Social 20: Chapter 3 - Development of Nationalism (The French Revolution)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Bourgeoisie (DEFINITION)
the middle class
Coup D’état
a sudden, forcible seizure of power from the government
Sovereignty
supreme power or authority.
self-governing
ex) King
Monarchy
a form of government in which a group, embodies the country's national identity and its head, the monarch, exercises the role of sovereignty.
Philosophes
French philosophers of the 18th century—such as Voltaire, Montesquieu, and Rousseau—who advocated the supremacy of human reason and dedicated themselves to the advancement of science and secular thought?
what encouraged/contributed to Age of Enlightenment
French Revolution Overview
During the French Revolution, a series of events and conditions prompted the French people to unite and revolt against the king and form a new nation based on early ideas of democracy.
Prior to 1789, France was an absolute monarchy and a feudal society that favored the aristocracy and the Catholic clergy. A shift began when the middle class began to question their loyalty to the king, Louis XVI.
French Revolution is a primary example of how the majority of a country transformed their world from a Feudal Society into a Constitutional Republic, where society would form the foundations of a democracy based on freedom and equality among its citizens giving birth to a new nation
Historical Factors that shaped France prior to the French Revolution
Absolutism
Enlightenment
Ancien Regime
Non-Secular Society
Growing National Debt
Absolutism/Absolute Monarchy
a system where the absolute monarch is given the power to rule the land and the people by the divine right of kings.
In his actions, the monarch is answerable only to God.
the practice of unlimited authority and absolute sovereignty of a monarch or dictator
the essence of an absolutist system is that the power of the monarch is not subject to any challenge or check by any other person or group.
The Divine Right of Kings
all power comes from God and as such, Kings were Gods representatives on Earth.
this “Divine Right” to govern prevented citizens from defying the King’s authority and to do so would be directly defying God
this divine right made for the King to rule absolutely as an absolute monarchy.
Enlightenment
a movement of politics, philosophy, science and communications in Europe
reason over superstition
science over blind faith

Ancien Regime
in French meaning “Old Order”
Political and Social system of Feudal France before the French Revolution.
Under the regime, everyone was a subject of the king of France as well as a member of an estate.
All rights and status flowed from the social institutions, divided into three orders:
First Estate: Clergy
Second Estate: Nobility
Third Estate: Serfs/Peasants, Merchants (Bourgeoisie), Artisans/Workers
There was no national citizenship.
Feudal France: Ancien Regime
KING
First Estate: Clergy (Church)
Second Estate: Nobility (Royalty)
Third Estate: Serfs/Peasants, Merchants (Bourgeoisie), Artisans/Workers (Everyone Else)
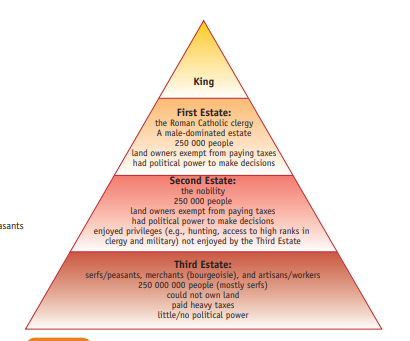
First Estate (Clergy)
Made up of members of the church
Owned commercial Property
Able to acquire enormous wealth
Entitled to collect Tithe, 10% of income
Exempt from paying taxes
Second Estate (Nobility)
½ True Nobles of the sword
Exempt from duties and taxes
Allowed to live/visit Versailles
Could become officers in army
Excused from civil crime
Did not pay Taille or Corvee
Third Estate: (Everyone Else)
Very diverse group
Divided into 3 groups:
Bourgeoisie: wealthy shopkeepers, lawyers, artisans
Urban workers: guild workers, trades, craftsmen
Peasants: poor farmers, small landowners, renters, Labourers
70% of income paid for taxes
Bourgeoisie
quite wealthy businessmen, educated, literate and understood the disparity between estates.
resented the 1st and 2nd estates due to the heavy tax load on the 3rd estate
desired to become part of the Farmers General to be able to collect taxes for the crown and earn wealth to purchase their nobility
opposed to being dictated to by the nobility and clergy
Urban Workers
guild system controlled the workers
skilled labour through apprenticeship to journeyman
paid well compared to peasants
unskilled workers suffered economic hardship and often starvation
Peasants
few wealthy farmers, small landowners, day laborers, renters mostly connected to agriculture industry
pay seventy percent of their income to tax:
Taille
Corvee
Vingtiemes
Tailee
property tax
Corvee
road tax
Vingtiemes
income taxes and feudal dues
Secular
not pertaining to or connected to religion
Non-Secular
structures of society are highly connected and related to religion
Non-Secular Society → Secular Society
due to the Enlightenment, society began to shape itself on fact rather than superstition.
began to believe that their life could progress into more than their class or position in life.
people began to question the power and authority of the church and the divine right of monarchs.
began to discover their own truths and not naively take the word of authority as fact and began to move away from church doctrine
Growing National Debt
7 Years War with Britain
American Revolution
Poor Harvests → Food Shortages
Reluctance of Tax Reform
Exuberant Spending of the Monarchy
Motivation for Revolution:
Age of Enlightenment combined with the successful revolution of America against the Monarch of Britain
French people who advocated for change to their own society began to take steps and make efforts that would ultimately trigger the revolution in France and pave the way to the creation of an entirely new way of life.
This new way of life would not come without sacrifice, blood and terror.
Liberty
freedom of the old regime and the privileges of the nobility
Equality
all members of society have the same rights and freedoms regardless of class distinction
Fraternity
all people of society bond together as members of a nation, brotherhood
The French Revolution Timeline (SIGNFICANT EVENTS)
May 1789: Meeting of Estates-General
June 1789: Creation of the National Assembly and the Tennis Court Oath
July 14, 1789: Storming of the Bastille
August 4, 1789: Abolition of the Feudal System (GREAT FEAR)
August 1789: Creation of the Declaration of the Rights of Man
1793-1794: Reign of Terror
Meeting of Estates-General (May 1789)
As a result of public pressure, Louis XVI called the representatives (Estates-General) to meet at Versailles.
brought cahiers de doléances (lists of grievances) to share with the king in hopes of encouraging political change
little was settled during these meetings due to disagreements between king and the three estates
National Assembly and Tennis Court Oath (June 1789)
After the failure of the meeting of the Estates-General, many of the representatives of all three estates proclaimed themselves to be the National Assembly
the king locked them out of their regular meeting room and they assembled at a nearby tennis court.
there, they swore not to disband until France had a constitution in what became known as the Tennis Court Oath.
Storming the Bastille (July 14, 1789)
The king refused to recognize the legitimacy of the National Assembly. He assembled royal troops near Paris.
rumours of an attack by the king spurred crowds to storm the royal prison, the Bastille, to release prisoners and collect weapons to use for defence.
Abolition of the Feudal System / The Great Fear (August 4, 1789)
Due to rumours of a poor economy and the scarcity of food, fear and panic in the countryside led to attacks on the estates of the nobility.
National Assembly abolished the Estates-General, ending the feudal system and gaining legislative power in France.
Creation of the Declaration of the Rights of Man (August 1789)
described the rights of individuals and guiding democratic principles.
the declaration ushered in a new era ending the Ancien Regime and the privileges of the nobility. the state emerged as the source of all power.
passed by the National Assembly
Girondins
moderates who wanted to maintain the monarchy
Jacobins
radicals who wanted to establish France as a republic
End of the Royal Family
Jan 1793: Trial and Execution of Louis XVI
tried and found guilty of treason by the new republic.
Oct 1793: Execution of Marie Antoinette
arrested and tried for a number of charges, including treason
found guilty and executed
marking the official end to the royal line as her son died of neglect a few years later
Reign of Terror (1793-1794)
The Revolutionary Government - the National Convention faced civil unrest across the country
arrested & executed up to 40,000 perceived enemies of the republic
led by Robespierre
End of French Revolution Overview
After the end of the Reign of Terror and the execution of Robespierre, the national convention dismantled the machinery of the Reign oftterror and introduced a period of moderation in France. France was filled with civil unrest and the country was unsettled.
1795: constitution returned power to those with property and the lowest levels of society were refused the vote. a two-house legislation was implemented stressing freedom and equality in line with the declaration of the rights of man. however, citizens were expected to obey the rule of law and respect property.
France would not find peace from war, true freedom and equality and would not be solidified as a nation until the the rule by napoleon 20 years later.