BSCI330: Central Dogma (pt. 1)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Steps of DNA to protein?
Transcribe (DNA to RNA) → Modify (only in eukaryotes) → EXPORT (nucleus to cytosol, only in eukaryotes) → Translate (RNA to proteins)
What transcribes DNA to RNA?
RNA polymerase!
What is mRNA?
messenger RNA, RNA after several processing steps
What happens to mRNA once it is exported from the nucleus to the cytosol?
It is translated into proteins by ribosomes
What is the flow of information called?
Central Dogma (DNA → RNA → protein)
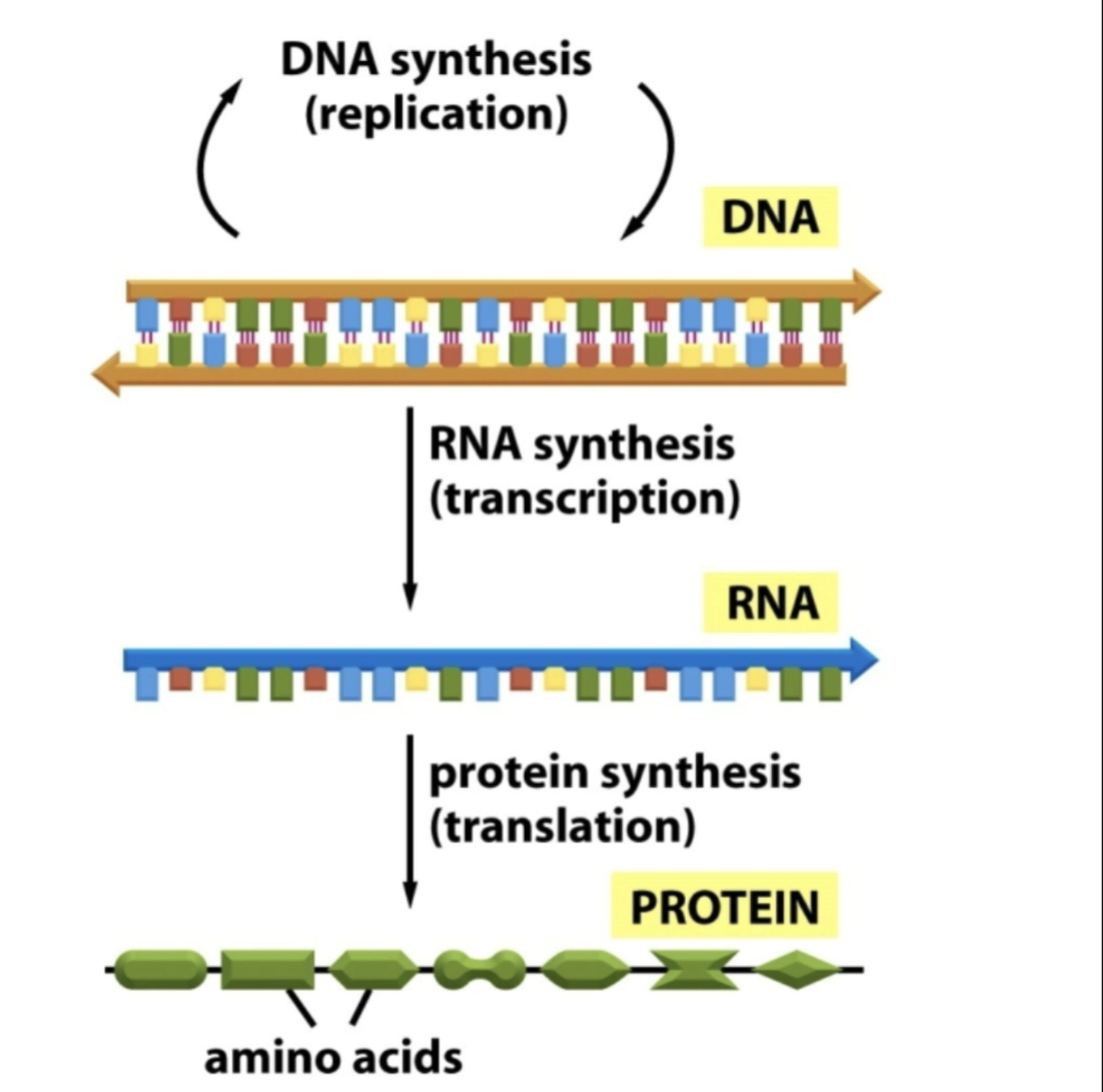
What is the order of information content?
DNA → mRNA → protein
greatest to least
Does the Ceontral Dogma apply to all cases of biological information?
NO
There are well-known exceptions (DNA that uses RNA as a template to synthesize DNA)
ex. telomeres and retrotransposons (jumping genes)
What is RNA transcription?
Generates a single-stranded RNA molecule is complementary to the template DNA strand
What order is RNA synthesized in?
5’ to 3’
DNA is read 3’ to 5’ and we’re synthesizing something complementary to it!
What types of RNA polymerases do prokaryotes have?
3
Prokaryotes only have 1
Where does RNA transcription initiate?
It initiates at the promoters!
RNA polymerase starts at the promoters.
What does transcription require in eukaryotes?
General transcription factors!
Help position RNA polymerase and start the process!
How do eukaryotes and prokaryotes differ in the way they regulate the initiation of transcription?
Eukaryotes require extra things!
general transcription factors
modification of chromatin (chromatin remodeling complex and histone-modifying enzyme)
What does extension of RNA chain require?
Elongation factors (provide energy)!
They use ATP hydrolysis to help RNA polymerase move along chromatin.
When does RNA transcription stop in both PROKARYOTES and EUKARYOTES?
Prokaryotes - RNA polymerase encounters a terminator sequence
Eukaryotes - RNA polymerase reaches a polyadenylation signal which cleaves RNA and adds an additional signal
What does RNA in eukaryotes require?
Post-transcriptional processing!
What’s the first modification of RNA?
Addition of 7-methylguanosine “cap” to 5’ end of RNA
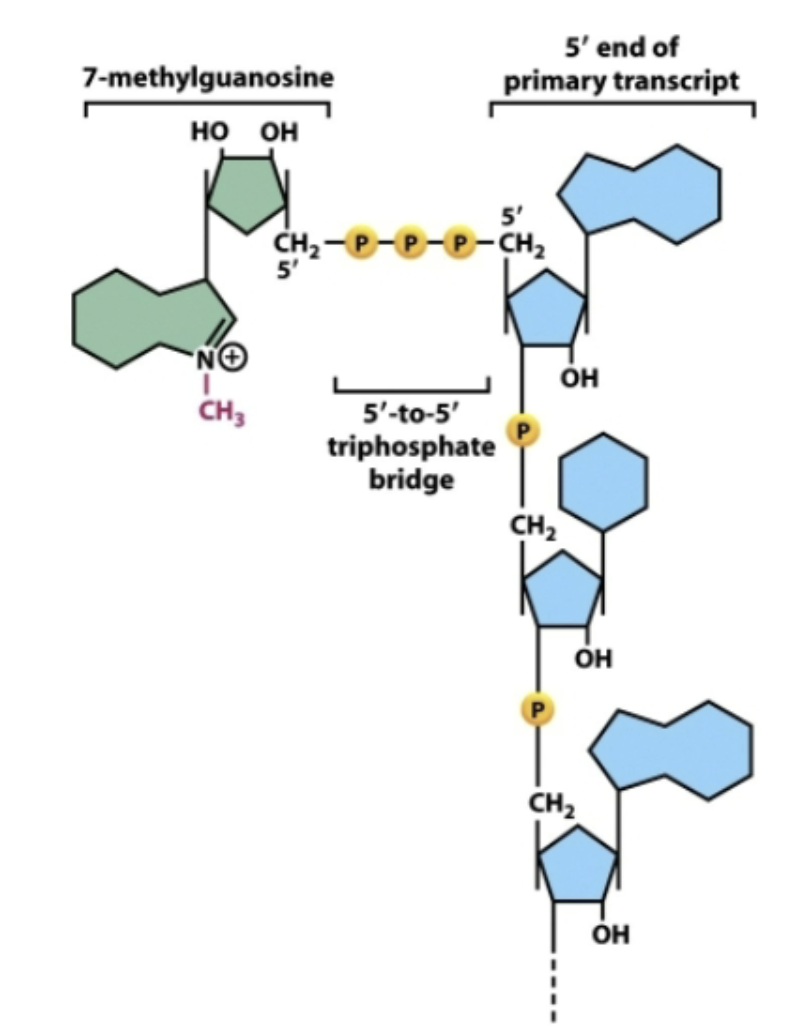
What’s the purpose of the 7-methylguanosine “cap”?
Marks an mRNA to be
Shows mRNA is intact at the 5’ end
Serves as a binding site for ribosomes
What are introns and exons (MUST KNOW)?
Introns (must stay IN) are non-coding sequences and exons (EXpressed and EXit) are coding sequences are mRNA.
Brewer’s yeast doesn’t have introns!
What splices introns?
Introns are spliced by spliceosomes!
What are spliceosomes made up of?
Small nuclear ribonuceloproteins (snRNPs) + small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) + multiple proteins
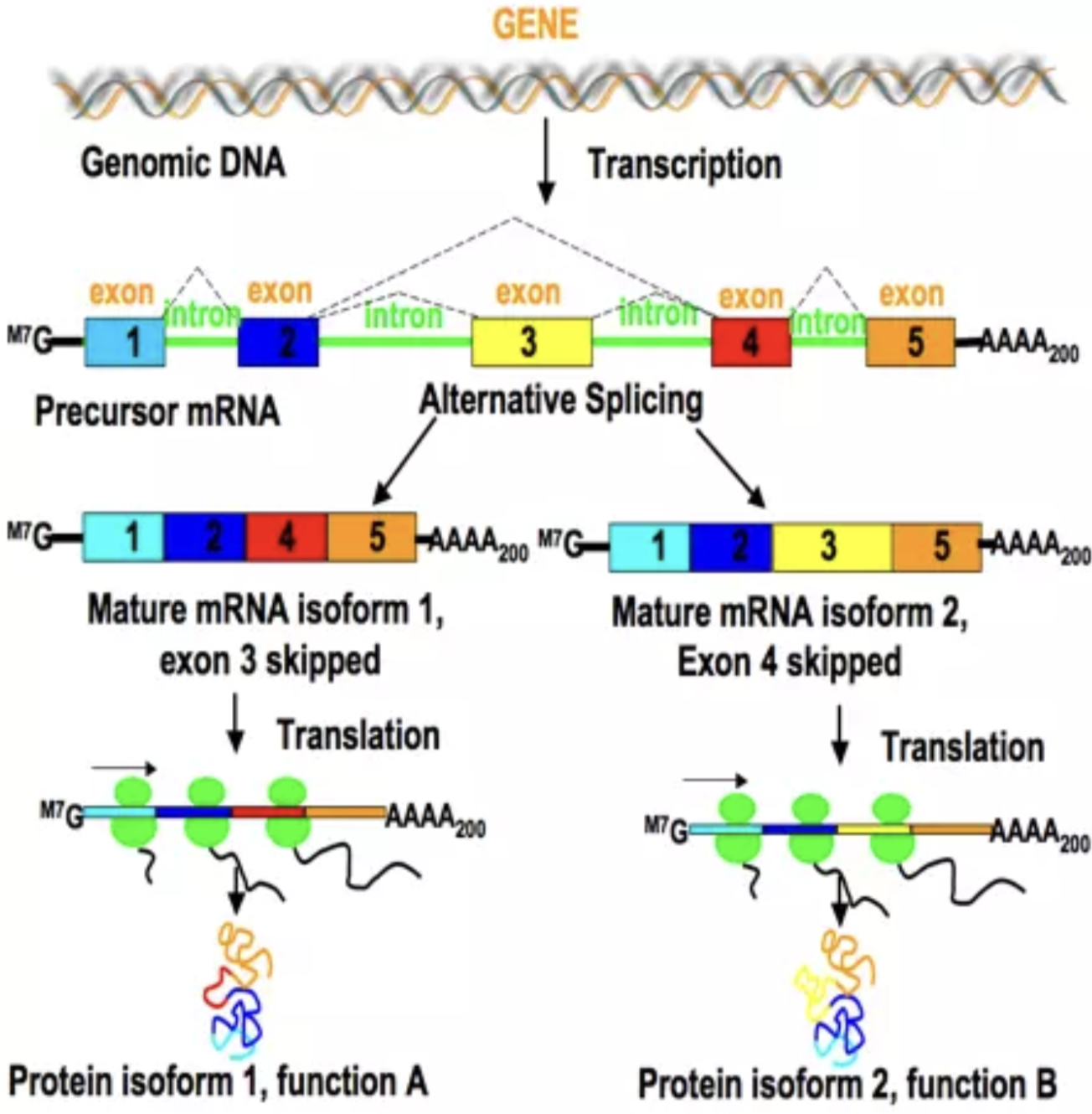
What is alternative splicing?
Precursor mRNA may form different mature mRNAs because different exons are kept.
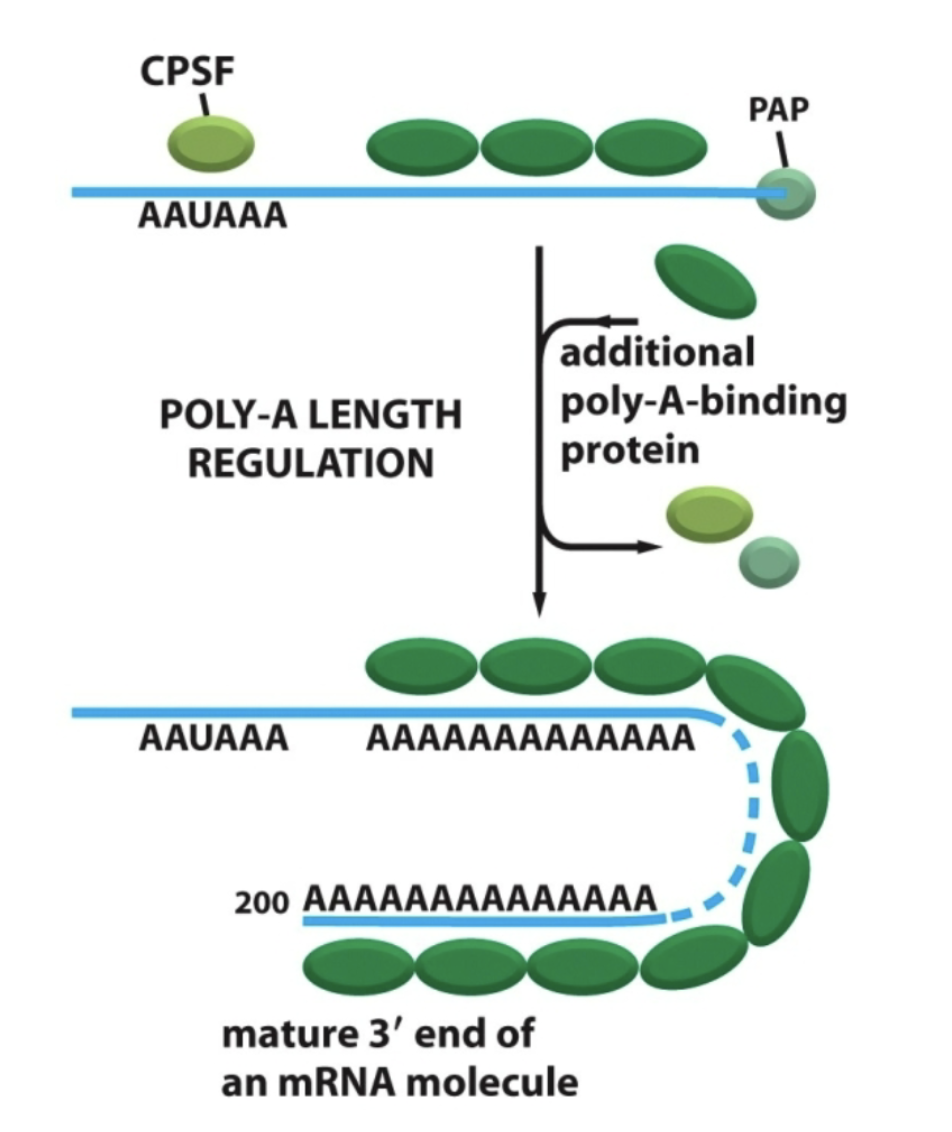
What’s the third RNA modification?
RNA 3’ receives a poly-A-tail (a string of As not coded in DNA).
Must first cleave the 3’ end of original RNA.
Important for exportation out of the nucleus!
Where does RNA synthesis and proccessing occur?
In the nucleus!
How does mRNA exit to the cytosol?
It binds to a nuclear export receptor!
What are the other RNAs?
mRNA - 5%
rRNA - 80%
noncoding RNA - snRNAs, snoRNAs, tRNAs, siRNAs, miRNAs
What is mRNA?
messenger RNAs, code for proteins
What is rRNA?
ribosomal RNAs, form the basic structure of ribosome
What is tRNA?
transfer RNAs, central to protein synthesis
What is snRNA?
small nuclear RNAs, function in a variety of nuclear processes