OSCM FADI TOLD US
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
7 major factors that affect location decisions
labor productivity,
exchange rates and currency risk
costs (tangible and intangible)
political risk, values, and culture
proximity to market
proximity to suppliers
proximity to competitors
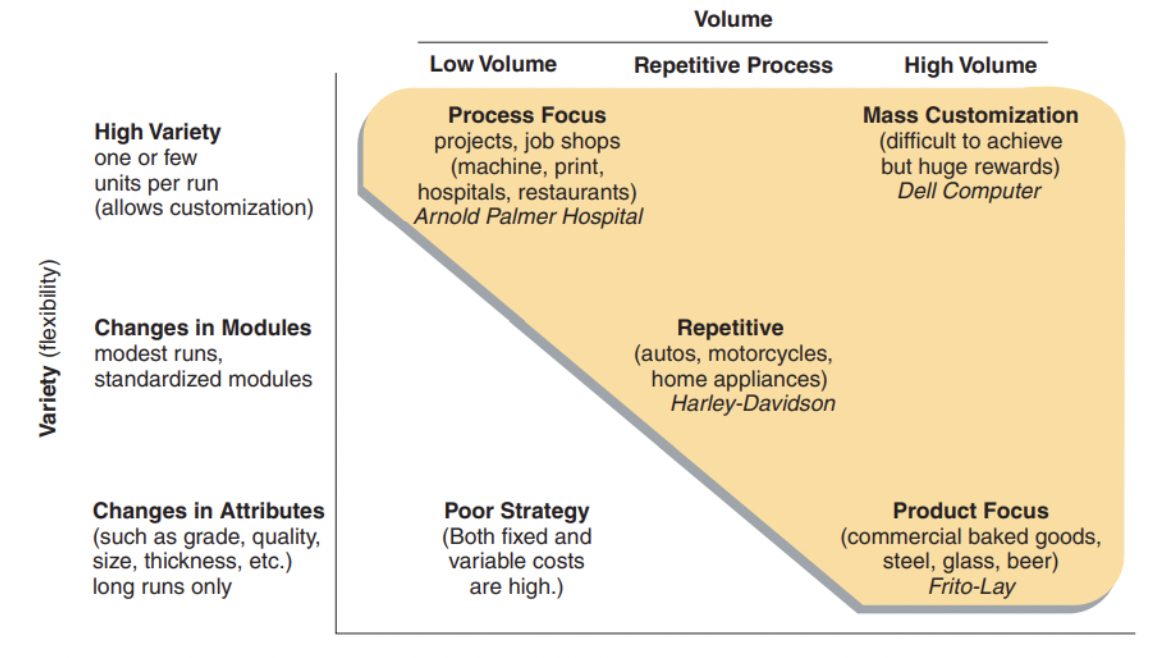
4 types of process strategies
process focus
product focus
repetitive focus
mass customization focus
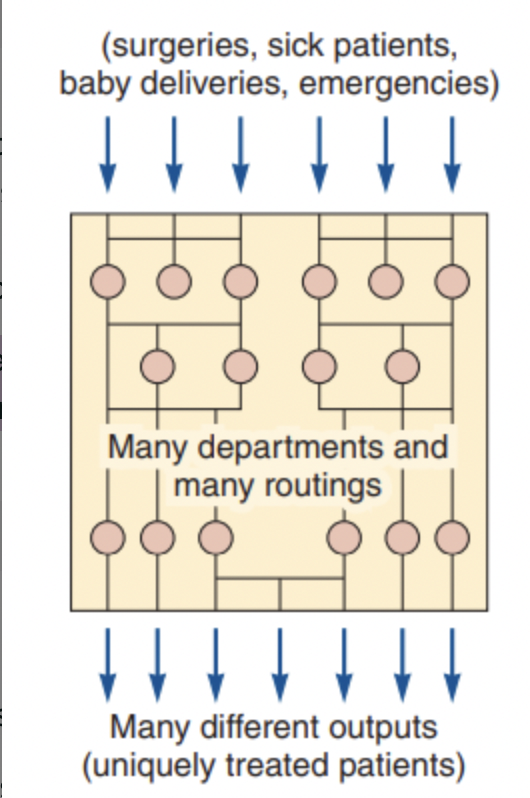
process focus
production facility organized around processes to facilitate low-volume, high -variety production
ex. Arnold Palmer Hospital, many inputs many outputs
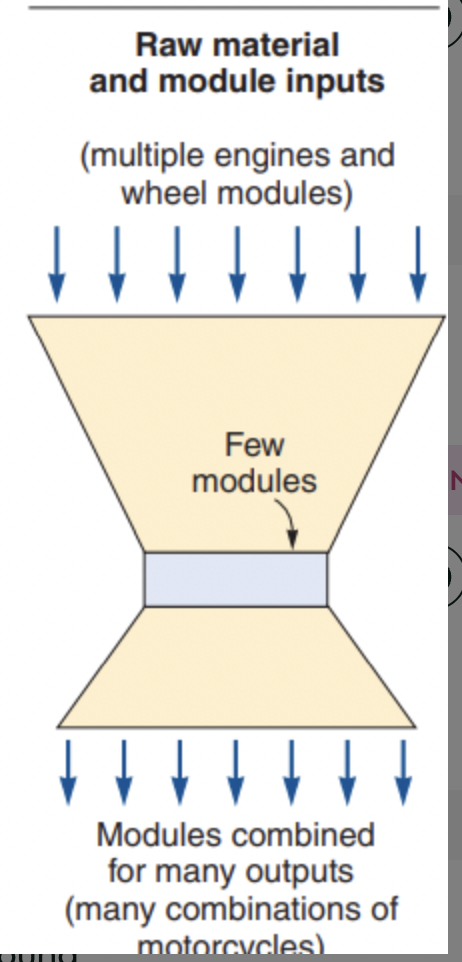
repetitive focus
Product oriented production process that uses modules
ex. Harley Davidson, raw materials and module inputs,
multiple inputs, few modules, multiple outputs
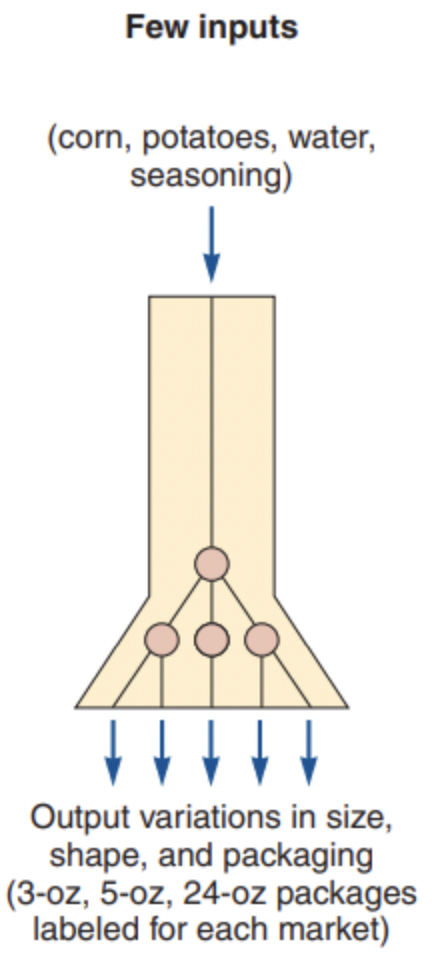
product focus
facility organized around products; a product-oriented high-volume, low-variety process (also called continuous processes)
ex. Frito-Lay, few inputs, many outputs
repetitive process
classic assembly line, product-oriented production process that uses modules
process strategy
organizations approach to transforming resources into goods and services
objective
create a process that can produce offerings that meet customer requirements within cost and other managerial constraints
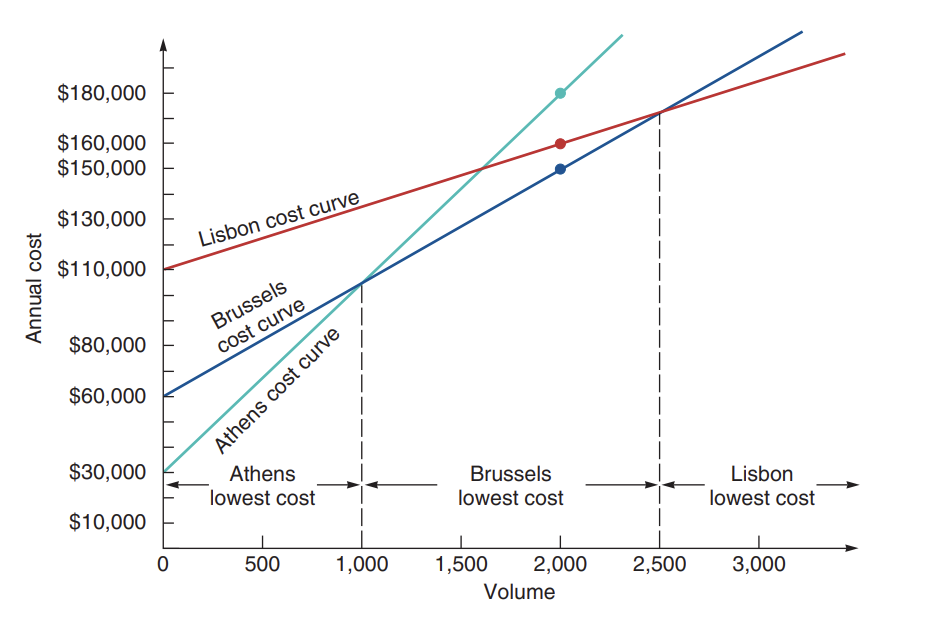
volume and variety chart
cross-over chart
chart of costs at the possible volumes for more than one process
Where the lines intersect is when you want to change production
starting point on y axis is where fixed costs occur, slope of line is the variable costs
vertical integration
developing the ability to produced goods and services previously purchased or to actually buy a supplier or distributor
a business strategy in which a company takes ownership of two or more key stages of its supply chain
horizontal integration
when a company acquires or merges with another company in the same industry that is operating at the same level in the value chain.
six sourcing strategies
many suppliers
few suppliers
vertical integration
joint ventures
keiretsu networks
virtual companies
bullwhip effect
increasing fluctuation in orders or cancelations that often occurs as orders move through the supply chain
methods of evaluating location alternatives
factor-rating method
locational cost-volume method
center of gravity method
transportation model
factor-rating method
location method that instills objectivity into the process of identifying hard-to-evaluate costs
steps to the factor rating method
develop list of relevant factors (key success factors)
assign weight to each factor
develop scale for each factor (1-10)
have management score each location for each factor
multiply score by weight
make recommendation based on number
center of gravity method
mathematical technique used for finding the location of a distribution center that will minimize distribution costs
locational cost-volume method
method of making an economic comparison of location alternative by identifying fixed and variable costs and graphing by each location to determine which one provides the lowest cost
three steps to LCV method
determine fixed and variable costs
plot the costs for each location (cost on y, volume on x)
select the location with lowest total cost for expected production volume
transportation model
technique for solving a class of linear programming problems
computer integrated manufacturing
manufacturing system in which CAD, FMS, inventory control, warehousing, and shipping are integrated
the manufacturing approach of using computers to control the entire production process
logistics
seeks efficiency of operations through the integration of all material acquisition, movement, and storage activities
inventory turnover equation
= COGS/average inventory investment
the higher the better
percent invested in inventory equation
= (average inventory investment/total asset) x 100
the higher it is the worse off it is
weeks of supply equation
= average inventory investment/ (annual cogs/52 weeks)
better to have it lower
TQM concepts
management of an entire organization so that it excels in all aspects of products and services that are important to the customer
continuous improvement, six sigma, employee empowerment, benchmarking, JIT, taguchi concepts, knowledge of TQM tools
CI-SSEEB-JiT-TAGCO- Know
Continuous Improvement
plan-do-check-act
six sigma
statistical sense - describes a process, product, or service with an extremely high capability
program designed to reduce defects to help lower costs, save time, and improve customer satisfaction
comprehensive system- strategy, discipline, and a set of tools
employee empowerment
involving employees every step of the production process
benchmarking
selecting domenstrated standard of practices that you aim to reach
JIT
only make once ordered
Taguchi Concepts
quality robustness, target oriented quality, quality loss function all used to improve product and process quality
knowledge of TQM tools
check sheets, scatter diagrams, cause-effect diagrams, pareto charts, flowcharts, histograms, statistical process control
how to mathamaticaly solve a crossover chart
set two equations equal to one another and solve for the units
low volume, high variety processes are also known as:
continuous processes
repetitive processes
process focused
product focused
process focused
a crossover chart for process selection focuses on:
labor costs
material costs
both labor and material costs
fixed and variable costs
fixed costs
fixed and variable costs
tools for process analysis include all of the following except:
flowchart
vision systems
service blueprinting
time-function mapping
value-stream mapping
vision systems
customer feedback in process design is lower as:
the degree of customization is increased
the degree of labor is increased
the degree of customization is lowered
both a and b
both b and c
the degree of customization is lowered
computer-integrated manufacturing includes manufacturing systems that have:
computer aided design, direct numerical control machines, and material-handling equipment controlled by automation
transaction processing, a management informations system, and decision support systems
automated guided vehicles, robots, and process control
robots, automated guided vehicles, and transfer equipment
computer aided design, direct numerical control machines, and material-handling equipment controlled by automation
the factors involved in location decisions include:
foreign exchange
attitudes
labor productivity
all of the above
all of the above (foreign exchange, attitudes, labor productivity)
If fender guitar pays $30 per day to a worker in its Ensenda, Mexico, plant, and all the employee completes four instruments per 8-hour day, the labor/cost unit is:
30.00
3.75
7.50
4.00
8.00
7.50 (30/4)
Evaluating location alternatives by comparing their composite (weighted-average) scores involves:
factor-rating analysis
cost-volume analysis
transportation model analysis
linear regression analysis
crossover analysis
factor-rating analysis
On the cost-volume analysis chart where the costs of two or more location alternatives have been plotted, the quantity at which two cost curves cross the quantity at which:
a) fixed costs are equal for two alternative locations
b) variable costs are equal for two alternative locations
c) total costs are equal for all alternative locations
d) fixed costs equal variable costs for one location
e) total costs are equal for two alternative costs
total costs are equal for two alternative costs
A regional bookstore chain is about to build a distribution center that is centrally located for its eight retail outlets. It will most likely employ which of the following tools of analysis?
assembly-line balancing
load-distance analysis
center of gravity model
linear programming
all of the above
center of gravity
What is the major difference in focus between location decisions in the service sector and the manufacturing sector?
there is no difference
the focus in manufacturing is revenue maximization, while the focus in service is cost maximization
the focus in service is revenue maximization, while the focus in manufacturing is cost minimization
the focus in manufacturing is on raw materials, while the focus on service is on labor
the focus in service is revenue maximization, while the focus in manufacturing is cost minimization
the objective to supply chain management is to
build a chain of suppliers that focuses on maximizing value to the ultimate customer
the term vertical integration means to:
develop the ability to produce products that complement or supplement the original product
produce goods or services previously purchased
develop the ability to produce the specified good more efficiently
all of the above
produce goods or services previously purchased
the bullwhip effect can be aggravated by:
local optimization
sales incentives
quantity discounts
promotions
all of the above
all of the above (local op, sale inc, quan disc, promo)
Supplier selection requires:
supplier evaluation and effective 3PL
supplier development and logistics
negotiations, supplier evaluation, supplier development, and contracts
an integrated supply chain
inventory and supply chain management
negotiations, supplier evaluation, supplier development, and contracts
a major issue in logistics is:
cost of purchases
supplier evaluation
product customization
cost of shipping alternatives
excellent e-procurement
cost of shipping alternatives
inventory turnover =
COGS / weeks of supply
weeks of supply / annual COGS
annual COGS / 52 weeks
average inventory investment/COGS
COGS/ avg inventory invest
COGS/ avg inventory invest