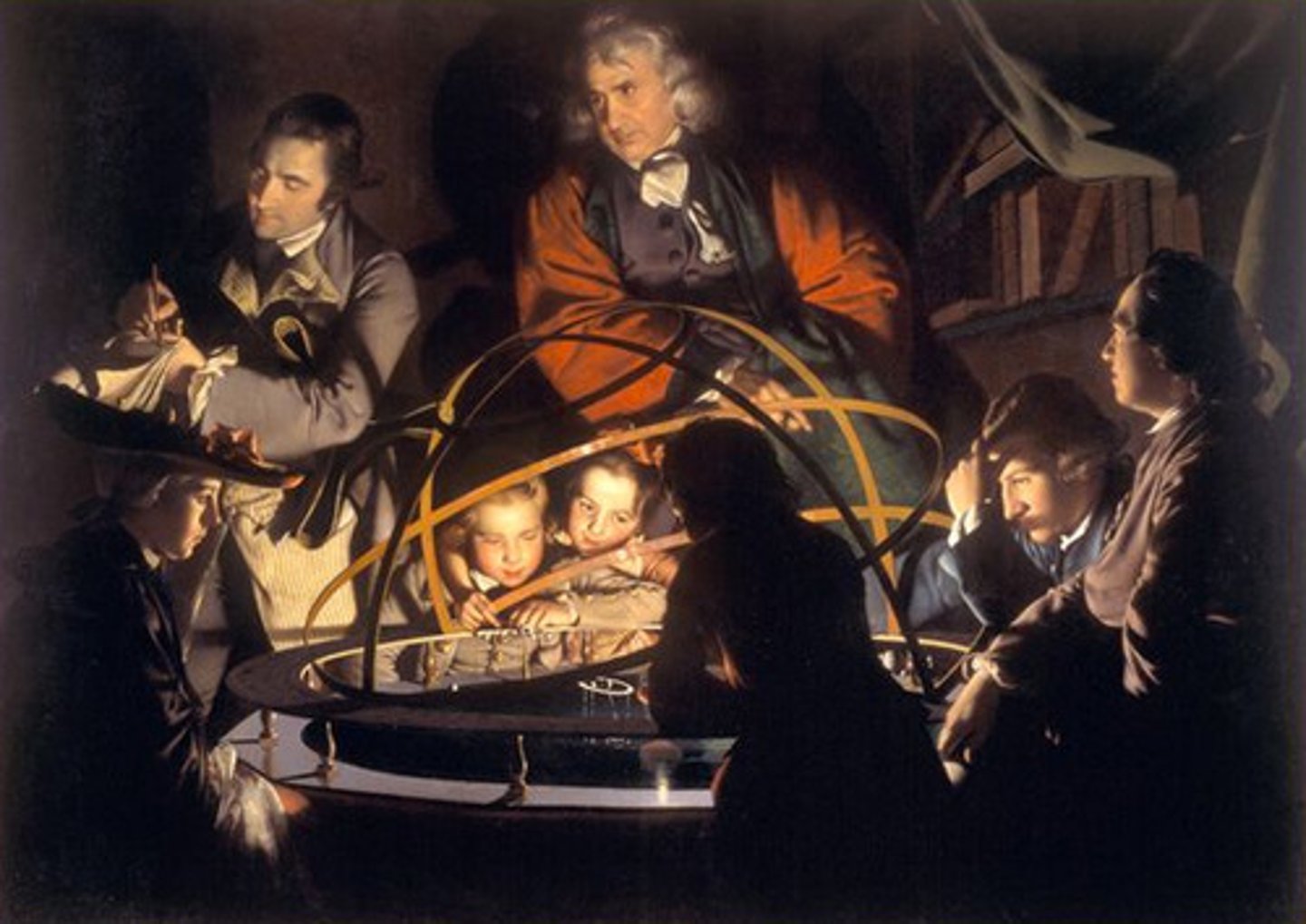
Scientific Revolution and Age of Enlightenment
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
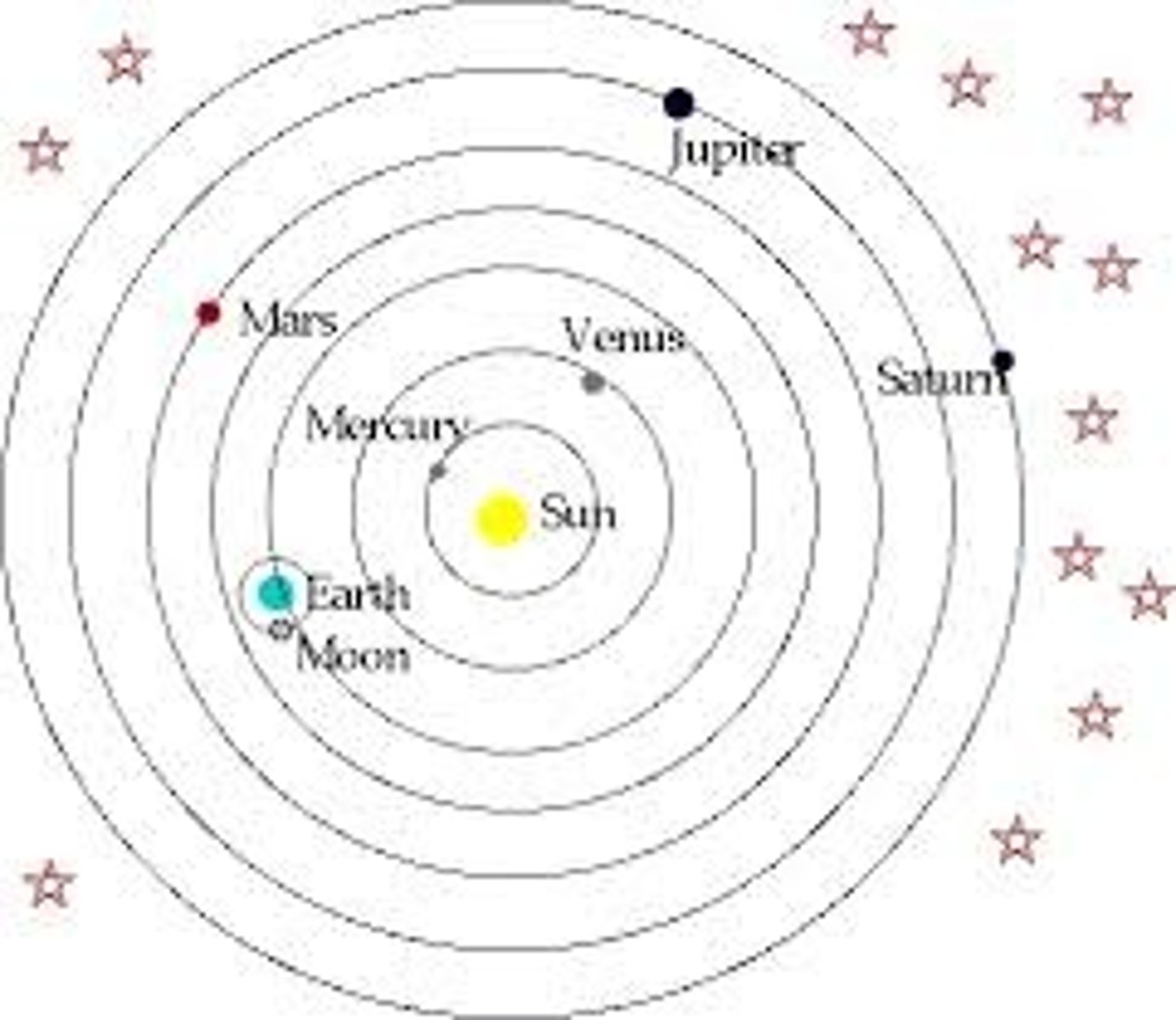
Geocentric Theory
Earth-centered view of the universe that came from the Greek philosopher Aristotle
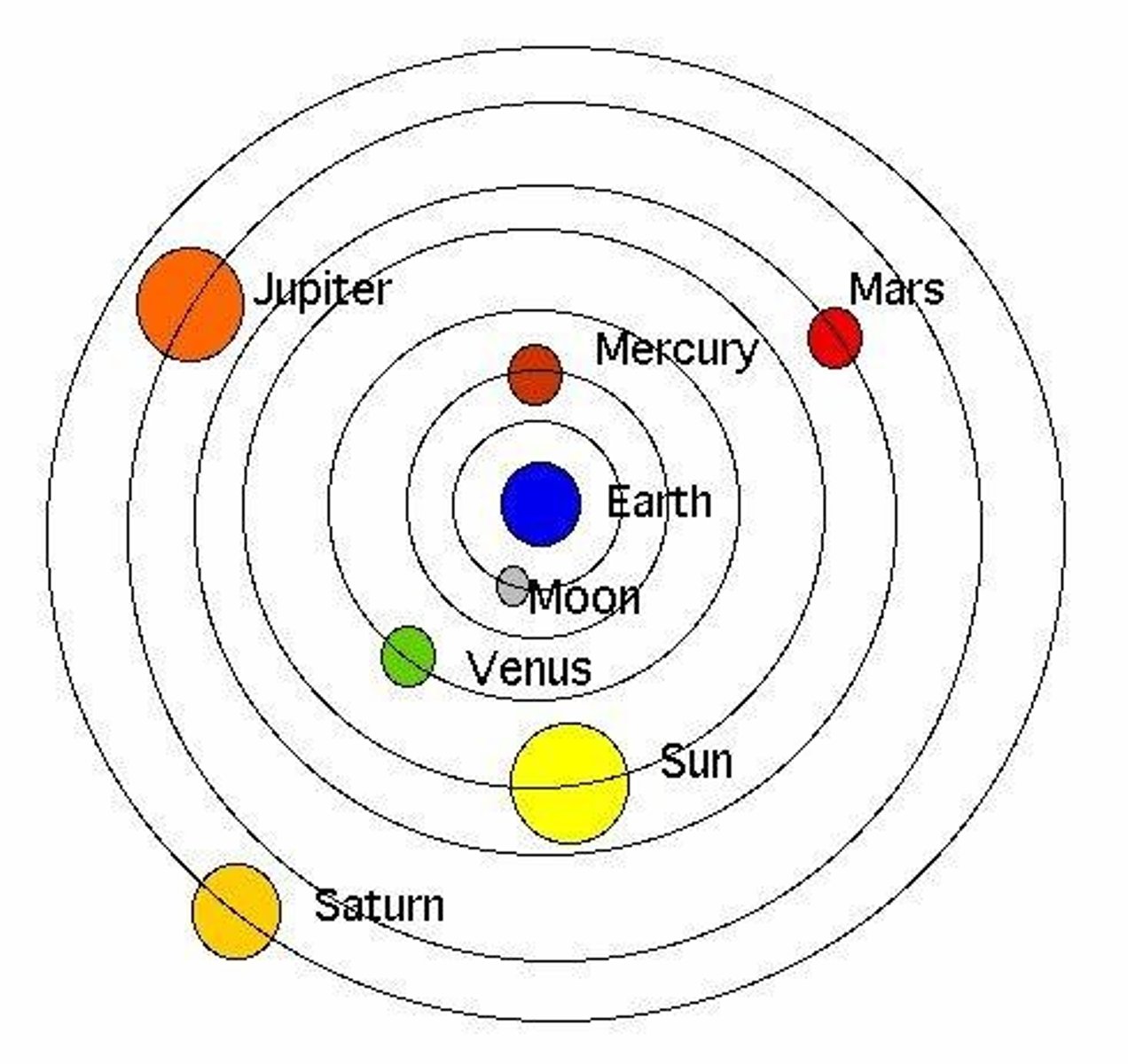
Heliocentric Theory
A theory that place is the sun at the center of the solar system with the planets, including earth, revolving around it. Helio is Greek for sun
Aristotle, Ptolemy & Galen
The three ancient scientists who all used as the basis for their knowledge.
Copernicus
Polish astronomer who produced a workable model of the solar system with the sun in the center (1473-1543)

Brahe
A Danish astronomer who provided evidence to support Copernicus. He set up an astronomical observatory and collected data.

Kepler
German astronomer/mathematician stated that the orbits of planets around the sun were elliptical, the planets do not orbit at a constant speed, and that an orbit is related to its distance from the sun.

Galileo
Italian astronomer and mathematician who was the first to use a telescope to study the stars; demonstrated that different weights descend at the same rate; perfected the refracting telescope that enabled him to make many discoveries (1564-1642)

Isaac Newton
English mathematician and scientist- invented differential calculus and formulated the theory of universal gravitation, a theory about the nature of light, and three laws of motion. was supposedly inspired by the sight of a falling apple.

Scientific Revolution
A major change in European thought, starting in the mid-1500s, in which the study of the natural world began to be characterized by careful observation and the questioning of accepted beliefs.
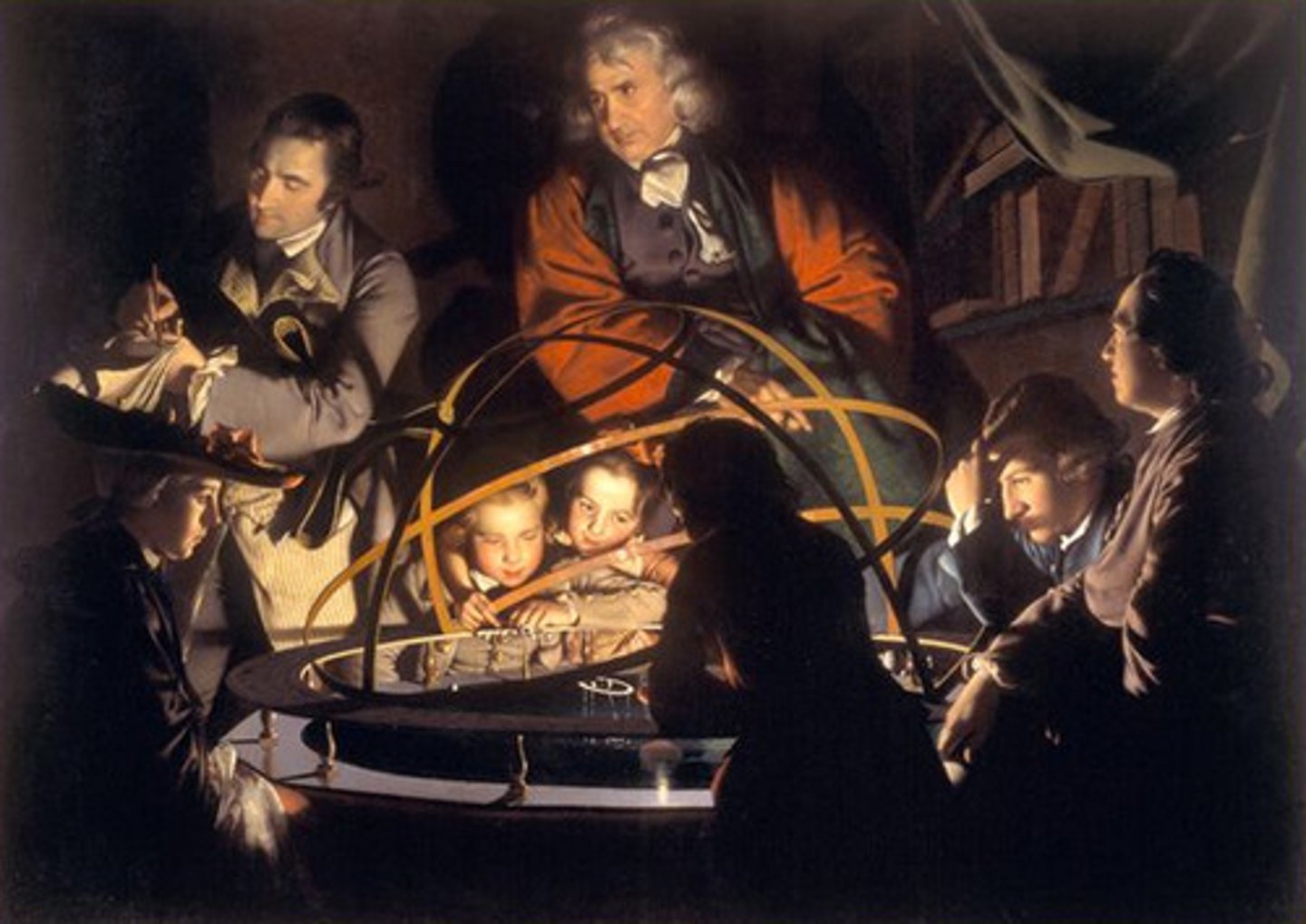
Scientific Method
A step-by-step method of investigation involving observation and theory to test scientific assumption.
Francis Bacon
(1561-1628) an early pioneer of the scientific method who created "empiricism" and inspired the scientific revolution.

Rene Descartes
17th century French philosopher who relied on mathematics and logic and believed that everything should be doubted until proved by reason.
"I think, therefore I am". He developed the concept of mind-body dualism and believed in doubting until finding something that could no longer be doubted to find absolute truth.

Leeuwenhoek
1670's ; father of modern microbiology; first to observe living cells

William Harvey
English physician from the 17th century who demonstrated circular movement of blood in animals, and the function of the heart as a pump
Vesalius
This was the scientist who began to study anatomy in depth. He is referred as the father of anatomy
The Enlightenment
A philosophical movement which started in Europe in the 1700's and spread to the colonies. It emphasized reason and the scientific method. Writers of the enlightenment tended to focus on government, ethics, and science, rather than on imagination, emotions, or religion. Many members of the Enlightenment rejected traditional religious beliefs in favor of Deism, which holds that the world is run by natural laws without the direct intervention of God.

Social contract
A voluntary agreement among individuals to secure their rights and welfare by creating a government and abiding by its rules.

Hobbes
English philosopher and political theorist best known for his book Leviathan (1651), in which he argues that the only way to secure civil society is through universal submission to the absolute authority of a sovereign.

Locke
Philosopher who held a different more positive view of human nature. Locke criticized absolute monarchy and favored the idea of self-government. Locke thought all people were born free and equal, with three natural rights. Said human nature lived free and had the natural rights of life, liberty, and property. He said government was created in order to protect these rights and if the government failed to do so it was the duty of the people to rebel.

Natural Rights
Life, Liberty, and Property
Philosophes
French thinkers who popularized Enlightenment ideas through their writings were known as this. Social critics of the eighteenth century who subjected social institutions and practices to the test of reason.

Voltaire
(1694-1778) French philosopher. He believed that freedom of speech was the best weapon against bad government. He also spoke out against the corruption of the French government, and the intolerance of the Catholic Church.

Montesquieu
(1689-1755) wrote 'Spirit of the Laws', said that no single set of political laws was applicable to all - depended on relationship and variables, supported division of government
Rousseau
Great philosopher who was committed to individual freedom. Rosseau strongly disagreed with other Enlightenment thinkers on many matters. He argued that civilizations corrupted people's natural goodness. A famous quote of his was "Man is born free, and everywhere he is in chains,". He thought the only good government was one that was freely formed by the people and guided by the "general will" of society.

Mary Wollstonecraft
An English writer who wrote "Vindication of the Rights of Women", arguing that women are not naturally inferior to men, but appear to be so because of lack of education

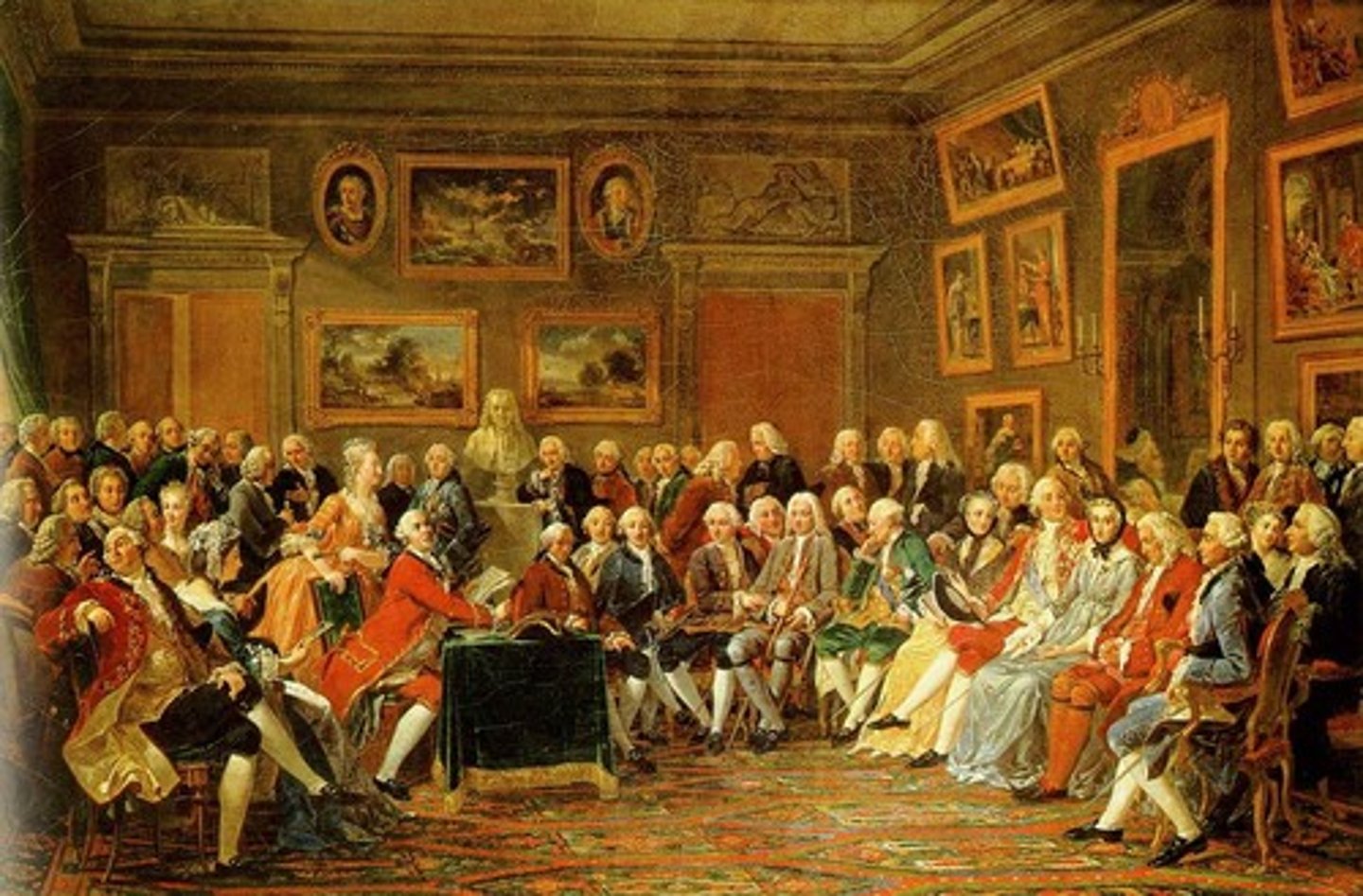
Salons
Informal social gathering at which writers, artists, and philosophers exchanged ideas; originated in France in the 1600s

Diderot
French philosopher from 1713-84 who composed a 28 volume encyclopedia that included and spread many Enlightenment ideas

Baroque
Style in art and architecture developed in Europe from about 1550 to 1700, emphasizing dramatic, curving forms, elaborate ornamentation, and overall balance of disparate parts. Associated with Catholicism. (A grand, ornate style.)

Neoclassical
Relating to a simple, elegant style (based on ideas and themes from ancient Greece and Rome) that characterized the arts in Europe during the late 1700s

Enlightened Despots
The absolute monarchs in 18th-century Europe who ruled according to the principles of the Enlightenment.

Natural laws
Patterns and explanations of the world discovered through reason and intelligence.
Deism
The religion of the Enlightenment (1700s). Followers believed that God existed and had created the world, but that afterwards He left it to run by its own natural laws. Denied that God communicated to man or in any way influenced his life.

Atheism
Belief that there is no god.
Carrolus Linnaeus
Swedish botanist who proposed the modern system of biological nomenclature (1707-1778) Father of taxonomy.

Philosophes
Thinkers of the Enlightenment; Wanted to educate the socially elite, but not the masses; were not allowed to openly criticize church or state, so used satire and double-meaning in their writings to avoid being banned; Salons held by wealthy women also kept philosophes safe; They considered themselves part of an intellectual community, and wrote back and forth to each other to share ideas.