CO3 - Analytic Geometry and Conic Sections
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Equations of Lines, Circles, Conic Sections: Parabola, Ellipse, Hyperbola
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
straight line
shortest path between two points
Standard Form of Line
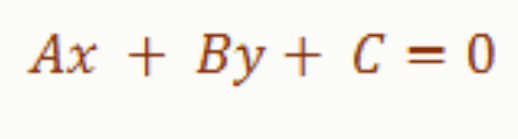
slope
measure of steepness
inclination
Positive angle measured counterclockwise from the x-axis to a nonhorizontal line
m=tanθ
If a nonvertical line has inclination θ and slope m
Slope of a Line
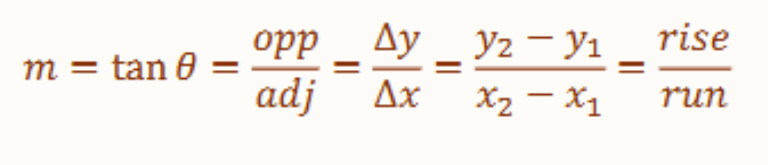
x-intercept
Point where line intersects with the x-axis
y-intercept
Point where line intersects with the y-axis
Slope-Intercept Form
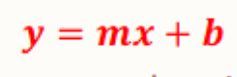
Point-Slope Form
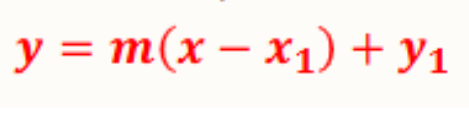
Two-point Form
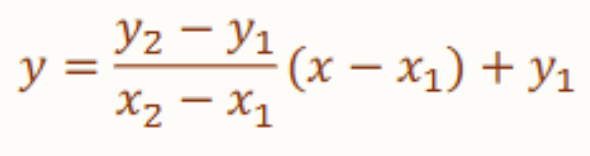
parallel lines
Lines with equal slopes
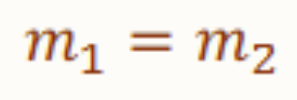
perpendicular lines
The slope of one line is the negative reciprocal of the other.
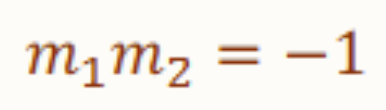
perpendicular lines
Finding the distance between a line and a point not on the
line is an application of __________.
Distance Between a Line and a Point
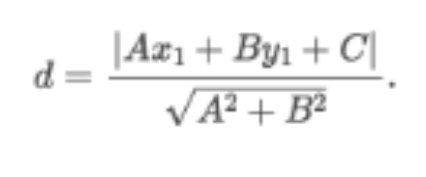
circle
a set of points that are equidistant from a fixed point, C(ℎ, 𝑘)
center
C(ℎ, 𝑘)
radius
The fixed distance 𝑟 from the center to any point on the circle
Standard Form of the Equation of a Circle
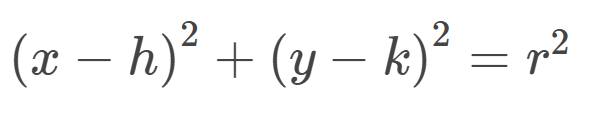
Equation of a Circle Centered at the Origin

General Equation of a Circle
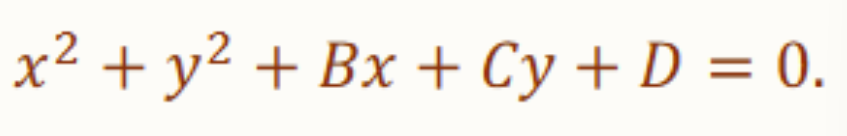
conics
Curve obtained from a cone’s surface intersecting a plane
conic sections
Parabolas, Ellipses, Hyperbolas
parabola
The set of points in a plane that are equidistant from a fixed line, the directrix, and a fixed point, the focus, not on the directrix
axis of symmetry of the parabola
The line that passes through the focus and is perpendicular to the directrix
vertex of the parabola
The midpoint of the line segment between the focus and the directrix on the axis of symmetry
vertex of the parabola
The midpoint of the line segment between the focus and the directrix on the axis of symmetry
latus rectum
The line segment that passes through the focus and is parallel to the directrix, and with endpoints on the parabola
ellipse
The set of all points in a plane such that the sum of the distances of P from two fixed points and of the plane is constant.