AP BIO Unit 2 Review - Cell Structure and Function
Eukaryotic vs Prokaryotic Cells
P
Bacteria and Archaea
Lack nuclei and other membrane-enclosed organelles
E
Internal membranes
Compartmentalized
- allows for concentration gradients
- cell components have own function in own space
- prevents molecules from roaming freely in the (selective)
Plant and animal cells have most of the same organelles: a nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and mitochondria. Some organelles are found only in plant or in animal cells. Chloroplasts are present only in cells of photosynthetic eukaryotes
Both
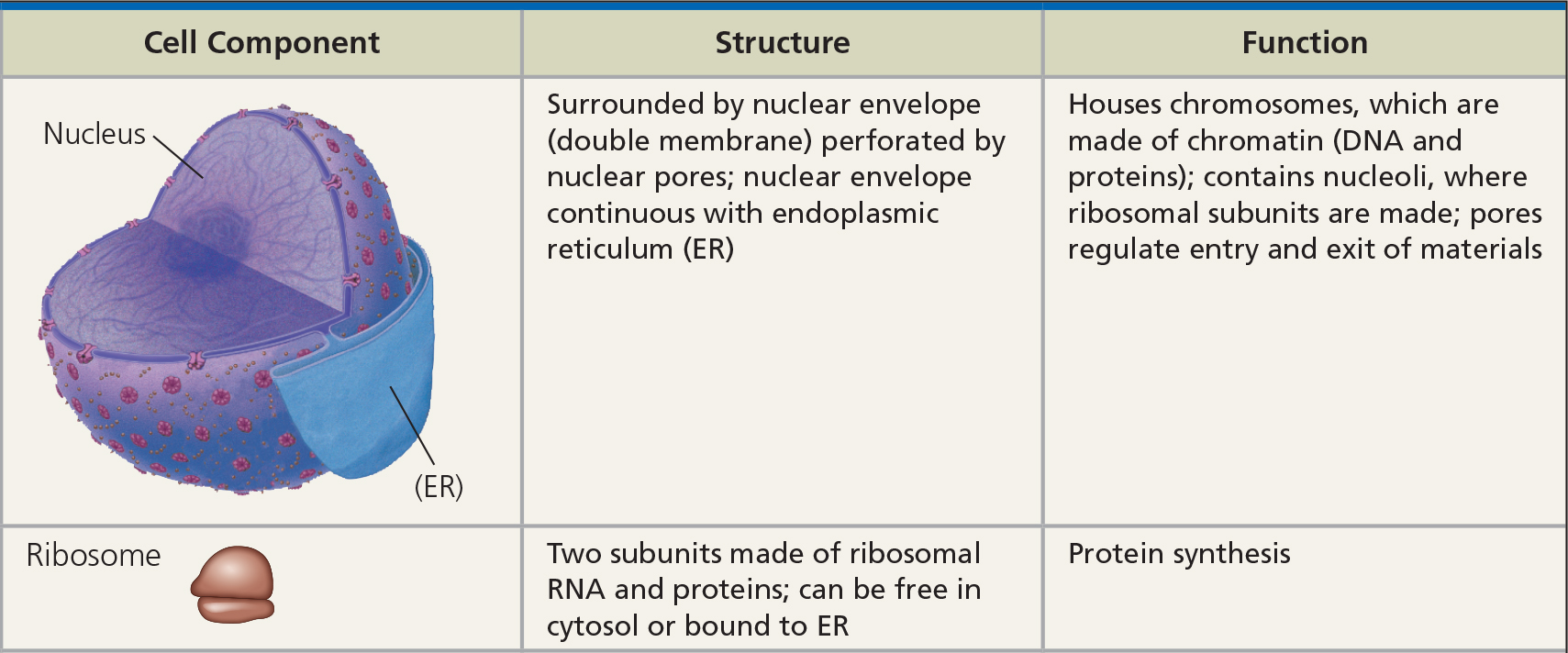
Ribosomes
Genetic Material
Cytoplasms: inside of a cell where reactions take place
Cytocol: the liquid in a cell
Plasma Membranes
Cellular Components
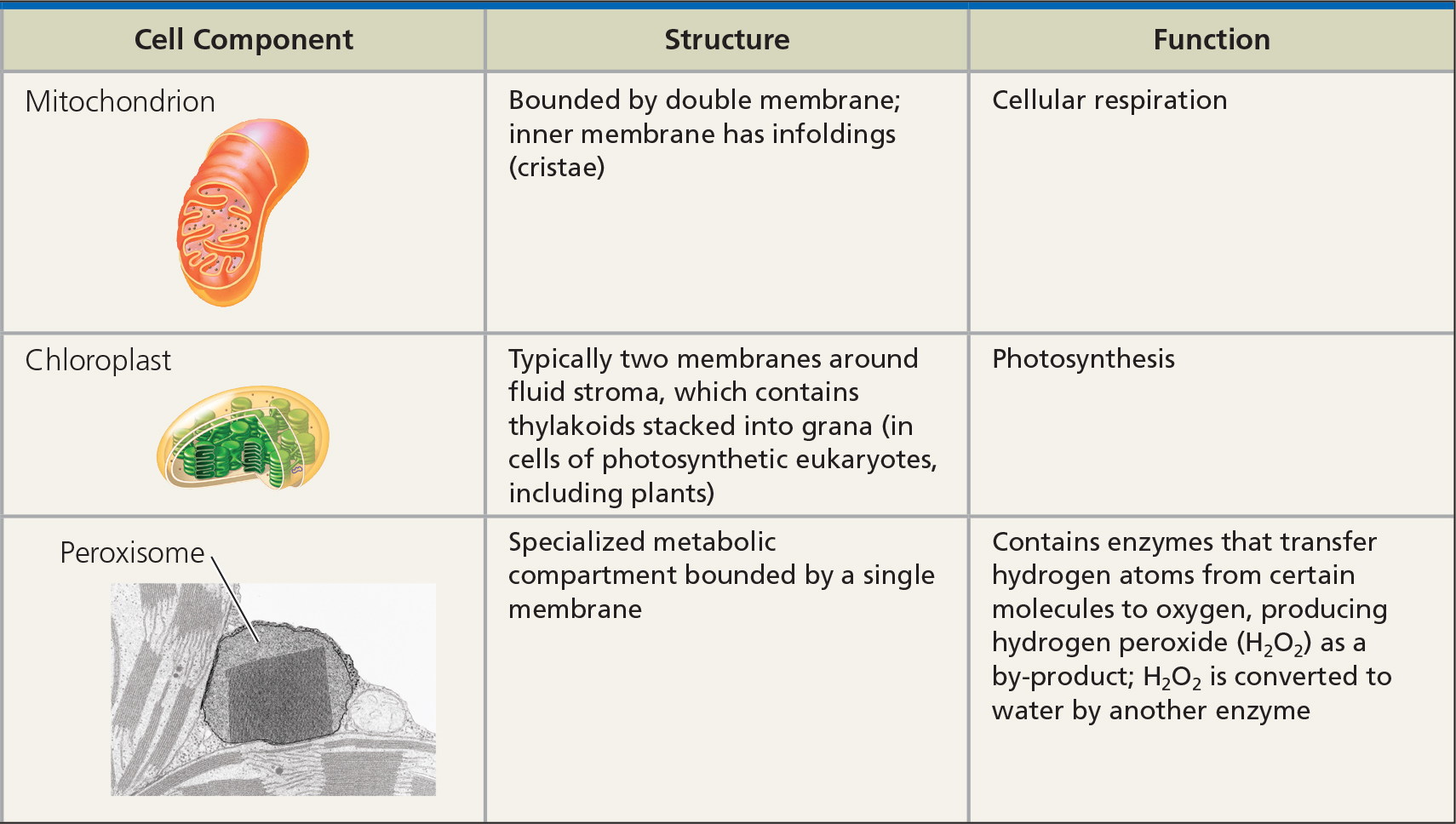
Chloroplast
Photosynthetic
Membranes contain chlorophyll pigments and e- transport proteins
Plants, algae
Own DNA + evolves independently -> endosymbiotic theory
Double outer membrane
- Intermembrane space
Stroma
- Fluid
- outside thylakoid
- Within the inner membrane
- Site of Calvin-Benson cycle
- Carbon fixation reactions of photosynthesis
- Contains ribosomes + DNA
- Helps synthesize organic materials from CO2 and H2O
Thylakoid
- Flattened membranous sac
- Light in -> chemical energy
Granum
- Stack of thylakoids
- Function in light reaction of photosynthesis
Plastid
- Family including chloroplasts, chromoplasts, amyloplasts
- In cells of photosynthetic eukaryotes
\n
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Mechanical support, protein synthesis, intracellular transport
\n
Plasma membrane
- Bounds all cells
- hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails
- charged p groups + hydrophobic fatty acid
- Amino acids with charged side groups are hydrophilic. These hydrophilic amino acids associate with the hydrophilic phosphate region of the cell membrane
- Bilayer of phospholipids
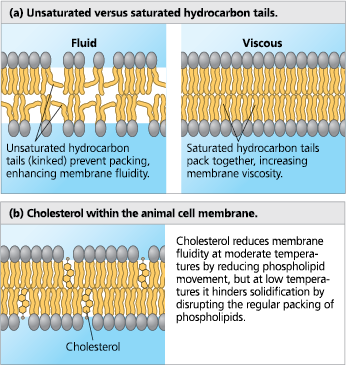
- fluidity
- cholesterol
- When temperatures are low, the fluidity of the cell membrane may decrease to a point that makes it nonfunctional. Cholesterol prevents this by packing between the phospholipids in the membrane. This increases the spacing between phospholipids, which increases the fluidity of the membrane
- The surface area must be large enough to adequately exchange materials
- Metabolic requirements set upper limits
- Surface area increases by n^2, volume increases by n^3
- Small cells have a greater surface area to volume ratio
- Increase in volume ->
- Surface area decreases
- Demand for internal resources increases
- Surface area increases
Plant Cell Walls
Cellulose fibers embedded in other polysaccharides and proteins
\n
Extracellular matrix
- Support, adhesion, movement, regulation
RIbosomes
- Comprise ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and protein
- Synthesize proteins according to mRNA sequence
- All forms of life
- Free ribosomes in the mitochondrial matrix
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Rough
- Membrane-bound ribosomes
- Compartmentalizes
- Phospholipid factory for the plasma membrane and organelles (endomembrane system)
Smooth
- Detoxification
- Lipid synthesis
- Liver cells
\n
Golgi apparatus
Membrane-bound
Flattened membranous sacs
Modifies and packages proteins
Cis side receives, trans face ships
\n
Mitochondria
ATP synthesis
Mitochondrial matrix
- Pyruvate oxidation
- Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle)
- Enclosed by the inner membrane
- Contains ribosomes, enzymes, and mitochondrial DNA
- Own DNA + evolves independently -> endosymbiotic theory
Double membrane
- Provides compartments for different metabolic reactions
- Outer smooth
- inner highly convoluted and folded
- increases surface area allows for more ATP to be synthesized
- E- transportation and ATP synthesis occur here
crista
- Infolding of the inner membrane
\n
Lysosomes
Recycle cell's organic materials
Membrane enclosed sacs
Hydrolytic enzymes
- Intracellular digestion
\n
Vacuole
Membrane-bound sac
Food
- Formed by phagocytosis (endocytosis)
COntractile
- Freshwater protists, pump out excess water
Central
- Mature plant cells, hold organic compounds and water
- Fills with water -> pressure to cell wall -> maintain cell shape
 \n
\n 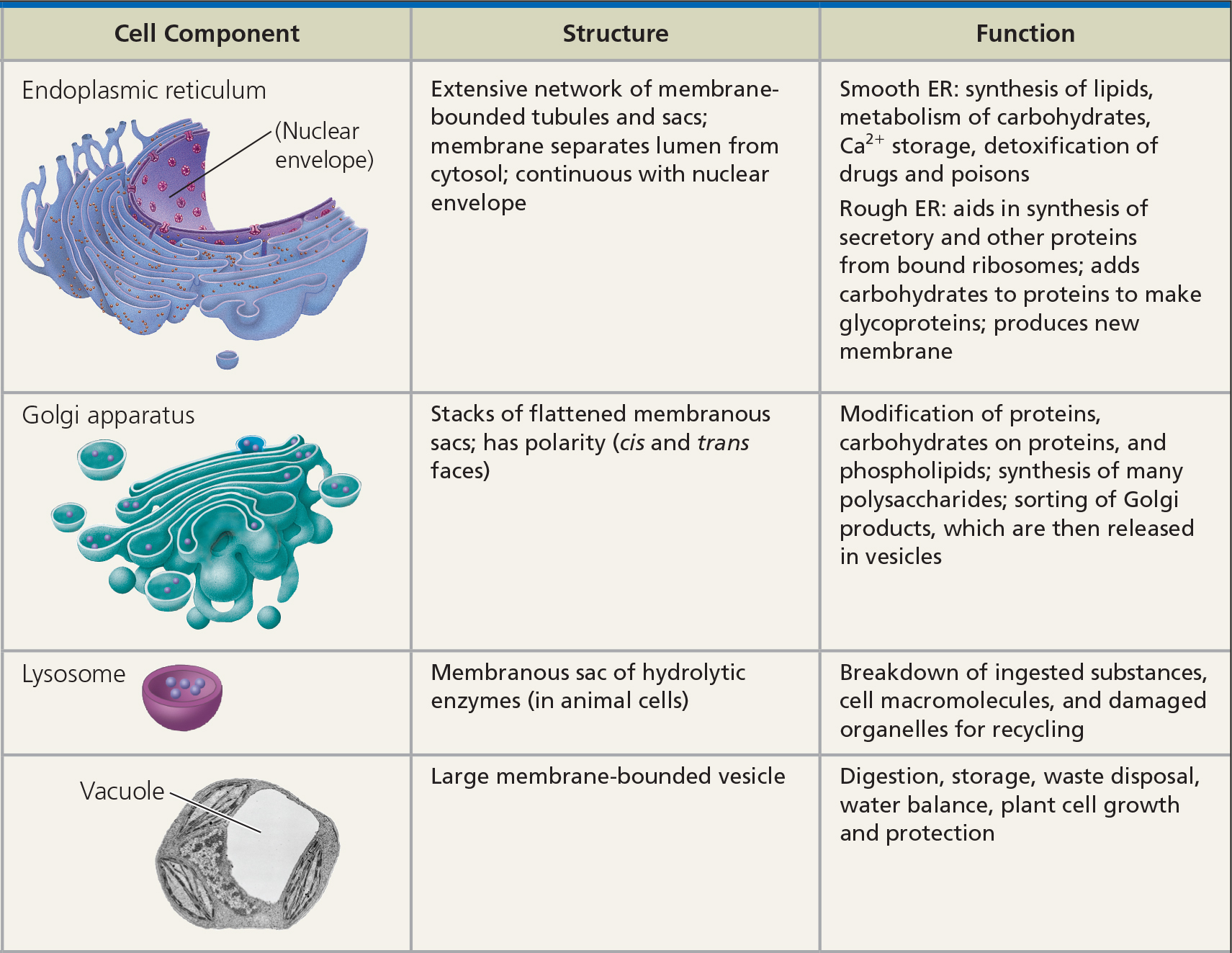
Cytoskeleton
Cytoskeleton
Struct support
Motility
Signal transmission
Motor proteins “walk” on
\n
Microtubules
Shape cell
Hollow
Tubulin polymer
Guide organelle movement
Separate chromosomes in dividing cells
Cilia
- Hair
- Flutters
- Brings up mucus
- The large number on the cell surface
Flagella
- One or few
\n
Microfilaments
Thin rod
2 acetone intertwined
- Actin interacts with myosin
- Contract muscle cells
- Amoeboid (crawling) movement
- Cytoplasmic streaming (circular flow of cytoplasm within cells)
Muscle contraction, amoeboid movement, cytoplasmic streaming, support microvilli
\n
Intermediate filaments
- Diameter between microtubules and microfilaments
- coiled
- Support cell shape, fix organelles in place
Communication, Transport, and Diffusion
[[Cell junctions[[
- Plasmodesmata
- Perforates cell walls
- Connects cytoplasm of adj plant cells
- Lets in water, small solutes, and larger molecules
- tight junctions
- neighboring cells tightly pressed and bound by proteins
- Continuous seal
- The barrier prevents EC leaks
- Desmosomes
- Cells -> sheets
- Anchored by int. Fil. (keratin)
- Attach muscle cells
- Gap/communicating junctions
- Cytoplasmic channel in adj cells
- Membrane proteins surround the pore
^^Most efficient^^
- sphere - equal distance all sides
- smaller cells - higher surface area to volume ratio
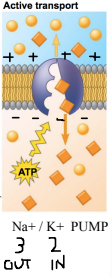
[[Active vs passive transport[[
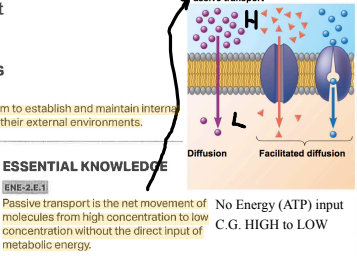
Active transport requires direct energy because it is against concentration gradients
^^Osmosis^^
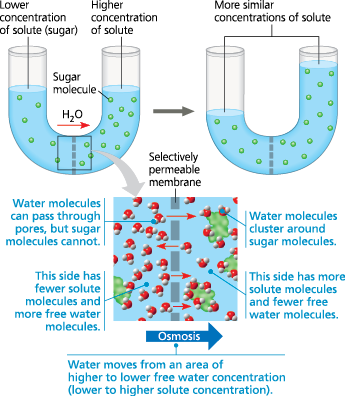
Water travels from low solute to high solute density
solute travels from high to low solute density
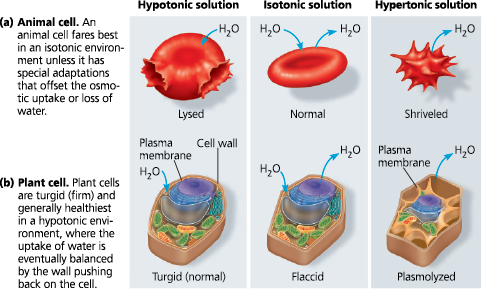
Hypotonic SOlution: The solution has a lower solute density which causes the cell to gain water
Hypertonic SOlution: The solution has a higher solute density which causes the cell to lose water
Isotonic SOlution: No net movement of water
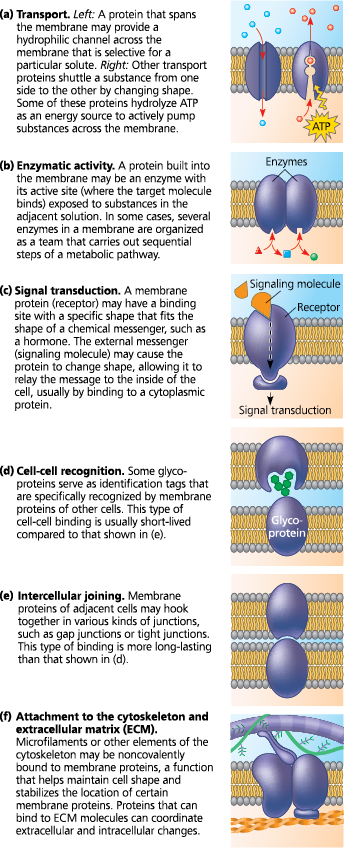
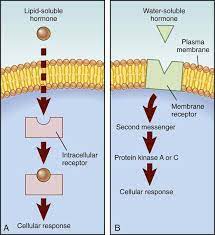
[[Membrne Proteins[[

Endosymbiont Theory

Membrane-bound organelles evolved from
previously free-living prokaryotic cells
via endosymbiosis.