Digestion
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/111
Last updated 2:25 AM on 11/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
1
New cards
Purpose of digestion
To break down nutrients (macromolecules) from food into smaller forms so that our cells can use it to maintain life
2
New cards
Carbohydrates
Macromolecules composed of Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen in 1:2:1 ratio
3
New cards
What macromolecule is the primary fuel source of the body
Carbohydrate
4
New cards
3 types of carbohydrates
Monosaccharides (simple sugar)
disaccharides (double sugars
Polysaccharides (complex sugars
disaccharides (double sugars
Polysaccharides (complex sugars
5
New cards
monosaccharide
Single sugar group with formula C6H12O6
6
New cards
3 types of monosaccharides
Glucose
Fructose
Galactose
Fructose
Galactose
7
New cards
Where are the monosaccharide sugars from? (3)
Glucose - from animals and plants
Fructose - fruits and honey
Galactose - milk sugar
Fructose - fruits and honey
Galactose - milk sugar
8
New cards
Types of Disaccharides
Sucrose (table sugar)
Maltose (grain sugar)
Lactose (milk sugar)
Maltose (grain sugar)
Lactose (milk sugar)
9
New cards
What is a disaccharide
Sugar made of 2 monosaccharides, one is alway a glucose molecule
10
New cards
Formula for each disaccharide sugar
Sucrose = glucose + fructose
Maltose = glucose + glucose
Lactose = glucose + galactose
Maltose = glucose + glucose
Lactose = glucose + galactose
11
New cards
Polysaccharides
Complex sugars made of 100s-1000s of sugar monomer, they are long chain polymers used for energy storage
12
New cards
Types of polysaccharides and uses
Starch - stored in plant cells
Cellulose - stored in plant cell walls
Glycogen - stored in animal cells
Chitin - insect and crustacean exoskeletons
Cellulose - stored in plant cell walls
Glycogen - stored in animal cells
Chitin - insect and crustacean exoskeletons
13
New cards
Example of protein function
Antibodies - defense OR
myosin - movement OR
enzymes - control chemical reactions
myosin - movement OR
enzymes - control chemical reactions
14
New cards
What are proteins made of?
Amino acids
15
New cards
What is the chemical makeup of amino acids?
Amino + acid + variable ‘R’ group
16
New cards
What is a chain of amino acids called?
Polypeptides
17
New cards
What is the function of amino acids
They link together to form proteins (sequences are determined by DNA)
18
New cards
How many amino acids cannot be made by the human body?
8
19
New cards
Lipids
Concentrated source of energy storage
20
New cards
T/F - lipids are soluble in water
F
21
New cards
What are the main functions of lipids
Aid in absorption of fat soluble vitamins
Insulate the body
Cushion the organs
Insulate the body
Cushion the organs
22
New cards
Types of lipids
Fats
Phospholipids
Steroids
Waxes
Phospholipids
Steroids
Waxes
23
New cards
Fats
Solid lipids - composed of triglycerides
24
New cards
Triglyceride
1 glycerol + 3 fatty acids
25
New cards
2 types of fats
Saturated and unsaturated fats
26
New cards
Difference between saturated and unsaturated fats
Saturated: straight chemical shape (single bonds), difficult to digest, should be limited, solid at room temp
Unsaturated: liquid at room temp, have double bonds which create ‘kinking’ and make molecule easier to break down
Unsaturated: liquid at room temp, have double bonds which create ‘kinking’ and make molecule easier to break down
27
New cards
2 types of unsaturated fats
Cis fats: 👍 molecule is bent
Trans fats 👎 kinks lock with e/o and are the hardest to break down
Trans fats 👎 kinks lock with e/o and are the hardest to break down
28
New cards
Example of saturated and unsaturated fat
Saturated: beef, pork, cheese fats
Unsaturated: corn, olive oils
Unsaturated: corn, olive oils
29
New cards
Phospholipids
Main component of cell membrane
30
New cards
Steroids example
Cholesterol and sex hormones
31
New cards
Waxes
Firm yet pliable fats like beeswax
32
New cards
What proportion of the human body is made up of water
2/3
33
New cards
What are the functions of water in the body
1. Transporting nutrients to cells (through blood)
2. Transports waste (urine and sweat)
3. Lubricates tissues and joints
4. Major component of blood and mucus (eliminating toxins)
5. Regulating body temp
2. Transports waste (urine and sweat)
3. Lubricates tissues and joints
4. Major component of blood and mucus (eliminating toxins)
5. Regulating body temp
34
New cards
Vitamins
Organic molecules typically count on foods, only small amount needed to change food into energy
35
New cards
Which vitamins are soluble in what?
A,D,E,K = fat soluble
B1, B2, C = water soluble
B1, B2, C = water soluble
36
New cards
Minerals
Found in inorganic nutrients/elements, variety needed in diet
Excessive amts can be just as harmful as not enough
Excessive amts can be just as harmful as not enough
37
New cards
Examples of minerals
Ca, Fe, P, K, Na, I
38
New cards
Alimentary canal
“Tube within a tube” which allows digestive processes to be separated into different regions
39
New cards
Do herbivores or carnivores have longer alimentary canals?
Herbivores - cellulose from plant walls take longer to break down
40
New cards
stages of food processing
1. Ingestion - taking in or eating food
2. Digestion - breakdown of food physically and chemically by enzymes
3. Absorption of nutrients in small intestine
4. Egestion (excretion) of undigested solid waste
2. Digestion - breakdown of food physically and chemically by enzymes
3. Absorption of nutrients in small intestine
4. Egestion (excretion) of undigested solid waste
41
New cards
Digestive enzymes
Proteins that break down complex molecules
42
New cards
digestive enzymes each have an optimum…
Temperature and pH
43
New cards
Where is pepsin found? + ideal pH
Stomach, opt pH 2-3
44
New cards
Where is amylase found + ideal pH
Oral salive, opt pH 7
45
New cards
Where is trypsin found + ideal pH
Small intestine, opt pH 9-10
46
New cards
Mouth
Where digestion begins, food is broken down mechanically (chewing) and chemically (saliva)
47
New cards
Bolus
Ball of food formed by the tongue
48
New cards
Saliva
Does chemical digestion in the mouth. Dissolves food particles, activates taste buds, lubricates food contains enzyme amylase
49
New cards
Salivary glands
Submandible, sublingual, parotid
50
New cards
Amylase
Enzyme found in saliva, breaks down carbs/starch to sugar
51
New cards
Pharynx
Short tube shared by digestive and respiratory tract, the throat
52
New cards
Epiglottis
a flap of cartilage that covers the trachea to prevent food entering airway while swallowing
53
New cards
Esophagus
Section of digestive tract responsible for pushing bolus and fluid into the stomach,
Made of smooth muscle that contracts to push food down
Made of smooth muscle that contracts to push food down
54
New cards
Peristalsis
Involuntary muscle contractions of the alimentary canal (notably in the esophagus) which pushed food along
55
New cards
Stomach
J shaped organ hat churns and stores food
Takes part in chemical (stomach acid) and physics (pummeling) digestion
Takes part in chemical (stomach acid) and physics (pummeling) digestion
56
New cards
Capacity of human stomach
1-1.5L
57
New cards
Chyme
Acidic nutrient rich liquid formed by the stomach churning a bolus
58
New cards
T/F, the stomach help absorbs nutrients
False! The stomach CANNOT absorb nutrients as they are still too large at that point of digestion
it CAN absorbs water, glucose, salts and alcohol through the membrane directly into the bloodstream
it CAN absorbs water, glucose, salts and alcohol through the membrane directly into the bloodstream
59
New cards
How long does the stomach take to empty after a meal?
2-6hrs
60
New cards
Parts of the stomach
(Esophagus)
1. Fundus
2. Body
3. Pylorus
(Duodenum)
1. Fundus
2. Body
3. Pylorus
(Duodenum)
61
New cards
sphincters of the stomach region
1. Cardiac sphincter- between esophagus and stomach
2. Phyloric sphincter -between pylorus and duodenum
2. Phyloric sphincter -between pylorus and duodenum
62
New cards
Cells lining the stomach
Parietal cells
Chief cells
Mucus
Chief cells
Mucus
63
New cards
Parietal cells
Secrete HCl (stomach acid) to
a) destroy bacteria in food
b) convert pepsinogen into pepsin
a) destroy bacteria in food
b) convert pepsinogen into pepsin
64
New cards
Pepsin
Enzyme that digests proteins into amino acids
65
New cards
Chief cells
Found in stomach, Secrete pepsinogen (broken down into pepsin by parietal cells)
66
New cards
Mucus
Secreted in the stomach to protect stomach lining and prevent ulcers from occuring
67
New cards
Small intestines
7m long tube (in humans) responsible for absorbing nutrients into the bloodstream through villi
68
New cards
Regions of the small intestine + lengths
1. Duodenum (0.3m)
2. Jejunum (2.7m)
3. Ileum (4m)
2. Jejunum (2.7m)
3. Ileum (4m)
69
New cards
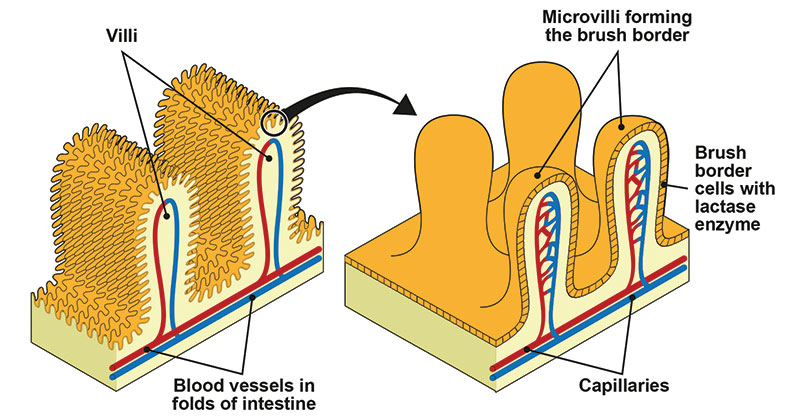
Villi
Finger-lined tubes in small intestine used to absorb nutrients into the bloodstream
70
New cards
Microvilli
Small villi lining the villi of the small intestine
71
New cards
Purpose of villi
Increase surface area for absorption of nutrients (allows faster absorption)
72
New cards
Core of villus
Lymph vessels (lacteal)
Access the bloodstream to distribute nutrients throughout the body
Access the bloodstream to distribute nutrients throughout the body
73
New cards
Why are the large and small intestine named as such?
The large intestine has a larger diameter, though not length
74
New cards
Is the small or large intestine smooth?
Small intestine - the large intestine is puskered and ridged
75
New cards
Length of the human large intestine
1.5m
76
New cards
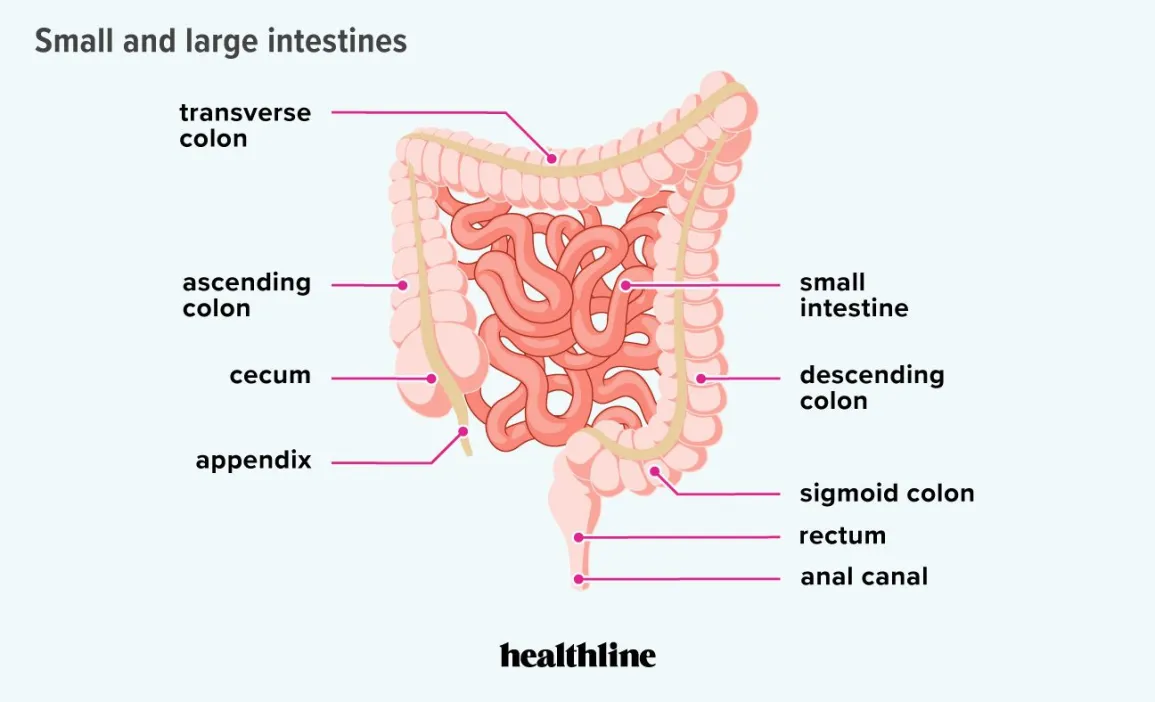
Sections of the large intestine
1. Caecum
2. Ascending colon
3. Transverse colon
4. Descending colon
5. Sigmoid colon
6. Rectum
2. Ascending colon
3. Transverse colon
4. Descending colon
5. Sigmoid colon
6. Rectum
77
New cards
Functions of the large intestine
1. Absorb water, minerals, and vitamins
2. House E. coli bacteria that use waste to make vitamins
3. Form feces
4. Move feces for excretion
2. House E. coli bacteria that use waste to make vitamins
3. Form feces
4. Move feces for excretion
78
New cards
Where is it healthy to find E. Coli bacteria in the body?
Large intestine - uses waste to make vitamins
79
New cards
Accessory organs
Organs which aid in digestion and are outside the alimentary canal
80
New cards
Ducts
Used by accessory organs to secrete their contents into the alimentary canal
81
New cards
Pancreas
a large ‘cottage cheese’ like gland located behind the stomach; secretes pancreatic juice and insulin
82
New cards
Pancreatic juices
Released into duodenum via pancreatic duct: Neutralizes stomach acid and contains digestive enzymes
83
New cards
Endocrine gland
secrete directly into the bloodstream
84
New cards
exocrine gland
a gland that secretes externally through a duct (not into the bloodstream)
85
New cards
Enzymes contained in pancreatic juices + functions
Amylase (turns carbs into sugars
Lipase (turns lipids into fatty acids + glycerol)
Trypsin (turns proteins into amino acids)
Lipase (turns lipids into fatty acids + glycerol)
Trypsin (turns proteins into amino acids)
86
New cards
Insulin
hormone secreted by the pancreas; regulates blood-glucose levels
87
New cards
Liver functions
1. Forms bile
2. Converts glucose to glycogen
3. Detoxifies blood
4. Breaks down hemoglobin from red blood cells
2. Converts glucose to glycogen
3. Detoxifies blood
4. Breaks down hemoglobin from red blood cells
88
New cards
What gives feces their colour and consistency
Colour: combination of broken down hemoglobin from RBCs and green bile colour
Consistency: how much water is absorbed in the large intestine
Consistency: how much water is absorbed in the large intestine
89
New cards
Gall bladder
Stores reserve supply of bile when the stomach is empty
90
New cards
Bile
Greenish fluid that contains cholesterol and bile salts
Responsible for breaking down fat into small droplets through emulsification
Responsible for breaking down fat into small droplets through emulsification
91
New cards
Gall stones
Large crystals of cholesterol which accumulate, only become problematic when they block gall bladder duct
92
New cards
Emulsification
Physical process whereby fat molecules are broken down into smaller droplets, increasing surface area for the lipase enzyme to work
93
New cards
Stages of emulsification
1. Body recognizes fats present in small intestine
2. Gall bladder releases bile
3. Bile salts break down large globs of fat
2. Gall bladder releases bile
3. Bile salts break down large globs of fat
94
New cards
Where do the accessory structures feed into?
The duodenum
95
New cards
Formula for total energy in food
(g fat) x 37kJ + (g protein) x 17kJ + (g carbs) x 17 kJ
96
New cards
What percentage of energy should you get from fat?
No more than 30%
97
New cards
How much total energy intake should be from protein?
15%
98
New cards
How much of your daily energy intake should be made of carbs?
50-55%
99
New cards
Fats, proteins and carbs yield how much energy per gram?
Fats: 37kJ
Proteins: 17kJ
Carbs: 17kJ
Proteins: 17kJ
Carbs: 17kJ
100
New cards
Metabolism
Chemical reactions used to maintain life