Chapter 14 Part 2. Mood Disorders and Treatments
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Major Depressive Disorder
Characterized by an absence of happiness rather than increased sadness
Major Depressive Disorder 2 Facts
Most common in women during the reproductive area
Most commonly comes in periodic episodes
Depression and genetics
Moderate degree of heritability
No one gene has been identified as clearly linked to depression
People with early-onset depression (before age 30) more likely to have relatives with depression and anxiety disorders
Late onset depression (after age 45) linked to relatives with circulatory problems
What are the four categories of anti-depressant drugs?
Tricyclics
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
Serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
Tricyclics
Block transporter proteins that reabsorb serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine into the presynaptic neuron after release
Downside to tricyclics
Because they also block histamine receptors, acetylcholine receptors, and certain sodium channels, they cause side effects of drowsiness, dry mouth, difficulty urinating, and (most dangerously) heart irregularities
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
Block the reuptake of the neurotransmitter serotonin
Prescribed more than tricyclics because it has fewer side effects, partly because it doesn’t block histamines and sodium channels.
Serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
Block the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine
Unlike other antidepressants, the SNRIs improve certain aspects of memory
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
These drugs DO NOT block transmitters, they block the enzyme Monoamine oxidase, which metabolizes serotonin and catecholamines, so they remain in the synapse
Catecholamines
Catecholamines are neurotransmitters namely epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and dopamine, that prepare the body for "fight-or-flight" stress
Three natural alternatives to anti-depressants
Cognitive-behavioural therapy
Exercise
Diet
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
Electrically induced seizure used for the treatment of severe depression
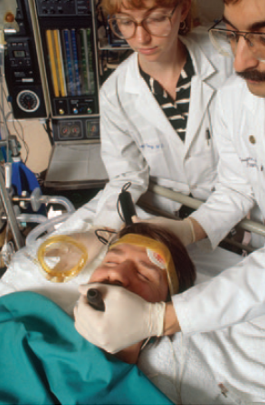
While the reasons why ECT relieves depression is unknown, what are some theories?
Because it increases Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF), which helps neurogenesis, being a neurotrophic factor
Unipolar disorder
Characterized by alternating states of normality and depression
Bipolar disorder (formally manic depressive disorder)
Characterized by alternating states of depression and mania
Bipolar disorder I vs bipolar disorder II
Bipolar disorder I is characterized by full blown episodes of mania, whereas bipolar disorder II is characterized by much milder manic phases, called hypomania
Why are anti-depressants not good for bipolar disorder?
Because you don’t want the patient to have the anti-depressant during the manic (happy) phase
First treatment for bipolar disorder
Lithium
The problem lithium is that the toxic dose is very close to the effective dose, so you could “treat and kill” the patient at the same time.
Second treatment for bipolar disorder
Valproate (Depakote) and Carbamazepine
Valproate (Depakote) and Carbamazepine
Designed to treat bipolar disorder by reducing over excitation, namely by increasing GABA activity and decreasing glutamine activity
Tardive Dyskinesia
Caused by a lack of dopamine, and involves tremors and involuntary movements
Antipsychotic drugs that are meant to treat schizophrenia often cause Tardive Dyskinesia