Benign Soft Tissue Pathology
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
soft tissue tumors are derived from .... tissues
mesenchymal
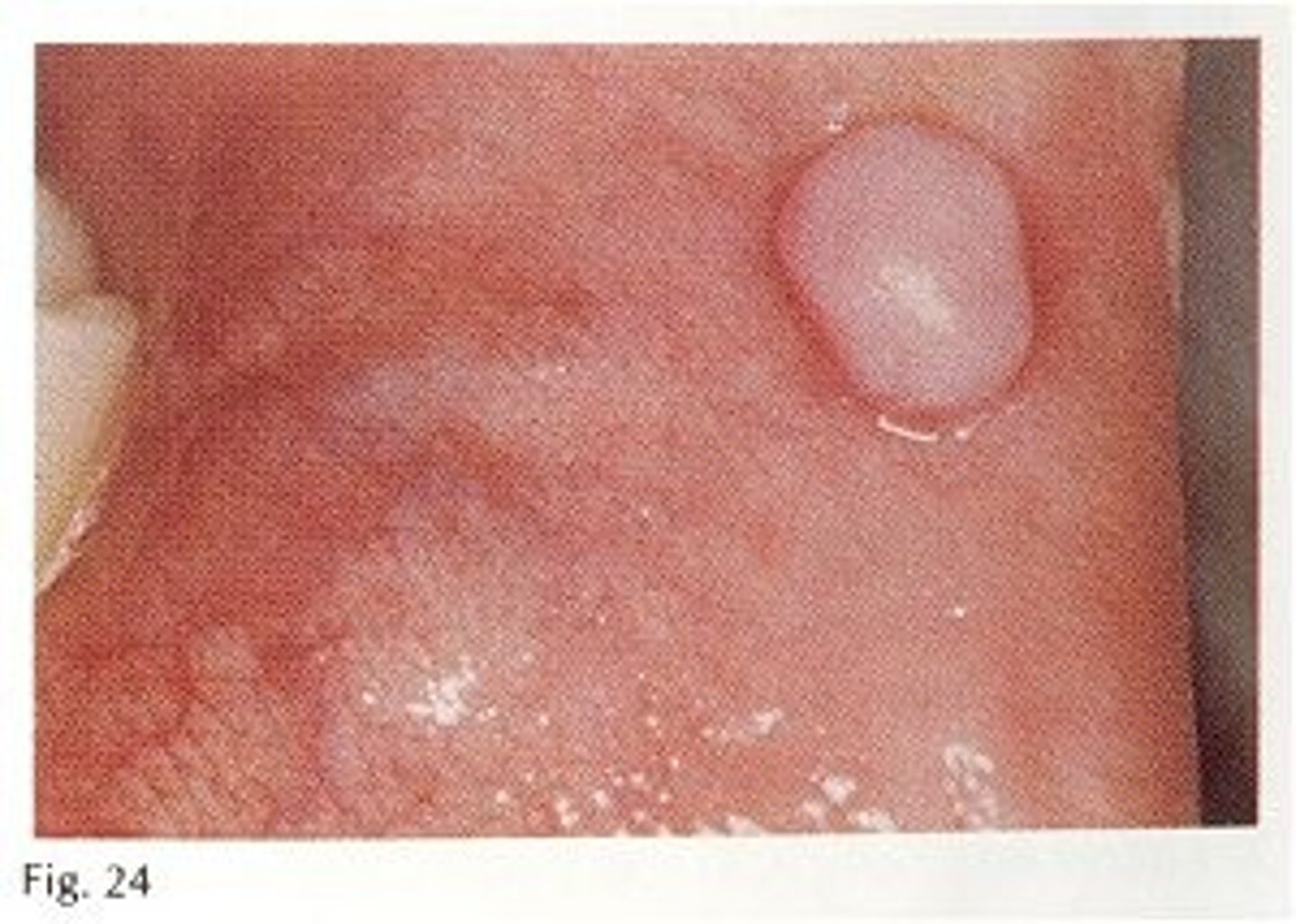
which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Most common benign soft
tissue mass
• Results from irritation or trauma
• Reactive lesion
• Well-localized
• Dome-shaped
• Asymptomatic (unless secondary
ulceration)
• Smooth surface
• Often pink but may be ulcerated
if traumatized
• Sessile or pedunculated
fibroma
which type of benign soft tissue histopathology:
• Nodular mass of fibrous connective tissue covered by stratified
squamous epithelium
• Surface may exhibit hyperkeratosis from secondary trauma
fibroma
fibroma
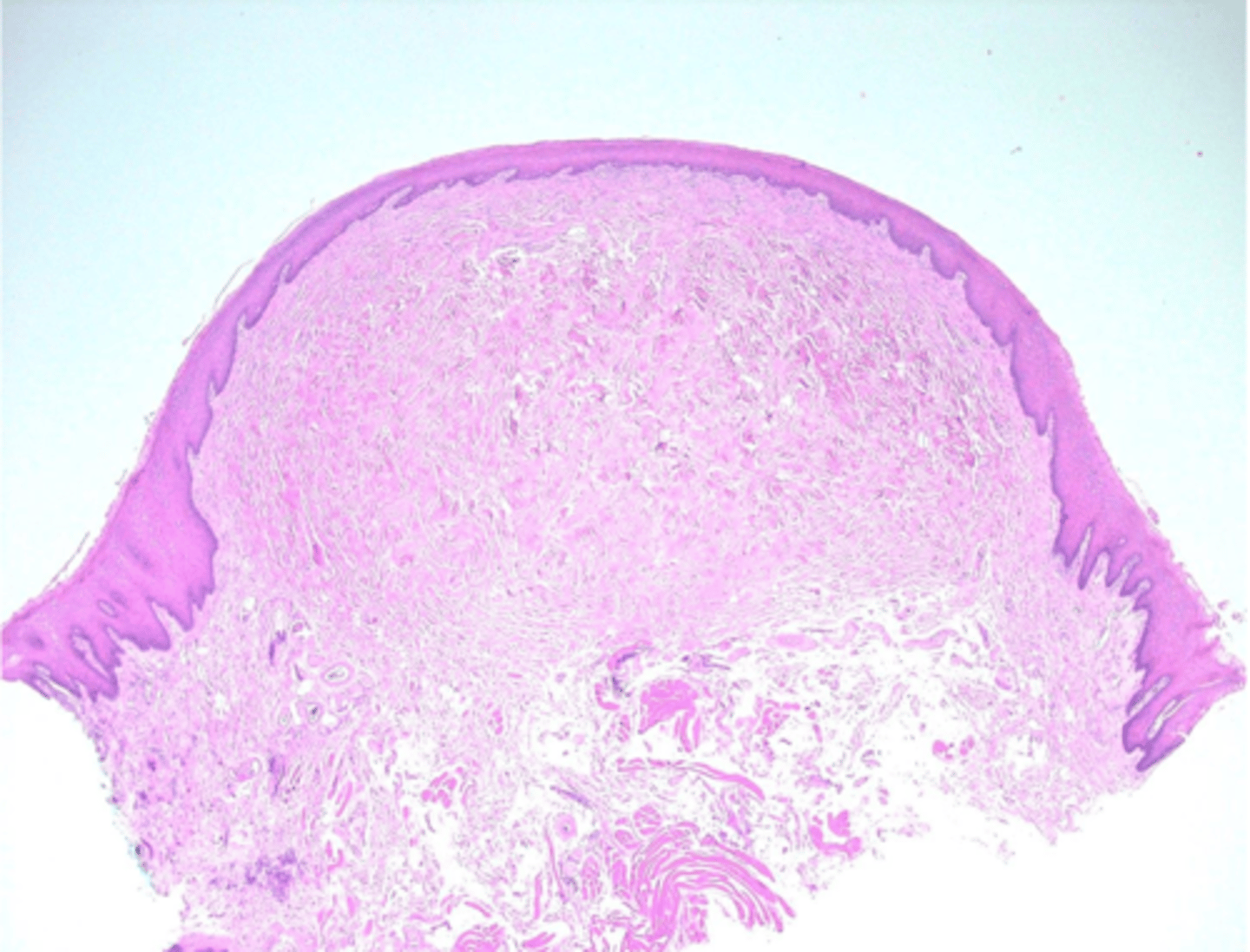
fibroma histology
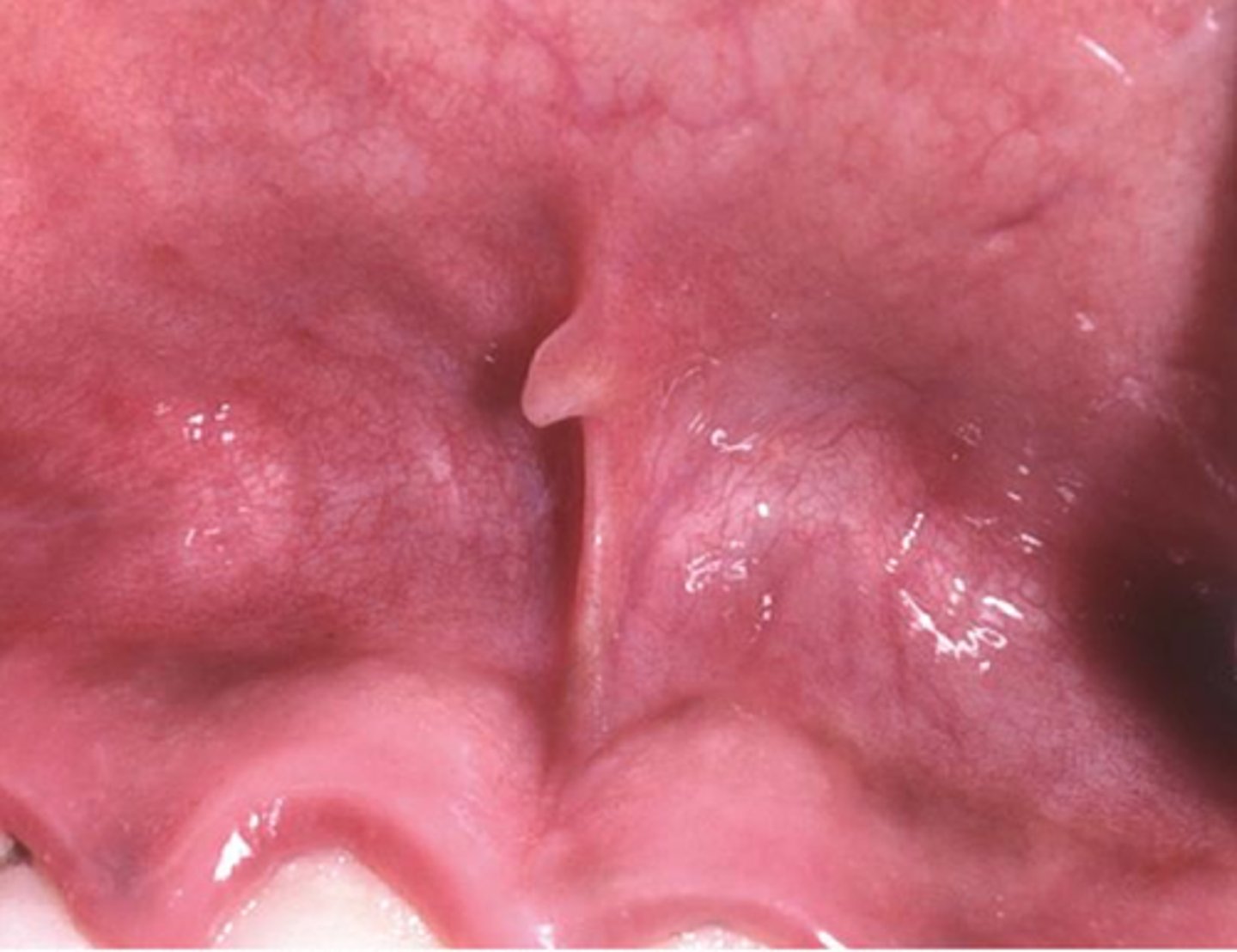
which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Fibrous hyperplasia
• Most common on the maxillary
labial frenum
• Small, asymptomatic, exophytic
growths
• Can be diagnosed clinically so no
treatment is necessary
frenal tag
frenal tag
treatment for which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
◦ Surgical excision
◦ Important to submit ANY tissue
removed for histopathologic
examination
◦ Malignancies can mimic
benign entities!
fibroma
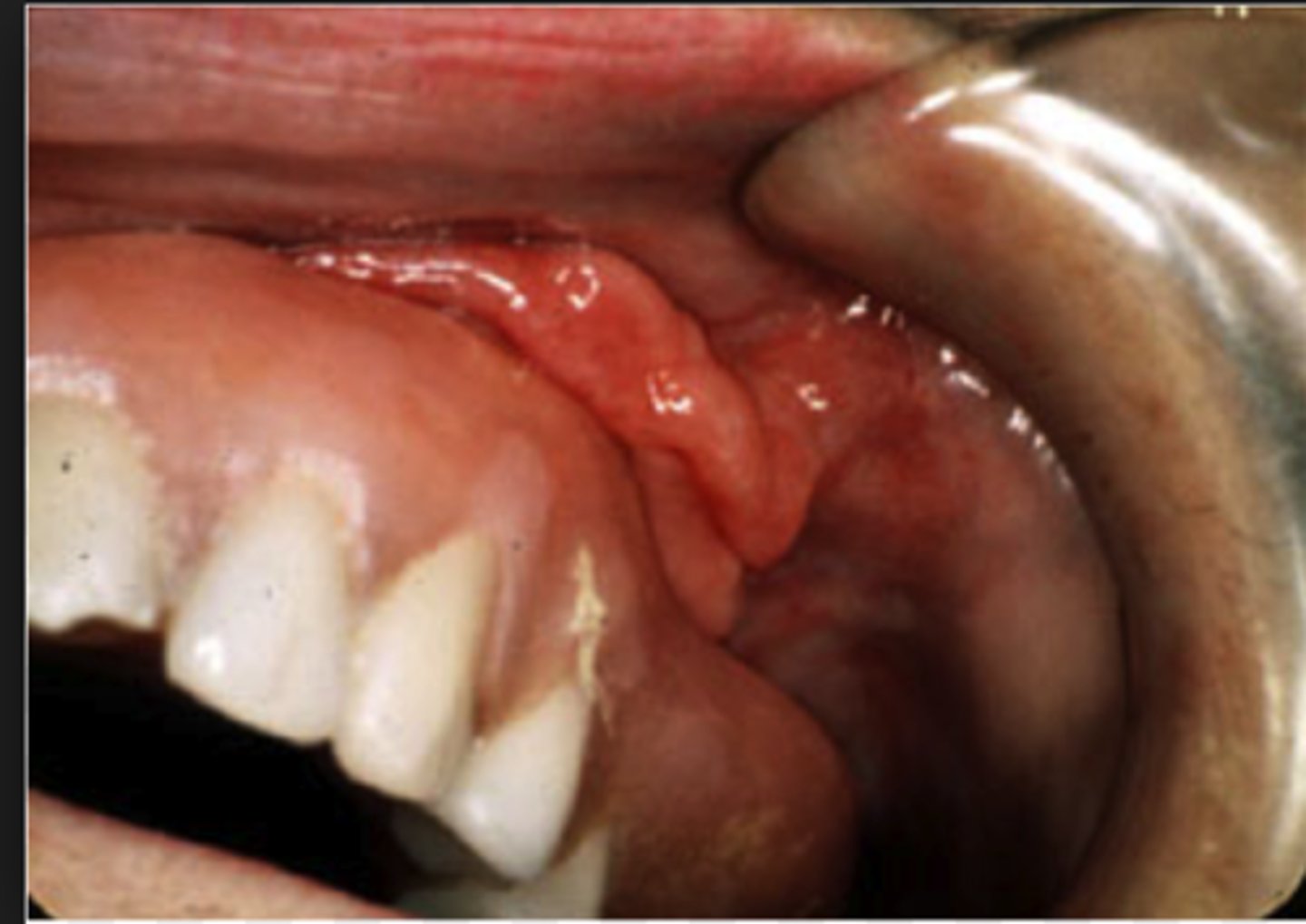
which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Reactive hyperplasia due to an
ill-fitting denture or alveolar
resorption
• Found in the vestibules
• Redundant folds
• Rubbery
• May be ulcerated
• Overgrowth of tissue along the
border of a denture
Epulis fissuratum
Epulis fissuratum
treatment for which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Excision (with histopathologic examination of the tissue)
• Remake or reline the denture
Epulis fissuratum
which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Reactive tissue growth related to:
-An ill-fitting denture
-Poor denture hygiene
-24-hour denture wearing
• Usually occurs on the hard
palate beneath a denture base
• Usually asymptomatic
• Mucosa is erythematous and has
a pebbly or papillary surface
Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia
treatment for which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Proper denture hygiene and
removal of dentures at night
• Fabrication of new dentures
• Excise excessive tissue if
necessary
Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia
Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia
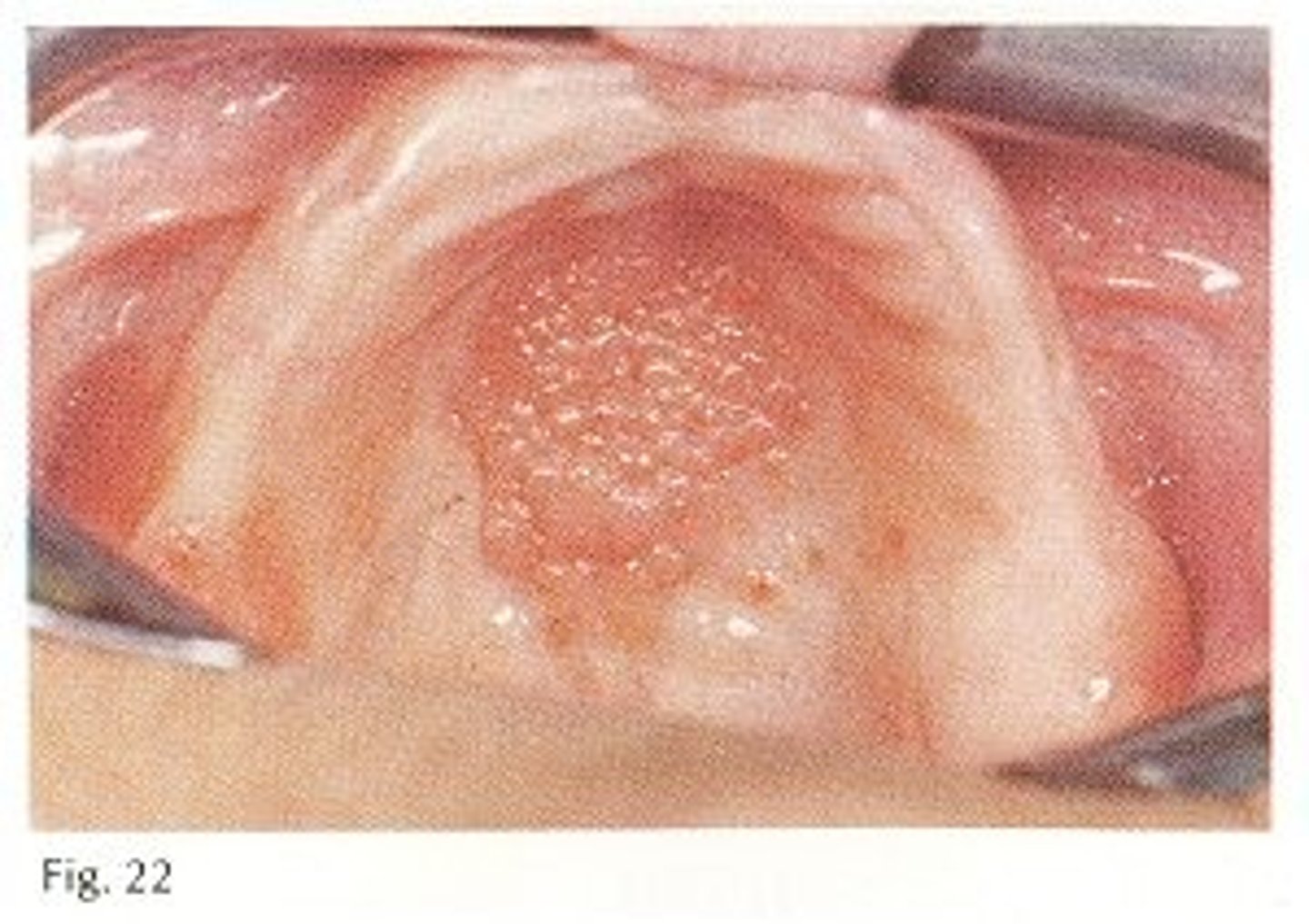
which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• May be hereditary
• May be medication related:
-Dilantin (Phenytoin)
-Cyclosporine
-Nifedipine
• Begins in the interdental
papillae
• Gingiva may cover the crowns
• Firm
gingival hyperplasia
treatment for which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Discontinuation of the offending medication
• Improved oral hygiene with frequent recall visits
• Gingivectomy
• Recurrence is common
gingival hyperplasia
gingival hyperplasia
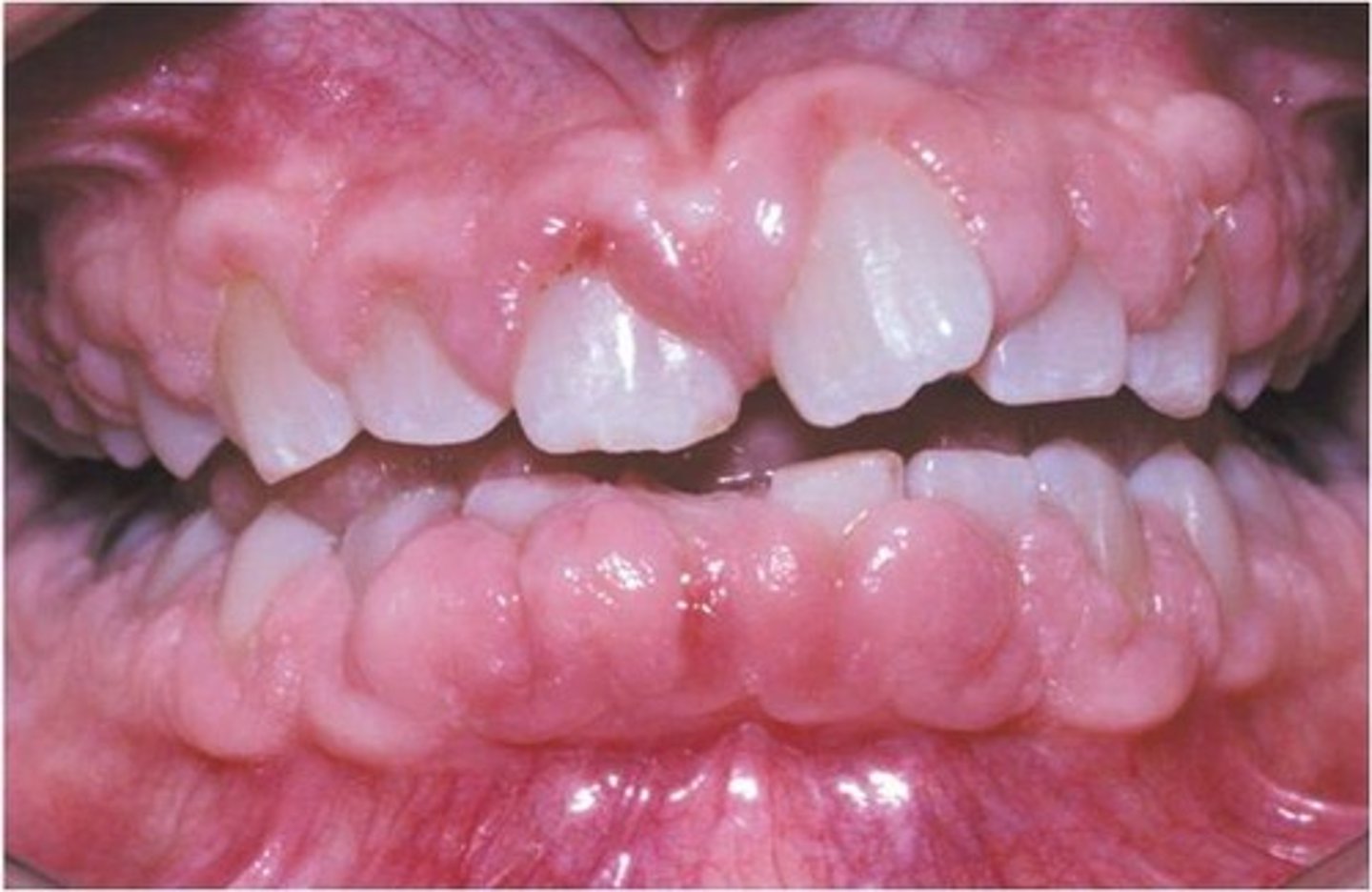
which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Common
• Cause: local irritation or trauma,
poor hygiene, or hormonal
factors
• 75% on the gingiva
• Sometimes called the
"pregnancy tumor"
• May grow rapidly
• Smooth or lobulated vascular
mass
pyogenic granuloma
treatment for which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Surgical excision with submission for histopathologic examination
• Excise to periosteum and scale adjacent teeth
• In pregnant patients defer treatment until after delivery when
possible (high recurrence rate)
pyogenic granuloma
which type of benign soft tissue histopathology:
• Ulcerated stratified squamous epithelium
• Vascularized fibrous connective tissue
• Mixed inflammatory infiltrate
pyogenic granuloma
pyogenic granuloma
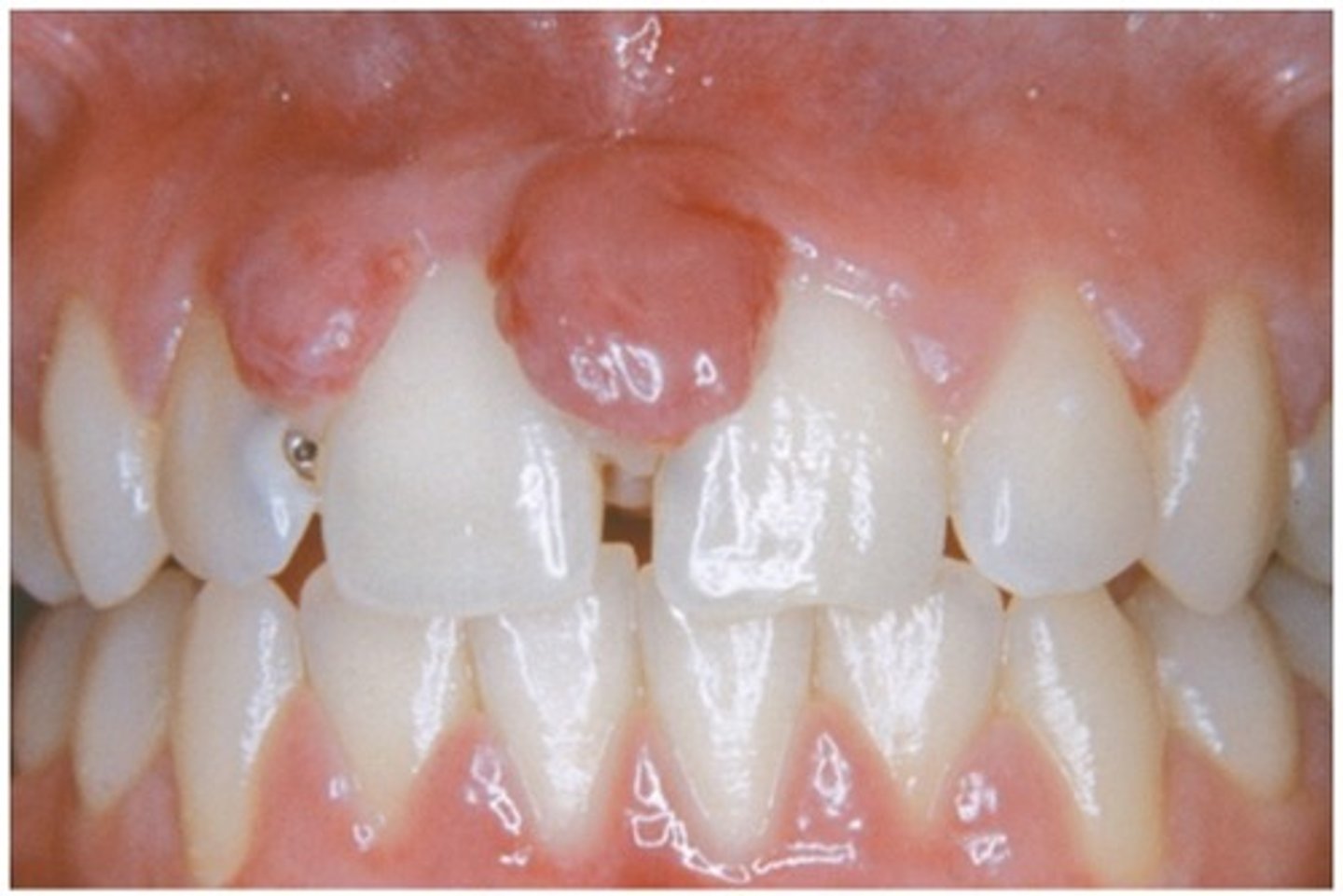
pyogenic granuloma histopathology
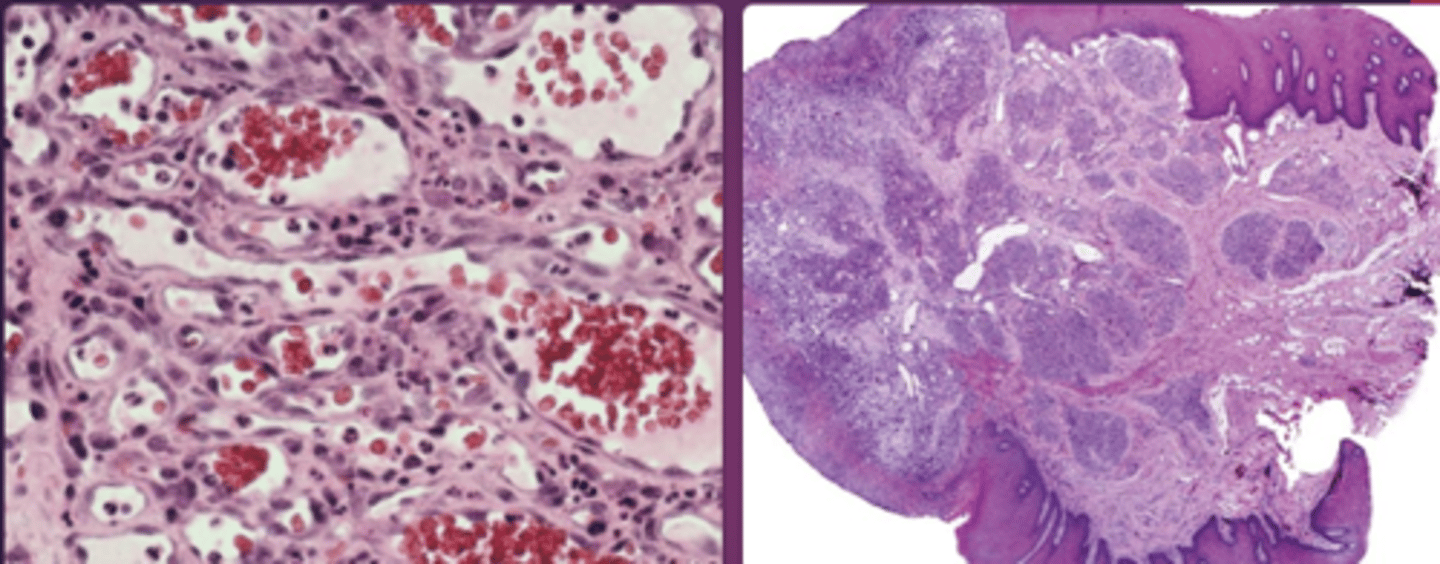
which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Common
• Reactive lesion caused by local
irritation or trauma
• Occurs exclusively on the gingiva
or edentulous alveolar ridge
• Red or red-blue nodular mass
• Frequently ulcerated
• "Cupping" resorption of the
underlying alveolar bone may be
noted
Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma
treatment for which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Local surgical excision down to the underlying bone with submission
of the specimen for histopathologic examination
• Adjacent teeth should be carefully scaled
Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma
Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma
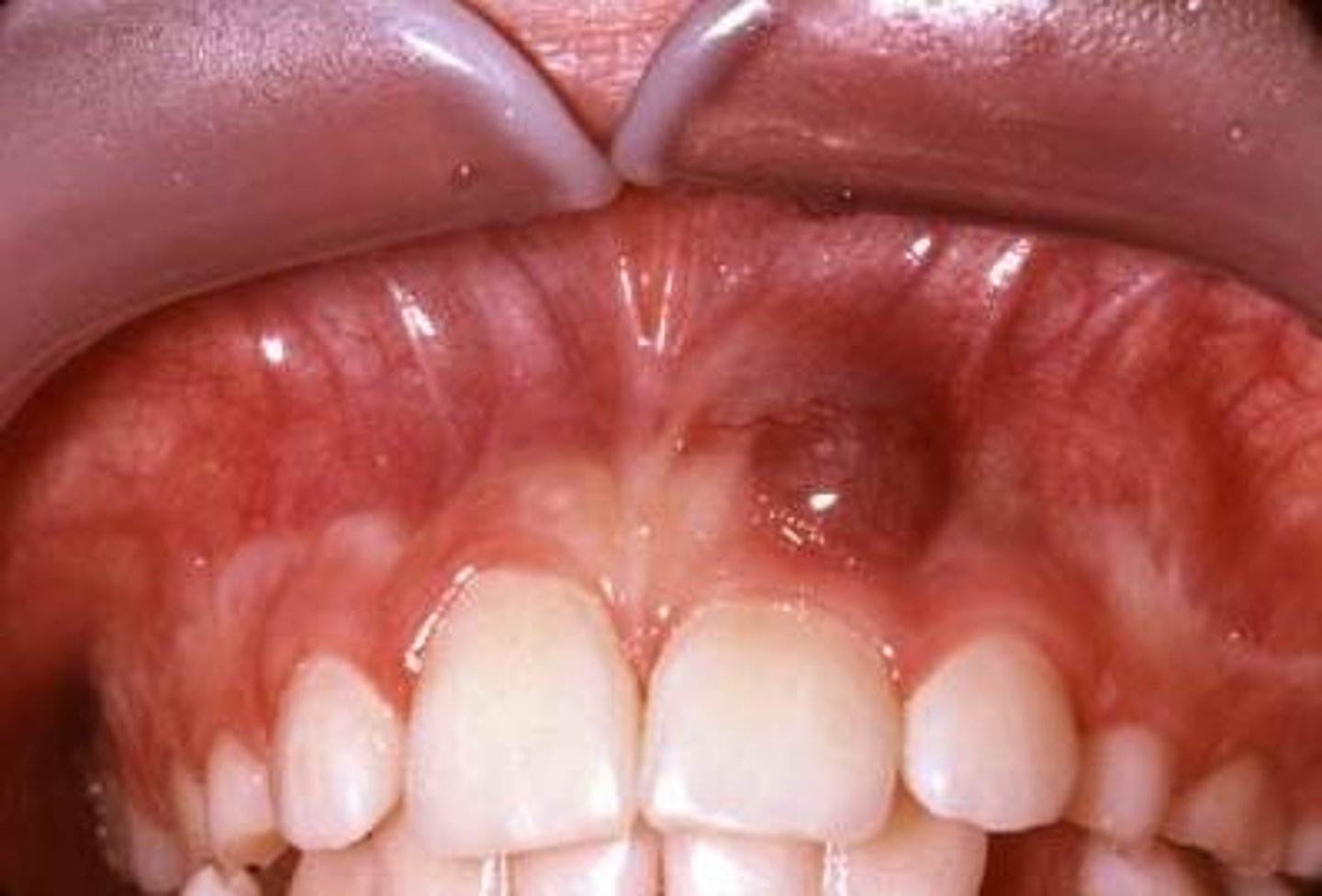
Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma histopathology
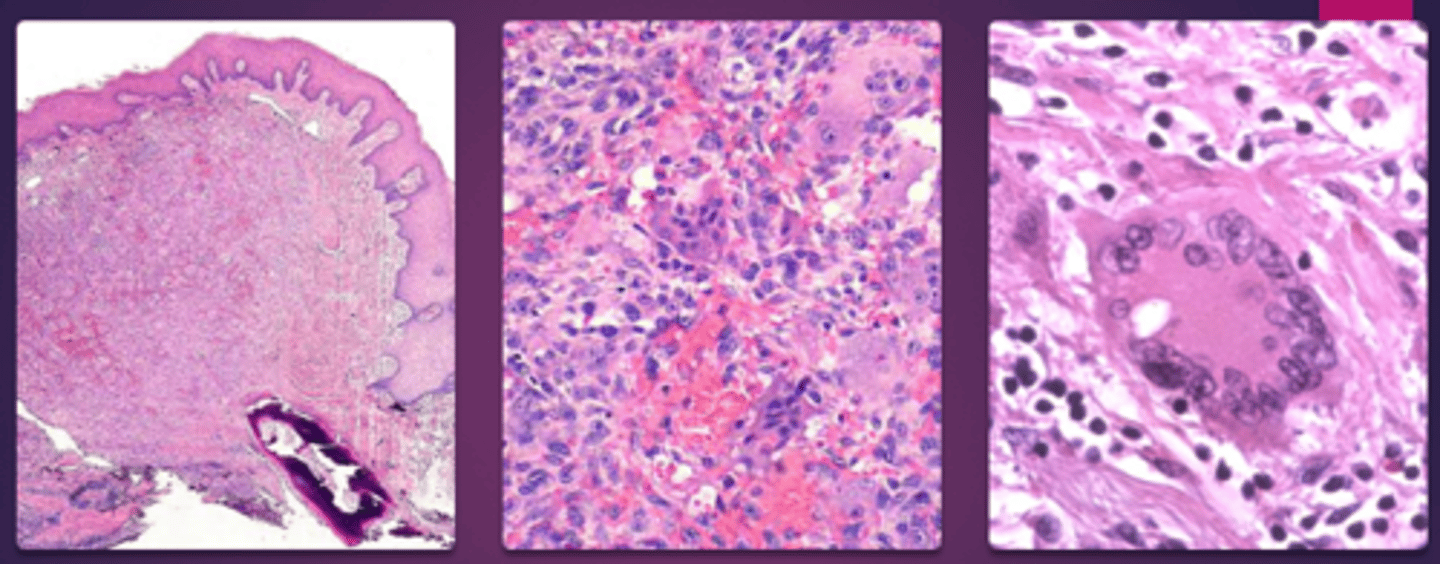
which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Common
• Reactive lesion caused by local
irritation or trauma
• Occurs exclusively on the gingiva
• Nodular mass
• Frequently ulcerated
• Red to pink
• Seen most commonly in teens
and young adults
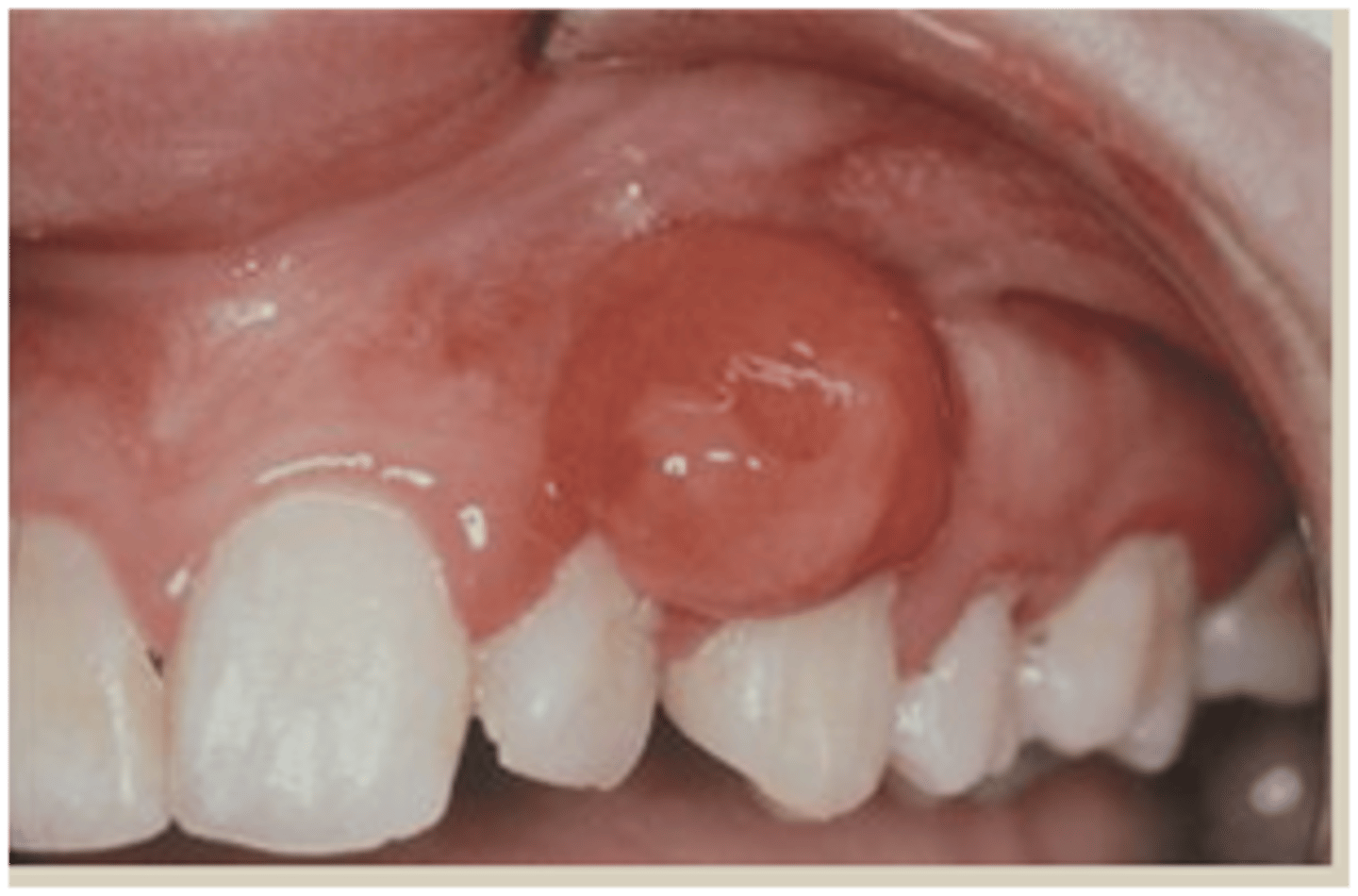
Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma
treatment for which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Local surgical excision down to periosteum with submission of the
specimen for histopathologic examination
• Adjacent teeth should be thoroughly scaled
Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma
Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma
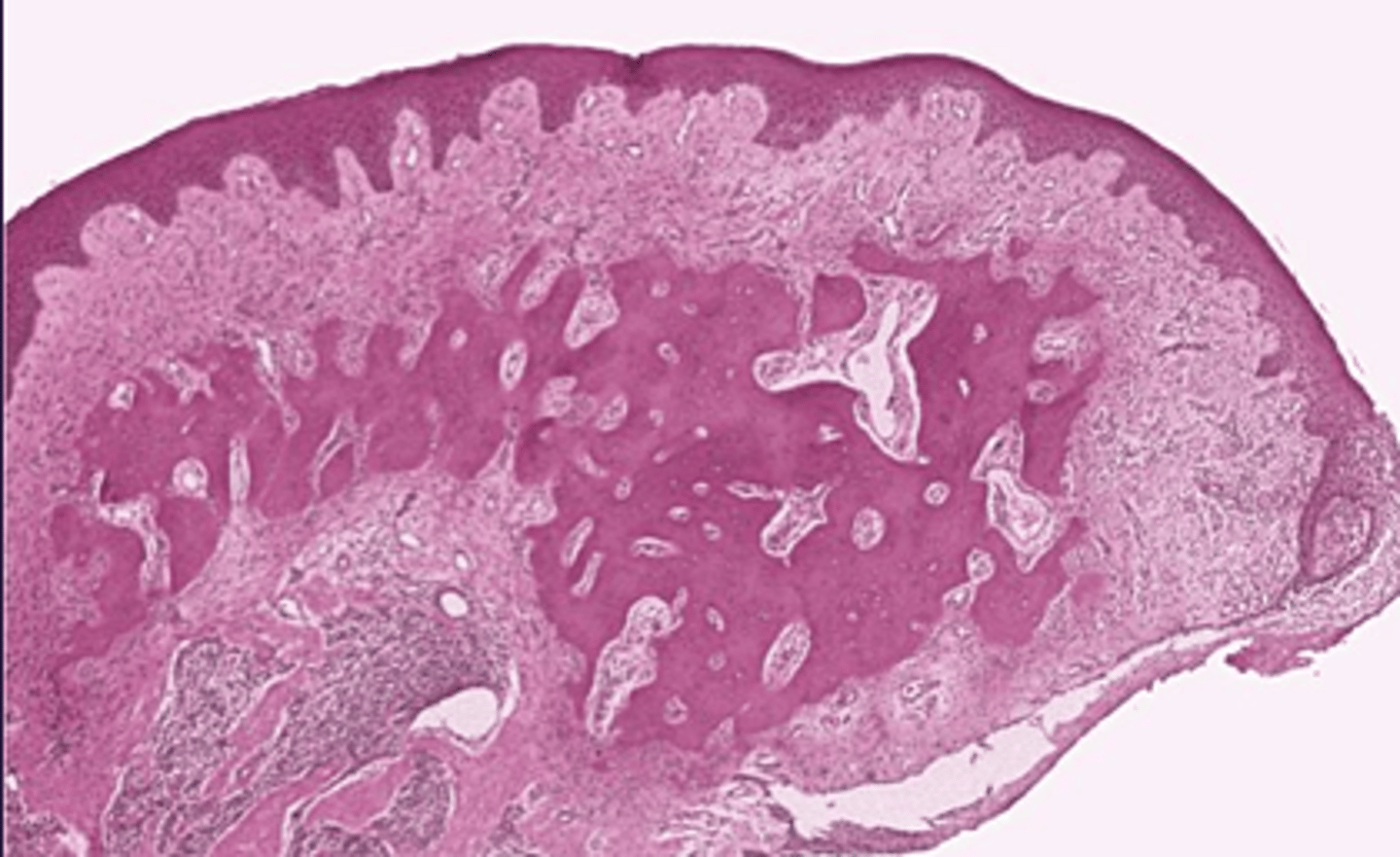
Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma histopathology
which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Fibrous tumor
• Unlike the traumatic fibroma, it
does not appear to be
associated with chronic irritation
• Common
• Asymptomatic
• The surface of the mass often
appears papillary
• More common in young patients
• Approximately 50% of all cases
occur on the gingiva
• Tongue and palate also are
common sites
giant cell fibroma
treatment for which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Conservative surgical excision with submission of tissue for
histopathologic examination
• Recurrence is rare
giant cell fibroma
giant cell fibroma
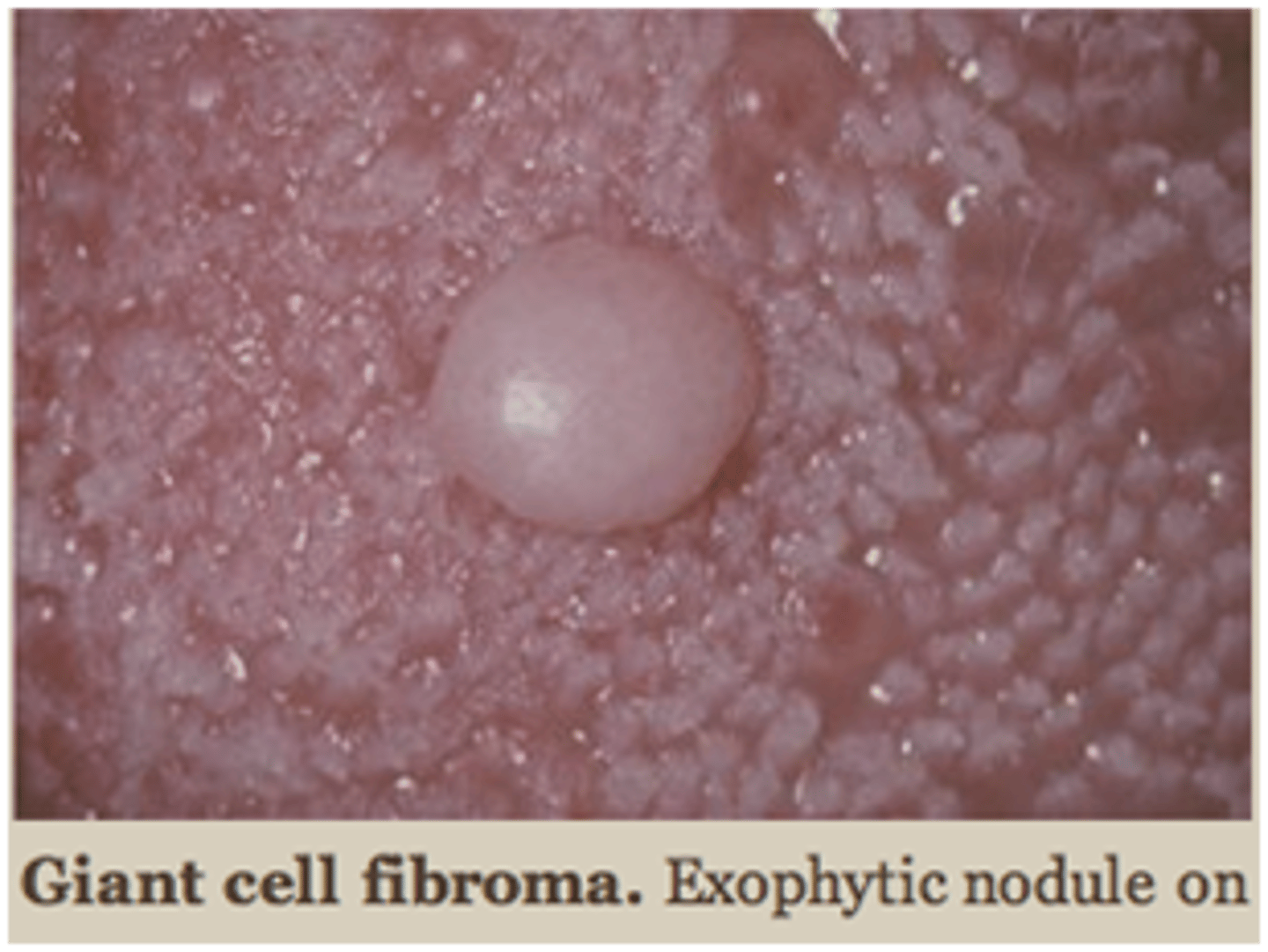
giant cell fibroma histopathology
which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Papillary-like growth
• Mandibular gingiva lingual to
canine
• Frequently bilateral
• 25-99% of children/YA
• Involutes with age
• Should be recognized clinically
as a normal anatomic variation
retrocuspic papilla
retrocuspic papilla
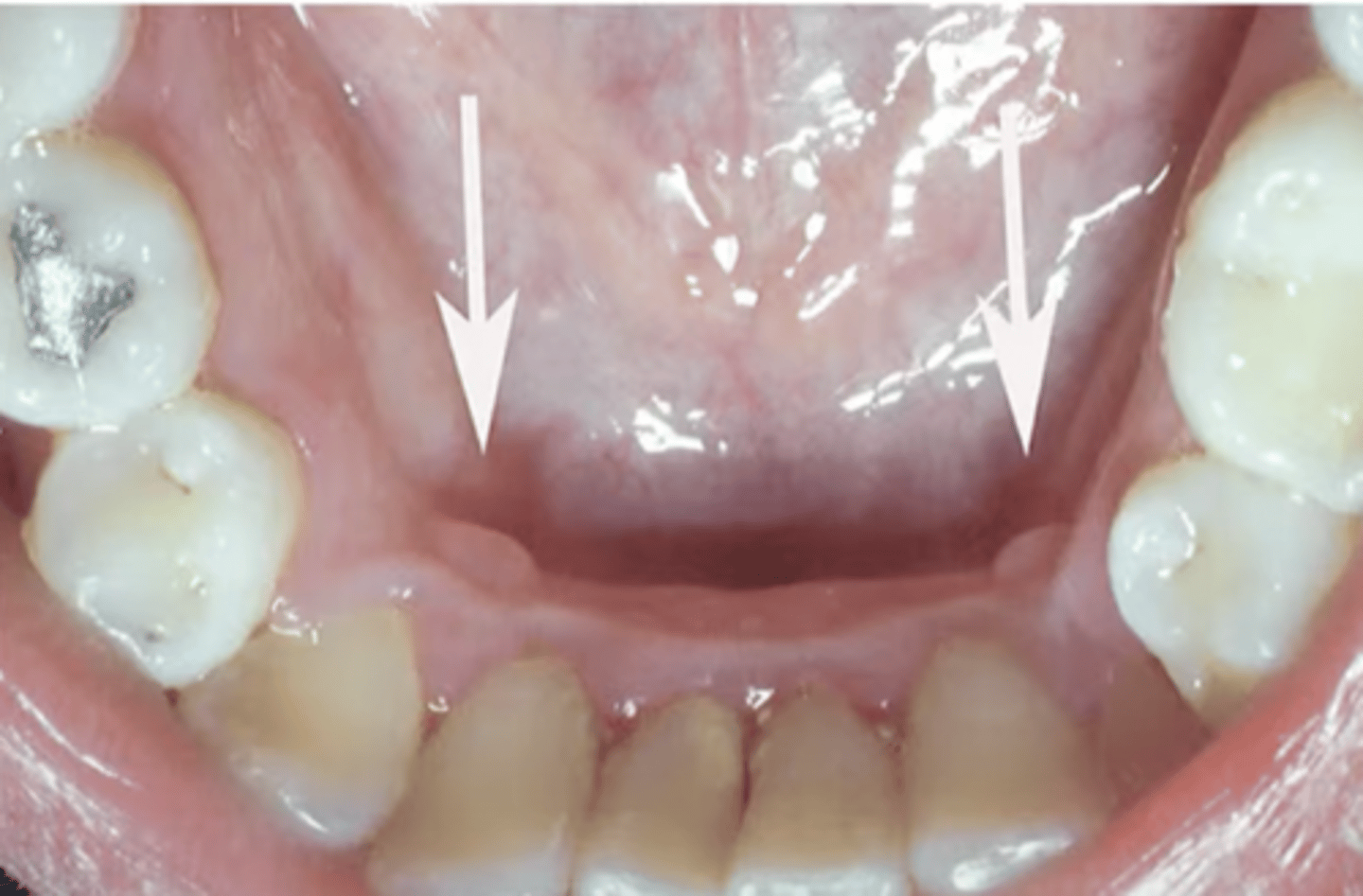
which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Uncommon
• Derived for Schwann cells
• Cytoplasm is granular because of
lysosomes
• Most commonly found on the
dorsal tongue
• Asymptomatic sessile nodule
• Pink to yellowish in color
granular cell tumor
treatment for which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Conservative local excision with
submission of tissue for
histopathologic examination
• Recurrence is rare
granular cell tumor
granular cell tumor
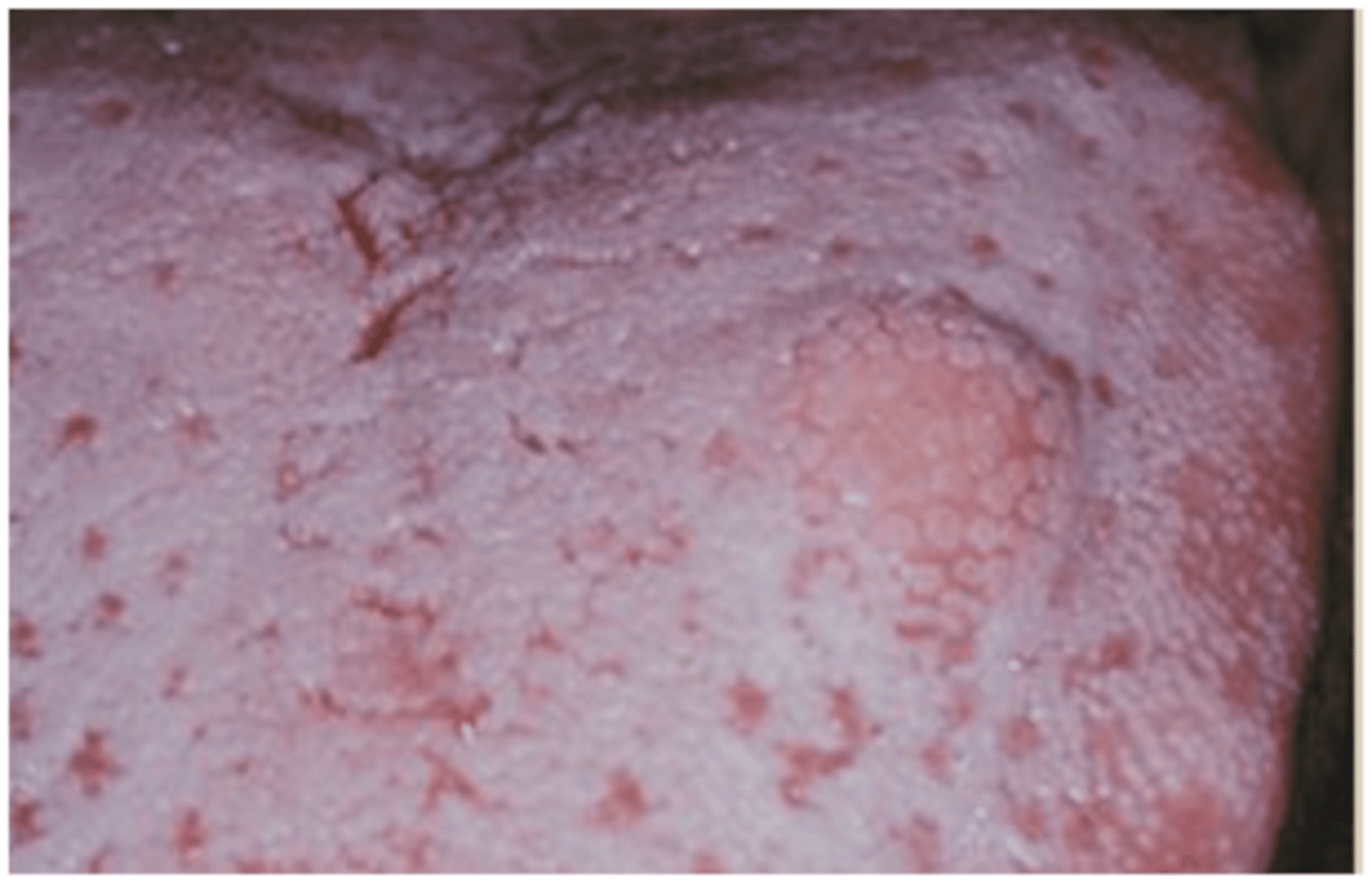
granular cell tumor histopathology
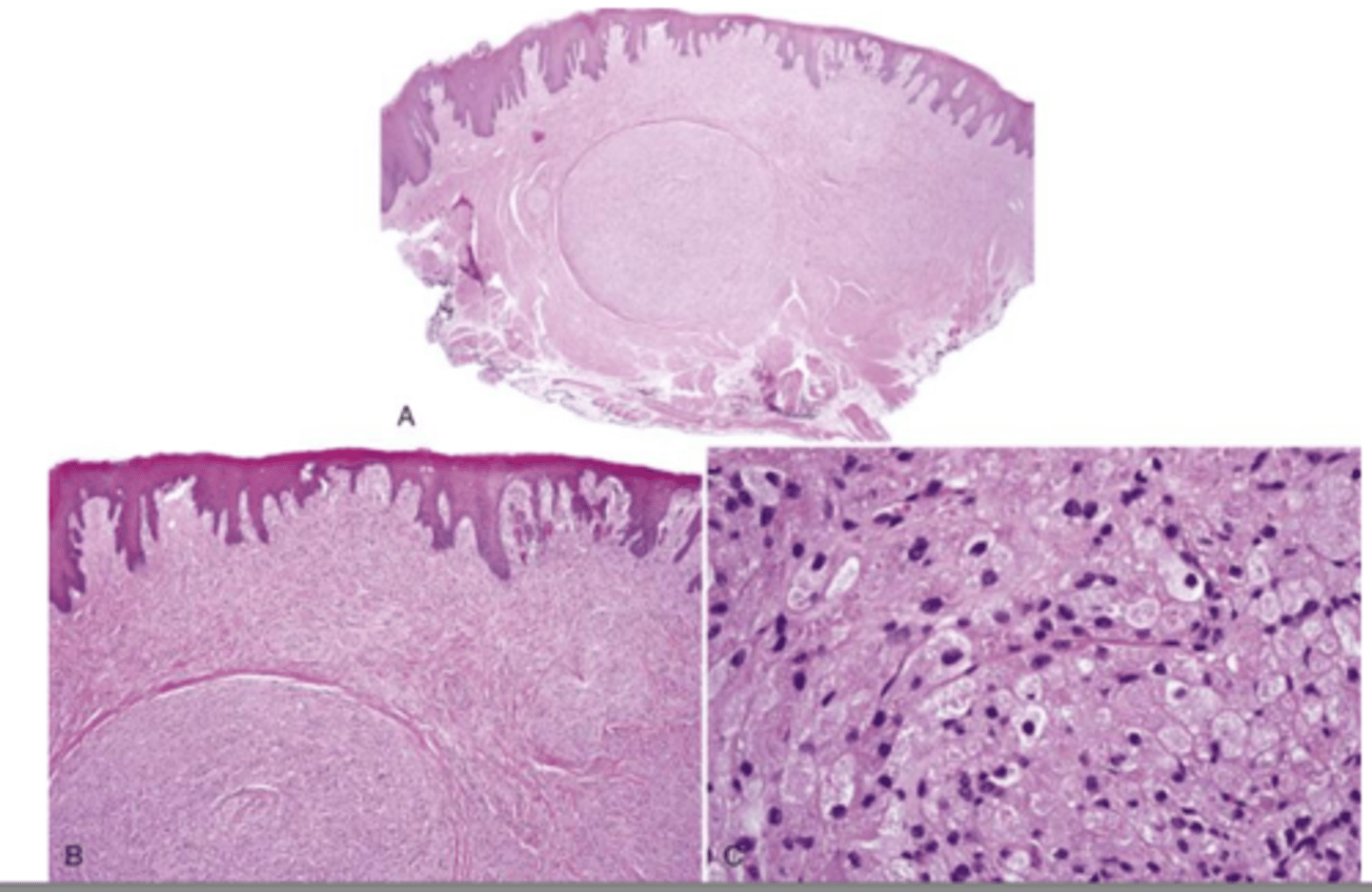
which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Uncommon
• Occurs almost exclusively on the
alveolar ridges of newborns
• Bears a microscopic
resemblance to the granular cell
tumor
• Pink-to-red, smooth-surfaced,
polypoid mass on the alveolar
ridge of a newborn
• More common on the maxilla
than the mandible
• 90% occur in females
Congenital epulis
treatment for which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Surgical excision with submission of tissue for histopathologic
examination
• No reports of recurrence, ever
Congenital epulis
Congenital epulis
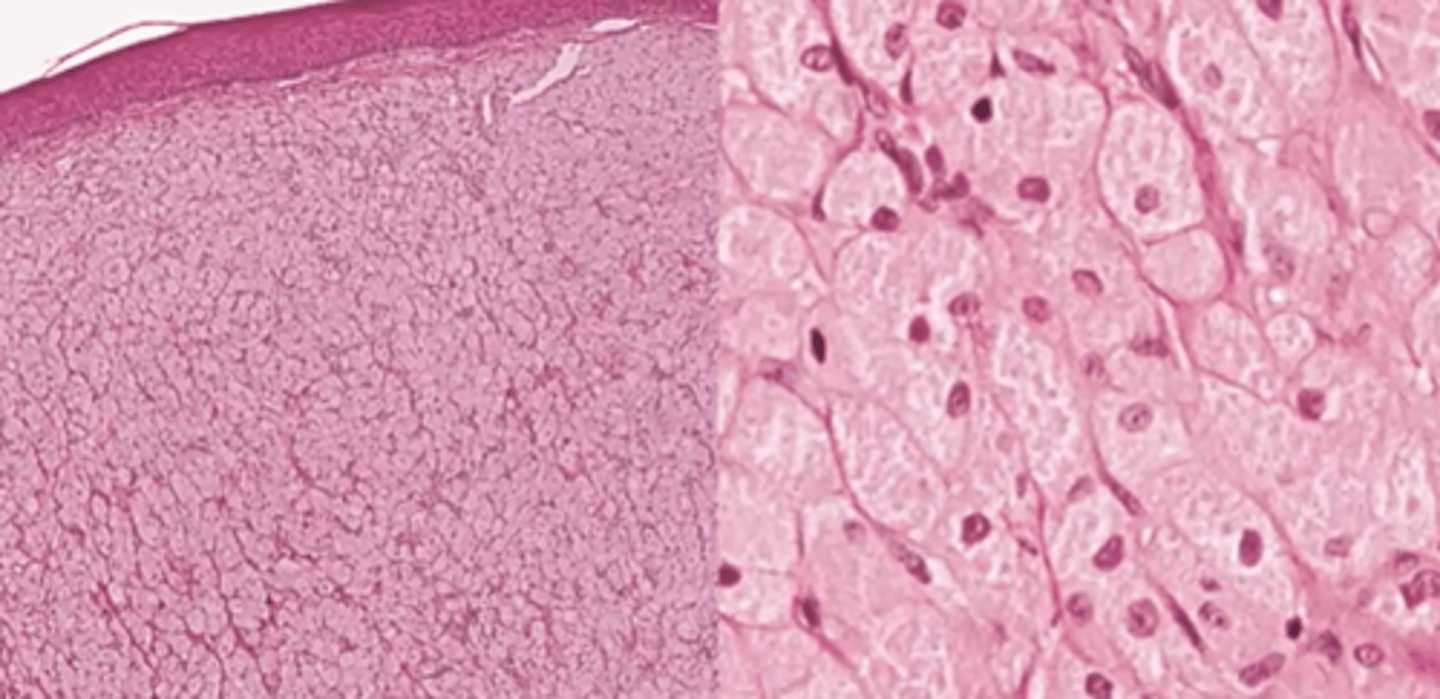
Congenital epulis histopathology
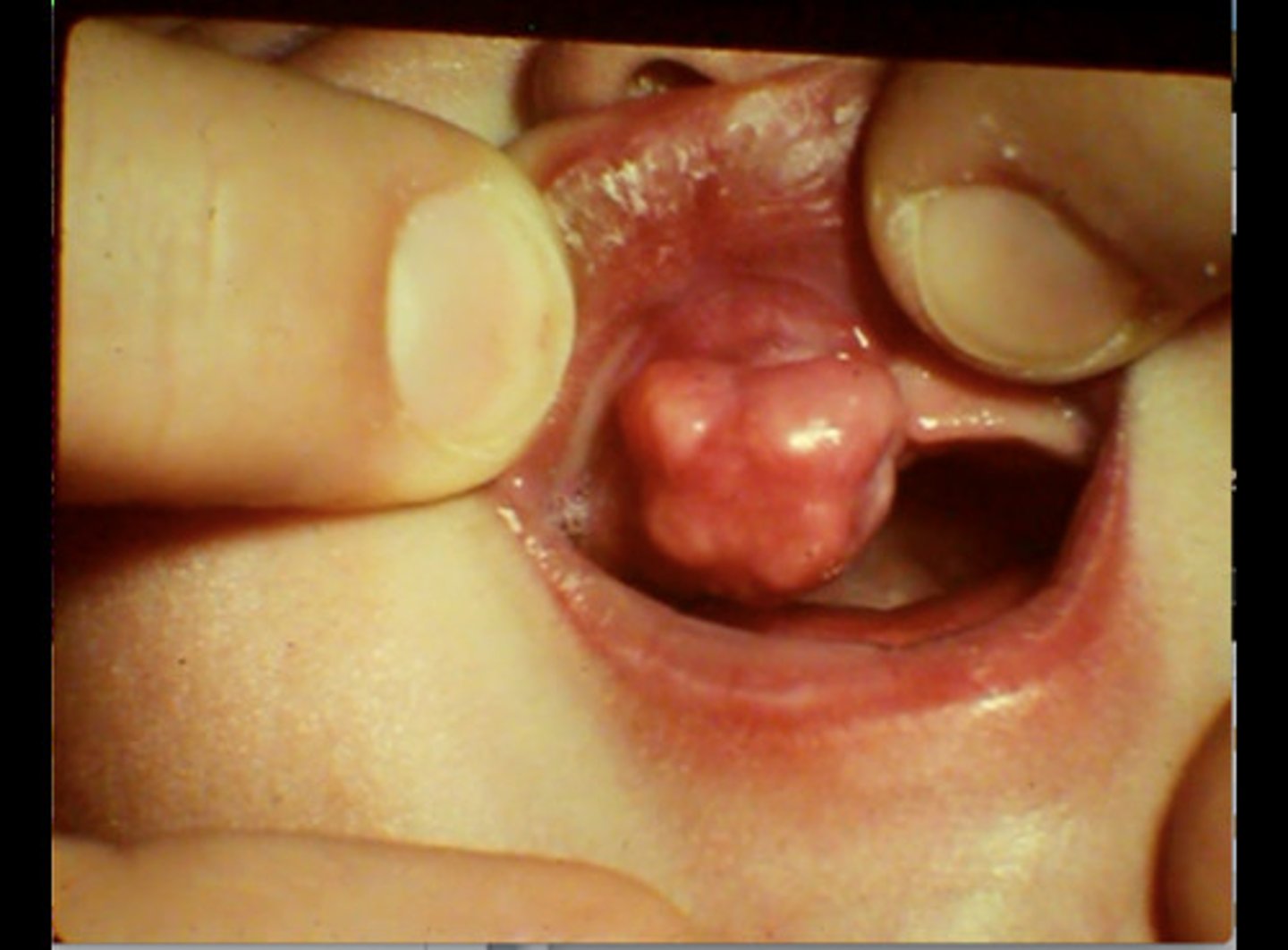
which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Benign tumor of fat
• 4% of mesenchymal tumors of
oral cavity
• Soft, doughy, smooth-surfaced
nodular
• Asymptomatic
• Pink to yellow in color
Lipoma
treatment for which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Conservative local excision with submission of tissue for
histopathologic examination
• Recurrence is rare
lipoma
lipoma
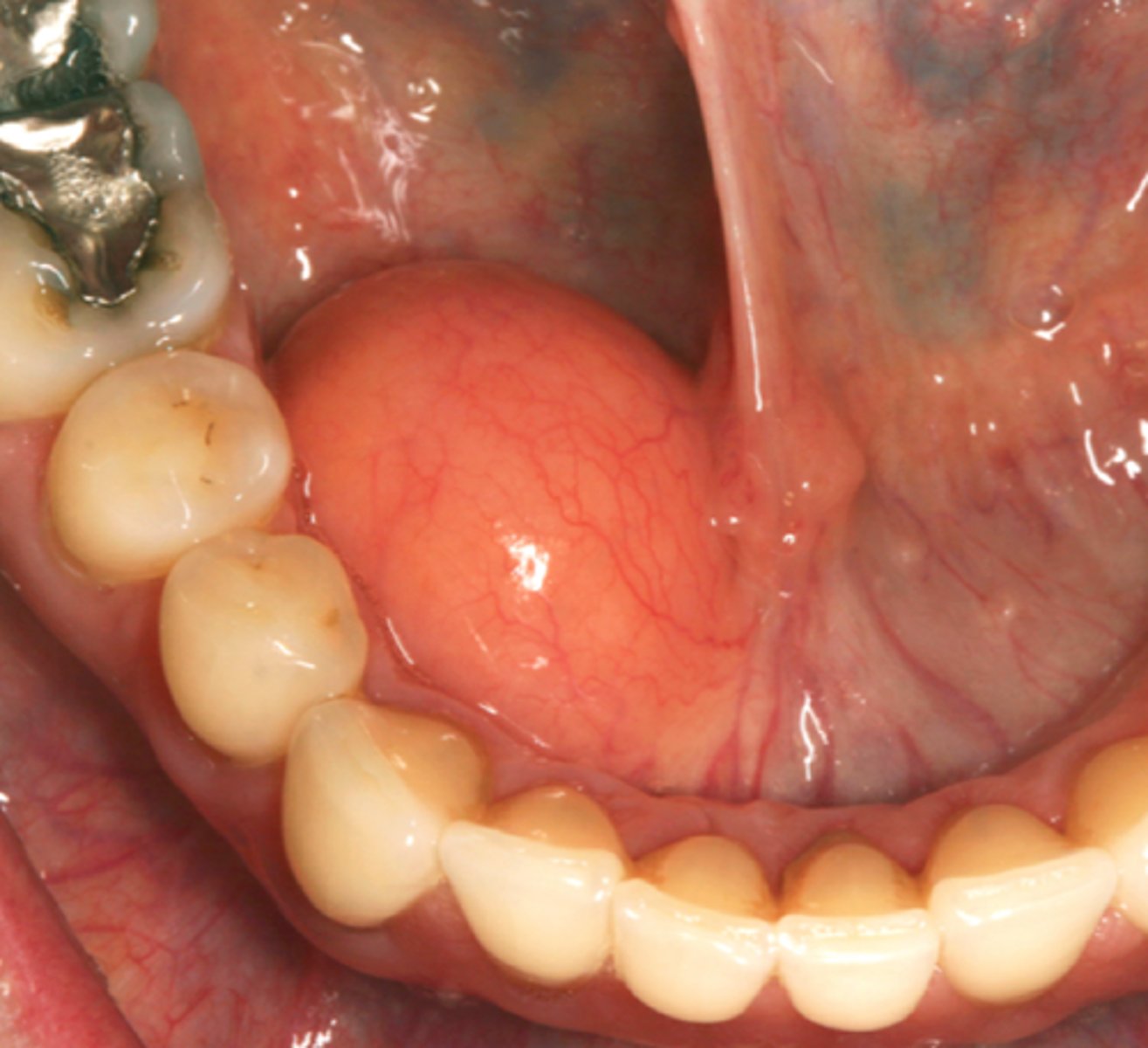
lipoma histopathology
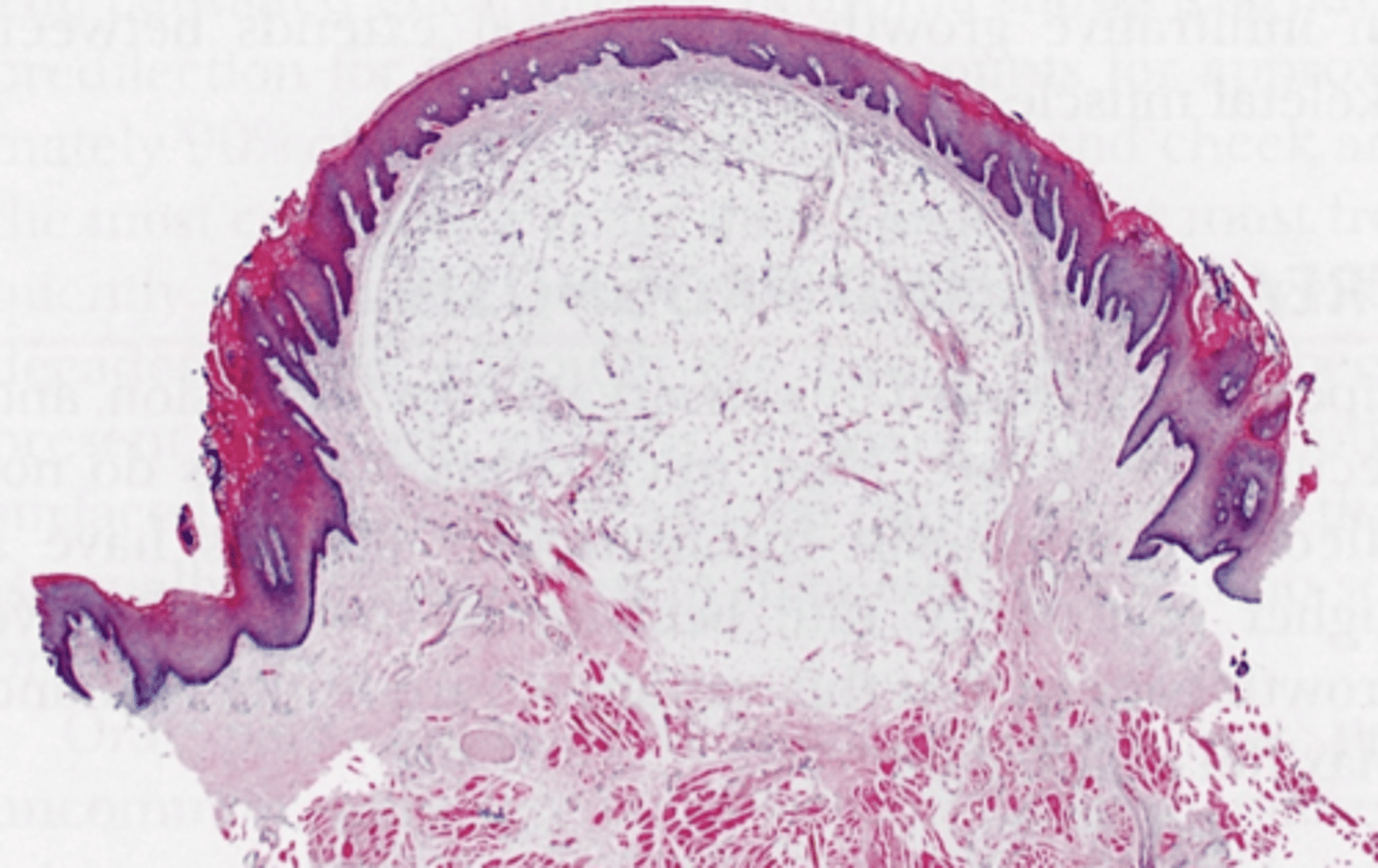
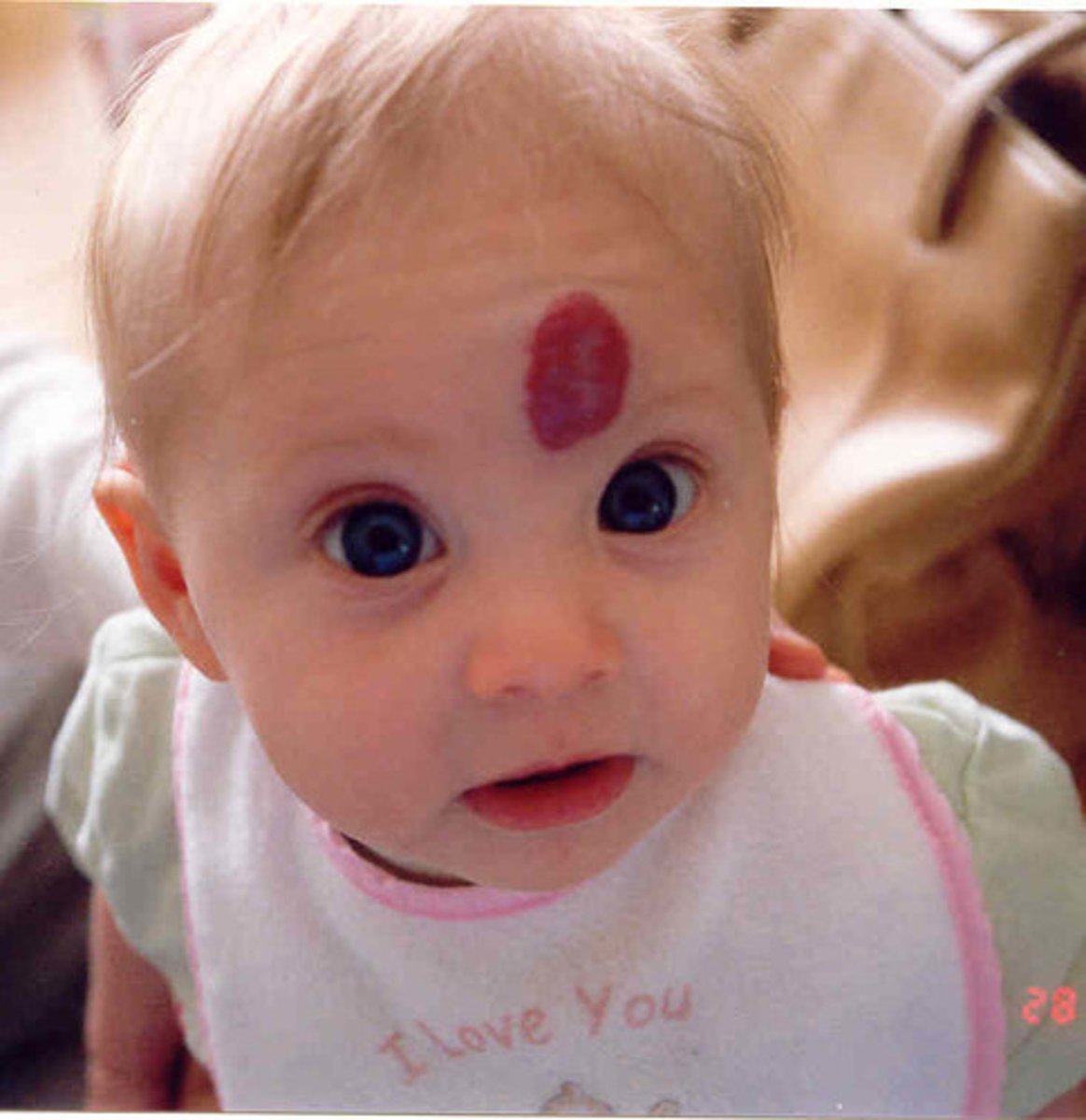
which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Congenital lesion
• Most common tumor of infancy
• Vascular proliferation
• Often red/blue
• Early rapid growth, followed by
slow involution
hemangioma
hemangioma
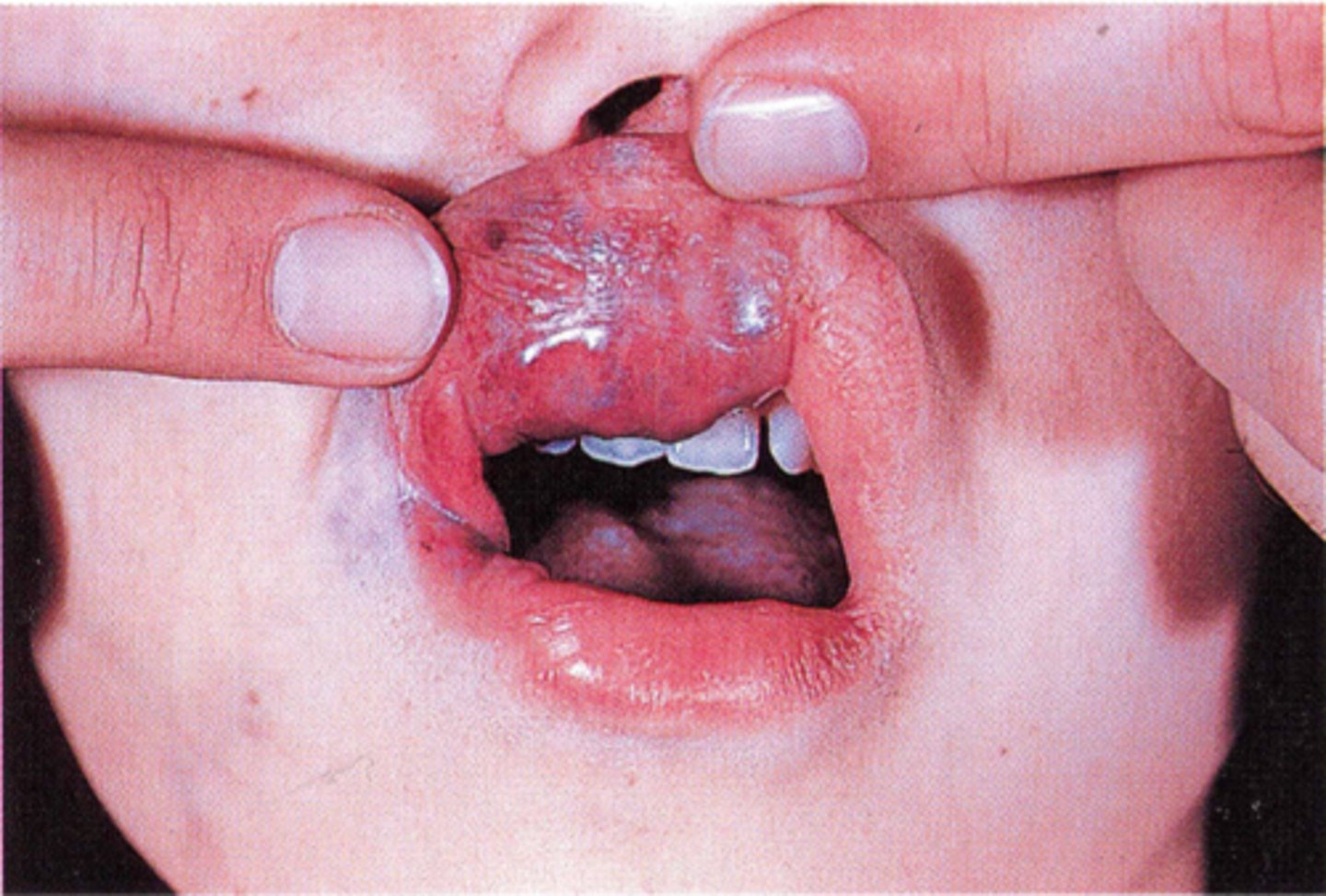
which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
◦ Most common sites in the head
and neck:
◦ Lips, tongue, buccal mucosa, or
palate
◦ Deep red or blue compressible
lesion
◦ Lesions can in the soft tissue or
central (intraosseous) in location
vascular malformation
vascular malformation
treatment for which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Can undergo spontaneous
remission
• Surgery
• Embolization
• Sclerosing agents
• Cryotherapy
• Laser
vascular malformation
which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Benign, hamartomatous
tumorlike growths of lymphatic
vessels
• Likely represent developmental
anomalies that arise from
sequestrations of lymphatic
tissue that do not communicate
normally with the rest of the
lymphatic system
• Predilection for the head and
neck
• Oral lymphatic malformations
are most frequent on the
anterior two thirds of the
tongue, where they often result
in macroglossia
• Demonstrates a pebbly surface
that resembles a cluster of
translucent vesicles
lymphangioma
treatment for which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Surgical excision
• Sclerotherapy
• May recur
lymphangioma
lymphangioma
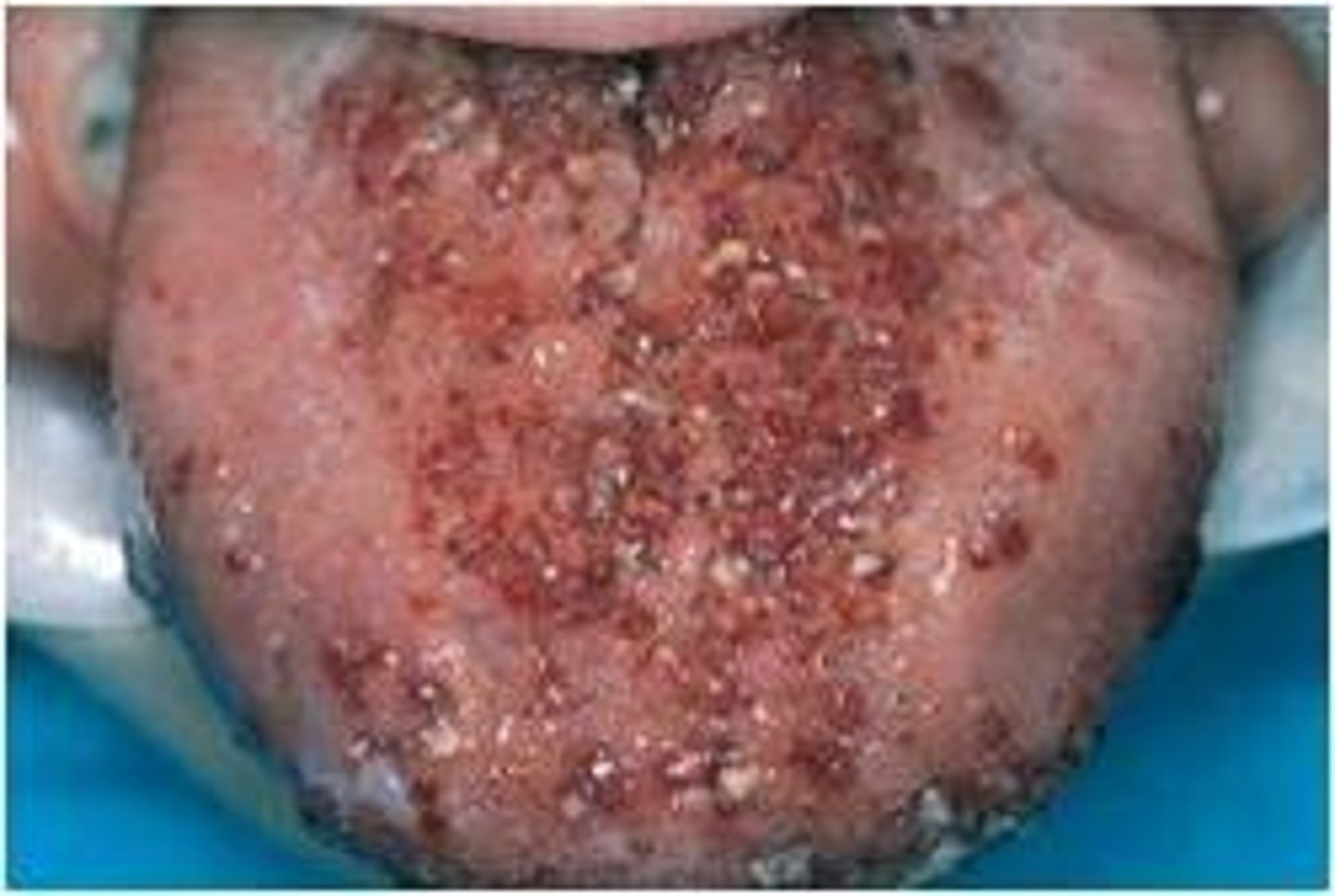
which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Most common peripheral nerve
neoplasm
• Can be a solitary tumor or be a
component of
neurofibromatosis*
• Slow-growing, soft, painless
lesions that vary in size from
small nodules to larger masses
• Can be in the soft tissue or
central (in bone)
neurofibroma
treatment for which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Surgical excision
neurofibroma (and schwannoma and traumatic neuroma)
neurofibroma
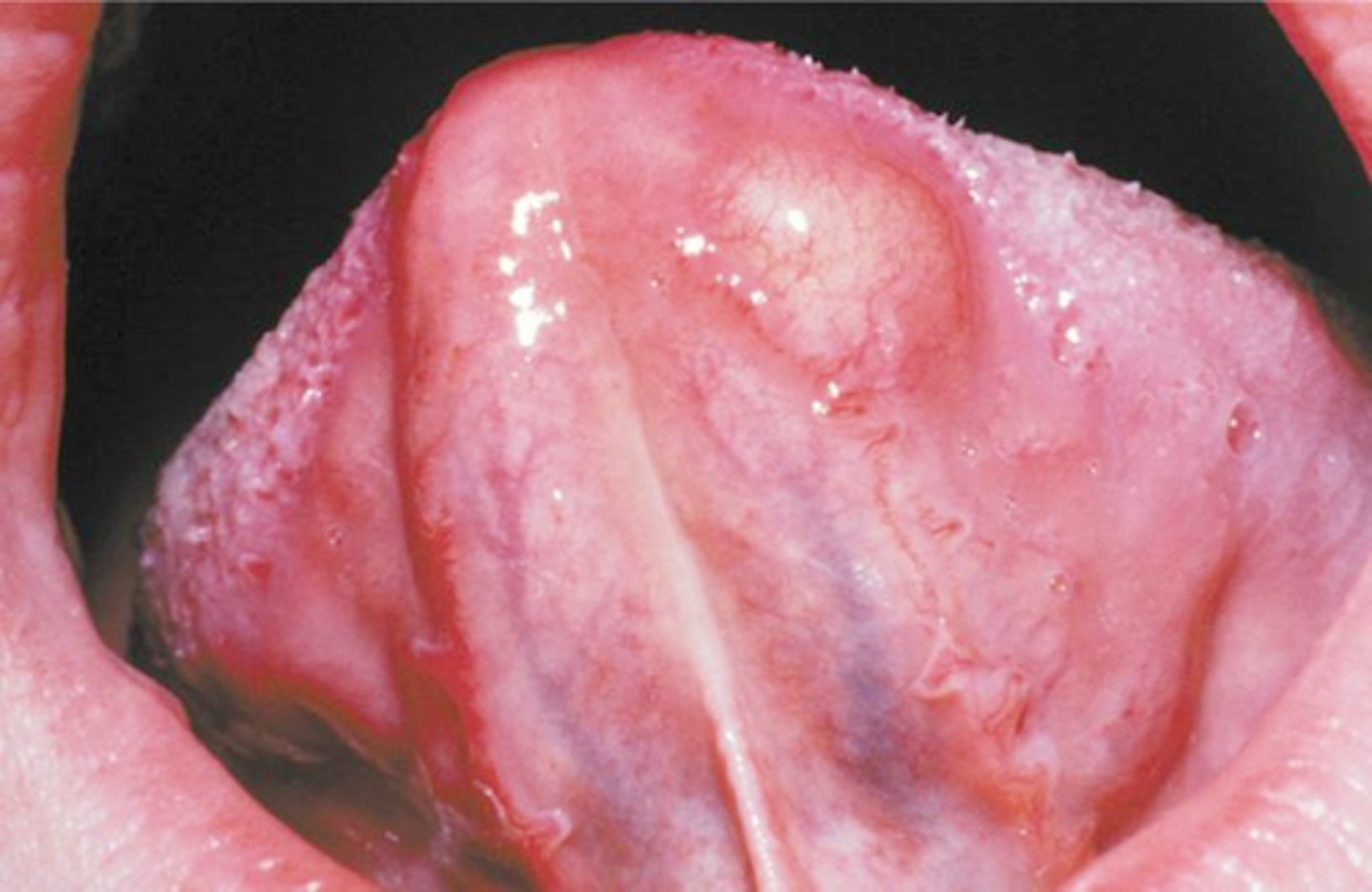
neurofibroma histopathology
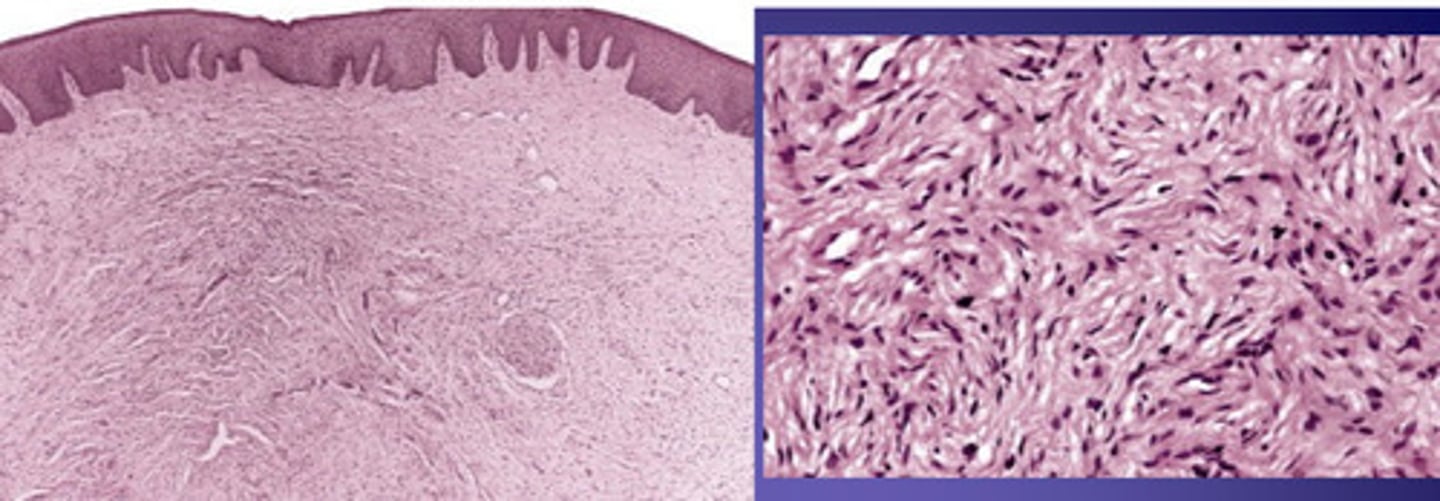
which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Common hereditary condition
• One of every 2,500-3,000 births
• Autosomal dominant trait
Neurofibromatosis Type I
Neurofibromatosis Type I
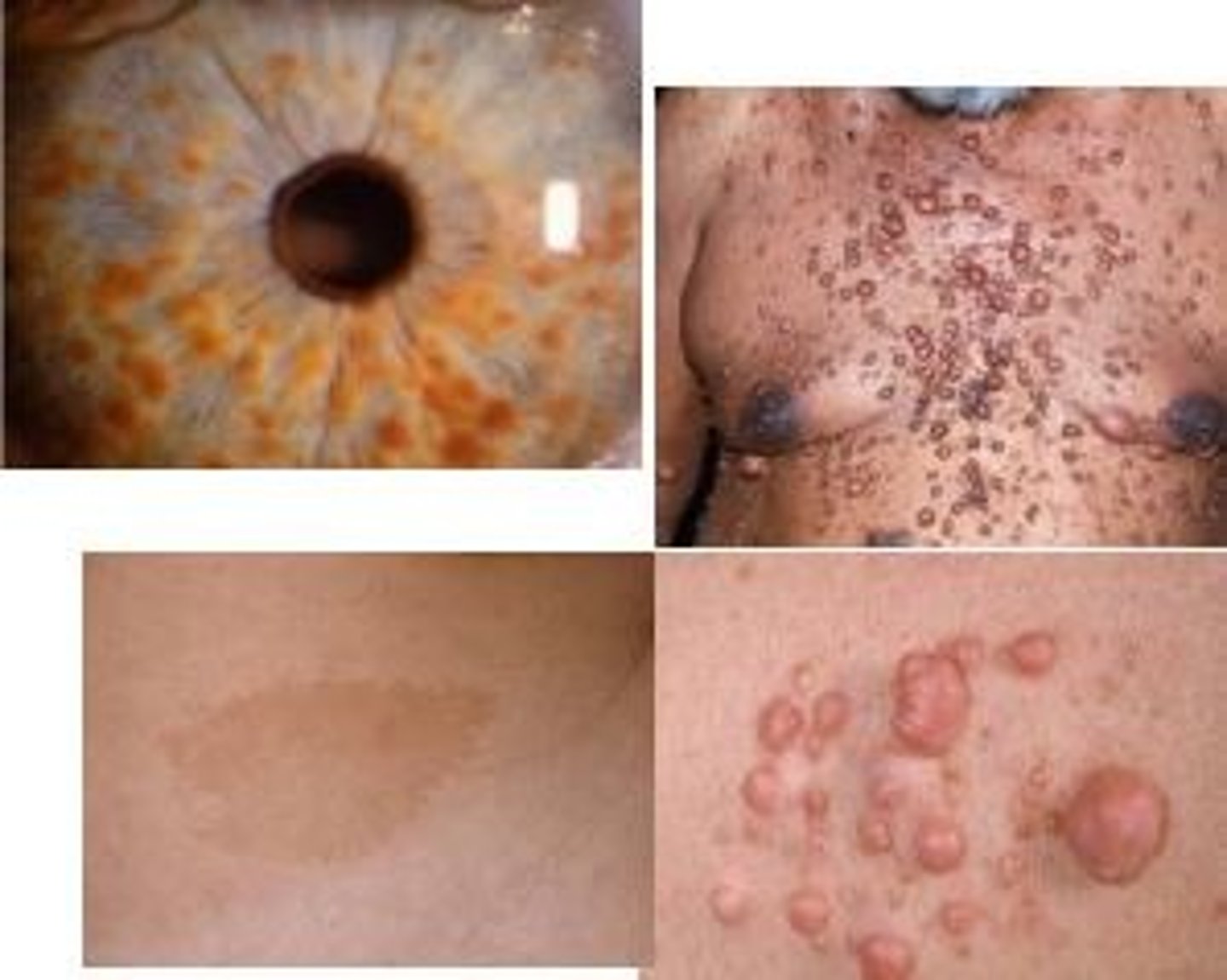
which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Benign neural neoplasm of
Schwann cell origin
• Uncommon
• Slow-growing, encapsulated
tumor that typically arises in
association with a nerve trunk
• Asymptomatic
• The tongue is the most common
location for oral schwannomas
• Can arise centrally
schwannoma
schwannoma
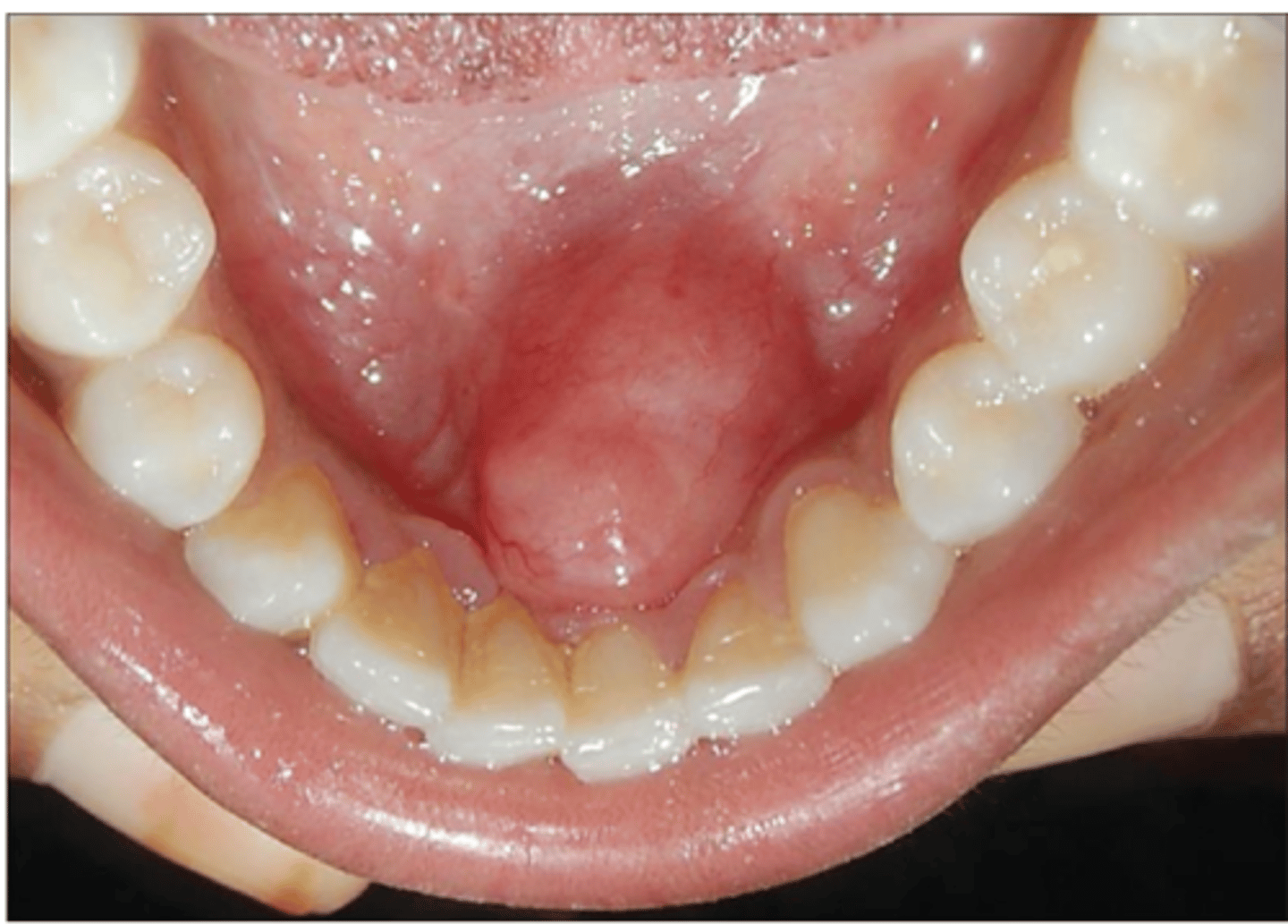
schwannoma histopathology
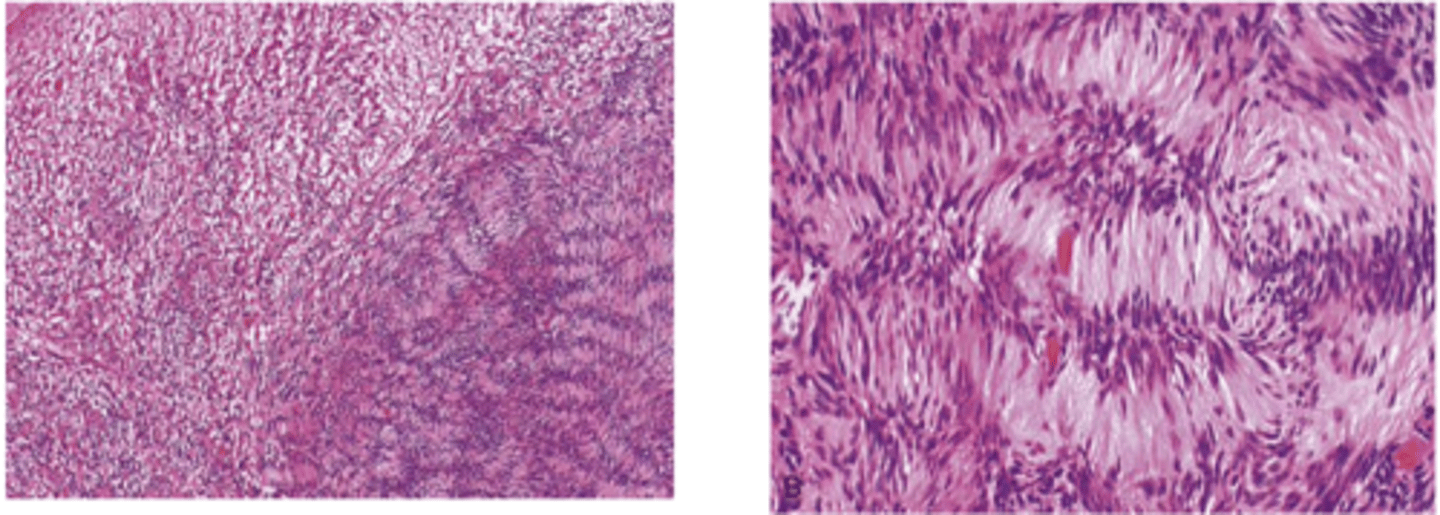
which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Reactive proliferation of neural
tissue after transection or other
damage of a nerve bundle
• Smooth-surfaced, nonulcerated
nodules
• Most common in the mental
foramen area, tongue, and lower
lip
• A history of trauma often can be
elicited
• May be intraosseous
• About 1/3 are painful
traumatic neuroma
traumatic neuroma
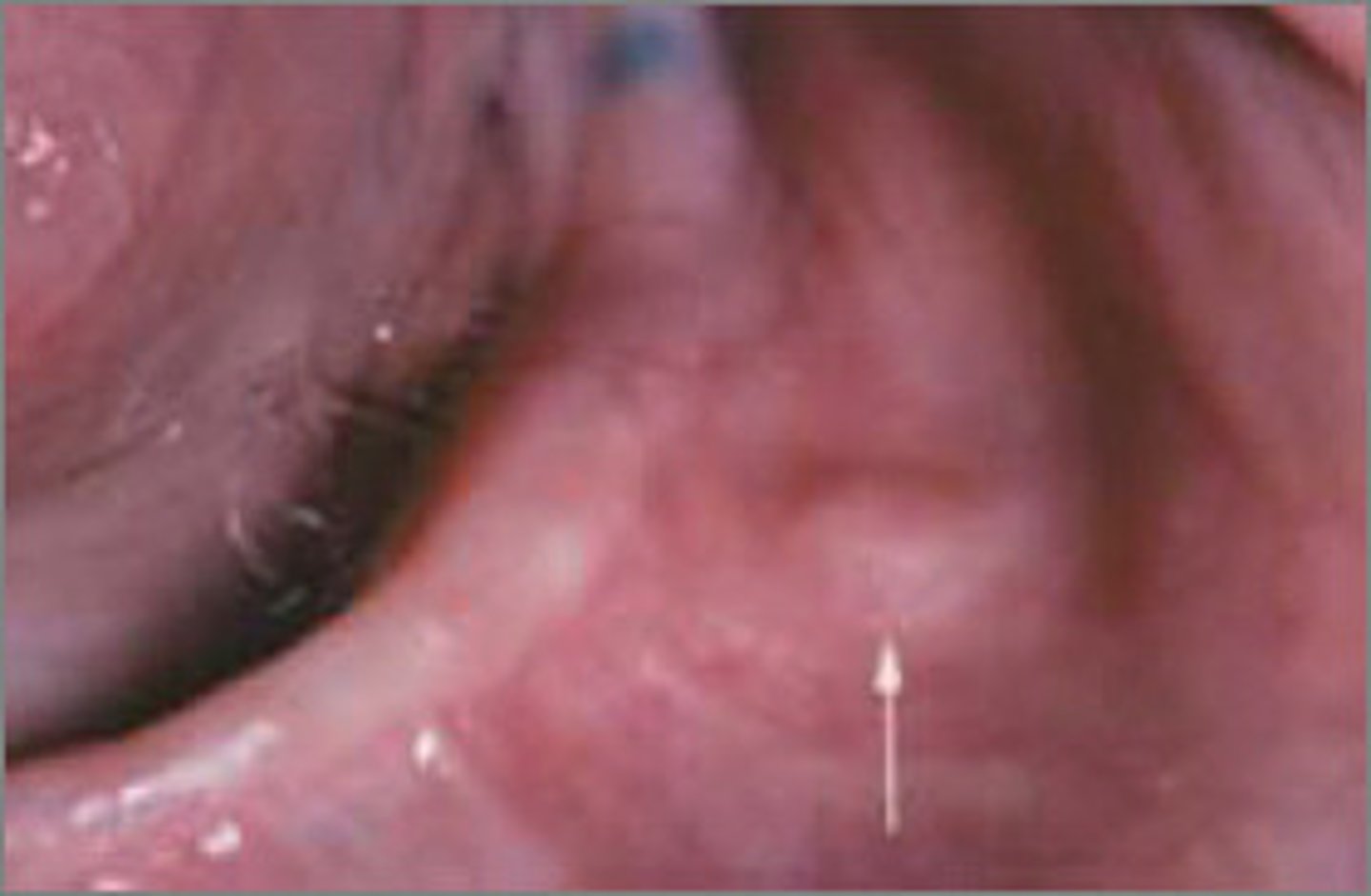
which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Benign neural lesion
• Associated with Multiple
Endocrine Neoplasia type 2B
(MEN2B)*
• Soft, painless papules or nodules
Locations:
-Lips, anterior tongue
-BM, gingiva, palate
mucosal neuroma
mucosal neuroma
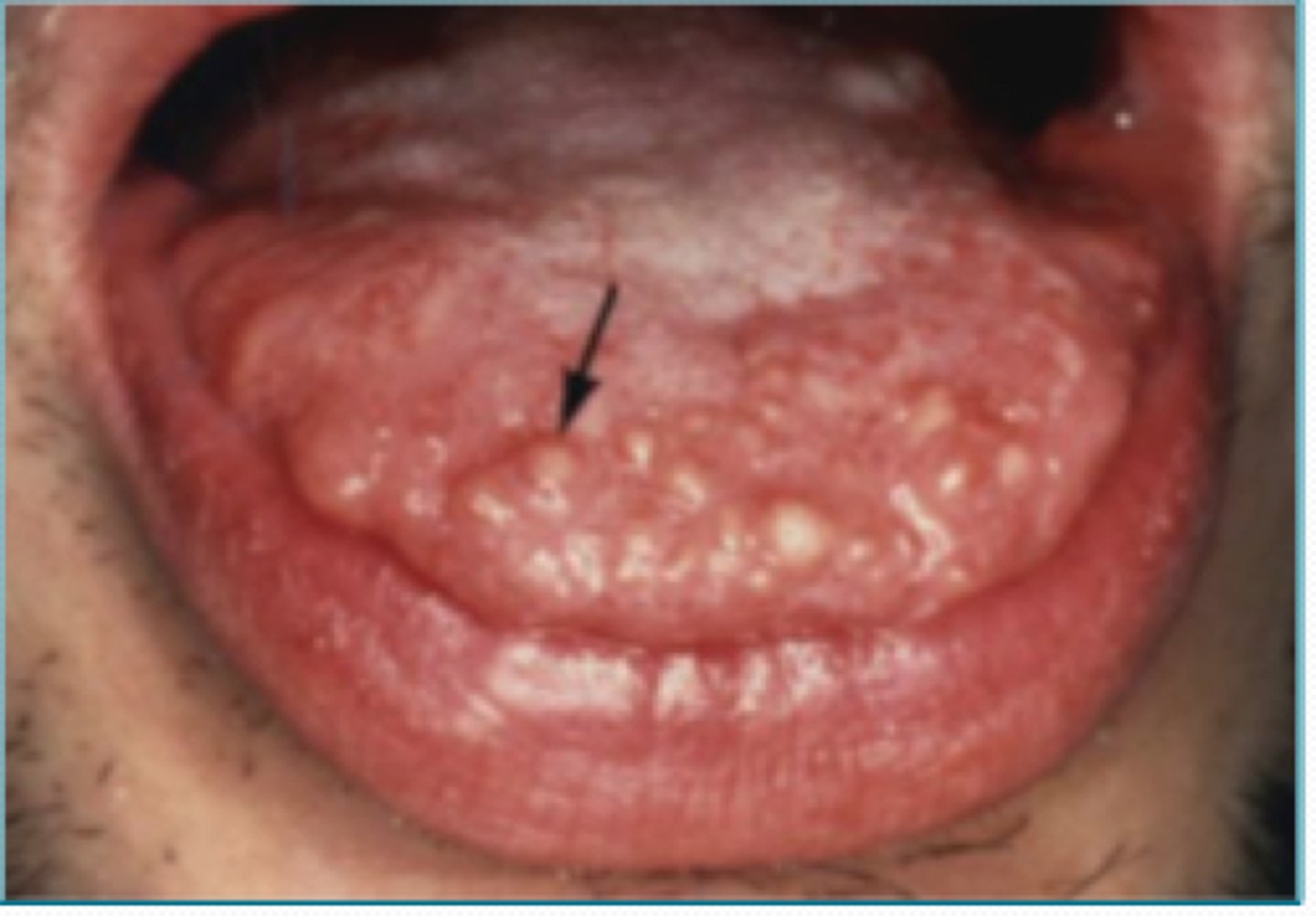
treatment for which type of benign soft tissue pathology:
• Surgical excision
• Multiple lesions should be evaluated for MEN 2B
mucosal neuroma