Chapter 6: Merchandising Operations and the Multistep Income Statement
5.0(1)Studied by 4 people
Card Sorting
1/60
Last updated 8:32 AM on 11/21/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
1
New cards
Operating activities
________ are done by companies and businesses to generate revenues.
2
New cards
Service companies
________ provides a service to their customers (ex: gym memberships, cleaning services).
3
New cards
Selling a service
Collecting payment
Using the cash to pay for operating expenses
Collecting payment
Using the cash to pay for operating expenses
The operating cycle for service companies:
4
New cards
Merchandising companies
________ buy products from manufacturers to resell to their customers.
5
New cards
Buy inventory
Reselling inventory
Collecting cash
Using the cash to pay for operating expenses
Reselling inventory
Collecting cash
Using the cash to pay for operating expenses
The operating cycle for merchandising companies:
6
New cards
Manufactoring companies
________ make their own products to sell.
7
New cards
inventory
The products made by manufacturers and sold by merchandisers is ________. The day you buy ________, it is an asset and once its sold, its an expense.
8
New cards
Sales Revenue
________ is the total selling price of all goods sold.
9
New cards
Cost of Goods Sold
________ is the total cost of all goods sold.
10
New cards
Gross profit
________ represents profit earned before taking into account other expenses such as salaries, wages, depreciation, etc. It is the most important calculation for the Multistep Income Statement.
11
New cards

\
Equation for Gross Profit:
12
New cards
Beginning inventory
________ is the stock of inventory we have at the start of an accounting period.
13
New cards
Purchases
________ are what you buy throughout the year.
14
New cards
Goods Available for Sale
________ is everything you can potentially sell.
15
New cards

\
Equation for Cost of Goods Available for Sales:
16
New cards

\
Equation for Cost of Goods Sold:
17
New cards
Cost of Goods Sold on the Income Statement.
Once goods available for sale are sold, they become ________.
18
New cards
Ending Inventory
________ is the stock of inventory you still have at the end of the accounting period.
19
New cards

\
Equation for Ending Inventory (perpetual):
20
New cards
periodic inventory system
A ________ updates the inventory records for merchandise purchases, sales, and returns ONLY at the END of the accounting period.
21
New cards
self owned, mom and pop shops
The periodic system is used for ________.
22
New cards
physical count of inventory at the end of the accounting period.
For the periodic system, there must be a ________.
23
New cards
Cost of Goods Sold equation
We use the ________ for the periodic system.
24
New cards
it cannot calculate theft
The disadvantage of the periodic system is ________.
25
New cards
perpetual inventory system
When using a(n) ________, inventory is updated every time it is bought, sold, or returned.
26
New cards
bigger businesses like Walmart or Target.
The perpetual system is used for ________.
27
New cards
Ending Inventory equation
We use the ________ for the perpetual system.
28
New cards
physical count at least once a year
For the perpetual system, there must be a ________.
29
New cards
shrinkage
The perpetual system can also estimate ________, which is the loss of inventory from theft, fraud, and error.
30
New cards
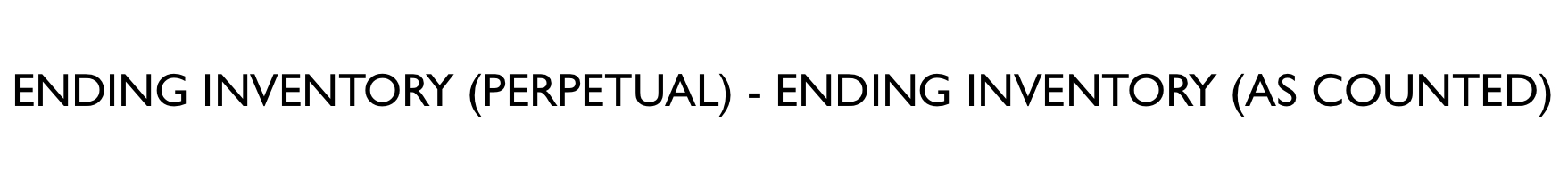
\
The equation for shrinkage:
31
New cards
inventory control
A perpetual system has better ________ because it is continuously updating its inventory count.
32
New cards
Free on Board
FOB stands for ________.
33
New cards
FOB shipping point
The sale for ________ is recorded when the seller loads the goods onto the truck.
Goods in transit belong to the customer at the point of shipping.
"Delivery" occurs when goods are loaded onto the truck.
Goods in transit belong to the customer at the point of shipping.
"Delivery" occurs when goods are loaded onto the truck.
34
New cards
FOB destination
The sale for ________ is recorded when the goods arrive to the customer.
Before this arrival, the goods belong to the seller until they reach their destination.
"Delivery" occurs when goods are ready to be unloaded by the buyer.
Before this arrival, the goods belong to the seller until they reach their destination.
"Delivery" occurs when goods are ready to be unloaded by the buyer.
35
New cards
Purchases Returns and Allowances
________ is a contra account to purchases. It has a normal debit balance.
36
New cards
allowance
If an item is damaged or unsatisfactory, the product can be returned for a full refund or kept by customer with a cost reduction, aka ________.
37
New cards
Purchase discounts
________ are an incentive for prompt payment.
38
New cards
discount period offered.
In 2/30, n/60:
The 2 represents the ________.
The 2 represents the ________.
39
New cards
discount period
In 2/30, n/60:
The 30 is the number of days the offer is available, aka the ________.
The 30 is the number of days the offer is available, aka the ________.
40
New cards
final payment
In 2/30, n/60:
The 60 is the maximum credit period and indicates when the ________ is due.
The 60 is the maximum credit period and indicates when the ________ is due.
41
New cards
net purchase
In 2/30, n/60:
The "n "is for "________ (after returns and allowances)
The "n "is for "________ (after returns and allowances)
42
New cards
One to record the sale at the selling price (debit Cash, Credit Sales Revenue) and one to record cost (debit Cost of Goods Sold, credit Inventory)
Every merchandise sale will have two journal entries and are recorded in a perpetual inventory system:
43
New cards
Sales Returns and Allowances
________ is a contra account to sales and has a normal debit balance.
44
New cards
One to updates sale records (debit Sales R & A, credit Cash) and one to update inventory records (debit inventory, credit Cost of Goods Sold)
There are two journal entries for Sales Returns and Allowances:
45
New cards
Sales Discount
When giving customers a discount, instead of lumping the discount into a sales revenue account, we use a contra-account called ________. It is attached to Sales Revenue and has a normal debit balance.
46
New cards

\
The equation for Gross Profit
47
New cards

\
The equation for Net Sales
48
New cards
bundle
A(n) ________ is packaging items together and selling them for one price to create a "deal "for the customer.
49
New cards
products and services (sometimes together)
Bundles can include ________.
50
New cards
if there is a product and service bundle, the service must be provided before recording revenue.
Bundles with products and bundles with products AND services are different because
51
New cards
The steps for the Five Step Revenue Model
Identify the contract.
Identify the seller's performance obligations.
Determine the transaction price.
Allocate the transaction price to the performance obligation.
Recognize revenue when each performance obligation is satisfied.
Identify the seller's performance obligations.
Determine the transaction price.
Allocate the transaction price to the performance obligation.
Recognize revenue when each performance obligation is satisfied.
52
New cards
Multistep Income Statement
The ________ reports alternative measures of income by calculating subtotals for core and peripheral business activities. It contains more than one year for comparative purposes.
53
New cards
Selling, General, and Administrative Expenses
________ groups expenses like salaries, wages, utilities, advertising, rent, and transportation.
54
New cards
Gross profit analysis
________ is used to help compare multistep income statements.
55
New cards

\
Equation for GROSS PROFIT PERCENTAGE %
56
New cards
What the ratio calculated from the Gross Profit % equation can be used for
Analyze the company's operations over the years, compare company to company, and to see if a company is getting enough income to cover its operating expenses.
57
New cards
higher percentage
We want a(n) ________ for our gross profit ratio.
58
New cards
Gross Method
The ________ correlates with the perpetual method.
59
New cards
"wait and see"
The Gross Method can also be called the ________ method because we see if the discount is taken before recording it.
60
New cards
Net Method
The _______ correlates to the periodic method.
61
New cards
"assumption"
The Net Method can also be called the ________ method because we record as if the discount was taken. If the discount is not taken, we update the record.