8.3 - Solid domestic waste
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Solid Domestic Waste (SDW)
Our trash and garbage from residential and urban areas. It is a mixture of paper, packaging, organic materials, glass, dust, metals, electronic waste, and more. It is collected from homes and shops and more.
Type of SDW - Biodegradable
Food waste, paper, green waste
Type of SDW - Recyclable
Paper, glass, metals, some plastics, clothes, batteries
Type of SDW - Electronic Waste
TVs, computers, phones, fridges
Type of SDW - Hazardous
Paints, chemicals, light bulbs
Type of SDW - Toxic
Pesticides, Herbicides
Type of SDW - Medical
Needles, syringes, drugs
Type of SDW - Inert
Concrete, construction waste
Type of SDW - Mixed
Tetrapaks, plastic toys
What are the aims of the circular economy
To be restorative of the environment
Use renewable enegy sources
Eliminate or reduce toxic wastes
Eradicate waste through careful design
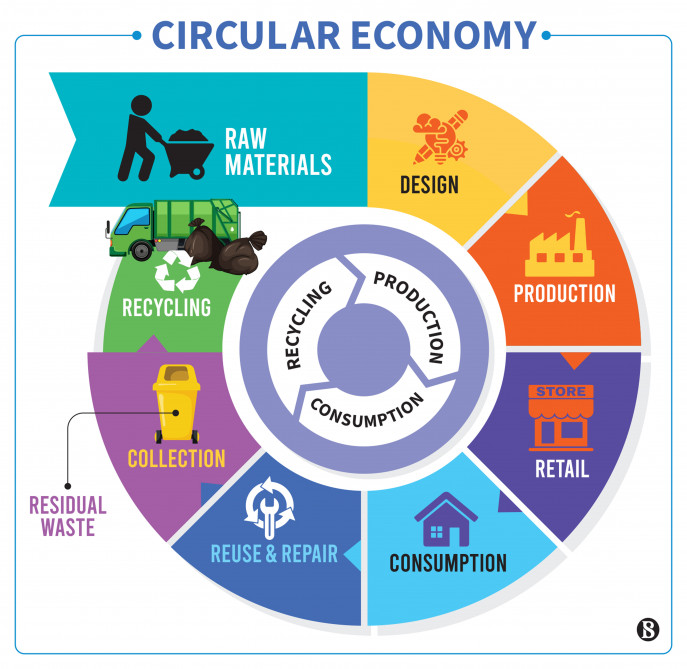
How does the circular economy work?
It relies on manufactureres and producers retaining ownership of their products and being responsible for recycling them or disposing them when the consumer has finished using them.
The producers act as service providers, selling use of their products, not the products themselves. This means that they take back products when they are no longer needed, disassemble or refurbish them and return them to the market
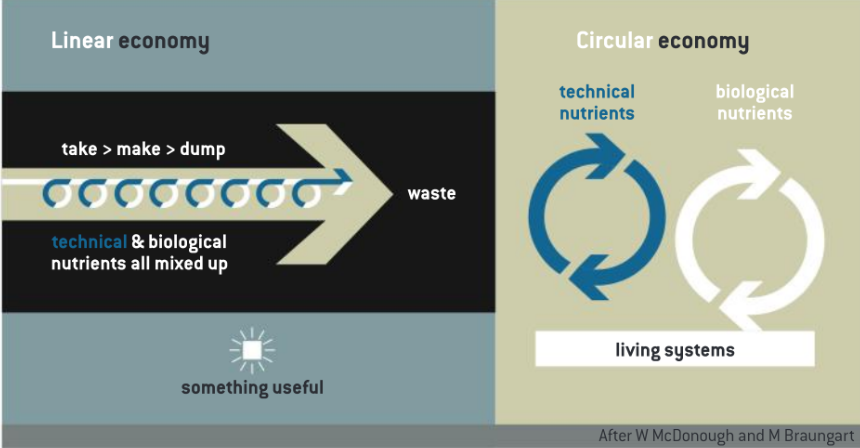
What are the three strategies to minimize waste?
Reduce
Use less resources, change shopping habits
buy things that last, look for items with less packaging, choose products that are energy efficient
Reuse
Products are used for something other than their original purpose or they are returned back to the manufacturer and used repeatedly
Returnable bottles - give back to manufacturer
Compost food waste
Use old clothes as cleaning rags
Read E-books
Recycle
Involves collecting and separating waste materials and processing them for reuse.
Ex. in Germany, each household has 4 bins for this
Strategies for waste disposal
Includes: Landfills, Incineration, Composting
How do Landfills work?
Waste is taken to a suitable site and buried there, hazardous waste can be buried as well. The cost is relatively cheap
They are carefully selected to not be too lose to areas of high population density, water courses and aquifiers. They are lined with a special plastic liner to prevent leachate seeping out
Methane produced as a resulting of fermenting organic material in the waste is either collected and used to generate electricity or vented into the atmosphere. Soil is pushed over the waste each day to reduce smells and pests
It is difficult to find new sites
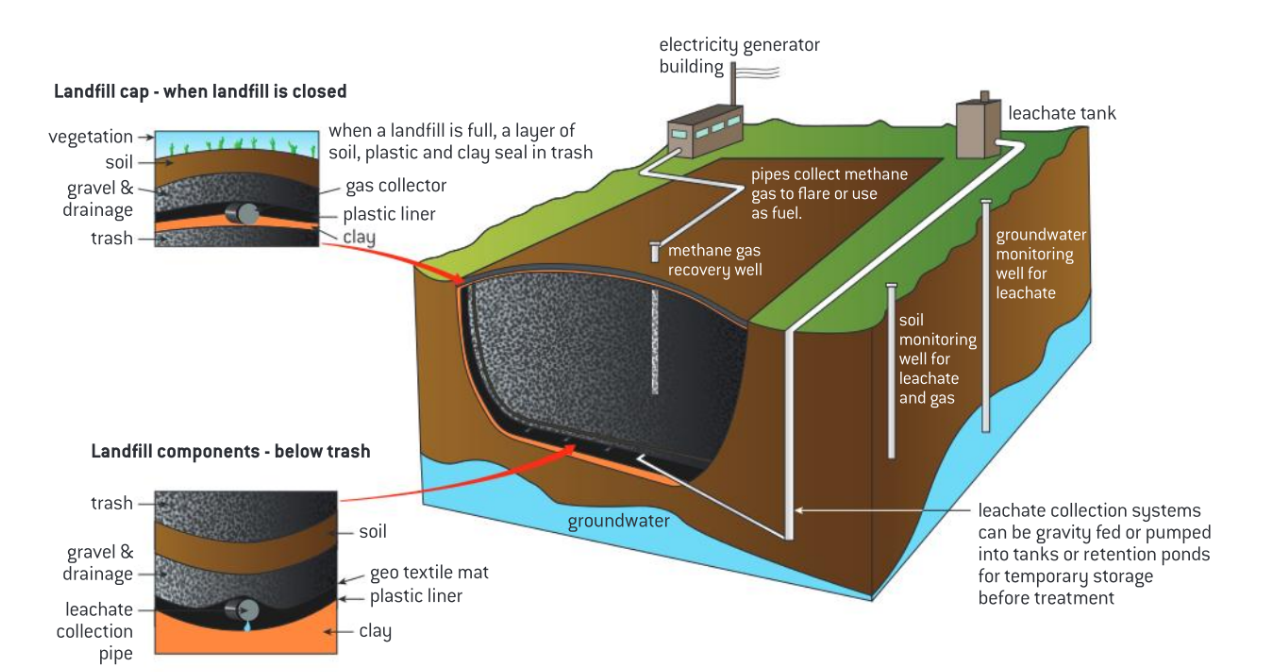
Advantages of Landfill sites
Cheap method of waste disposal with low setup and running costs
Gases such as methand can be collected for waste-to-energy schemes
Creates jobs for the local community
Old landfill sites can be landscaped and re-used for building projects
Disadvantages of Landfill sites
These sites give off dangerous gases that cause air pollution and global warming (methane)
There is also potential for explosions if methane builds up
Liners can fail and leachates leak into the local environment and groundwater sources
Settling after compaction can cause problems for future uses - must be left a long time to settle fully
Waste collection vehicles have to travel a long way to alternative sites
Landfills are filling up = lifespan of landiflls is limited
Poorly managed sites can result in rats, mice, flies increasing the spread of diseases
Heavy vehicles cause traffic problems and damage local roads
Poorly managed sites can cause problems with dust, odor, visual, and noise pollution - can negatively impact local property prices in the area
Contribution to marine debris - poorly managed sites have litter that gets blown by the wind to seas and oceans
How do incinerators work?
They burn waste at high temperatures up to 2,000° C. In some, the waste is pre-sorted to removie incombustible or recyclable materials. Then the heat produced is often used to generate steam to drive a turbine or heat buildings directly (waste-to-energy incineration).
In others, waste is burned but this can cause air pollution from burning plastics, heavy metals, burning batteries, and nitrogen oxides. The ash from ______ can be used in road building and the space taken up is less than landfills
However, they are expensive to build and need a constrant stream of waste, encouraging people to produce waste
Advantages of Incineration
Reduces the volume of waste by 80-85% therefore it is very popular in countries where land is scarce (ex. Japan)
Very useful for clinical waste or hazardous wate contaiing pathogens
Used to generate local district heating in Denmark and Sweden
Can be used to generate electricity
Incineration plants retrieve metal from the ashes and this can then be recycled
Disadvantages of Incineration
Emits varying levels of toxic heavy metals (manganese, chromium, nickel, arsenic, mercury, lead)
New incinerators are taking away the funding from other renewable energy research and development
Old incinerators emit dioxin and furan, carcinogenic gases
Causes property devaluation in surrounding areas
Causes visual pollution due to intrusive chimney stack
Filters do not remove the finest particles from air emissions
Many people in LEDC’s live on sifting waste, incinerators take away this livelihood
Set up costs are high (expensive)
Anaerobic digestion
When biodegradable matter is broken down by microorganisms in the absence of oxygen.
The methan produced can be used as fuel and the waste later used as a fertilizer or soil conditioner
Domestic organic waste
This can be composted or put into anaerobic digesters. Composting can be done at home on a small scale or local government authorities can collect home organic waste and compost on a larger scale