Evolutionary and Behavioural Ecology
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Evolution
Evolution is change: changes in traits (or allele frequency) over time. Is driven by natural selection.
Natural selection
The mechanism that drives adaptive evolution. Evolution by natural selection results in adaptations to the ancestors' environment. Not random.
Famous example:
Peppered moth (Biston betularia) in England during the industrial revolution.
Mutations
Mechanism that drives evolution. Can be a positive or negative change in the genetic composition of an individual. Occurs randomly.
Variation
Differences in traits among individuals. Variation arises through random mutations or from natural selection.
Heritability
A measure of how well differences in people's genes account for differences in their traits. Offspring inherit many traits from their parents.
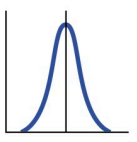
Directional selection
A single phenotype is favoured, causing the allele frequency to shift in one direction.
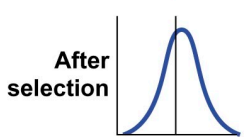
Stabilizing selection
Genetic diversity decrease as the population stabilizes on a particular trait value.
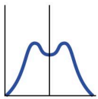
Disruptive selection
Extreme values for a trait are favoured over intermediate values.
Counter gradient variation
The environment conceals genetic variation.
Ex. tadpoles in northern vs. southern Scandinavia.
Ecomorphs
Genotypes that correspond differently to certain climates.
Allopatric speciation
Speciation by division of a natural barrier. Occurs from geographical isolation.
Sympatric speciation
Speciation happening in the same area. Occurs in the same geographical area.
Character displacement
Natural selection favors a divergence in the characters when two similar species inhabit the same environment.
Genetic drift
The change in the frequency of an existing gene variant (allele).
Phenotypic plasticity
A single genotype alters its phenotype in response to environmental conditions.
Fitness
Contribution of an individual to future generations. Individuals have higher fitness if they leave more descendants.
Fitness benefits are maximized when…
… the difference between costs and benefits are the largest.
Coevolution
Occurs when two or more species mutually affect each other's evolution through the process of natural selection.
Gametic selection
Important form of selection but rarely in the context of ecological interactions. Occurs at the gametic level (haploid stage).
Kin selection
As relatives share genes, natural selection favors alleles that benefit close relatives. Important in evolution of social organization and co-operation.
Inclusive fitness
Individual selection and kin selection together determine an individual’s inclusive fitness, which is the sum of direct fitness and indirect fitness.
Altrusitic
A trait (often behaviour) which is beneficial to the recipient but costly to the donor.
Group selection
Occurs at the level of (isolated) groups of organisms. For example altruistic behavior for the good of the species or the group.
Monophage
Consumer of only one type of food. Specialists.
Oligophage
Consumer of a limited variety of food. Specialists.
Polyphage
Consumers of a high variety of food. Generalists.
h
“Handling time” - ex. time it takes for a predator to handle its prey.
s
“Search time” - ex. time it takes for a predator to search for its prey.
h < s
Predators with long search time should be generalists because it takes relatively short time to handle a prey when it is found.
h > s
Predators with long handling time relative to search time should be specialists since searching for prey is not an issue.
Why do animals live in groups?
Predation:
More eyes – higher chance of finding food, easier to spot predators. Individuals on the edges/corners are usually the ones that are on the lookout for predators – often younger individuals that require less food.
Numerical dilution of risk > predator attraction – if you’re in a flock, the chances that a predator picks you specifically significantly reduce
Edge effect
Confusion effect
Defence – prevents predators from attacking from behind for an example
Food:
More eyes find more food
Copying successful individuals
Cooperation when hunting
Copying successful individuals
Cooperation when hunting