Biochemistry Chapter 2
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
In the structure of DNA, the bases in complementary strands interact through ___, while the bases within one strand interact through ___; lastly, phosphodiester groups interact with magnesium ions through ___
hydrogen bonds; pi-pi interactions; ionic interactions
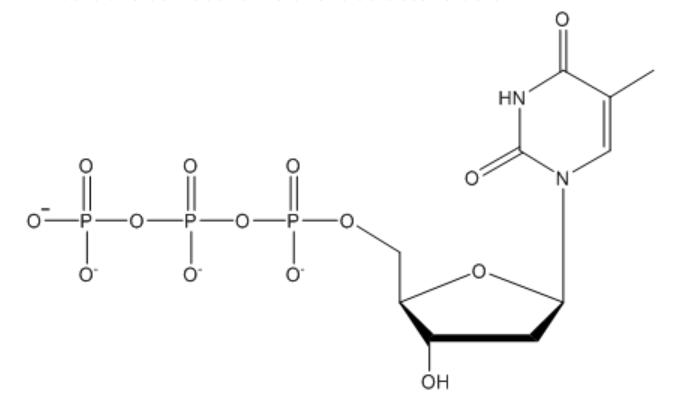
What is the correct name of the structure?
2-deoxythymidine triphosphate
phosphothymidylate
2-deoxythyminidine
thymidylate triphosphate
2-deoxythymidine triphosphate
Which of the following statements about DNA and RNA is TRUE?
DNA is synthesized in the 5’ to 3’ direction, whereas RNA is synthesized in the 3’ to 5’ direction
DNA has a major groove whereas RNA has a minor groove
The nitrogenous bases that are commonly found in both DNA and RNA are adenine, guanine, and cytosine
DNA forms a double-stranded helical structure that contains base pairs whereas RNA is single stranded and does not form base pairs or adopt a double helical conformation
The nitrogenous bases that are commonly found in both DNA and RNA are adenine, guanine, and cytosine
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding phosphodiester bonds that link adjacent nucleotides in both RNA and DNA?
Phosphodiester bonds join the 3’ hydroxyl of one nucleotide to the 5’ hydroxyl of the next
Phosphodiester bonds are uncharged at pH 7.0
Phosphodiester bonds always link G with C and A with either T or U
Phosphodiester bonds are positively charged
Phosphodiester bonds join the 3’ hydroxyl of one nucleotide to the 5’ hydroxyl of the next
Nucleotides play a central role in living organisms because ___
they mediate transport of energy within the cell
they are involved in oxidation-reduction reactions
they are involved in intracellular signaling
they function as building blocks for nucleic acids
all of the above
all of the above
Which group is attached to the pyrimidine ring in thymine and is not present in uracil?
ribose
-CH3
-NH2
deoxyribose
none of the above
-CH3
Inside our cells, free nucleotides are almost always associated with ___
cholesterol
Mg2+ counterions
proteins
Cl- counterions
fatty acids
Mg2+ counterions
Nucleoside triphosphates carry energy in the form of ___
amide linkages
glycosidic bonds
phosphoester bonds
hydrogen bonds
phosphoanhydride bonds
phosphoanhydride bonds
Knowledge about the tautomeric forms of the bases of nucleic acids is needed ___
to understand H-bonding between the complementary bases
to distinguish the 5’ end of a DNA strand from the 3’ end
to understand how bases are linked to deoxyribose
to understand how the bases are linked to ribose
to understand the ability of nucleotides to act as energy carriers
to understand H-bonding between the complementary bases
Describe the structure of DNA molecule by listing the characteristics.
1) DNA forms a double ___
2) The two strands run ___
3) The sugar is ___
4) The sugar-phosphate groups ___
5) The location of the bases are ___
6) The bases are planar, and their plane is orientated ___ to the axis of the helix
7) There are ___ bases: ___, ___, ___, ___
8) The strand are held together by H-bonding between complementary bases: ___ to ____, and ___ to ___
9) The helix has a minor and a major ___ on its surface
1) helix
2) antiparallel
3) deoxyribose
4) are on the outside of the helix
5) are in the center of the helix
6) perpendicular
7) four; adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine
8) A-T, G-C
9) groove
What type of bond is made between nucleoties?
ester
phosphoester
phosphodiester
glycosidic
none of the above
phosphodiester
Which of the following correctly describes the B-DNA double helix?
antiparallel strands
right-handed helix
base pairs are located in the center of the helix
one helical rotation has a rise of 3.4 nm
all of the above
all of the above
Phosphodiester bonds link DNA monomers to form a polymer by which mechanism?
The OH group on the C-2 in the 2-deoxyribose monosaccharide forms a covalent bond to elongate the DNA polymer
The OH group on C-2 in the ribose carbohydrate forms a covalent bond to elongate the DNA polymer
The OH group on C-3 in the 2-deoxyribose carbohydrate forms a covalent bond to elongate the DNA chain
The OH group on C-3 in the ribose carbohydrate forms a covalent bond to elongate the DNA chain
The OH group on C-3 in the 2-deoxyribose carbohydrate forms a covalent bond to elongate the DNA chain
What is the purpose of DNA polymerase?
It facilitates annealing
It is required for transcription in order to generate more DNA
It adds the correct nitrogenous base to the template strand
It is used to replicate DNA in the 5’ → 3’ direction
It is used to replicate DNA in the 5’ → 3’ direction
In most organisms, replication proceeds in a ___ manner from the ___
bidirectional; replication origin
bidirectional; theta site
bidirectional; lagging strand
unidirectional; chromosome ends
none of the above
bidirectional; replication origin
Polypeptide synthesis proceeds from the ___ to the ___
C-terminus; N-terminus
peptidyl site; aminoacyl site
N-terminus; C-terminus
entrance site; exit site
50S subunit; 30S subunit
N-terminus; C-terminus
Dideoxy analogs are used in Sanger sequencing for what reason?
they facilitate fluorescent DNA sequencing
They facilitate polymerization of the DNA
They facilitate elongation of the DNA fragments
They block further elongation of the DNA
They block further elongation of the DNA
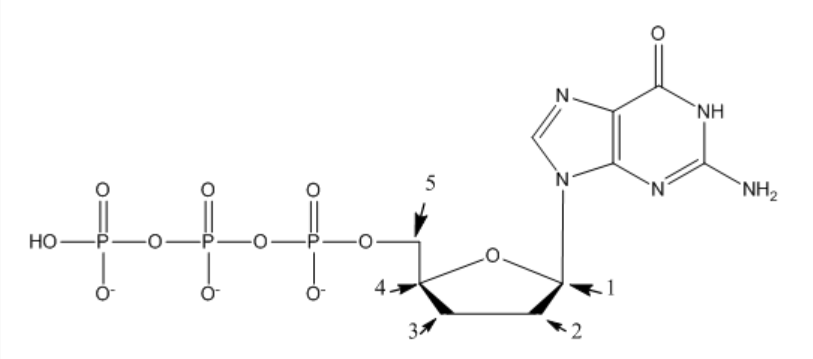
Which carbon(s) are deoxygenated for use with Sanger sequencing?
1
2
3
1 and 2
2 and 3
2 and 3
In Sanger dideoxy DNA sequencing, DNA polymerase 1 is used to add nucleotides to the ___ end of the growing polynucleotide chain
5’
3’
dideoxy-nucleotide-containing
sticky
blunt
3’
DNA sequencing by the chain'-termination method uses DNA polymerase 1 to make a complementary copy of the target or template DNA molecule. A reaction with a 20 bp template and dideoxyadenosine nucleotides as terminators results in the production of a 5 bp fragment. Based on this result, we can conclude that the template contains ___
a cytosine at position 5
a thymine at position 5
a thymine at position 16
a uracil at position 5
a cytosine at position 16
a thymine at position 16