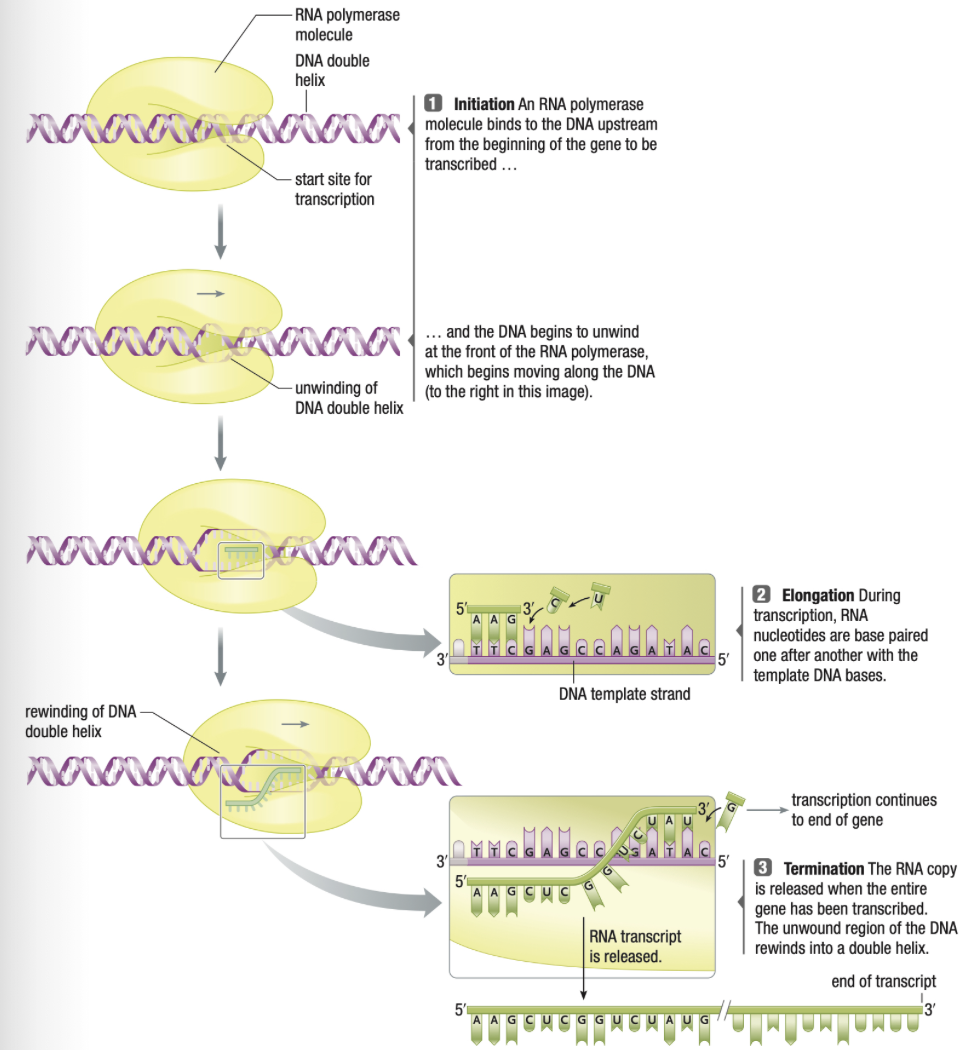
7.2 Transcription
Initiation
- %%RNA polymerase%% binds to template DNA at promoter (sequence before start of gene) by recognizing TATA (lost of A, T)
- DNA strands are seperated (like helicase)
Elongation
- RNA polymerase synthesizes complementary RNA strands 3’ direction
- no primer necessary
- while DNA is opened, many RNA polymerases may be active synthesizing many RNA strands
Termination
RNA polymerase recognizes termination sequence and dissociates from DNA
RNA also dissociates and leaves nucleus via nuclear pores into cytosol
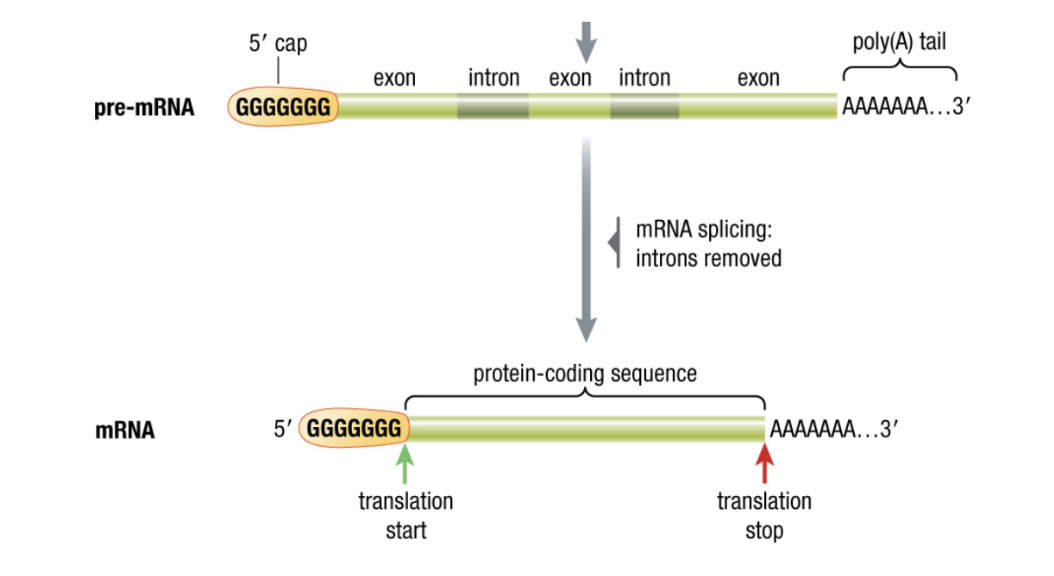
Post-Transcription Modifications
RNA known as pre-mRNA
Must me modified before it can leave the nucleus
- addition of poly-A tail
- prevents degredation
Removal of introns (non-coding regions) and splicing of exons (coding regions )
- makes mRNA functional
- alternative splicing can produce difference mRNAs from the same pre-mRNA