Muscular System
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/26
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
1
New cards
Describe origin
Insertion of attachment, does not move
2
New cards
Describe insertion
Attachment that moves
3
New cards
Describe synergist muscles
Does the exact same action (biceps)
4
New cards
Describe antagonist muscles
Does the exact opposite action of synergist muscles (tricepts)
5
New cards
List the anatomy of a muscle cell
Sarcolemma (PM of the muscle cell), t-tubule (brings action potention to the center of the cell), multiple peripheral nuclei (store DNA, make RNA), sarcoplasmic reticulation (store and release calcium), mitochondria (create ATP to power cell), myofibrils (organized cytoskeleton that allows for contraction; thick and thin myofilaments), neuron (neuronmuscular junction - brings action potential from brain to activate the muscle)
6
New cards
List the steps of muscle contraction
Myosin head binds to actin, power stroke, bring the actin closer together; The sarcomere shortens but the filaments stay the same size
7
New cards
When can myosin bind to actin
When calcium is present
8
New cards
List the organization of myofilaments
Thick myofilaments (myosin), thin myofilaments (actin), z-disk (dystrophin), titin proteins, sarcomere (z-disk to z-disk)
9
New cards
What is a motor unit
A neuron and all of the fibers it attaches to
10
New cards
What is the cross section of a muscle
Epimysium (dense irregular CT, continuous with tendons), muscle, perimysium (moderately dense CT), fascicles (bundles of muscle fibers), endomysium (areolar CT), muscle fibers (cells), satellite cells (muscle stem cells, heal if you tear them), nerve (bundles of neurons, controls contraction)
11
New cards
Describe hypertrophy
Growth in size of muscle fibers, active muscles
12
New cards
Describe atrophy
Reduction of size, inactive muscles
13
New cards
Describe skeletal muscle
Moves the body, striated, cylindrical cells, multi-nucleated, voluntary, strong contractions (tire easily), contract 25-35% of length, heals quickly, actin and myosin are neatly organized
14
New cards
Describe smooth muscle
Walls of organs, non-striated, tapered cells, uni-nuclear, involuntary, weaker contractions (do not tire), contract 50% of length, heals slowly, actin and myosin are not neatly organized
15
New cards
What are the types of fascicle arrangements
Parallel, convergent, circular, unipannate, bipennate, multipennate
16
New cards
Describe parallel fascicle arrangement
Goes straight, longest distance of contraction, the WEAKEST
17
New cards
Describe convergent fascicle arrangement
Fans out
18
New cards
Describe circular fascicle arrangement
Anywhere you have sphincters (ex: mouth and eyes), (weakest, non-existent)
19
New cards
Describe unipennate fascicle arrangement
Fascicles on ONE side of one ligament
20
New cards
Describe bipennate fascicle arrangement
Fascicles on BOTH sides of one ligament
21
New cards
Describe multipennate fascicle arrangement
Fascicles on BOTH sides of MULTIPLE ligaments, shortest distance of contraction, the STRONGEST
22
New cards
First class lever system
Fulcrum is in the middle, no set of force or distance
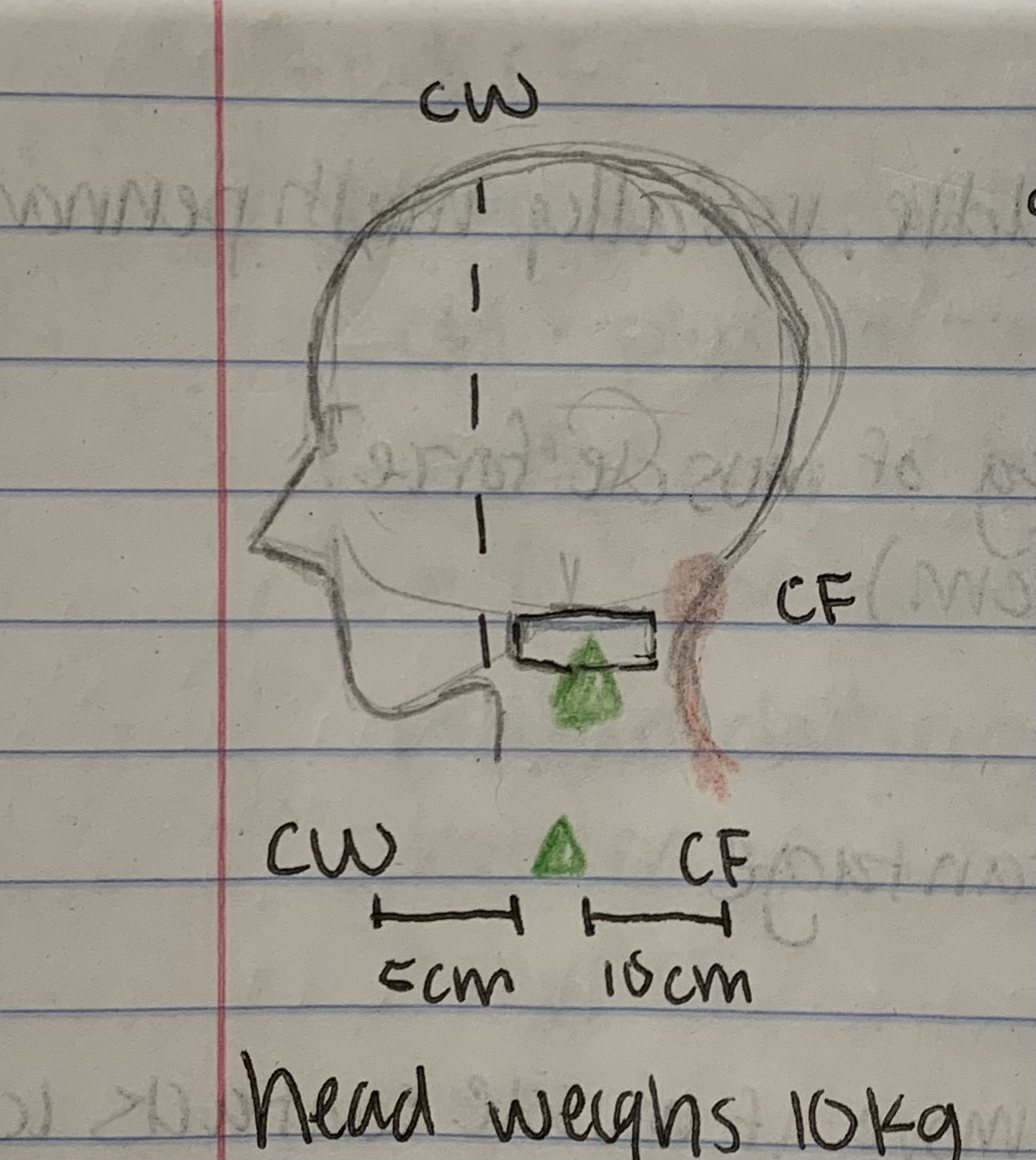
23
New cards
Second class lever system
Center weight is in the middle, force advantage, distance disadvantage
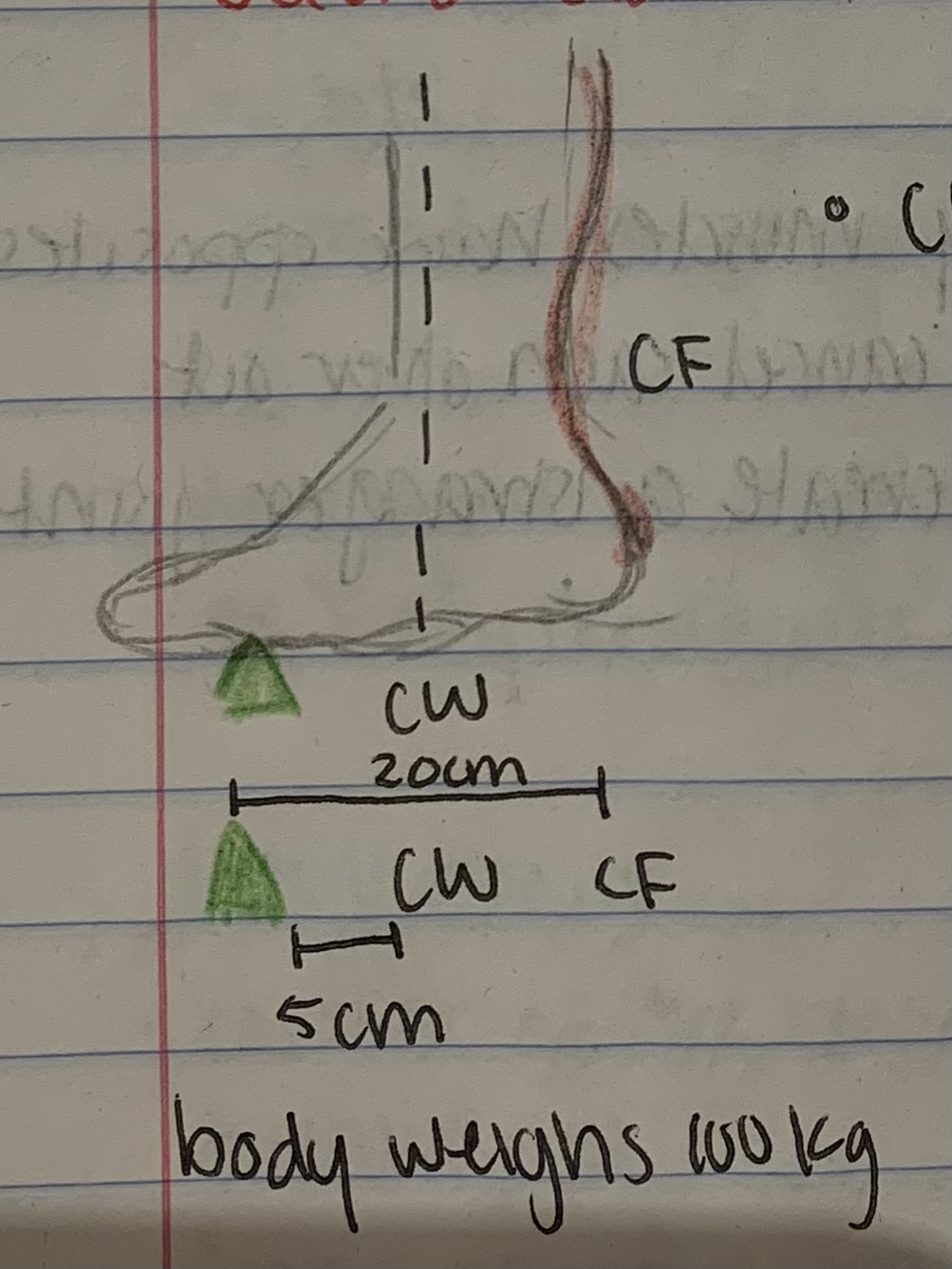
24
New cards
Third class lever system
Center force is in the middle, force disadvantage, distance advantage
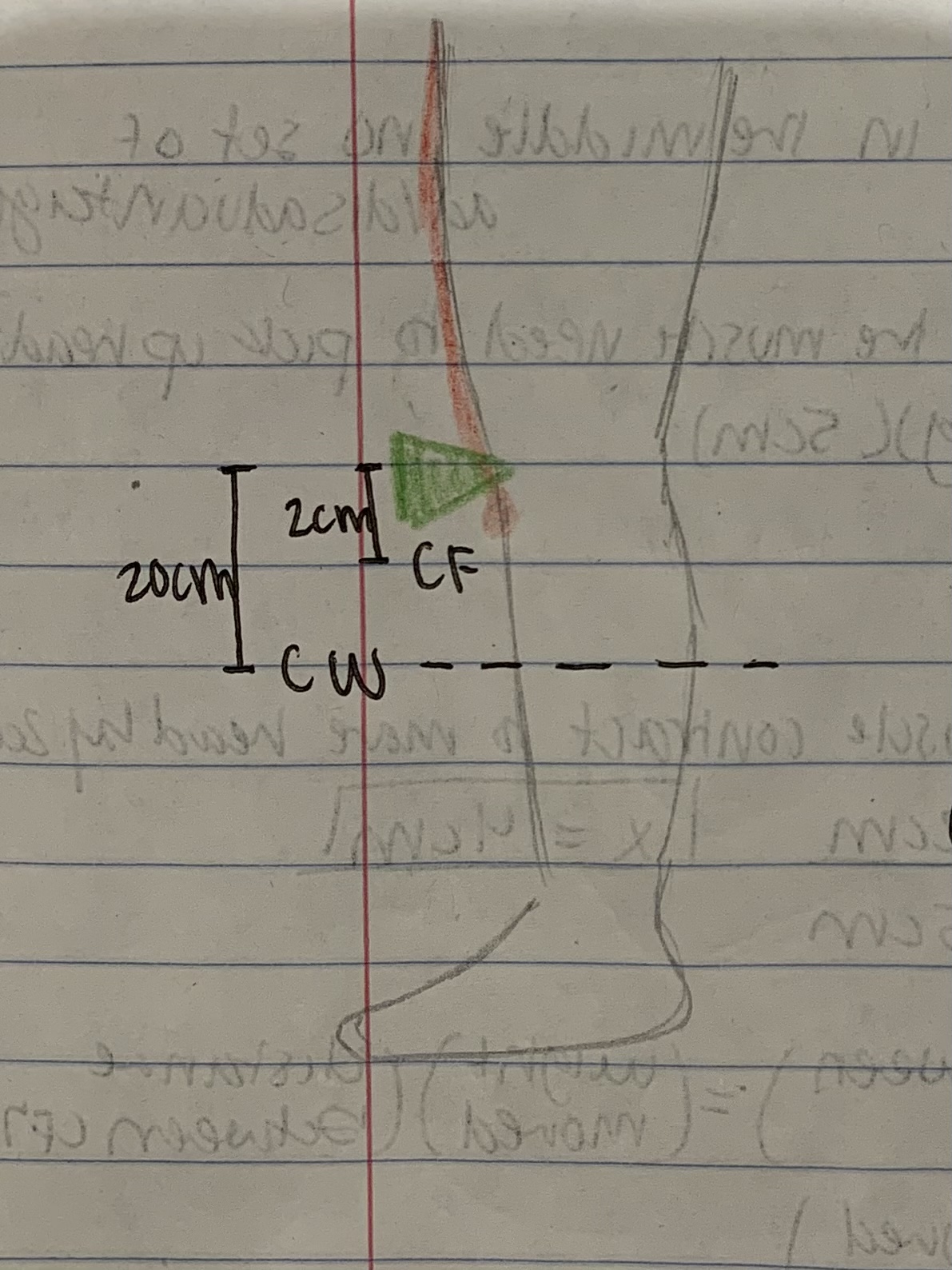
25
New cards
What is the formula for force
(Force of muscle)(Distance between CF and fulcrum) = (Weight moved)(Distance between CF and fulcrum)

26
New cards
What is the formula for distance
(Distance moved by muscles/Distance between CF and fulcrum) = (Distance moved by body part/Distance between CF and fulcrum)

27
New cards
Why do muscles of the same joint have opposite class lever systems
To cancel each other out and create a stronger joint