C nucleophiles
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
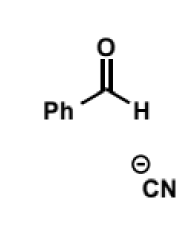
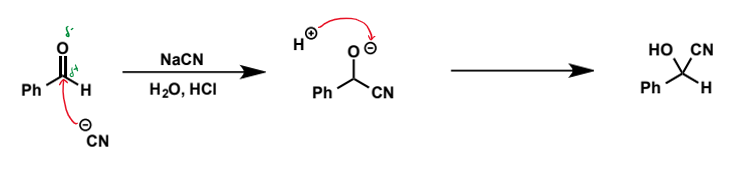
cyanide as a nucleophile. equilibrium? name of products?
show mechanism for benzaldehyde
acts as a nucleophile in SN2 reactions and for addition to aldehydes and ketones. equilibrium usually lies to the side of the product under acidic conditions. products are called cyanohydrins - reduction or hydrolysis of the nitrile group in these generates useful building blocks for pharmaceutical synthesis.
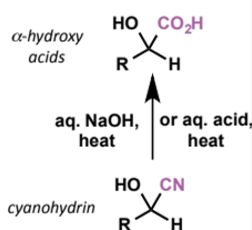
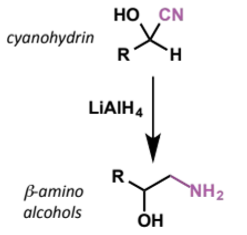
2 further reactions of cyanohydrins
functional groups created?
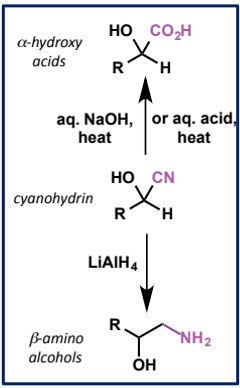
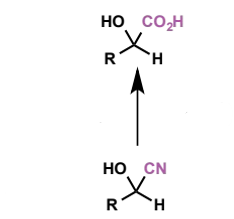
reagents/conditions
characterise reactant + product
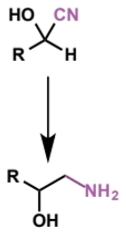
reagents/conditions
characterise reactant + product
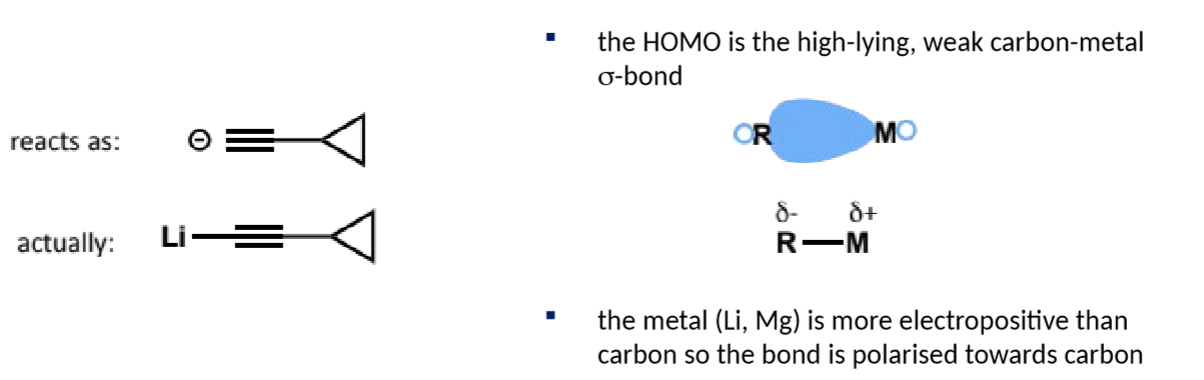
acetylide anions
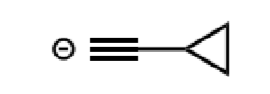
organometallics as nucleophiles
how do they react
give example for acetylide anions
HOMO?
the reagent is not actually a free anion but instead has a polar carbon-metal bond (to Li for acetylide)
remember that although R-M react as R- the metal is still heavily involved in the reaction
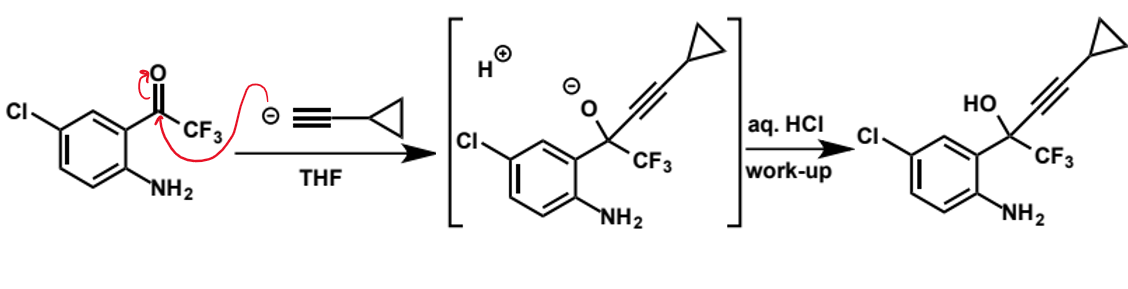
mechanism of acetylide with this (need to know reaction not structures)
how are organometallics made
reaction of organic halides (usually Br or I) with the elemental metal (Li/Mg). they are air and moisture sensitive and must be used in dry, aprotic solvents like THF or Et2O.
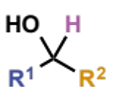
how are secondary alcohols synthesised
reduction of ketones
or addition of organometallics to aldehydes - if R1 ≠ R2 there are two possibilities for this

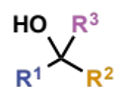
how are tertiary alcohols synthesised
addition of organometallics to ketones - if R1 ≠ R2 ≠ R3 there are three possibilities
what are grignard reagents
organomagnesium halide reagents
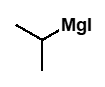
R-MgBr with aldehyde (methanal)
which group in an organometallic is the nucleophile/base?
the organic group as the carbon has a partial negative charge due to the electropositivity of the metal