natural selection + sex
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
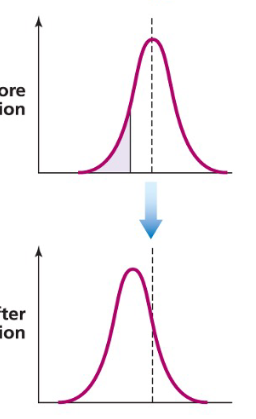
directional selection
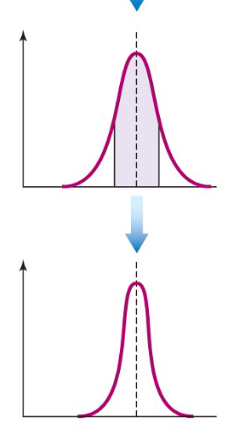
stabilizing selection
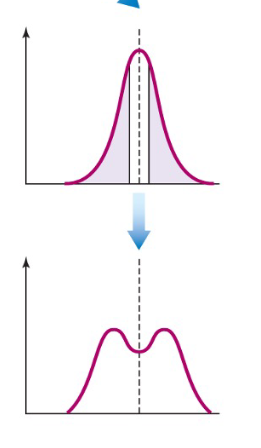
disruptive selection
twofold cost of sex
the cost of males
half of the offspring are males who cannot themselves produce offspring
saying what sex doesn’t make sense
disadvantages of sex
twofold cost of sex
search cost
reduced relatedness
risk of sexually transmitted infections
advantages of sex
combining beneficial mutations
generation of novel genotypes
faster evolution
clearance of deleterious mutations
clearance of deleterious mutations
deleterious mutations can accumulate in asexual lineage rapidly (mullers ratchet) and genetic load increases
genetic load
the burden that the accumulation of mutations places on the fitness of individuals
red queen hypothesis
predicts evolutionary arms race between hosts and parasites
consequence is persistent fluctuating alleles
hosts have to constantly evolve to stay in same place
Anisogamy
sexual reproduction involving the fusion of two dissimilar gametes
larger gametes→ female
smaller gamete → males
Isogamy
sexual reproduction in which the gametes are the same size
no gametes, mating types instead
female reproductive success limited by
how many eggs she can produce and provision (=fecundity)
choosier sex
female
intersexual selection
males trying to be with females
leads to evolution of elaborate male plumage, courtship displays, and other traits used by males to gain access to females
intrasexual selection
competition between males for access to females
leads to evolution of male fighting ability, which doesnt make sense otherwise
why do males typically invest less
uncertain paternity
operational sex ratio
ratio of males to females capable of reproducing at a given time
indicates which sex experiences more sexual selection
Slower rate of reproduction by females typically leads to male-biased OSR
Male-biased OSR leads to sexual selection favoring males that can outcompete other males for access to females