CCM Quiz #2 - IPC & Advocacy
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
interprofessional collaboration
What is an important pedagogical approach for preparing health professional students to provide patient care in a collaborative team environment?
once health care professionals begin to work together in a collaborative manner, patient care will improve. Interprofessional teams enhance the quality of patient care, lower costs, decrease patient length of stay and reduce medical errors
what is the premise of interprofessional collaboration?
1. role clarity
2. trust and confidence
3. the ability to overcome adversity
4. the ability to overcome personal differences
5. collective leadership
*always want it to be collective!
what are the important ingredients for successful interprofessional team work (5)
role clarity
Successful Teamwork:
______________ describes how each member is relief on to execute his/her own roles
-individual contributions should be valued yet the focus should be on team success
Diagnosticians (e.g., PA, MD, NP), prescribers, medication experts (pharmacists), and members who tend do pts daily needs all have different roles/responsibilities
Successful Teamwork:
Examples of role clarity in healthcare?
trust & confidence
Successful Teamwork:
_____________ describes how members must be confident in their own abilities to develop team trust
Proximity & time builds trust/confidence in the team, as well as exposures to other healthcare disciplines
Successful Teamwork:
Examples of trust/confidence in healthcare?
ability to overcome adversity
Successful Teamwork:
_____________ describes challenges that require every member to remain committed to the collective goal despite setbacks
Dealing w/ complex patients or staff shortages.
Successful Teamwork:
Examples of ability to overcome adversity in healthcare?
ability to overcome personal differences
Successful Teamwork:
____________ describes members being able to overcome personal issues even if they do not always get along
Members working together no matter what, putting pt care FIRST
Have to put personal differences aside
Successful Teamwork:
Examples of overcoming personal differences in healthcare?
collective leadership
Successful Teamwork:
____________ describes the philosophy that takes pressure off any one individual and disperses it throughout the group
Everyone is responsible
integration
________________ is the degree to which harmony of effort exists among different units
-intensified when individual members of each unit know what the other units are doing (if you are working with a team and what everyone is doing, you are able to build that trust that everyone is busy)
interaction, sharing of information and joint decision making about strategies and goals among the relevant units
what does integration require
cross understanding
What describes the extent to which group members have an accurate understanding of one another’s mental models?
Mental models can affect the way individuals make decisions & define/solve problems
how much we understand each others mental model
-improve the quality of communication (allowing group members to use terminology that is both known and respectful to other group members)
-deepen one's interpretation of another's contribution
-predict how their actions affect others and make adjustments to their behavior in advance
how can you better understand other's mental model
realistic
Occupational interest that frequently involves work activities that include practical, hands-on problems and solutions?
Example: surgeons (appendix is bad - take it out)
investigative
Occupational interest that frequently involves working with ideas and require an extensive amount of thinking?
Example: endocrine (problem solving & complex thought)
artisitic
Occupational interest that frequently involves working with forms, designs and patterns?
social
Occupational interest that frequently involves working with, communicating with and teaching people?
Example: nursing & social work
enterprising
Occupational interest that frequently involve starting up and carrying out projects?
Example: healthcare admin/management
conventional
Occupational interest that frequently involves following set procedures and routines?
Example: surgical tech
cross-understanding
The differentiation btw professional identities makes __________________ a vital component to successful interprofessional teamwork
advocacy
activity on someone's behalf directed towards a specific goal
-well being of patients
-promotion of health in society as a whole
how should we exhibit advocacy in our profession?
1. individual
2. community
3. structural
4. global
what are the 4 levels of advocacy?
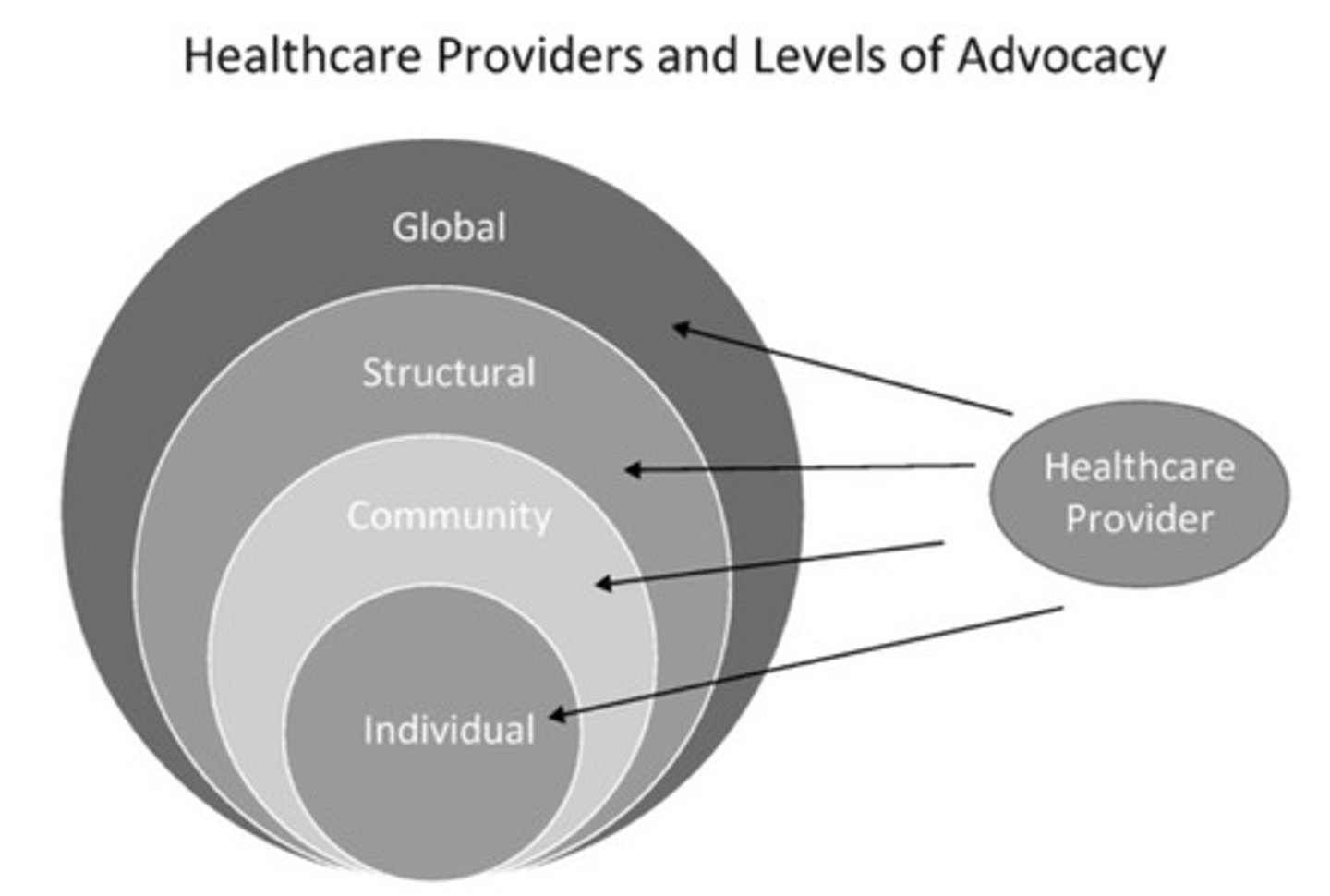
individual advocacy
What is being described?
-starts with providing care that integrates the full spectrum of pt's needs
-an the individual level is a core components of a proviers professional obligations
-include navigating complex health care system, communicating with pharmacies/insurance companies to cover medication and referring pts to social service agencies
In Scranton, it is AHEC
What we do
institutional advocacy
_________________ can be utilized to advocate for system or structural changes that improve care
ex. interpreter services, philanthropy policies. convincing the hospital leadership to expand interpreter services or more generous philanthropy policies
health-care advocacy
What targets health care system policies or societal laws governing health care?
-include supporting a single-payer system with universal coverage, needle exchange programs (want prevent HIV spread!!)
-advocate on behalf of pts by acting to change health care regulations (want more health coverage)
community advocacy
What has an impact on broader population beyond pts seen in the health-care setting?
-advocate for changes in policy such as support for social welfare programs, food policy, public support for housing, education, and prison reform
-things that affect social determinants of health
-advocating for increased funding for research and health-care delivery for various diseases
-individual
-family
-community
-policy/systems
What are the 4 levels of community advocacy?
audience
These two questions describe _______________.
Who are we advocating for?
Whom are you advocating to?
Issue
This question describes _______________.
What are you advocating?
method
This question describes _______________.
How are you doing it?
70
More than _____% of premature mortality is caused by behavioral, social and environmental factors
undeserved communities
who is most vulnerable to social factors, access to health care, and most likely to become sick?
Those living in underserved communities are more likely to become sick but also less likely to be able to change conditions that make them sick.
Ability to influence the social factor such as housing conditions, food availability and access to health care is a function of power to change one’s circumstances.
-Physicians think social condition are more important to address but not confident enough to address
-Physicians believe public roles are important and connected to patient's health but not involved
-disconnect between responsibility of provider vs responsibility of profession
-a focus on self interest issues rather than societal ones
What are the barriers to advocacy (according to study conducted by Robert Wood Johnson & other surveys)?
False - they are LESS likely to do so as they are more engaged for efforts in self-interested gains than broader social ones
T/F: Health professionals are very likely to engage w/ health-related issues at the community level such as through civic engagement and working w/ community organizations
1. identify the problem
2. research & data collection
3. identify target and tools
Taking Action for Advocacy (1):
What are the steps to taking action for advocacy?
True
T/F: Broader social activism is considered a responsibility of the profession rather than the individual provider
When an unresolved problem that requires intervention beyond the scope of typical practices is identified in the course of patient care
Taking Action for Advocacy (2):
What does community advocacy begin with?
research & data collection to identify underlying behavioral, social, and environmental determinants of these problems
Taking Action for Advocacy (3):
Once you define an unresolved problem in patient care, what is the next step?
False - now, you can identify your target for advocacy efforts & a strategy to impact those targets (e.g., what tools you can use)
Taking Action for Advocacy (4):
T/F: The process of taking action ends with identifying the problem
-support legislation or ballot measure
-lobby officials
-vote
-testify at a hearing if its appropriate
strategy for legislative advocacy
-assisting agencies in writing or changing regulations
strategy for regulatory advocacy
-lead change in a leadership position or as a community member
-work with a professional society to influence practice
strategy for institutional advocacy
-initiate an education campaign
-hold a rally
-demonstration or press conference
-participate in media or social media campaigns
-write opinion pieces
strategy for public advocacy
Episodic: writing letters to the editor, publishing opinion pieces in media, calling/writing to legislators, meeting w/ reps or senators, voting, phone bank, joining a campaign
Longitudinal: run for elected office, conduct research, serve on board of directors, lead healthcare organization, form community coalition
What are the 2 types of health professional community advocacy activities? Give examples!
letter to the editor
concisely written response to a newspaper about a recent article or a issue facing the community
commonly read by decision makers to gauge public opinion
public medical writing
longer form narrative to be published by outlets such as medical journal, local newspaper, blog, community weekly
-share personal experience and present arguement
social media campaign
-sue of social media to broadcast an advocacy message
-format to build a like-minded community and communicate directly to influencers
lobbying
meeting to educate and persuade an elected official on an advocacy position
Developing a relationship and offering oneself as a resource to an elected official
organized involvement
involvement and leadership in a professional society or advocacy organization
-forum to meet like minded colleagues and coordinate activities for larger scale change
1. ask question
2. review medical evidence - to support claim that something is wrong
3. collect stories - what are their individual stories
4. engage with community groups - joining maternal family health services
5. get involved with a professional society - ASPA, surgical PAs, etc.
6. vote
what are the steps for advocacy