ap gov unit 5
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
Electorate
All citizens who are eligible to vote
Most common form of political participation
voting
which type of election are people more likely to vote in
presidential
Franchise
the right to vote
15 amendment
grants african american men to vote
17th amendment
direct election of senators
19th amendment
grants women the right to vote
23rd amendment
grants washington DC citizens right to vote
24th amendment
eliminated poll taxes
26th amendment
lowers voting age from 21 to 18
1957 civil rights act
addressed voting registration and created US office of civil rights
1964 civil rights act
prevents discrimination based off of race, color, religion, or sex
1965 voting rights act
allowed fed gov’t to oversee elections in the south, eliminated many voting barriers
rational choice voting model
examines platforms and candidates to make sure their vote goes to someone who benefits them
retrospective voting model
voters look back at a candidates track record to determine who to vote for, incumbents usually win
prospective voting model
voters try and predict the future to se how policies may affect them or the country
party line model
voting w the party you feel most loyal to
pocket book model
voting based on the economy
Voter turnout
amount of people who show up to vote, highest in late 1800s
state elections
states make their own voter registration laws as long as they fit the requirements + restrictions of the fed gov’t
local elections
counties cities and towns are divided into wards, which are then divided into precincts
national voter registration act (motor voter act)
requires states to offer a chance to register to vote @ state run agencies. You can also register by mail, online, or in person
2000 election
Bush v Gore, Very controversial, gore wanted a recount, response was- Help america vote act
Help america vote act
required states to update voting methods, make polling places more accessible to disabled, soldiers overseas must have access to vote, must provide DL or last 4# of SSN @ poll place
ID
most states require ID to vote, felons cant vote, ID laws becoming more common
australian ballot
Used in US, provides names of all eligible cands., only available @ polling place, completed in private
provisional ballot
Used when identity cannot be verified
Absentee ballot
used when one cannot vote in person, mailed in, more common after C19.
Voter ID laws
35 states require voter ID, R favors, D opposes
Act of voting
Avg. person waits in line for 14 mins, but can take longer in places w less volunteers.
Voter trust
Voter turnout lower in times of gov’t distrust
Voter apathy
not voting bc you think your vote does not matter
political efficacy
feeling that your vote makes an impact
gender gap
women- want less punishment, death penalty, favor gov’t spending. typically vote D. Men- harsh pun., fiscally cons., vote R
Age
old ppl vote more
race
AA + Black voters r typically L, Asians are typically R but that is shifting
religion
evangelicals= R, catholics= switch between both parties, Jewish= D
Linkage channels
help connect ppl to gov’t (pol. parties, interest groups, media). Pol. Parties influence voters, fundraise, eng. community, choose cands.
Nat. Convention
where party nominee is announced + chosen, finalize platform
Cand. recruitment
parties want cands who are well funded, scandal free, energetic, and have a following
Campaigning
V important, raising and spending $ for cand., TV ads = most $$$
FEC
exec agency that monitors and controls campaign finance laws, control how much a donor can give to a candidate,
OG 2 ideologies
Feds and Anti Feds ( large national gov’t vs large state gov’t)
Superdelegates
high ranking delegates that are not tied to a states primaries, typically high ranking officials
party realignment
change in elec. forces due to a change in party identification, happen after critical elections, have been 5 of these
what were the 5 realignments
1) democratic republicans to democrats, 2) republican party, 3) big business, 4) Great depression, 5) After the 60s
Party dealignment
ppl are becoming less aligned w/ a party + becoming independant voters, make decisions based on cand.
3rd parties
competitive but minor parties, many barriers against them
ideological 3rd party
form as a way to get voices heard abt issues not included in the major parties
splinter 3rd party
a large fraction of members from a major party break off
economic protest 3rd party
protest any scrutiny in economy
single issue 3rd party
fight for 1 issue, typ. absorbed into a major party
3rd party barriers
less recognition, less media coverage, ballot access is difficult, less following, less resources, many agendas get incorp. into major party
winner takes all voting
whoever wins the majority of the pop. vote in states get all of that states EC votes. Major barrier for 3rd parties, increases value of BG states
Pluralism
There are many ppl in the US w/ diff opinions + ideologies in gov’t that work together to run it
Lobbying
applying press. to influence gov’t, many interest groups pay lobbyists due to their connections + ability to influence politicians
how do interest groups get their point across
directly talking to politicians and using media to influence ( direct lobbying)
grassroots lobbying
interest groups try to inform, persuade, and mobilize lots of ppl
state gov structure
V similarto fed gov, bicameral legis., state courts, state agencies, another access point for IG
negatives of interest groups
can lead to upper class bias due to cost, projmote interest of the mems more than gen. interest. could lead to political corruption
free rider problem
when ppl benefit from IG’s without paying
Iron triangle
interactions between bureaucracy, congress, and IG’s. Bureaucrats benefit by cooperating with congress mems. who fund + provide oversight. Congress benefits by listening to what ppl want from IG’s while recieving more campaign donations and voters, IG’s benefit by having their interests accounted for
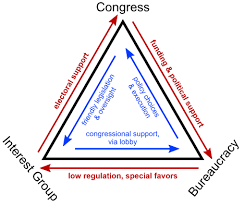
Non profit IG’s
fall into 2 groups based on tax classification- 501©(3) and 501(c)(4)
501c3
churches, some hospitals. recieve tax donations for charity, can influence govt, cannot lobby gov officials + donate to campaign
501c4
some welfare groups, can lobby + capaign but cant spend over 50% of expenditures on pol. issues
Endorsements
public expression of support, IG provide this
growth of IG
grow w/ population. EX- farmland to cities, war veteran return, fight for injustice
progressive era
1180-1920s, cities bad, more immigration, inc. wage gap. 4 amends passed- 16, 17, 18, 19
60-70s
civil rights movement, env. movement, consumer movement
interngovernmental lobby group
gov officials and political offices lobby congress for funds
professional associates
white collar workers concerned w business law
Purposive IG incentive
philosophical satisfaction
Solidary incentive
allows mems. to gather occasionally
material incentive
travel discounts, magazine subscriptions, free items
honest leadership and open gov act
bans gifts to congress from lobgbyists. lobbyists must provide quarterly spending reports
primaries
must win these to receive party nomination
invisible primary
cands. monitor pub opinion to judge fundraisng ability
closed primary
only party mems can vote
open primary
anyone can vote for either party
blanket primary
vote for both parties, top 2 cands. win
incumbvent advantage penomenon
incumbents can use all resources from the presidency to support their 2nd term. reelection rate~80%
caucus
party mems meet + have discussion and debate about cands.
electors
ppl that vote in EC, cant be in congress
midterm elections
cong. elecs. occur in the middle of pres. term
coattail effect
when a pres is liked, members from their party fare well in elections
PACs
donate money and run ads on cands. behalf. fund 40% of incumbents, and 9% of challengers
campaign steps
biography, issues, attack. Incumbs. dont debate
fed elections campaign act
tightened reporting requirements, limited cand spending. 1974 amend sets amounts ppl can donate
hard money
donated to candidate, traced and regulated
soft money
donated to party or group, not tracked
BCRA(2002)
banned soft money, inc. limits on hard money and spending
Citizens united v FEC
overturned BCRA. said it violated 1st amend freedom of speech. Reinstated soft money
connected pac
PAC sponsored by another organization
nonconnected PAC
not sponsored, form around single issue
leadership PAC
NCPAC, started by former elected official
superPAC
can spend unlimited as long as they dont formally coordinate w/ cands
press
additional check on gov, linkage institution
investigative reporting
attempts to expose gov corruption, started in progressive era, nicknamed muckrakers.
gatekeeper media role
medioaq can decide what is newsworthy regardless of provable importance