proteins - biochemistry
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
amino acids
proteins are made of AMINO ACIDS
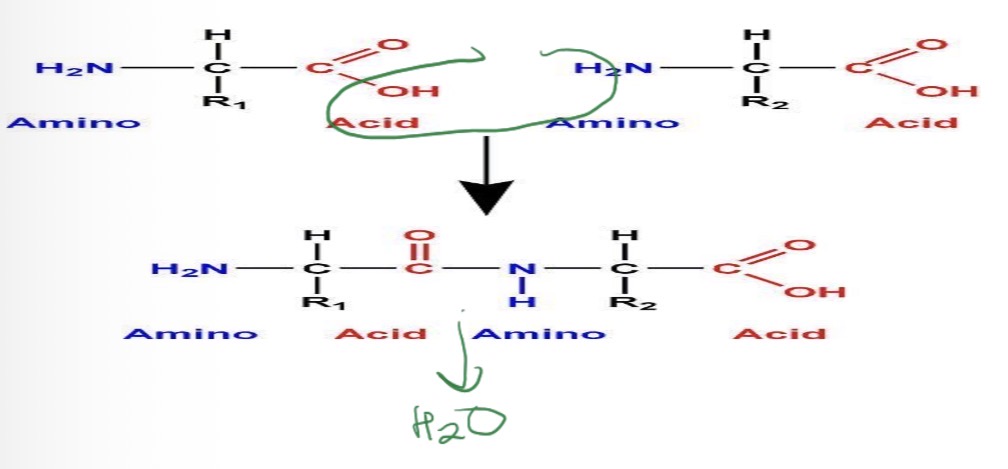
each amino acid is a 2 carbon long structure with an AMINE & CARBOXYL functional groups
link together using CONDENSATION REACTION for amine group to carboxyl group → called a ‘peptide bond’
2 amino acid sequence based → called a dipeptide
3 long amino acid → tripetide
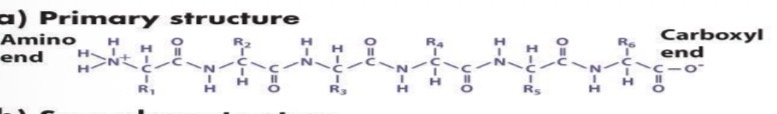
primary structure
basic amino acid sequence
based on covalent
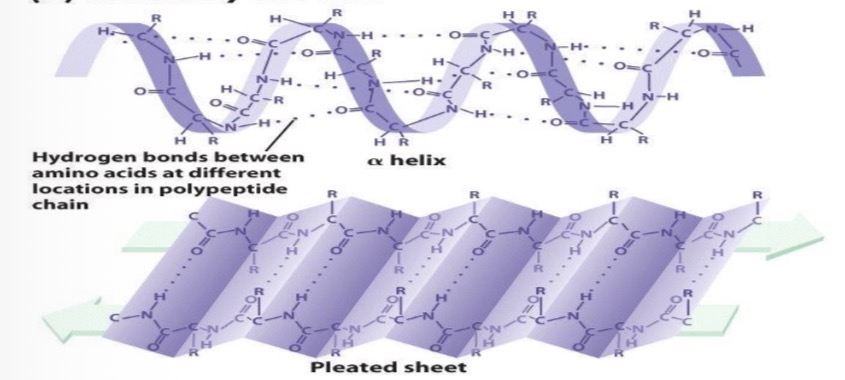
secondary structure
folding pattern
alpha helices
beta sheets
electrostatic attractions
hydrogen bonds
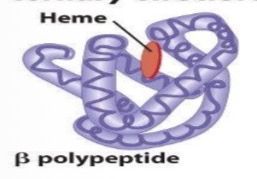
tertiary structure
overall folding pattern of whole polypeptide
electrostatic attractions
hydrogen bonds
disulfide bridge
quaternary structure
once folded, two or more polypeptides link together
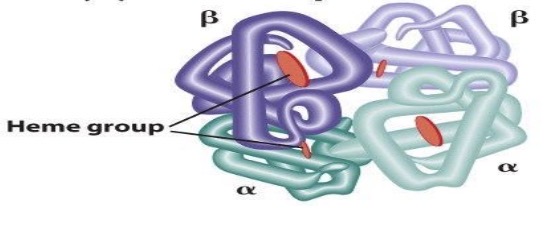
prosthetic groups
non protein complexes that are attached to the protein to make the protein function
protein denaturation process
an egg is made up of protein called ALBUMIN
when egg is raw, the albumin is clear and runny
once heated, albumin changes to solid white
still a protein but no longer has the same function
four types of amino acids by r-group
non-polar (hydrophobic)
polar (hydrophilic)
acidic (negative charge)
basic (positive charge)
protein folding
driven by hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, hydriphobic interactions, disulfide bridges
proper folding
functional protein
misfolding
loss of function → can cause disease (ex: alhiemers)