exam 1: soil fertility (copy)
1/280
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
281 Terms
most recent impact on farmers
pandemic
world population’s fertility rate is _
declining
what factor helps with fertility rates
immigration
_ is the country with the highest population as of 2024
India
most densely populated city in the world
Manila, Philippines
most soils are unable to produce max crop production without additions of _
nutrients
what country is known for infertile soil
Africa
what is the main point source in the Mississippi basin
sewage from rural areas
what countries produce more calories than the population consumes
US, Brazil, China, Russia
the US, Brazil, China, & Russia do thiswhen nutrients from produce do not return to the soil
export nutrients
what should end in order to solve world hunger
corruption
_ is not an issue when involving world hunger
money
hunger is still common in developing countries because:
the lack of resources to purchase or redistribute available food
enough calories are produced, it just isn’t _ in the best way possible
utilized
US/European: pays people to implement a practice
US
US/European: performance based
European
where is the biggest mine of phosphate rock in the US
Florida (south of Tampa)
there’s an infinite/finite amount of phosphorus
finite
in Iowa, _lb of soil is list for every _lb of corn grain produced
3, 1
soil nutrient management greatest concern: impact of excess nutrients in the environment, particularly _
nitrate-nitrogen
nutrients absorbed primarily as chemical ions from the soil solution
C, H, O, B
macrounits include:
H, C, O, N, K, Ca, Mg, P, S
these elements are macro/microunits: H, C, O, N, K, Ca, Mg, P, S
macro
micronutrients include:
Cl, Fe, B, Mn, Zn, Cu, Ni, Co, Mo
these elements are macro/microunits: Cl, Fe, B, Mn, Zn, Cu, Ni, Co, Mo
micro
nutrients with soil mobility include:
H, O, nitrate, S, Cl, B
_ is controlled by chemistry and based on function
mobility
nitrate movement is controlled by _
water
_ is plant essential due to structure
Ca
mnemonic about macronutrients hahah
Big HOe CaNt Kick Cat Magic on PlayStation
mnemonic about micronutrients hahah
Little FeCline Better reMain Zen Cuz Nickel Counting Mortgage
what makes the nutrients essential?
plants can’t complete their life cycle without it
deficiency symptoms for the element can be only corrected by supplying the element
element is directly involved in the nutrition of the plant, apart from its effect on chemical or physical properties of the soil
what affects nutrient ion solubility
strongly influenced by the charge of the ion
cations include:
H, Na, K, Mg, Ca, Al
these elements are cations/anions: H, Na, K, Mg, Ca, Al
cations
anions include:
Cl, O
these elements are cations/anions: Cl, O
anions
charge of an atom that results when the electrons in a covalent bond are assigned to the more electronegative atom
oxidation number/state
electrostatic forces that exist between ions of opposite charge (left side metals combined with right side NM)
ionic bond
sharing of electrons between two atoms
covalent bond
each metal atom is bonded to several neighboring atoms (give rise to electrical conductivity and luster)
metallic bond
(N/P/K):
forms in soil
very versatile
amino acids
chlorophyll
ADP & ATP
N
(N/P/K):
ADP & ATP
photosynthesis & respiration
key component of DNA, RNA, nuclear material of cells
cell division
P
(N/P/K):
meristematic tissue - plant growth
cell water regulation
metabolism
used as a catalyst in some enzymes
K
another name for potassium
potash
what’s the most important growth stage for P
reproductive growth
where is the majority of K found in the plant
stomata
what macrounits are non-mineral
H, C, O
what macrounits are mineral
N, K, Ca, Mg, P, S
which microunits are mineral
Cl, Fe, B, Mn, Zn, Cu, Ni, Co
applying nutrients _ the plant needs nutrients is the best way to maximize nutrient up take
before
how does soybean nutrient uptake differ from corn?
different nutrient needs due to a higher protein content
_ has fewer electrons than protons
cation
_ has more electrons in its electron shells than it has protons in its nuclei
anion
sum of negative and positive charges in an atom, which indirecltly indicate the number of electron it has accepted or donated
oxidatioin state/number
O’s oxidation number
-2
H’s oxidation number
+1
N’s oxidation number
0
NH4+ name
ammonium
NO3- name
nitrate
NO2- name
nitrite
NH3 name
ammonia
SO42- name
sulfate
PO43- name
phosphate
HPO42- name
phosphate
H2PO4- name
phosphate
CO32- name
carbonate
HCO3- name
bicarbonate
MoO42- name
molybdate
H3BO3 name
boric acid
what’s the general effect of ion charge on solubility
An+ + Bm- ←→ AmBn
the higher the charge of either cation or anion, the (greater/less) is the tendency for the compound or solid to be formed
greater
regarding the general effect of ion charge on solubility:
if the cation and anion are both single-charged, then the compound (is/is not) as easily formed
is not
with regard to solubility of inorganic compounds, we may expect that when both cation and anions are single charged, the resulting compound is usually very (insoluble/soluble)
soluble
strong acid is to _ electrolyte
strong
strong acid is to _ electrolyte
weak
whenever either the cation or anion is single charged and reacts with a multiple charged ion, the resulting compound is usually very (soluble/insoluble)
soluble
when monovalent anions react with any of the multi-charged cations, the solid compounds are all quite (insoluble/soluble)
soluble
if both the cation and anion are divalent, the resulting compound will be only sparingly _ (insoluble/soluble)
soluble
if one of the ions is divalent and the other is trivalent, the compound will be moderately (soluble/insoluble)
insoluble
as the sum of the charge increases, the solubility of the compound would (increase/decrease)
decrease
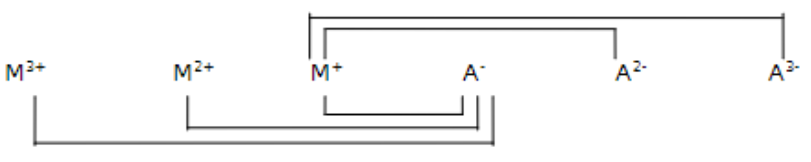
relative solubility of compounds formed from the reaction of anions (An-) and cations (Mn+): all compounds with a monovalent ion are _
soluble

relative solubility of compounds formed from the reaction of anions (An-) and cations (Mn+): compounds with both ions divalent are _
sparingly soluble

relative solubility of compounds formed from the reaction of anions (An-) and cations (Mn+): compounds with one divalent ion and one trivalent ion are _
moderately insoluble

relative solubility of compounds formed from the reaction of anions (An-) and cations (Mn+): compounds with both trivalent ions are _
insoluble
founded by Justus von Liebeg where a agriculture is constrained by the most limiting factor
law of the minimum
who discovered CE
Thomas Way
who developed process for the commercial fixation of ammonia & fueled the Green Revolutino
Haber-Bosch
what is considered as the sole nutrient
water
the earliest effort to maintain a “field laboratory” for the purpose of conducting scientific research to improve out understanding of how plants grow & interact
Rothamsted Experiment Station
shortly after the station was started, the US congress passed the _ and established the _
Morrill Act, Department of Agriculture
as leaves develop and capacity to capture sunlight and photosynthesis increases there is a rapid increase in growth or _
biomass
growth diminishes as the plant enters the _ phase and begins seed development, stopping with full _.
reproductive, maturity
(corn/wheat) has a higher above ground biomass production
corn
whenever a growth factor is limiting, it will (increase/lessen) the plant’s need for other growth factors
lessen
when cool weather limits plant growth, there is (less/more) demand by the plant for nutrients and water
less
why is there a quadradic graph response to growth factor compared to nutrient uptake
there is only a finite ability to produce biomass
when a limiting growth factor is removed by installing an irrigation system, it will generally (decrease/improve) plant response to fertilizer used to correct nutrient deficiencies that are also limiting growth
improve
yield increase will be proportional to the difference between max yield obtained by adding the growth factor and yield at the given level of the growth factor
law of diminishing returns
the level of the deficient growth factor can be expressed as a _
percent sufficiency level