CUS 1150 LINUX LECTURE 2
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Kernel
Core part of the operating system, acting as a bridge between the software apps and the hardware.
OS Components
Kernel as its core, user interface, file management, network services and various utility applications.
Shell
Facilitates communication between hardware and applications, ensuring efficient and secure multitasking.
Manages system stability and secure access.
Monolithic Kernel
All OS services run in the kernel space, which is fast but has less fault isolation.
Unix, Linux, Open VMS, XTC-400.
Microkernel
Most services moved to user space, allowing for better reliability but more overhead.
Minix 3 and Mach.
Hybrid Kernel
Mixes monolithic and microkernel to allow for speed and better safety.
Windows NT and MacOS.
Nanokernel
Extremely minimal kernel, providing also basic hardware abstraction.
Nemesis and MIT Exokernel projects.
Exokernel
Separates protection and management, gives app direct control over hardware abstractions so apps decide what to build.
Function of Kernel
Process, memory, device, file system, resource, security and access control, and inter process communication management.
Key Points in Kernel
First part of the OS to load at boost, and stays active.
Operates in privileged mode, where user apps can't directly access hardware.
Applications request the kernel via system calls/software interrupts.
Kernel executes requested operation, and returns result to user space.
Context switching as needed to allow multitasking.
Shell
Allows users to interact with the OS by entering commands. Support scripting to automate tasks and provide control over system operations either through the Command Line Shell or the Graphical Shell.
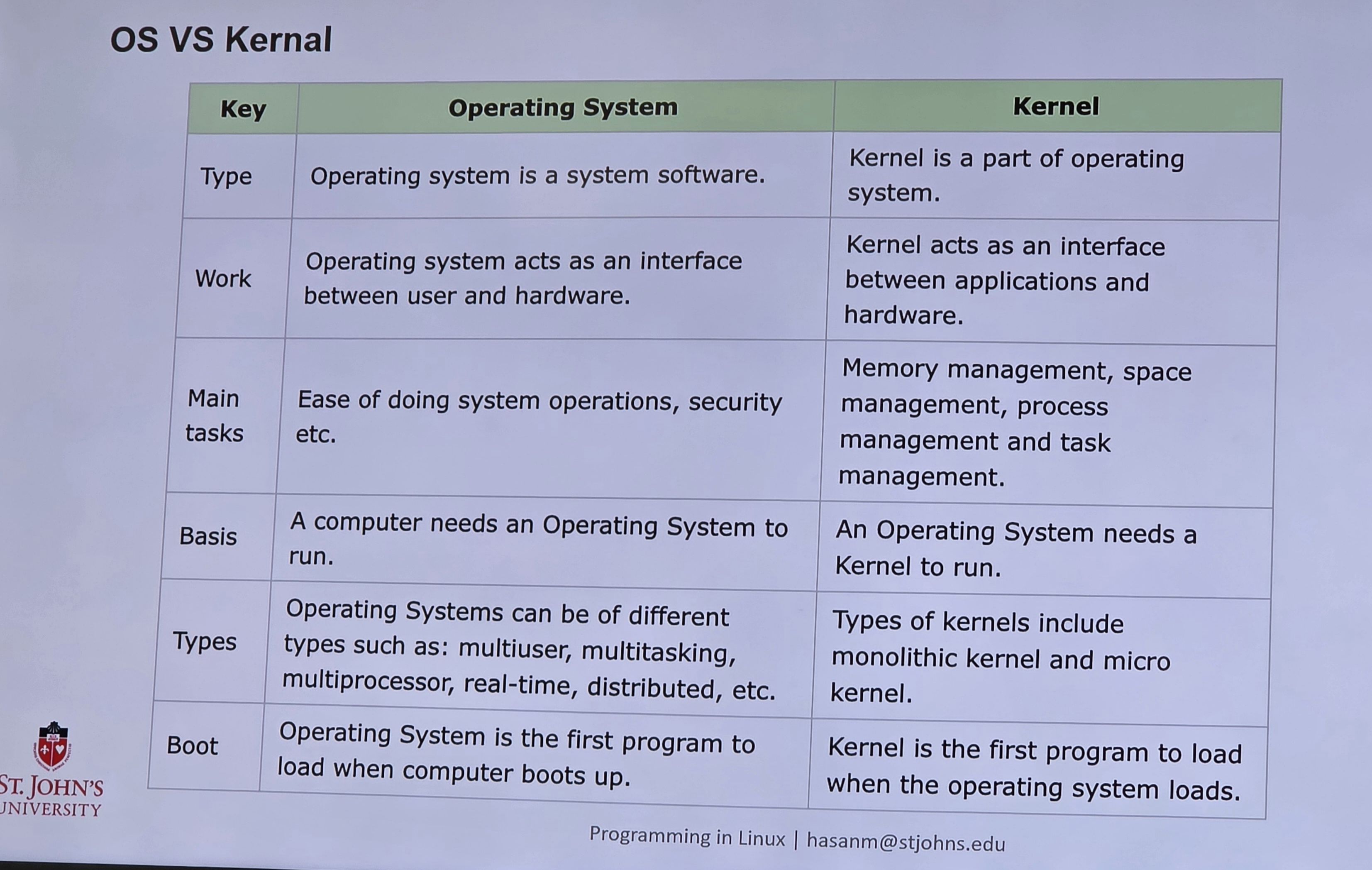
OS vs Kernel
Kernel Input/Output Subsystem
Fundamental component of modern operating systems responsible for managing all input/output operations on a computer.
I/O Request Scheduling
Core responsibility of the I/O subsystem.
Determines order of Execution to improve overall system performance and fair sharing of I/O devices.
Hopes to reduce wait time, response time, and turnaround time.
Maintains a wait queue, and reorder requests to optimize disk access and minimize seek time/latency.
Buffering
Temporary memory area technique used in data transfer to handle speed mismatched between devices and apps for different transfer sizes to allow smooth data flow.
Buffer may exist between two devices or a device and an app.
Roles of UI And Kernel of OS
User can access the kernel or the OS through system calls this is a programmatic way in which a computer program requests a service from the kernel.
User mode cannot access hardware resources, while kernel mode can access hardware like RAM and printer.
Structure of Systems Call
Due to security reasons, user apps cannot access hardware, so it requests the OS through system calls for these.
Monolithic Pros and Cons
Faster process execution and smaller source at the expense of one failure crashing the entire system, not being portable, and its large difficult management size.
Microkernel Pros and Cons
New services can be added without OS modification and kernel process crashes don't crash the whole system, at the cost of more software requirements, complicated process management and difficult to fix messaging bugs.
Hybrid Pros and Cons
No need for testing reboot and faster third-party integration, at the expense of increased bugs due to multi interfaces and difficult module maintenance for some admins.
Nanokernel Pros and Cons
Small footprint and low overhead for high performance, along with high modularity and flexibility for more customization, at the expense of being more complex of a system design.
Exokernel Pros and Cons
High performance and low overhead as user apps can directly control hardware resources and flexibility, at the expense of the kernel having to provide fine-grained control over hardware resources to user apps.
Linux Distribution
OS built on the Linux kernel, bundled with essential software, tools and package managers and customized to serve different users.
Ubuntu
One of the mostly widely used Linux distributions, especially for beginners.
Easy to install, long term support versions and a large software repository.
Used in DevOps, AI and data science environments.
Benefits include no licensing cost, strong community support, high customization and reliable production systems.
Kali Linux
Specifically designed for cybersecurity takes with over 600 security tools for penetration testing, digital forensics, network monitoring, reverse engineering and ethical hacking.
Developed by Offensive Security as a Debian-based open source Linix distribution.
Kali Key Features
Preinstalled Security Tools
Free and Open Source
Cross-Platform and Lightweight
Live Boot and Customization directly from a USB
Regular Updates with Strong Community Support
Kali Origins
Evolved from Backtrack, which was itself based on Ubuntu.
Released in March 2013 by Offensive Security as a modern, standardized penetration-testing environment.
Base system built on the Debian repository for a balance between stability and cutting-edge features for compatability with tools and hardware.
Developed by Offensive Security, experts in penetration testing training.
Goal is to offer a complete, ready-to-uze toolkit for ethical hackers.
Debian
Known for stability and is often used as the base for other distributions. Good voice for a solid, secure system without the latest features.
Robust environment for desktops and servers that are mainly used by advanced users and developers.
Layered Structure of Debian OS
Hardware
Linux Kernel
System Utilities
Application and Desktop
Debian Hardware
Represents physical components of the computer, like CPU, memory, storage and input/output.
Allows for multiple architectures.
Debian Linux Kernel
Core of the Debian OSm
Manages tasks like memory allocation, process scheduling, file handling, device control and overall resource management.
Debian System Utilties
Includes the APT ( advanced package tool ) package manager, dpkg, system libraries and GNU to provide access to over 59k software packages.
Essential tools for system administration, file management,text processing and package operations.
Debian Applications
Represents user-facing apps, desktop environments ( GNOME, KDE, Xfce ) and third party software.
Underlying layer used to provide web browsing, office productivity, development tools and multimedia.
Debian Free Software Guidelines
Main repository contains only free sofrware, giving users complete freedom to run, study, modify and distribute the software.
Fedora Linux
Linux distribution known for cutting-edge features, modern design, and strong security. Developed by the Fedora Project and sponsored by Red Hat, its mainly used for software development, enterprise systems and general desktop use.
Fedora Uses
Software devs, system admins, cloud computing, containerization and desktop productivity.
Stock Gnome Desktop
Provides clean, modern, unmodified GNOME desktop.
Smooth user friendly experience with a keyboard centric workflow.
Editors in Fedora
Workstation
Server
CoreOS
IoT
Silverblue
Fedora requires 64-bit Intel CPU, 2 GB minimum RAM, minimum 20 GB free, and 8 GB USB for bootable media.
Arch Linux
Independently developed Linux distribution known for its simplicity, and does not come with pre-installed graphics so you can shape how you want with a DIY approach.
Full control over installed packages, clean and minimal installations, continous updates through rolling release, and extensive documentation through the famous Arch wiki.
Mint
User-friendly and community driven Linux distribution based on Ubuntu, aiming to provide a reliable and elegant operating system with a focus on simplicity.
Features the Cinnamon desktop environment for users transitioning from other operating systems.
Pros of Mint
Beginner friendly
Good functionality
Stability and performance
Secure and privacy focused
Customization
Long Term Support and Updates
Use Case of Linux Distributions
Enterprise ( Red Hat, CentOS )
Cybersecurity ( Kali Linux )
Developers ( Fedora )
Multimedia Creation ( Ubuntu )
Lightweight and old hardware use ( Lubuntu )
Benefits of Linux
Cost Free and Open Source
Customizable
Secure
Resource Efficient
Development
Diverse Options
Stability and Reliability
Active Community
Desktop Environments of Fedora
KDE Plasma ( Highly Customizable )
Gnome
Xfce ( Lightweight and Fast )
Lxqt/Lxde ( lightweight old system design )