(CHEM) Topic 3 - Periodicity
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Define atomic radius
Distance from nucleus to the outermost electron
Trend in atomic radius down a group
Increasing — electron in higher energy level is further from the nucleus
Define ionic radius
Distance from the nucleus of an ion to the outermost electron of the ion
Define electronegativity
Ability of an ion to attract pairs of bonded electrons
Define first ionization energy
Energy required to remove one electron from an atom in gaseous state
Define electron affinity
Energy change when an electron is added to an atom in gaseous state
Effective nuclear charge (Zeff) calculation
Number of protons minus number of shielding electrons
Trend in ionic radius down a group
Increasing — electron in higher energy level is further away from the nucelus
Trend in electronegativity down a group
Decreasing — extra energy level, more shielding effect
Trend in first ionization energy down a group
Decreasing — outermost electron is further from nucleus, less energy needed to remove it
Trend in electron affinity down a group
Decreasing — (less negative/exothermic) increasing shileding effect, electrons attrated less
Trend in atomic radius across a period
Decreasing — more protons, more nuclear charge, more attraction of valance electrons
Trend in ionic radius across a period
Decreasing — more protons, more nuclear charge, more attraction of valance electrons
Trend in electronegativity across a period
Increasing — increasing nuclear charge (extra electrons insignificant because they fill the same energy level)
Trend in first ionization energy across a period
Increasing — increasing nuclear charge (extra electrons insignificant because they fill the same energy level)
Trend in electron affinity across a period
Increasing — (more negative/exothermic) increasing nuclear charge
Trend in metallic character down group 1 (alkali metals)
Increasing
Trend in non-metallic character down group 17 (halogens)
Decreasing
Trend in reactivity down group 1 (alkali metals)
Increasing
Trend in reactivity down group 17 (halogens)
Decreasing
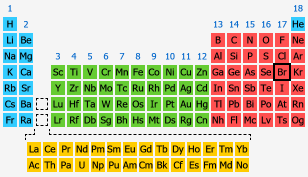
Electron configuration of bromine
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p5
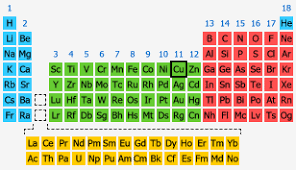
Condensed electron configuration of copper
[Ar] 4s13d10
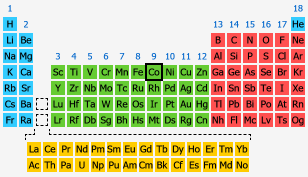
Condensed electron configuration of cobalt
[Ar] 3d74s2
pH of metal oxides
Basic
pH of metalliods
Amphoteric
pH of non-metal oxides
Acidic
Main gasses resposible for acid rain
SO2, NOx
Atmospheric gas causing ocean acidification
CO2