Adaptations to the 3 different habitats
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Habitat 1
High altitude
What adaptations does this plant have?
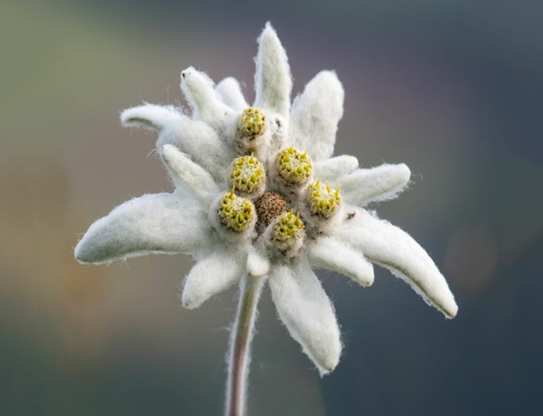

is white, reflective, and has wooly hair
What is the purpose for these structures (1.1)
hair traps and insulates against low temperatures
white hair protects against high UV radiation/ The Sun
What adaptations does this plant have?
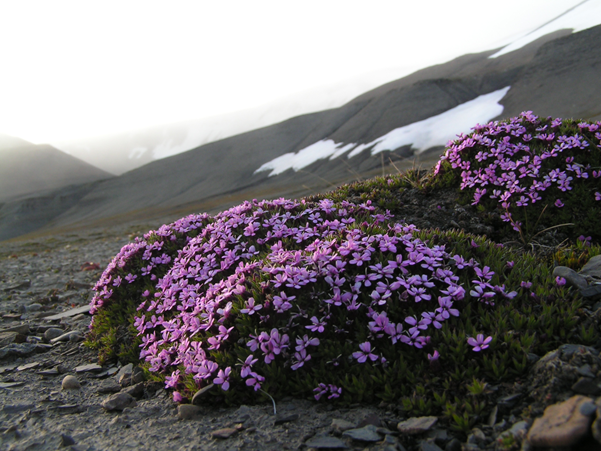

small leaves, stunted growth to stay low to the ground
What is the purpose of these structures (1.2)
prevents excessive transpiration
protects from harsh weather conditions
What adaptations does this plant have

thick fleshy leaves
What is the purpose of this structure (1.3)
helps with water conservation/during dry periods
Habitat 2
Sand dunes (dry)
What adaptations does this plant have
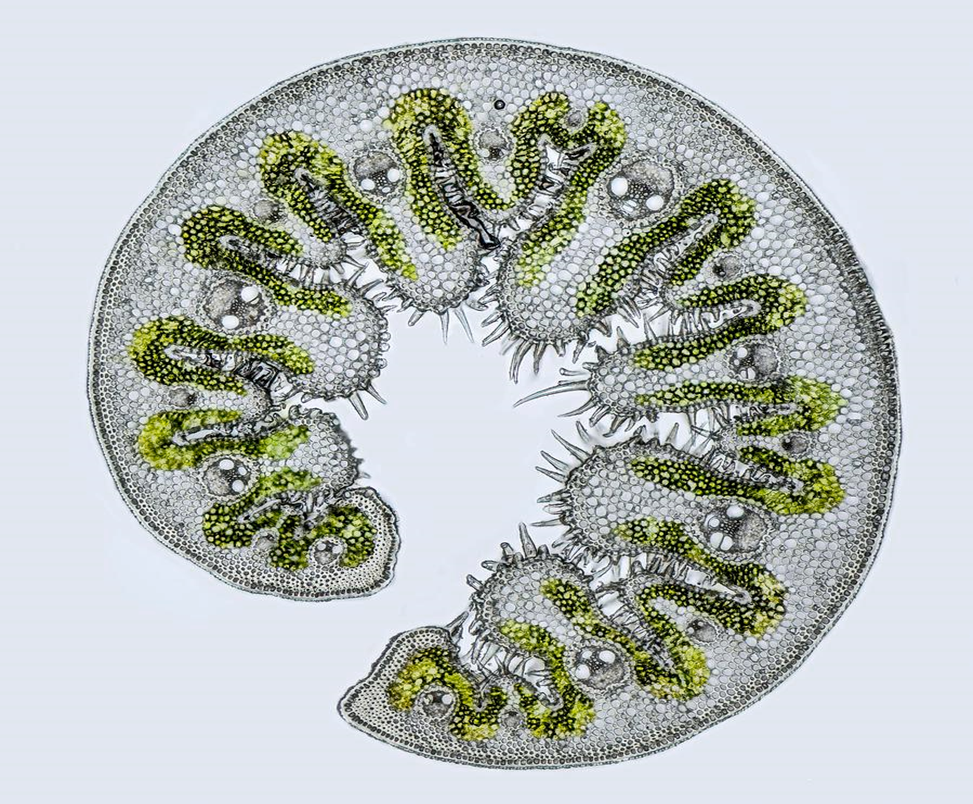
thick waxy cuticle
leaves can roll during drought
indented stomata
What is the purpose of these structures (2.1)
reduces water loss through
rolled up leaves make a humid chamber reducing exposure to
keep humid air no exposure to wind transpiration
What adaptations does this plant have
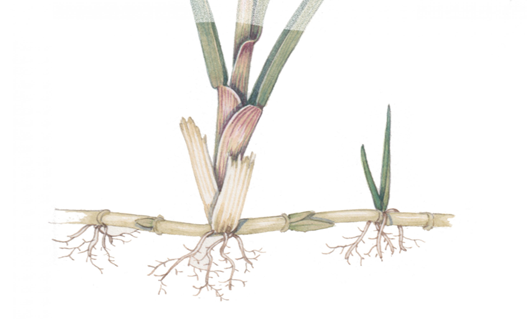
underground stems (rhizomes)
What is the purpose of this structure (2.2)
provide stability
can extend deep into the ground to obtain water
What adaptations does this plant have
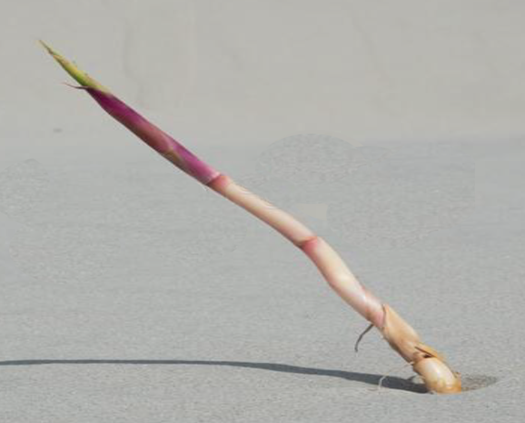

accumulation of carbohydrates in root/leaf cells
What is the purpose of this structure (2.3)
storage for sugars = increase osmotic potential = help absorb water
Habitat 3
Mangrove tree (waterlogged soil)
What adaptations is this for the mangroves?
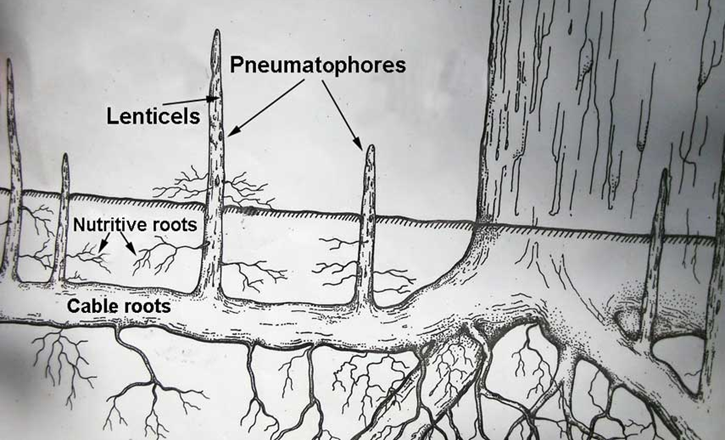
pneumatophores
cable roots
What do these roots do (3.1)
grow into the air and absorb oxygen
provide stability, grow to the ground to absorb O2

What adaptation does this plant have
still roots growing in a downward arch from the stem
What do these roots to (3.2)
anchor the tress into the ground and increase stability

What adaptation do these seeds have
buoyant seeds
What is the purpose of this structure (3.3)
carried away by ocean currents and allow dispersal to fertile soil