Animal nutrition lab practical study guide
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What are the 8 categories of feed?
Roughsges
Describe roughages/forages/silages & haylaged
>18% crude fiber (CF)
Animal is harvesting themselves
Hay needs to be dried out to be out in storage for winter: if not done properly (not to dry and not to moisture) it can cause dryness to breaking or spontaneously combustion due to microb
Silage: immediately stored in anaerobic conditions. 65-70% moisture-To test squeeze it
Haylage: 40-50% moisture
Describe energy feeds
<18% CF and < 20% crude protein (CP)
Describe protein supplements
>20% CP
Unless heat treated before hand they can inhibit digestion
Describe mineral/vitamin supplements
Added to base rations (more is not better)
Source: are individual or feed source
Describe non-nutritive additives
Enhance effectiveness of nutrients
Not a nutrient
Function in gut and target gut cell wall
Includes anti microbial, probiotics, antibiotics, and anti fungal, buffers, enzymes, hormones, medicines, modifiers of rumen fermentation
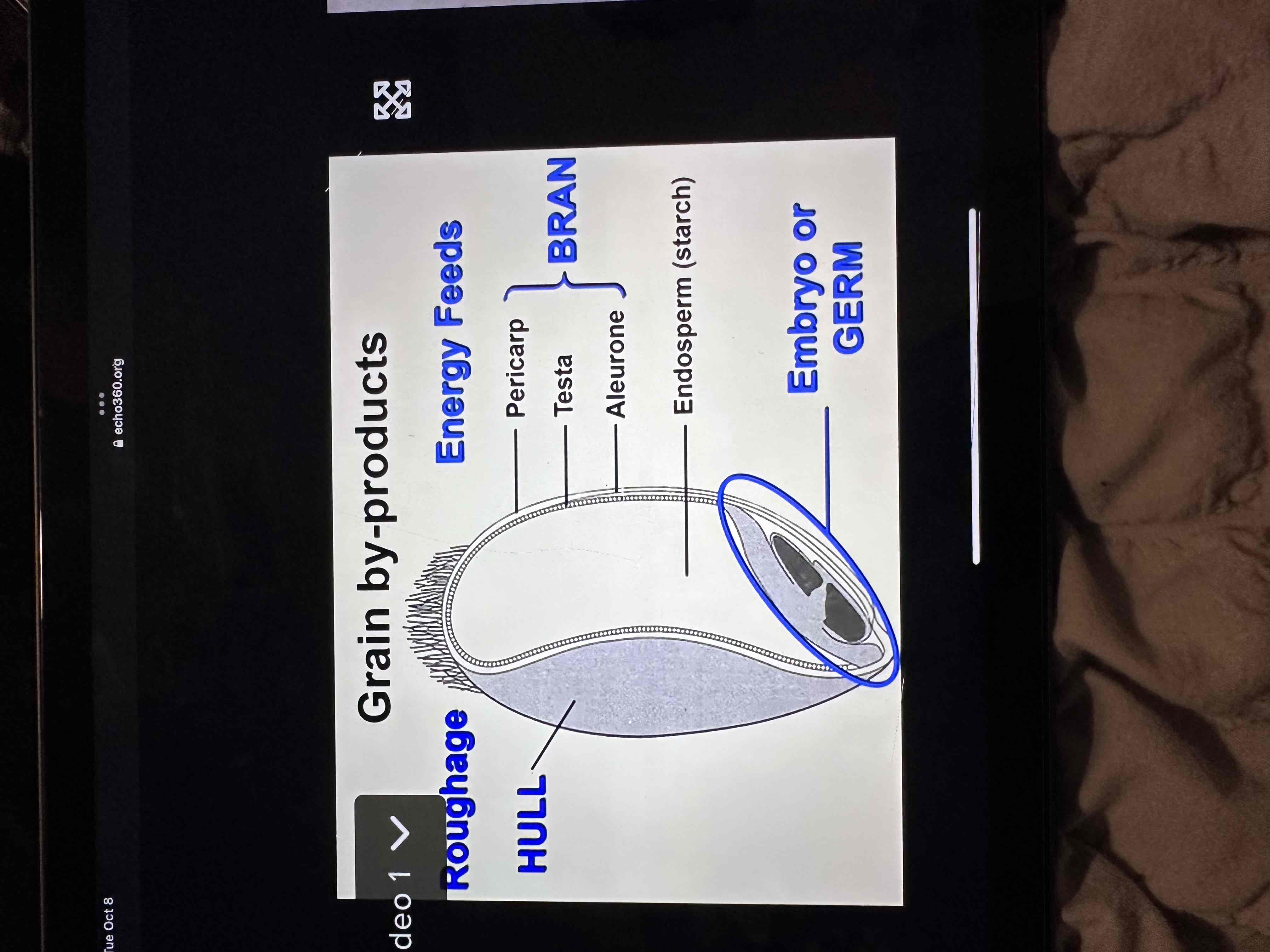
Diagram parts of seed and tell what feed classification these fractions fall into?
Describe different types of non-nutrient additives
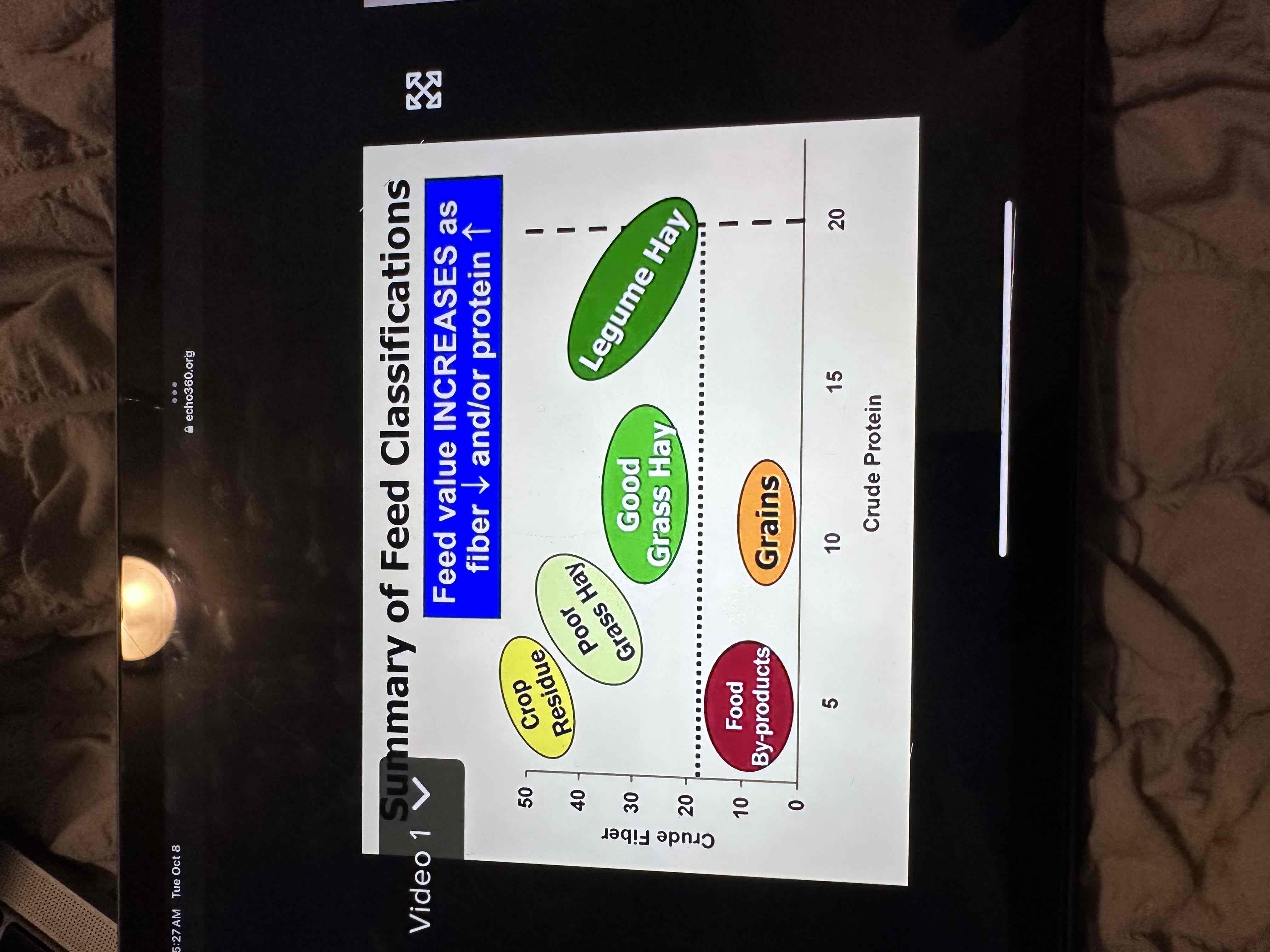
Summaries feedstuffs according to their fiber and protein content?
Describe different parts of a feed label?
A. Requirements
Product name
Brand name (if any)
Animal it’s intended for
Guaranteed analysis (max and mins)
List of ingredients
Directions for use (warnings (if any)) -medicated
Name and address of manufacture
Net weight - product in bag
B. Feed label ingredients
May be listed as individual feeds or product groups
C. Calcium: phosphorus ratio
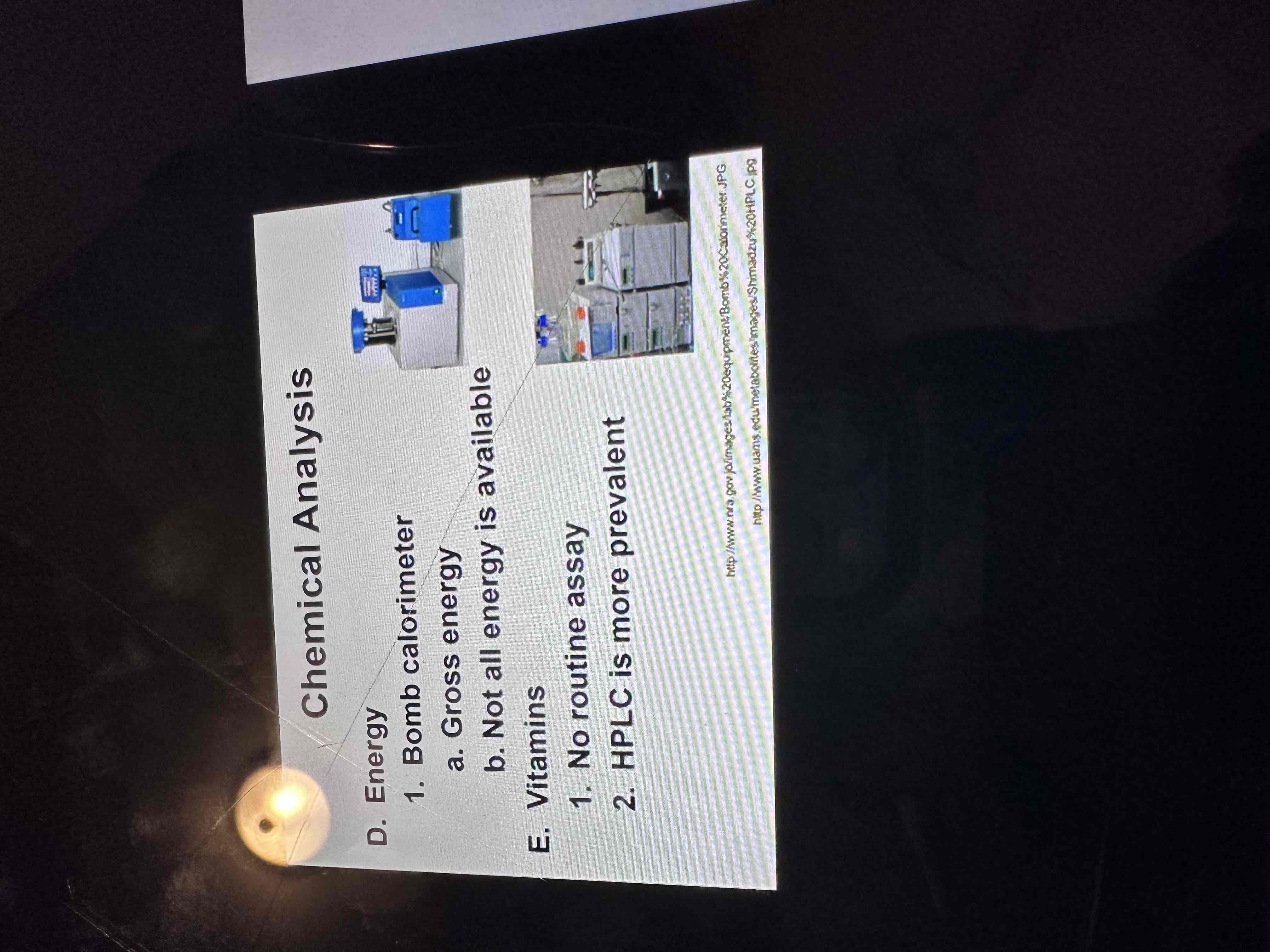
Define primary differences bw the 3 types of nutritive analyses of feed
Chemical analysis
Nutrient content
What’s presented to the animals
fairly quick and inexpensive to analyze
Biological analysis
Use animals
Measure utilize of nutrients
Best way but costly and tedious
Microbiological analysis
Measure ability of microbes to use feed
Intermediate
Chemical analyzes
Proximate analysis
Developed in Germany 100 yrs ago
Mostly commonly used
Crude methods - possible errors
6 fractures
-water, ash, CP, ether extract (EE), CF, Nitrogen Free Extract (NFE)
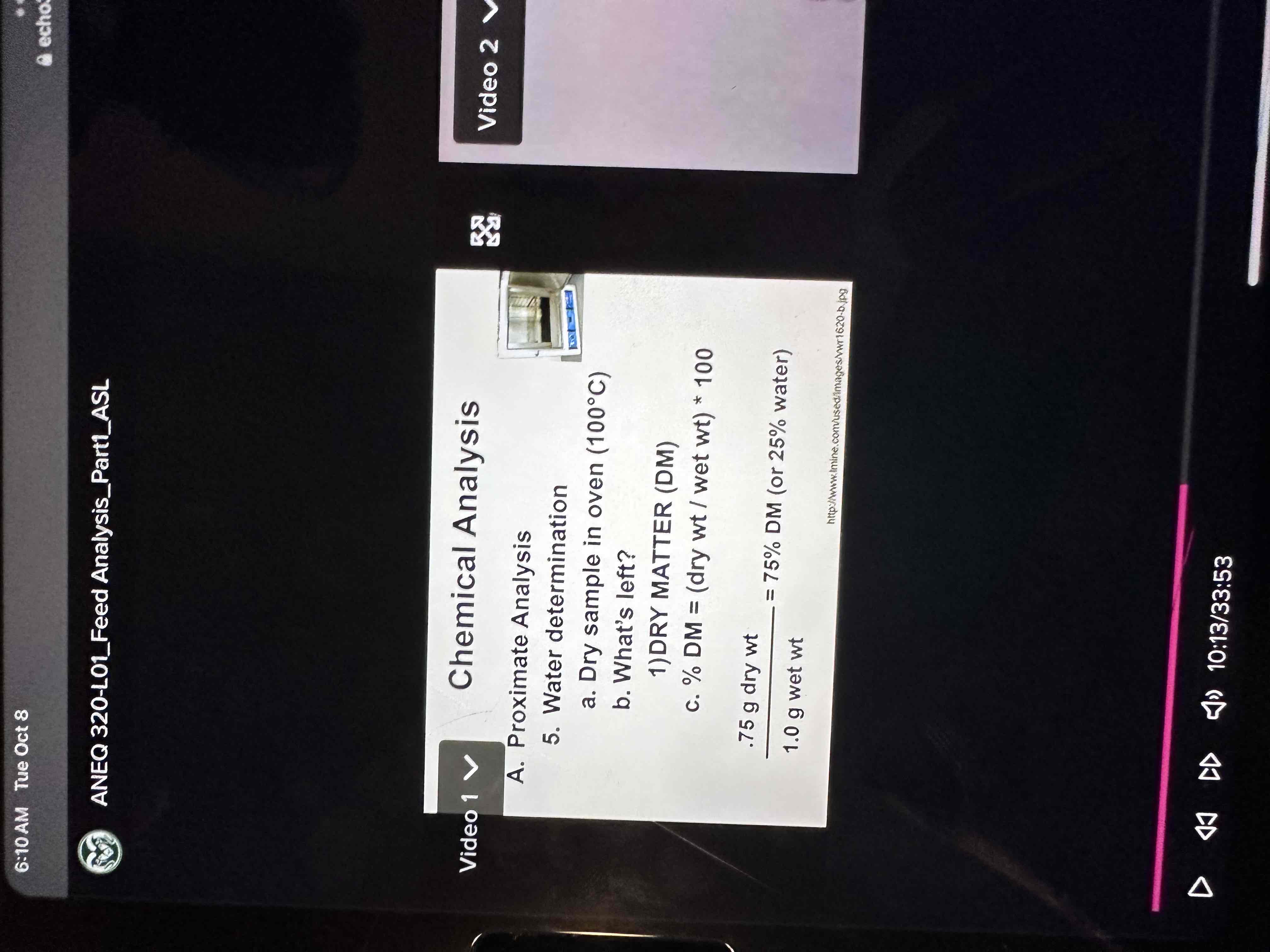
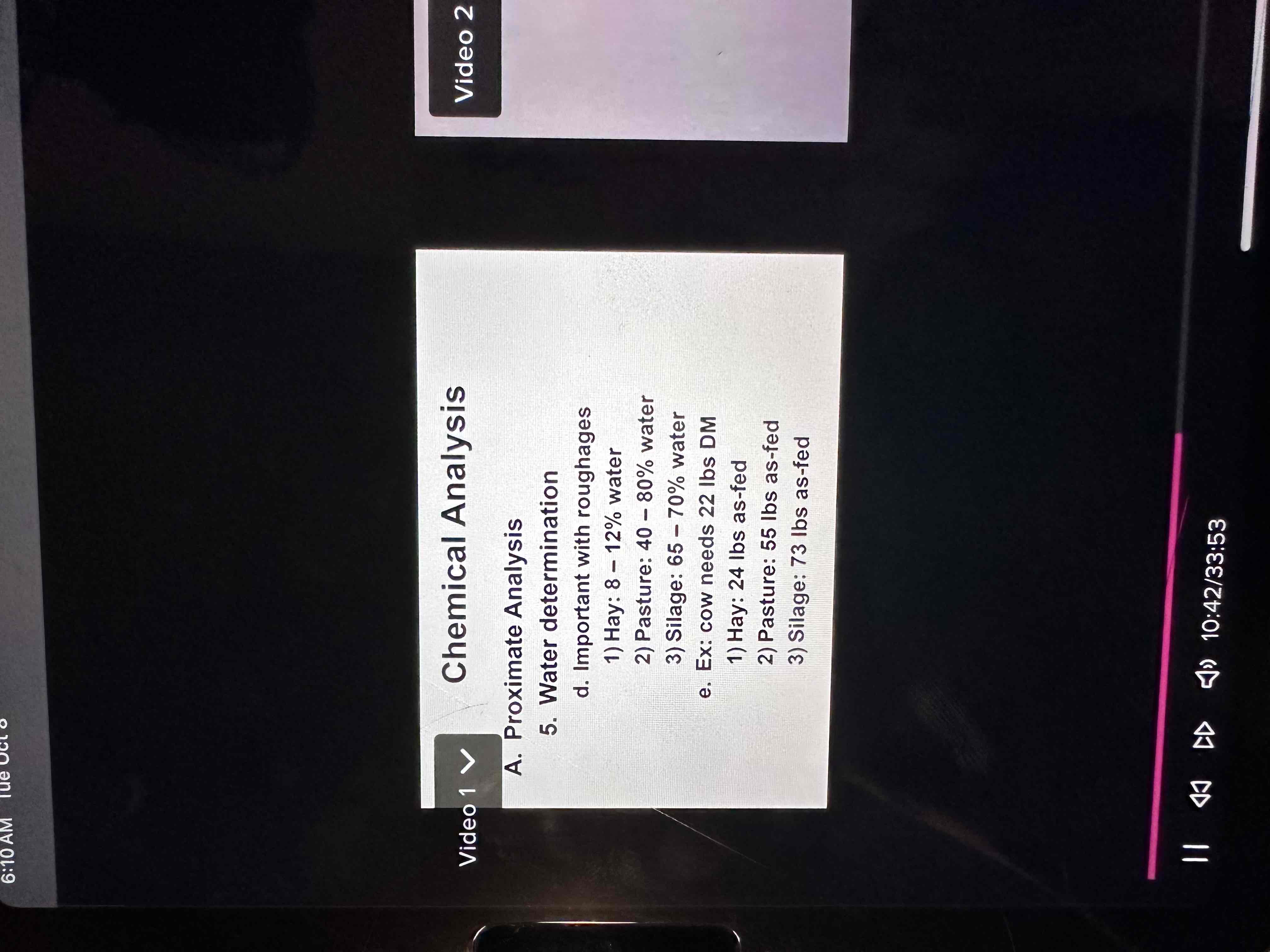
Water
For equation- always adds to 100
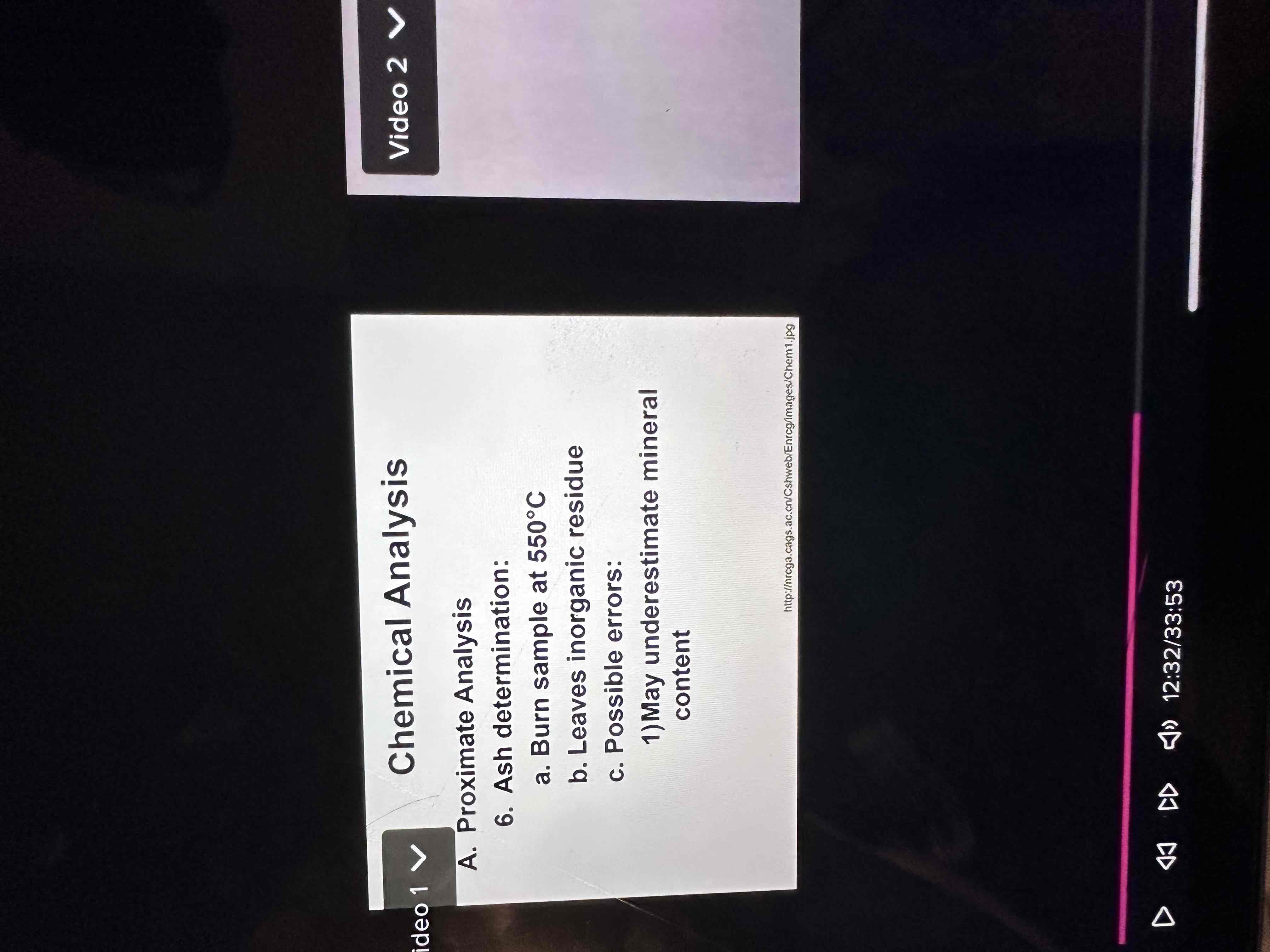
Ash

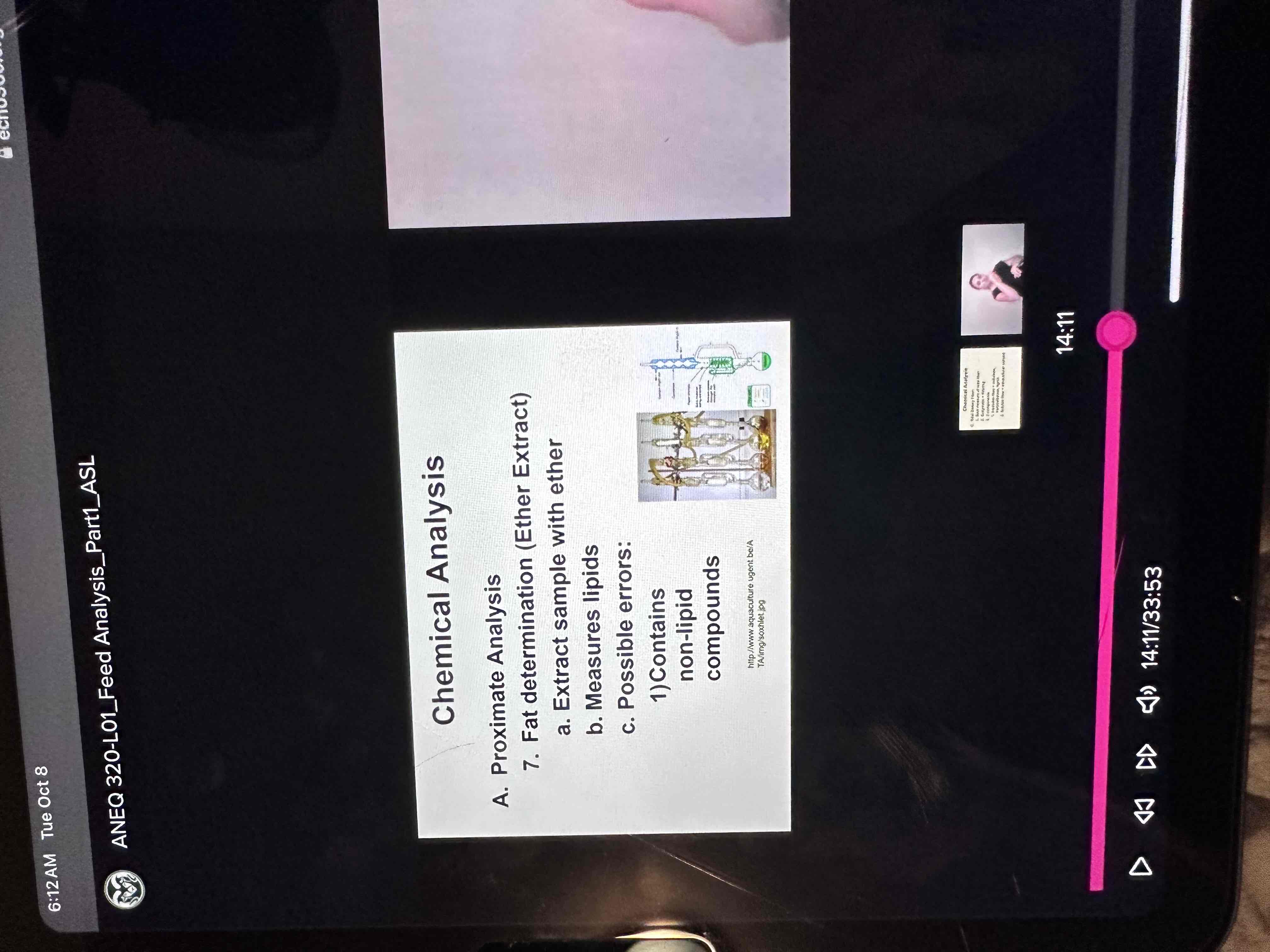
Ether extract
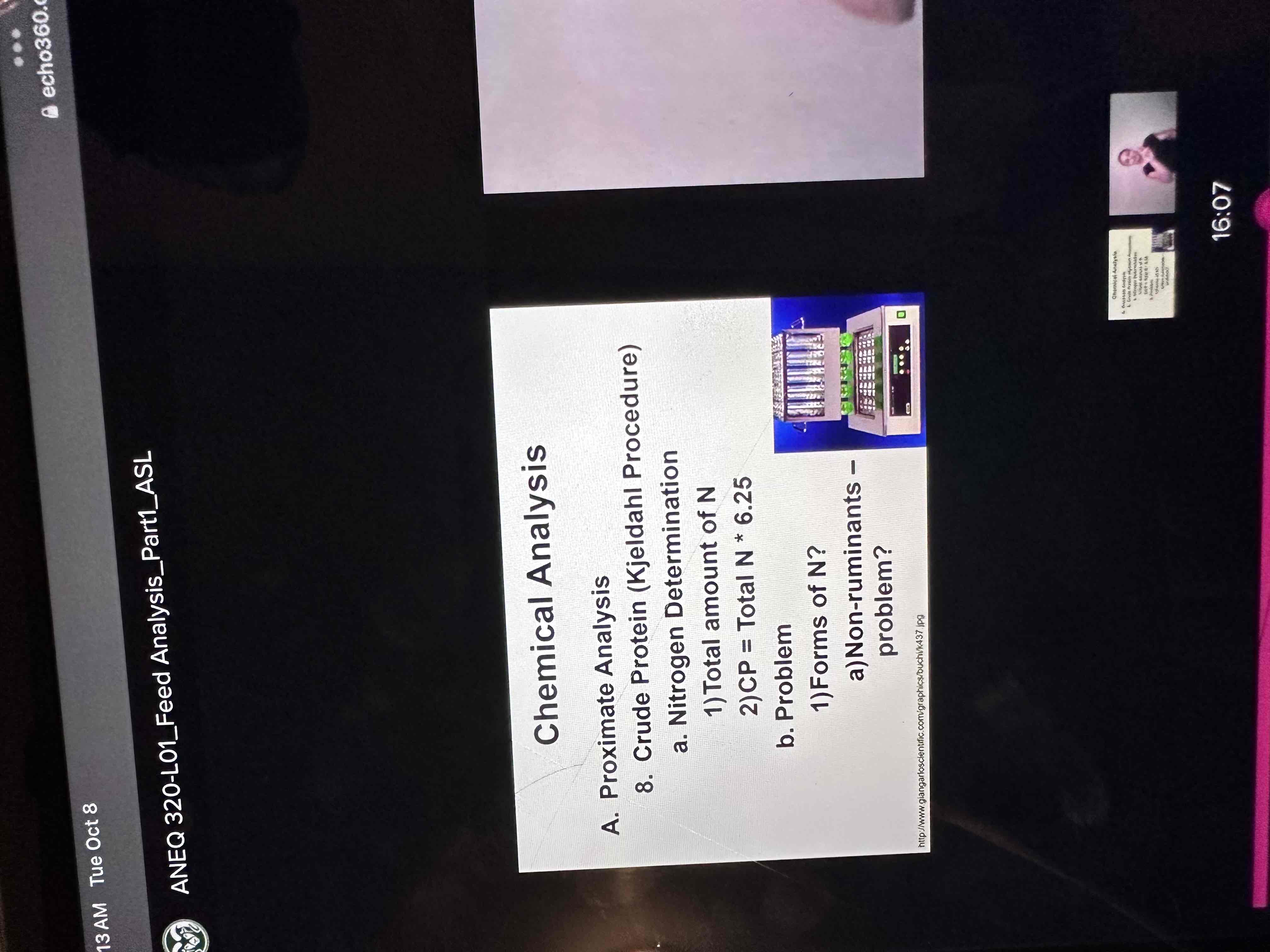
Crude protein
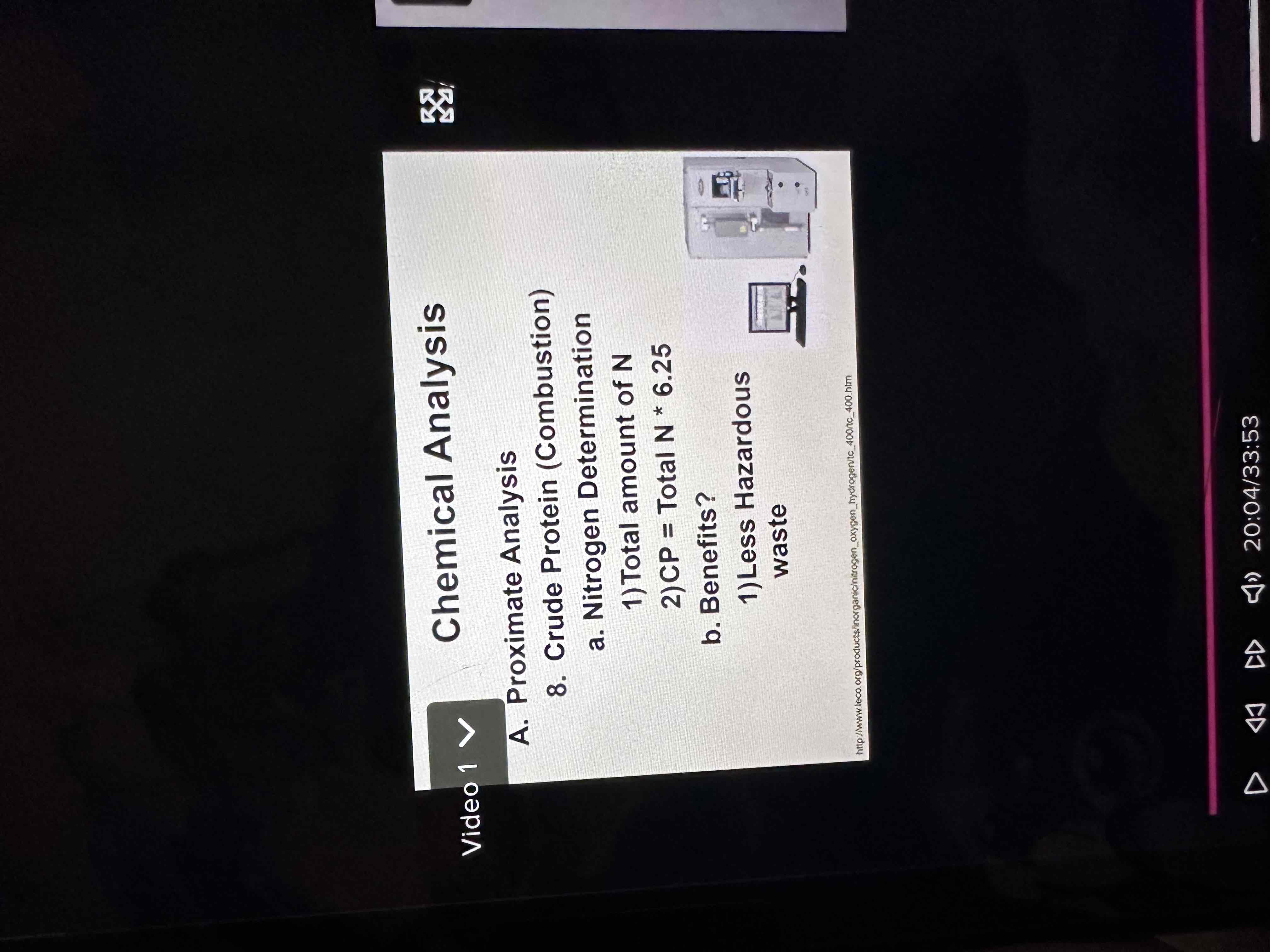

Carbohydrate determination
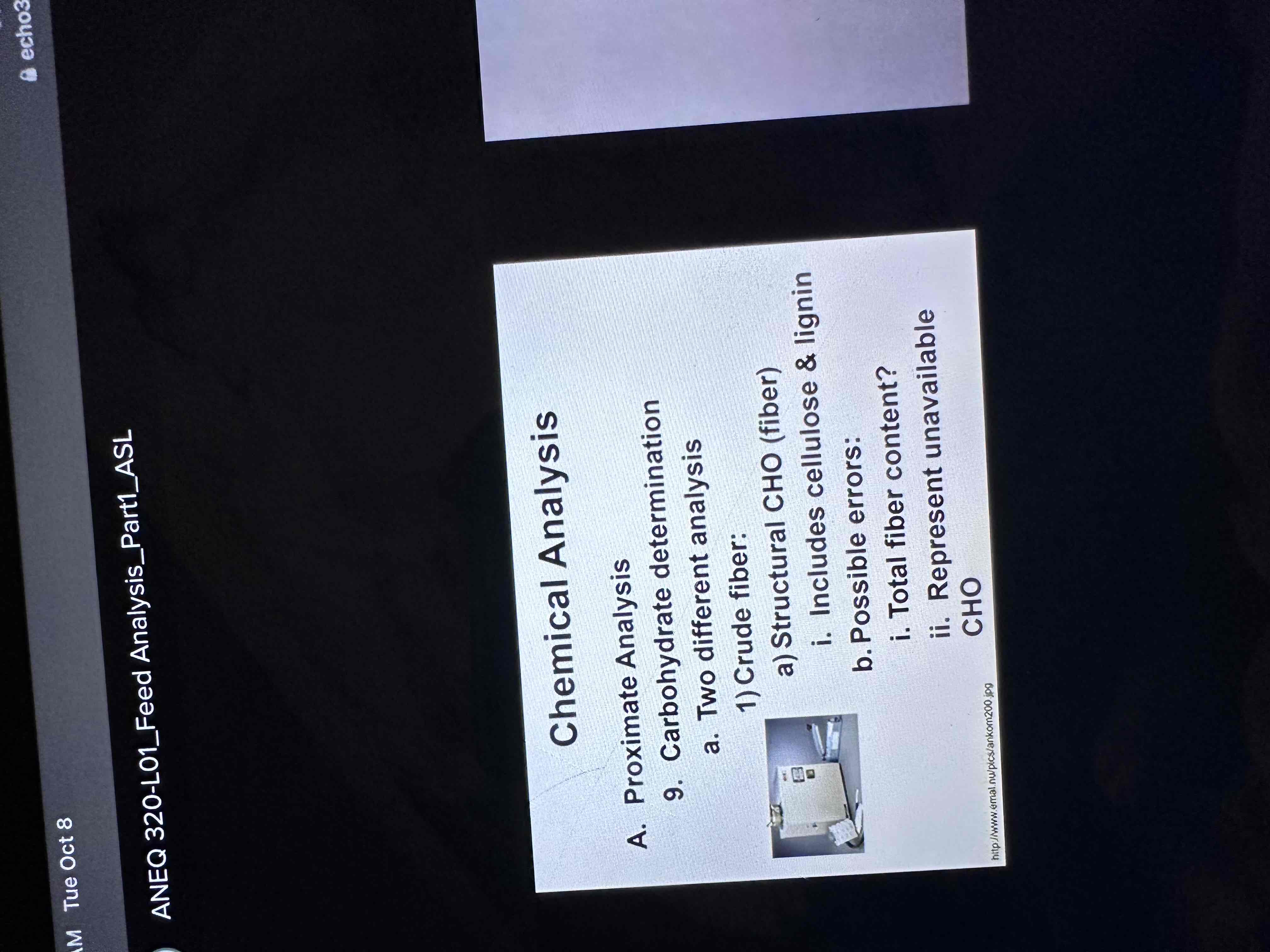

Carbohydrate determination
List components of Proximate Analysis, nutrients they include, & potential error

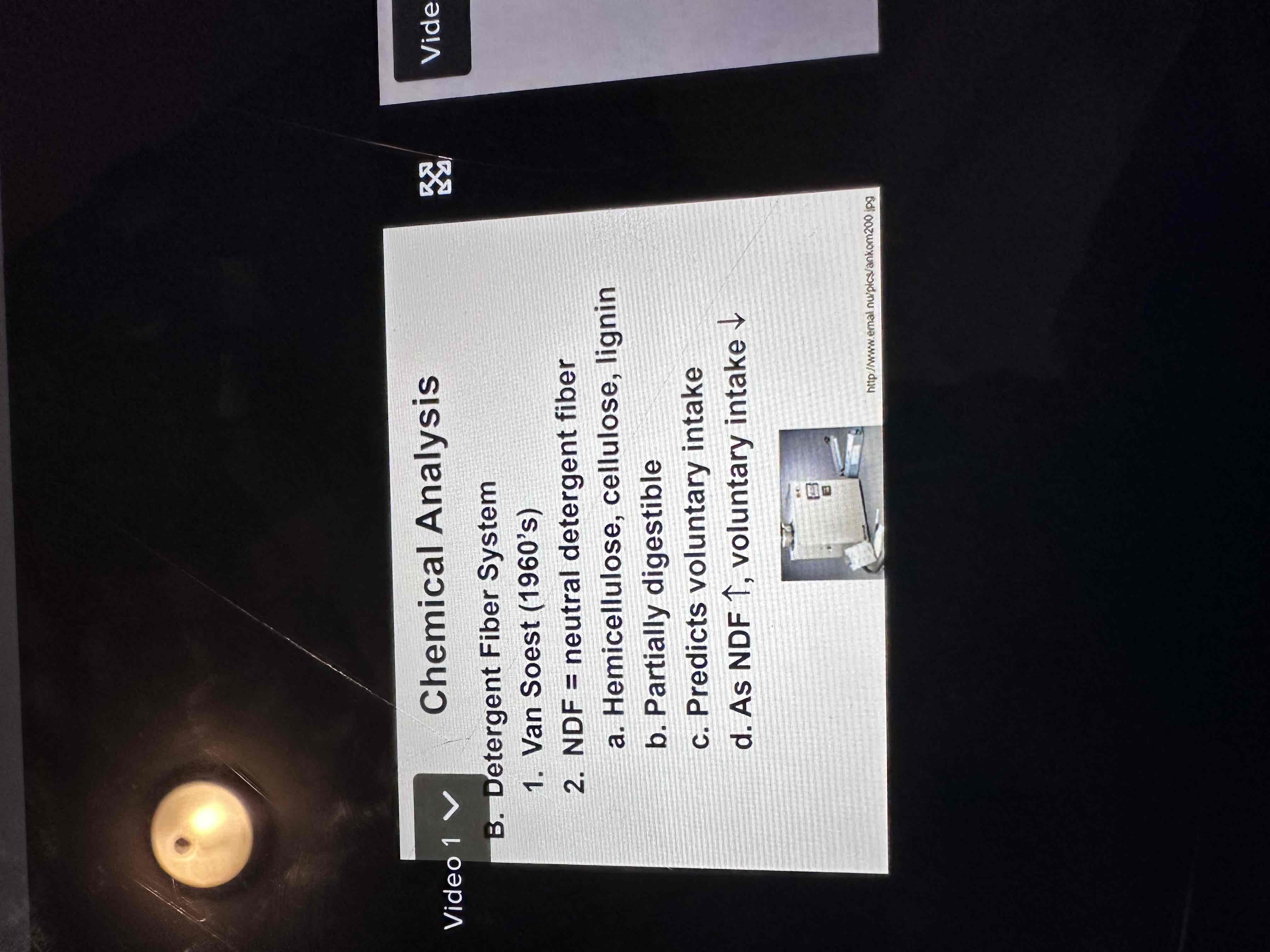
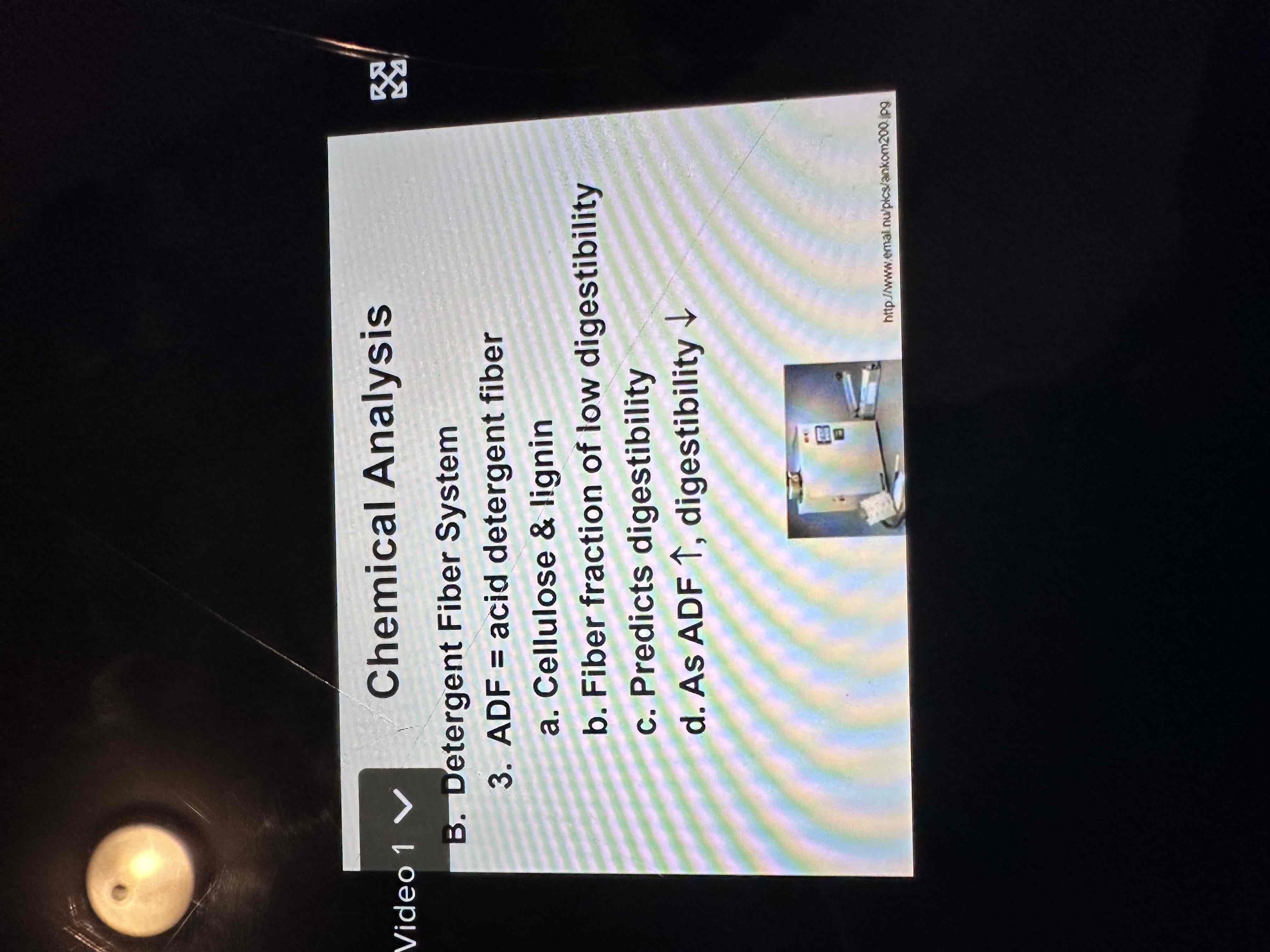
What’s included in ADF or NDF?

What’s included in insoluble & soluble fiber within the TDF system?

Describe partitioning of energy?
Calculate TDN?
Make sure to get a representative sample
Good sample
Classify the digestive system
Nutrient metabolism is similar for all animals
The differences are how the animals process the feed and what the feed is
Digestive tract differ for what they eat determines what the animal can eat
Classification of digestive system
A. Based on
Anatomical differences - ruminant or nonruminant
Dietary differences -carnivorous(enzymatic digestion, short GI tract), omnivorous(eat plant and animal tissue, enzymatic and some microbial), herbivorous(microbial fermentation, ruminant -most nutrients in small intestine absorption) ruminants are true herbivores. Nonrument - microbial digestion after enzymatic digestion, hind gut)
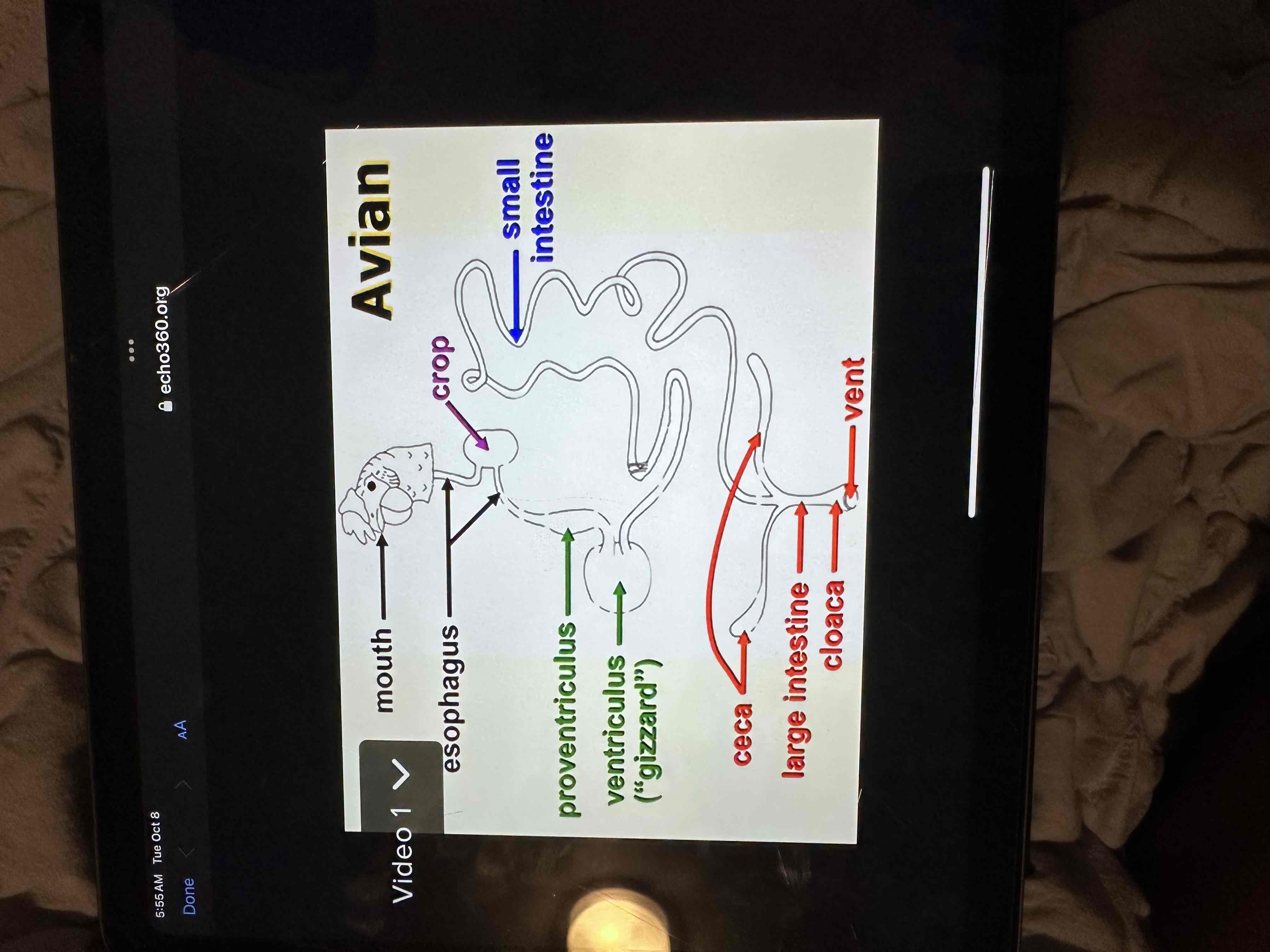
Label anatomy of each species - Poultry

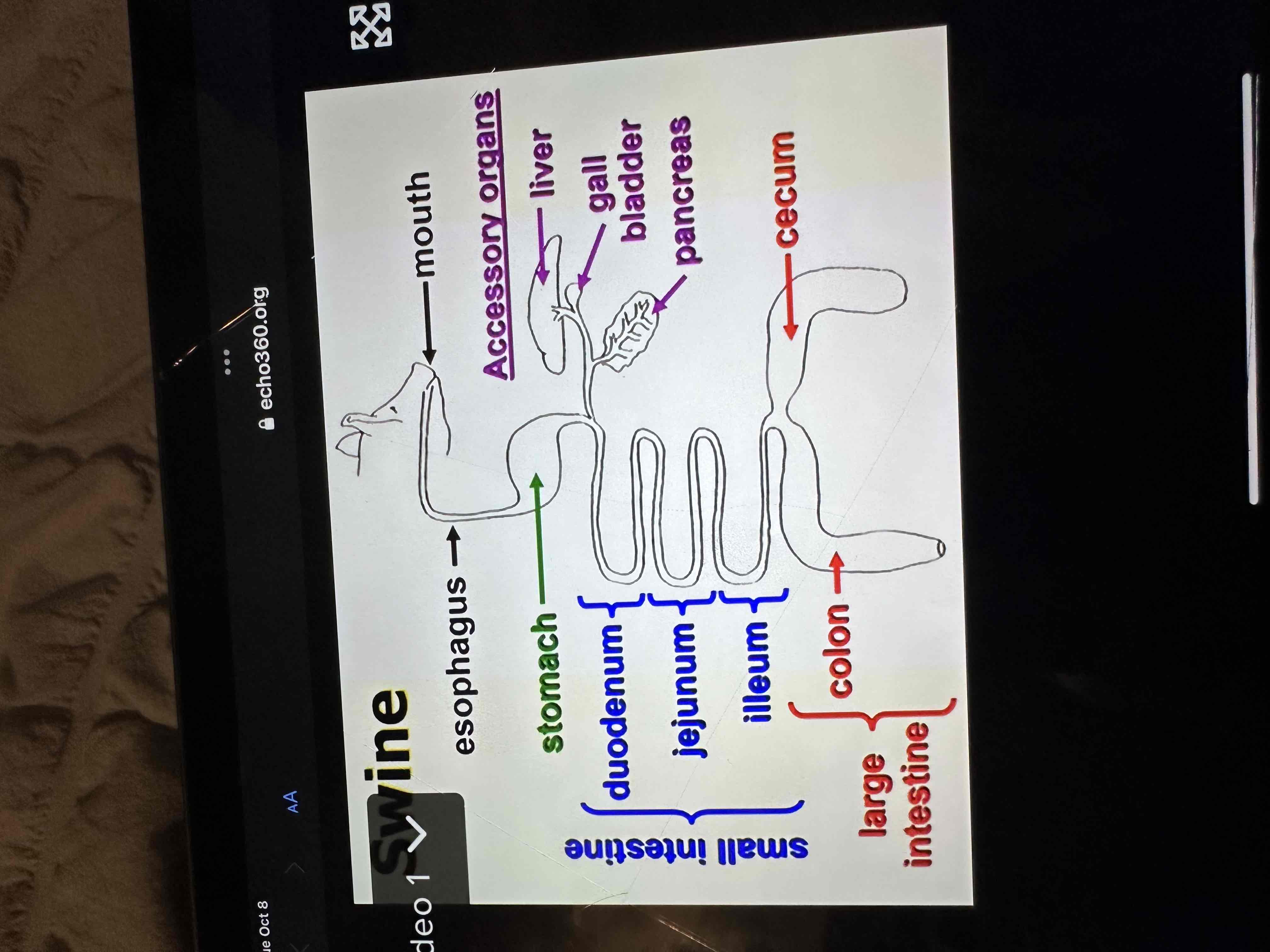
Label anatomy of each species - Swine

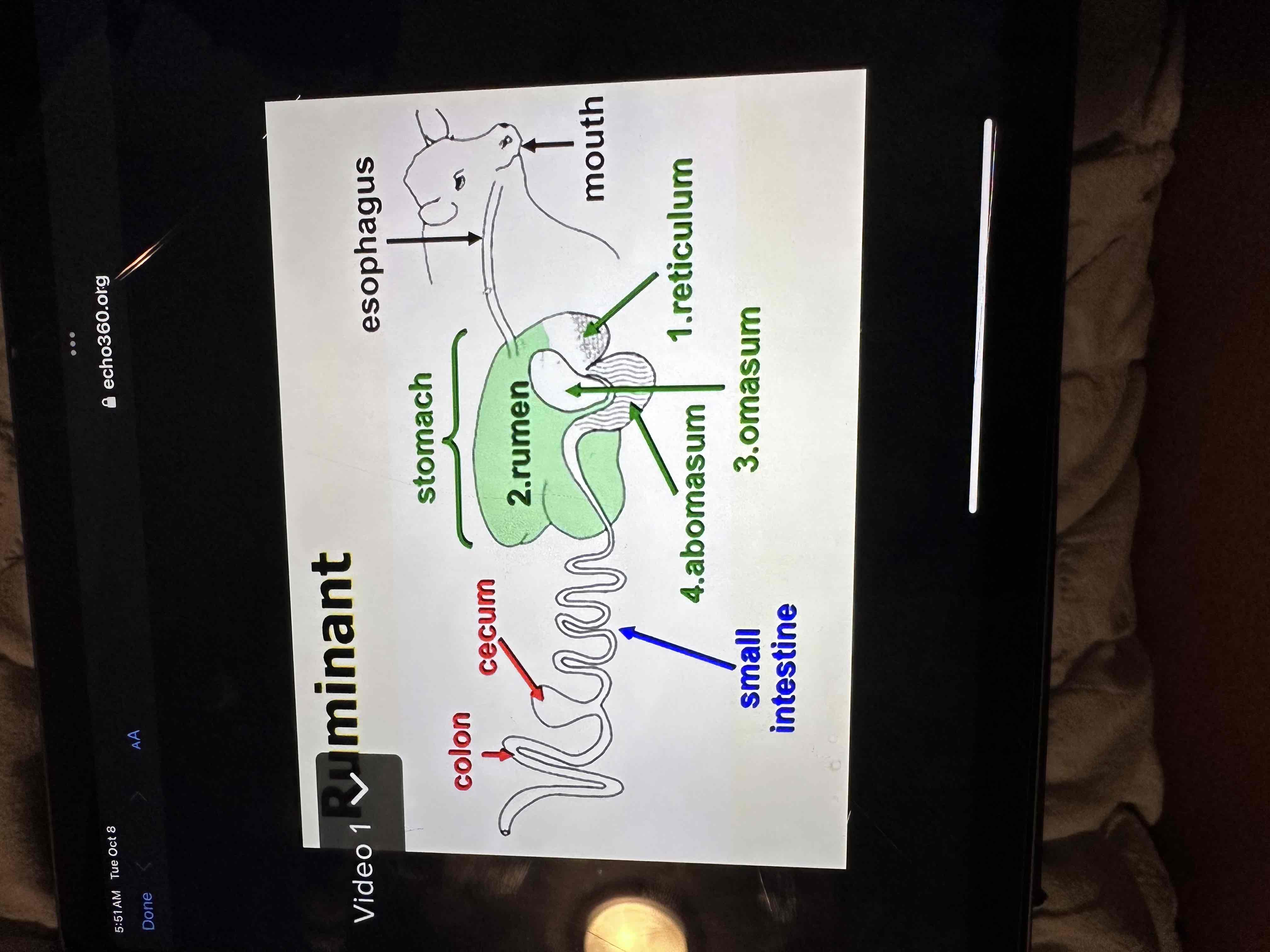
Label anatomy of each species - Ruminants
They also have the other organs like the swine just not in image
Reticulum - honeycomb structure- microbial fermentation, pacemaker, hardware disease
Rumen- papillae- they get bigger or smaller depending on food
Omasum / many folds- filter
Abomasum on looks like nonruminent
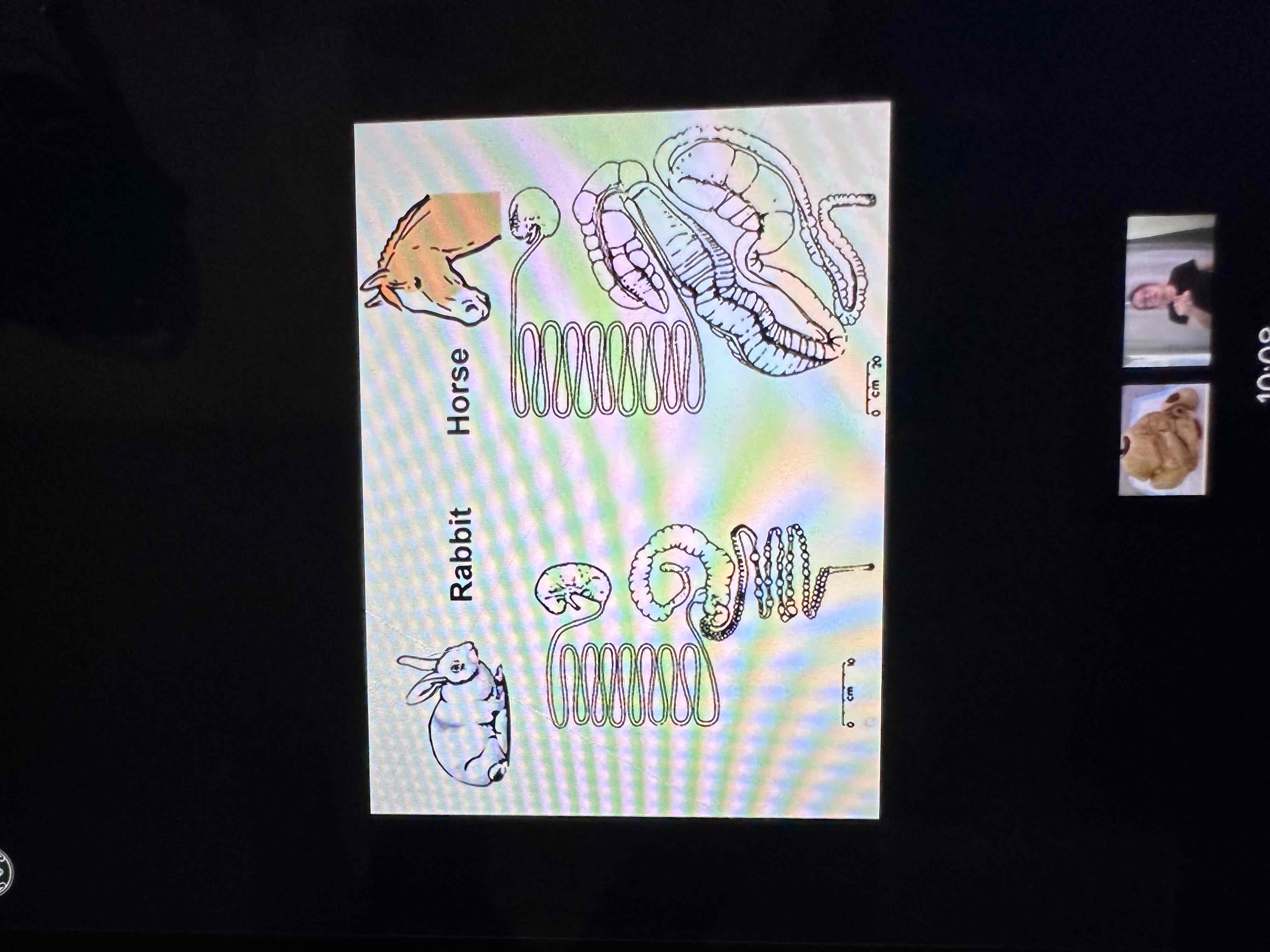
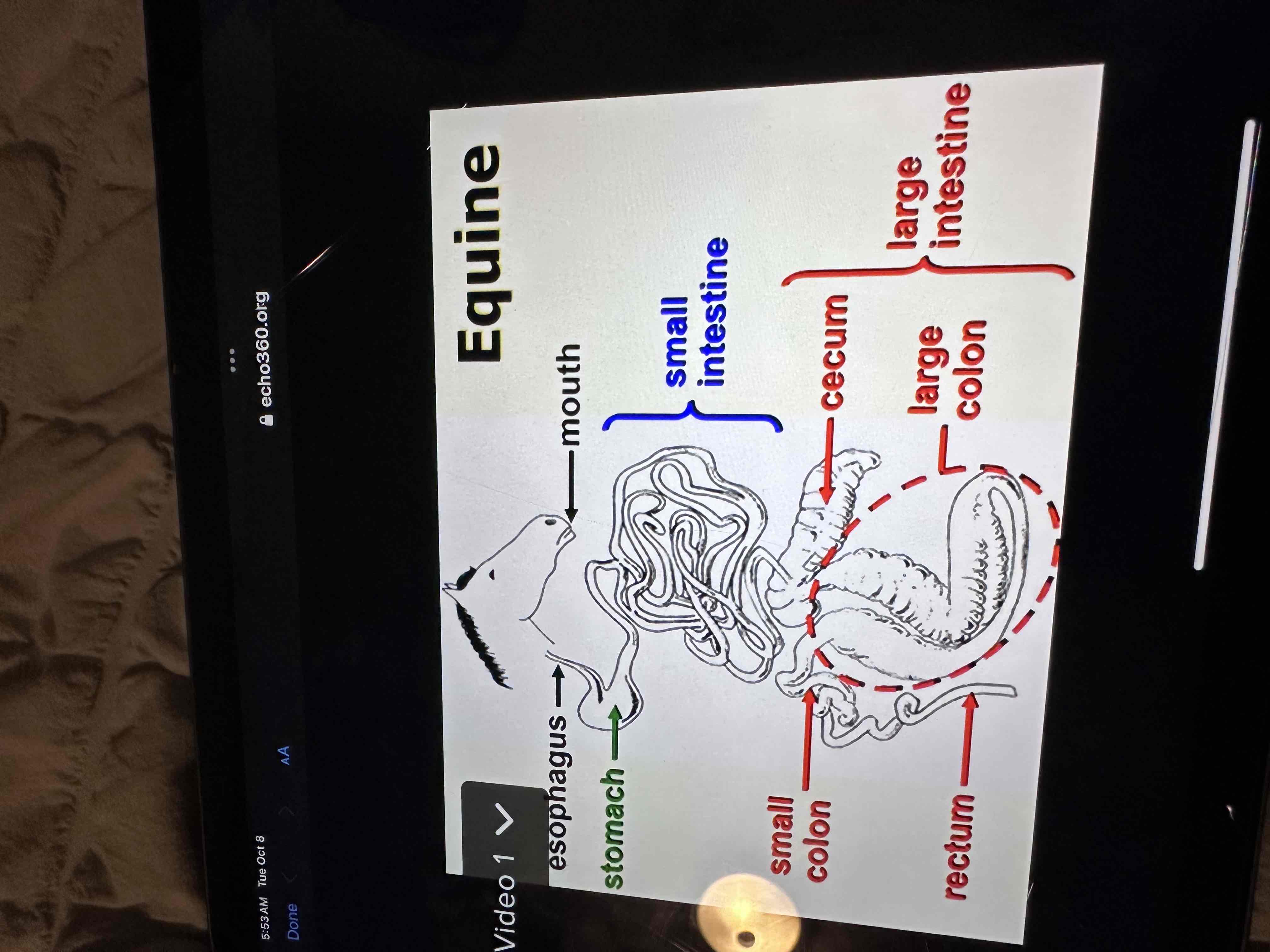
Label anatomy of each species - Horses
Massive large intestine
Hind gut
No gallbladder
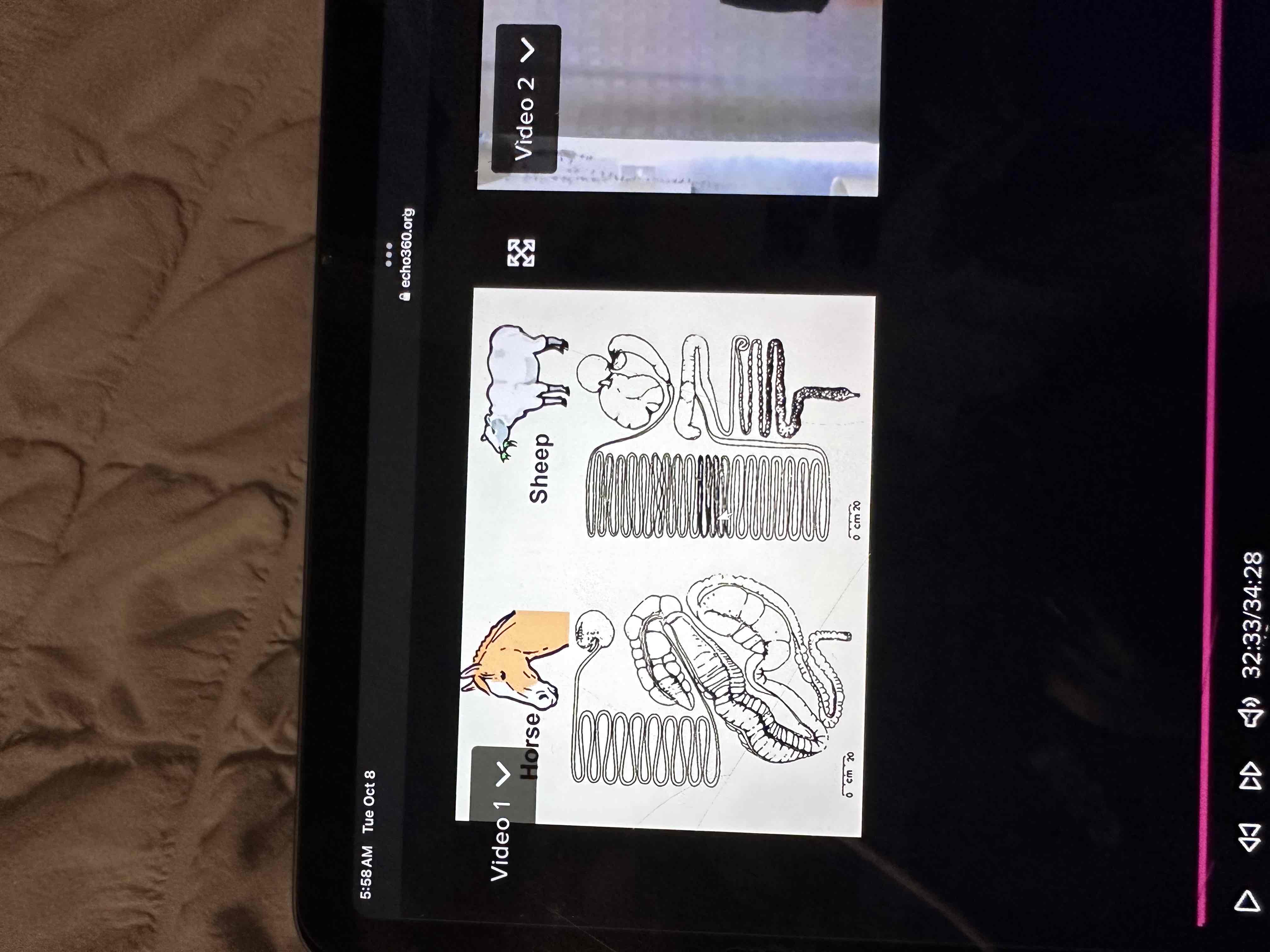
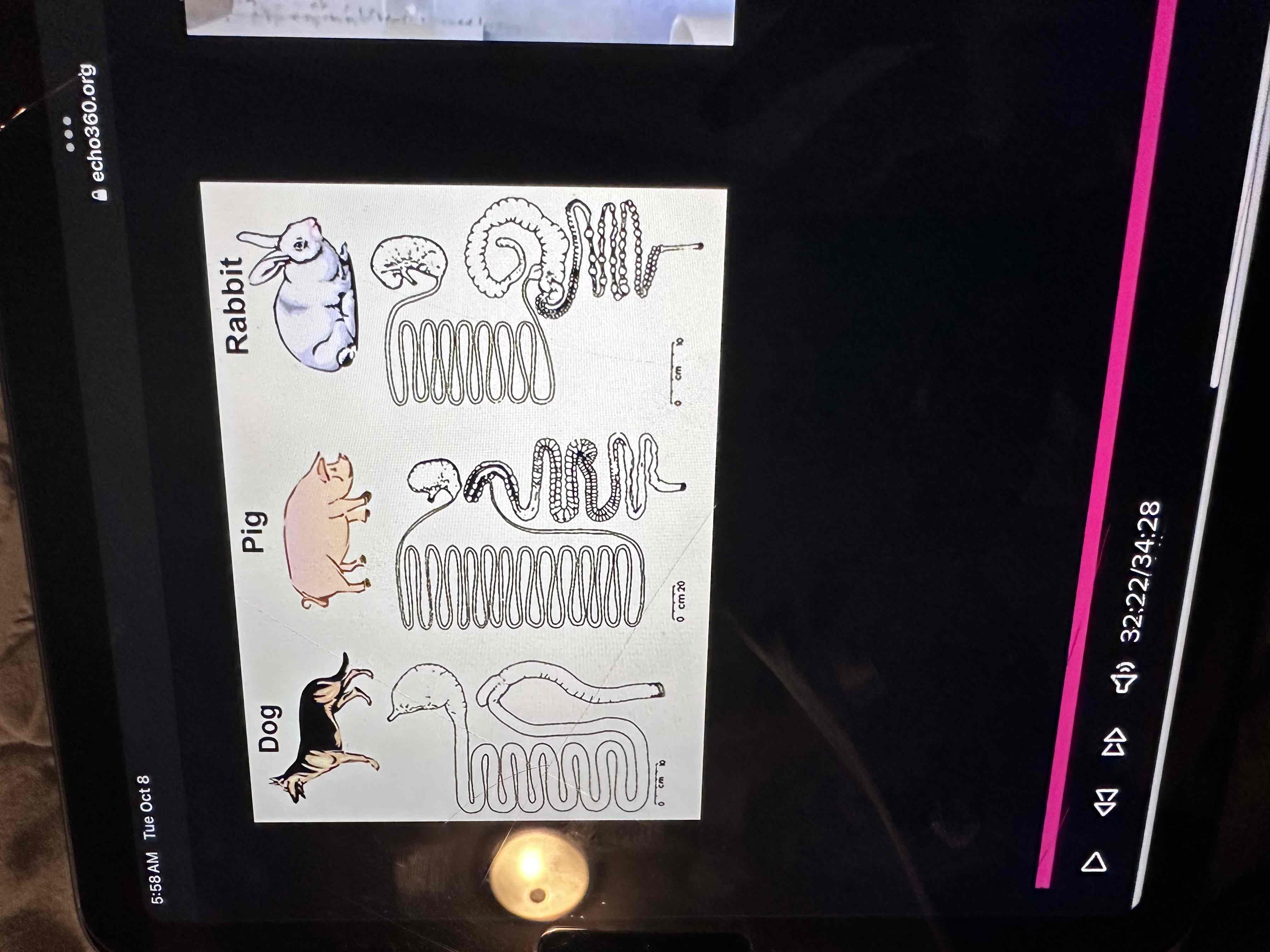
Compare and contrast the digestive anatomy among poultry, swine, ruminants, and horses?
Avian digestive system
No teeth
Crop - storage
Proventriculus -true stomach
Ventriculus -gizzard (grit is added to food to act like teeth)
Ceca (2cecums) - related to flight blance
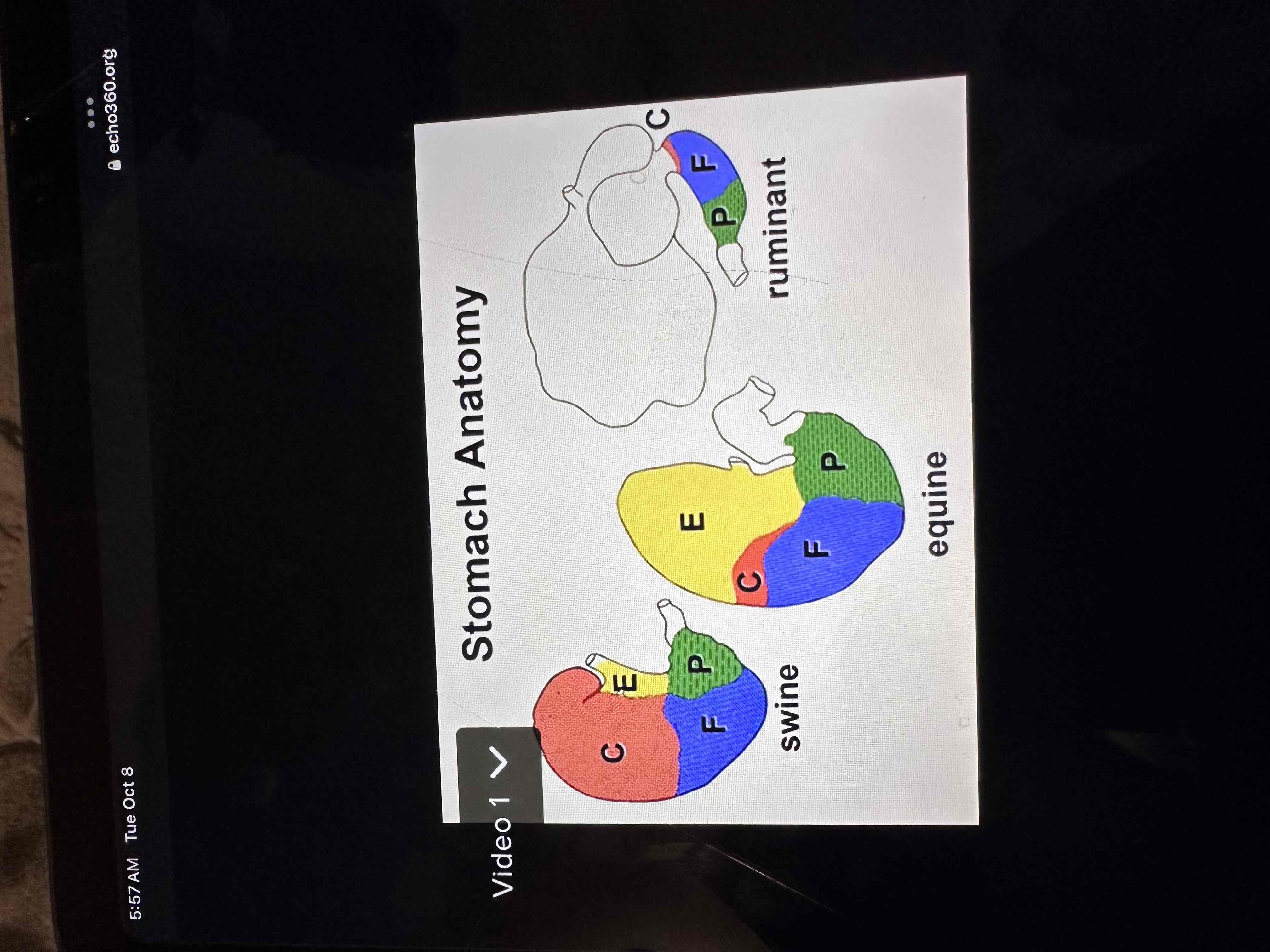
Stomach anatomy
4 regions
Esophageal
Cardiac
Fundic
Pyloric