crystallography disproved Kekulé’s model
Using X-ray crystallography, scientists found that
All the C-C bonds were the same length
All C-C-C bonds had bond angles 120
Explain how hydrogenation enthalpies disproved Kekulé’s model
The enthalpy of hydrogenation was less exothermic than expected
If Kekulé’s model was correct, benzene would have an enthalpy change of hydrogenation 3 times that of cyclohexene
The enthalpy change was less exothermic, so benzene must therefore be more stable than Kekulé’s model
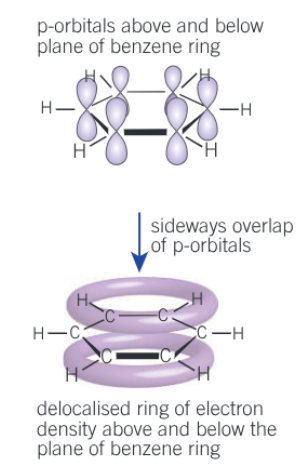
Show the delocalised model of benzene and give the main features
Planar (flat), cyclic, hexagonal hydrocarbon
Each carbon uses three of its four electrons to bond to 2 carbons and one hydrogen (3 σ bonds per each C)
Each carbon has one electron in a p-orbital at right angles to the plane of the bonded carbon and hydrogen atoms
Bond angle 120
Overlapping of p-orbitals creates delocalised system of π-bonds above and below plane of carbon atoms
What types of reactions does benzene take part in?
Only substitution reactions
How is a benzene derivative formed?
When one of the hydrogen atoms on the benzene is replaced with an atom or group
Benzene therefore forms the root of the name
How do we name monosubstituted aromatic compounds?
The benzene ring is the parent-chain
Alkyl groups, halogens and nitro groups are all considered prefixes to benzene
When do we use the term phenyl?
When a benzene ring is attached to:
An alkyl chain with a functional group
An alkyl chain with seven or more carbon atoms
Benzene is considered a substituent
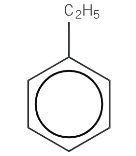
Ethylbenzene
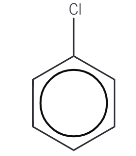
Chlorobenzene
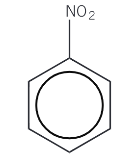
Nitrobenzene
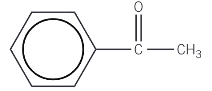
Phenylethanone
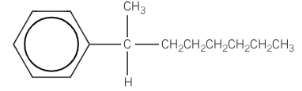
2-phenyloctane
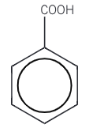
Benzoic acid
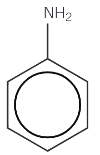
Phenylamine
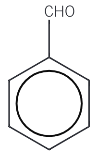
Benzaldehyde / Benzanal
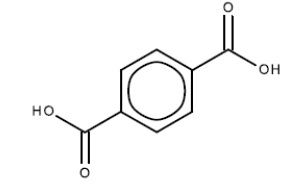
1,4-benzoic acid
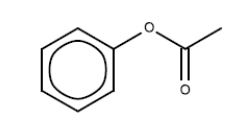
Phenyl ethanoate
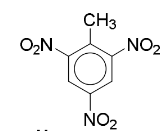
2,4,6-trinitrotoulene (TNT)
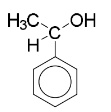
phenylethanol
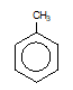
methylbenzene (toulene)
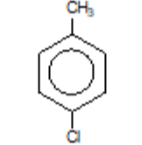
4-methylchlorobenzene
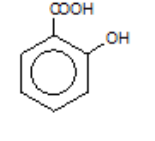
2-hydroxybenzoic acid
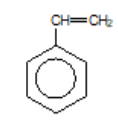
phenylethene
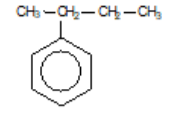
2-phenylbutane
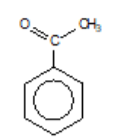
phenylethanone
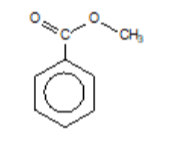
methyl benzenecarboxylate (methyl benzoate)
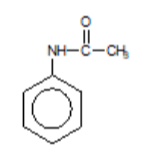
N-phenylethanamide
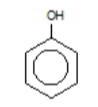
phenol
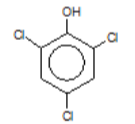
2,4,6-trichlorophenol (TCP)
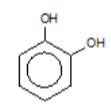
benzene-1,2-diol
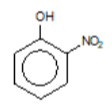
2-nitrophenol
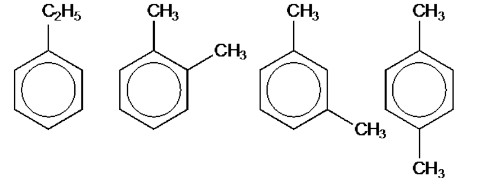
Draw all the structural isomers of the aromatic compound with the molecular formula of C8H10