Unit 5 - History of Life
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
When did life originate?
~3.5 - 4 billion years ago
Life
a self-sustaining chemical system capable of biological evolution
For life to be considered self-sustaining, it must be able to…
grow
reproduce
respond to stimuli
harvest and transform energy
Abiogenesis
life arising from non-living matter
the origin of replicating entities
Abiogenesis can be explained by _____ theory.
chemical
True or False: Organic molecules can be created via abiotic processes.
True
Where do many (approximately ~30 tons per day) organic molecules come from?
Space
Self-assembly
spontaneous formation of larger molecules and structures
Some macromolecules have catalytic properties. This means they can…
induce chemical reactions
True or False: Macromolecules can self-replicate.
False.
They are synthesized based on genetic instructions and metabolic pathways.
Marine snow
a shower of organic material that falls from upper waters to the deep ocean floor; forms chalk and limestone deposits

Strata
a layer or series of layers caused by sedimentation over time

True or False: Fossilization is common and happens all the time, so the fossil record is always up to date.
False.
Fossilization is rare, which makes our fossil record very limited.
Radiometric dating
scientific technique used to determine the age of materials, such as rocks and fossils, by measuring the decay of radioactive isotopes within them
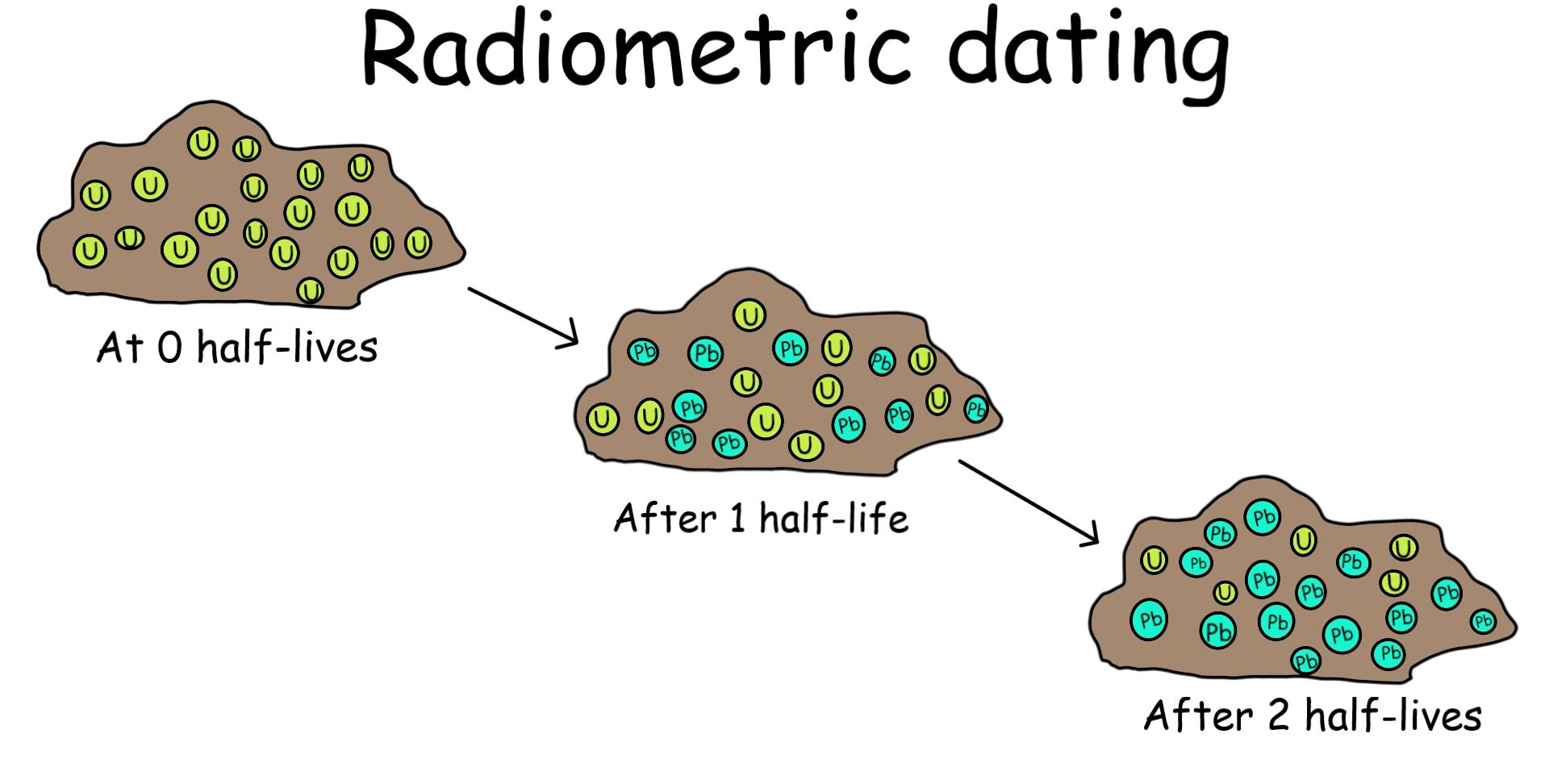
What is the approximate age of the Earth?
~4.5 billion years
When were the first signs of photosynthesis on Earth discovered to be?
3.2 billion years ago
The Earth’s atmosphere became oxygen-rich approximately…
2.5 billion years ago
The first eukaryote originated approximately…
1.8 billion years ago
Multicellular life originated approximately…
1.5 billion years ago
Prokaryotes originated approximately…
3.5 billion years ago
(and were the sole inhabitants of Earth for nearly 1.5 billion years)
The first animals originated approximately…
500 million years ago
The first vertebrate land animals originated approximately…
380 million years ago
The first mammal originated approximately…
250 million years ago
The first hominins originated approximately…
2 million years ago
Homo sapiens AKA humans originated approximately…
250,000 years ago
Why was there a lag in between the time period that photosynthesis began occurring and the time period that oxygen levels in Earth’s atmosphere began to rise?
Oxygen dissolves in water and oxidizes iron, turning into iron oxide (ie. rust), which precipitated out into the ocean.
The iron acted as a sponge that cancelled out the oxygen being made from cyanobacteria, until eventually, it was all oxidized.
In terms of eukaryotes, which cellular compartment was likely the first to evolve?
Nucleus
Organelles evolved from the process of…
endosymbiosis
Endosymbiosis
a biological relationship where one organism lives inside of another

The mitochondria originated from highly efficient ATP-making bacteria. Where did chloroplasts come from?
Cyanobacteria
Which evolved first: mitochondria or chloroplasts?
Mitochondria
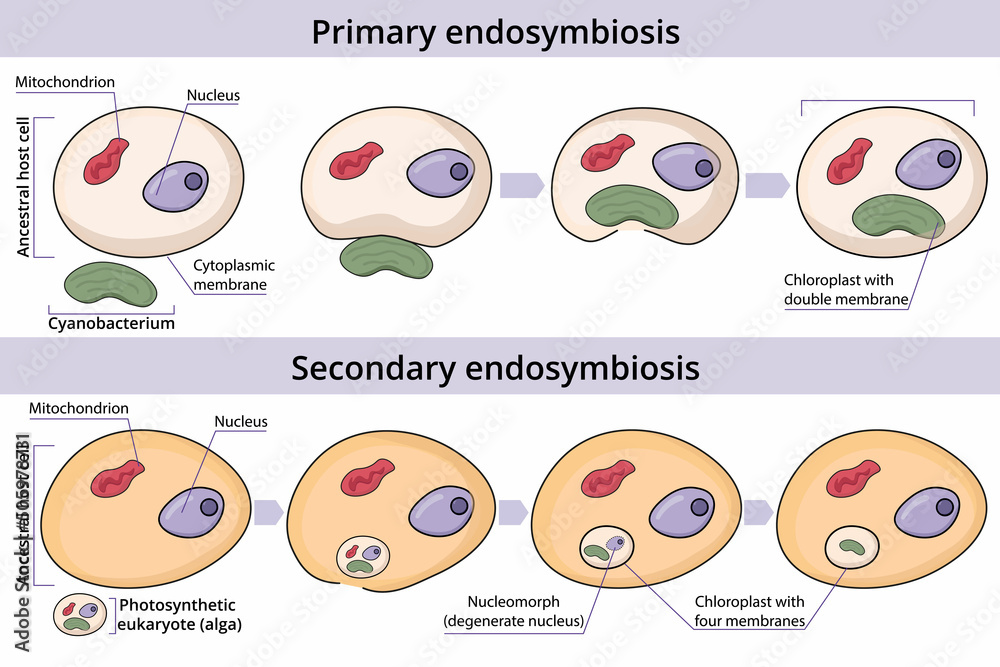
Primary endosymbiosis
prokaryote enters or is engulfed by a eukaryote
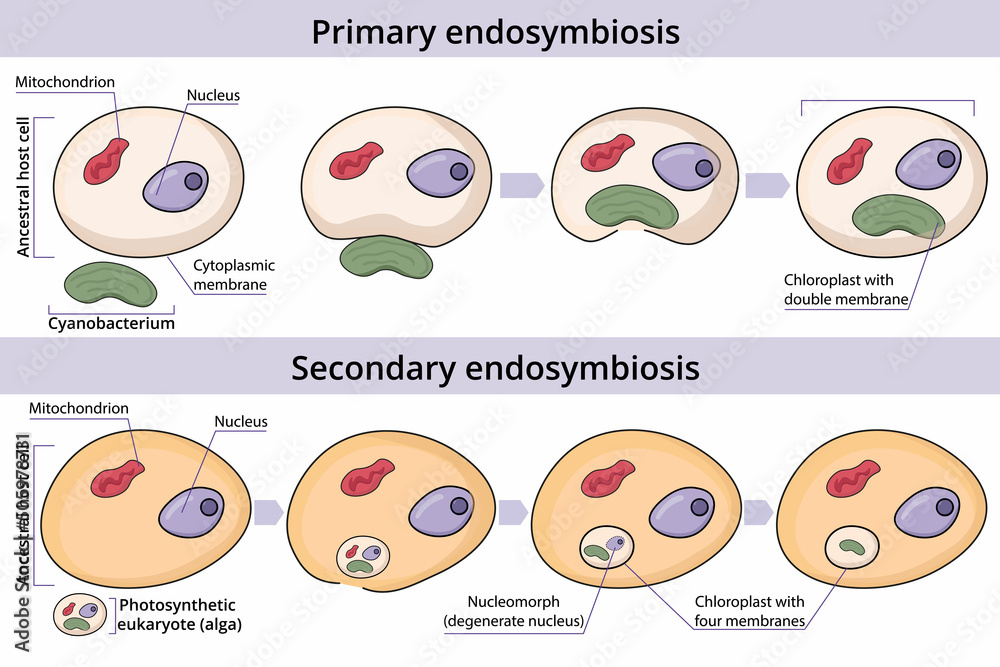
Secondary endosymbiosis
eukaryote that has already undergone primary endosymbiosis enters or is engulfed by another eukaryote
True or False: Multicellularity has evolved independently many times (at least six).
True
What are the benefits of multicellularity?
Larger organisms
Better division of labor between cells (it’s not one single cell trying to do everything!), which allows for specialization
What is required for multicellularity to evolve and be sustained?
Cell adhesion (aggregative vs cohesive)
Self/non-self recognition (ex. immune response attacking foreign cells)
Programmed cell death (apoptosis)
Regulated cell division
Cell differentiation
Distinction between soma and germline
Intercellular communication
Defector cells
cells that function abnormally to the point of detriment to the organism AND have a reproductive advantage over normal cells
(ex. tumors)
Defector cells are caused mostly by…
loss of function in genes that regulate cell division
What is the solution to dealing with defector cells?
Unicellular bottleneck - purges defector cells by introducing a unicellular life stage (ex. the ova in meiosis)
Sex
the recombination of DNA from more than one source
What are the disadvantages of sex, or sexual reproduction?
It takes time and energy
There is a two-fold cost (it’s only half as productive as asexual reproduction)
Why are asexual lineages usually short-lived?
They are unable to recombine their DNA, so they’re unable to adapt as easily or purge deleterious (harmful) alleles.
What are the advantages of sex, or sexual reproduction?
Creates new combinations of traits = genetic diversity
Allows for purging of deleterious (harmful) alleles
True or False: Arthropods were the first true animals to colonize the land.
True
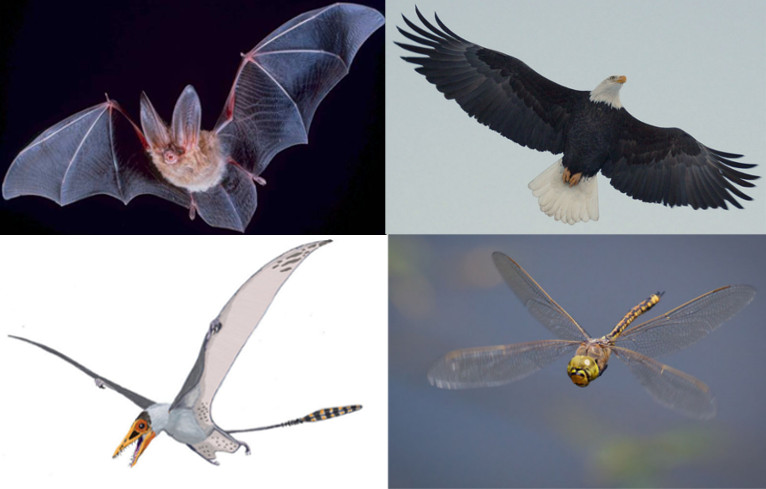
Flight has evolved independently only four times (that we know of). What are these origins?
Insects
Pterosaurs
Dinosaurs
Bats

True or False: Defining features evolve all at the same time, or over a short timespan.
False.
Defining features (such as what differentiates a bird from a mammal) all evolved gradually.
Species radiation
a single species undergoes speciation and evolves into many new species very quickly
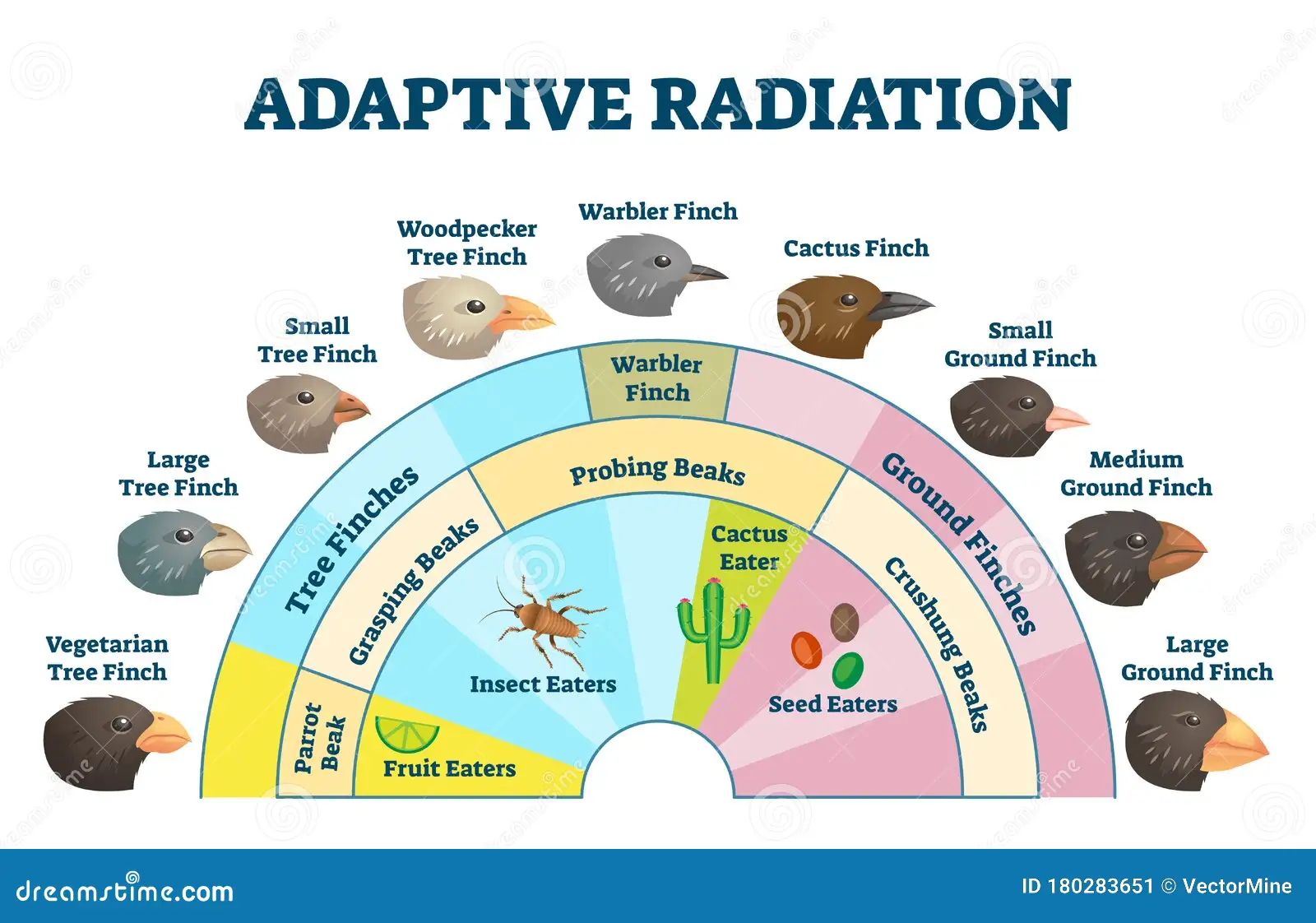
Plate tectonics
the moving of the Earth’s continents on the surface due to convection cells in its crust; contributes to speciation
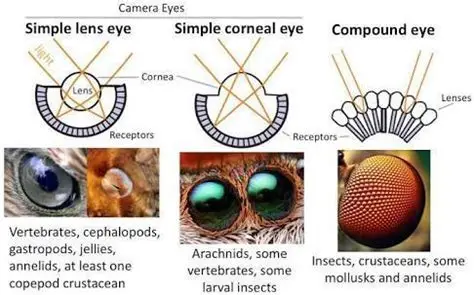
True or False: Complex structures and traits are always better than simple structures and traits.
False!
Simple is better than nothing, but complex can sometimes be less efficient or effective.
(Ex. eye structures of a jellyfish vs cephalopods vs insects vs vertebrates)
Co-option
a change in function that facilitates adaptation
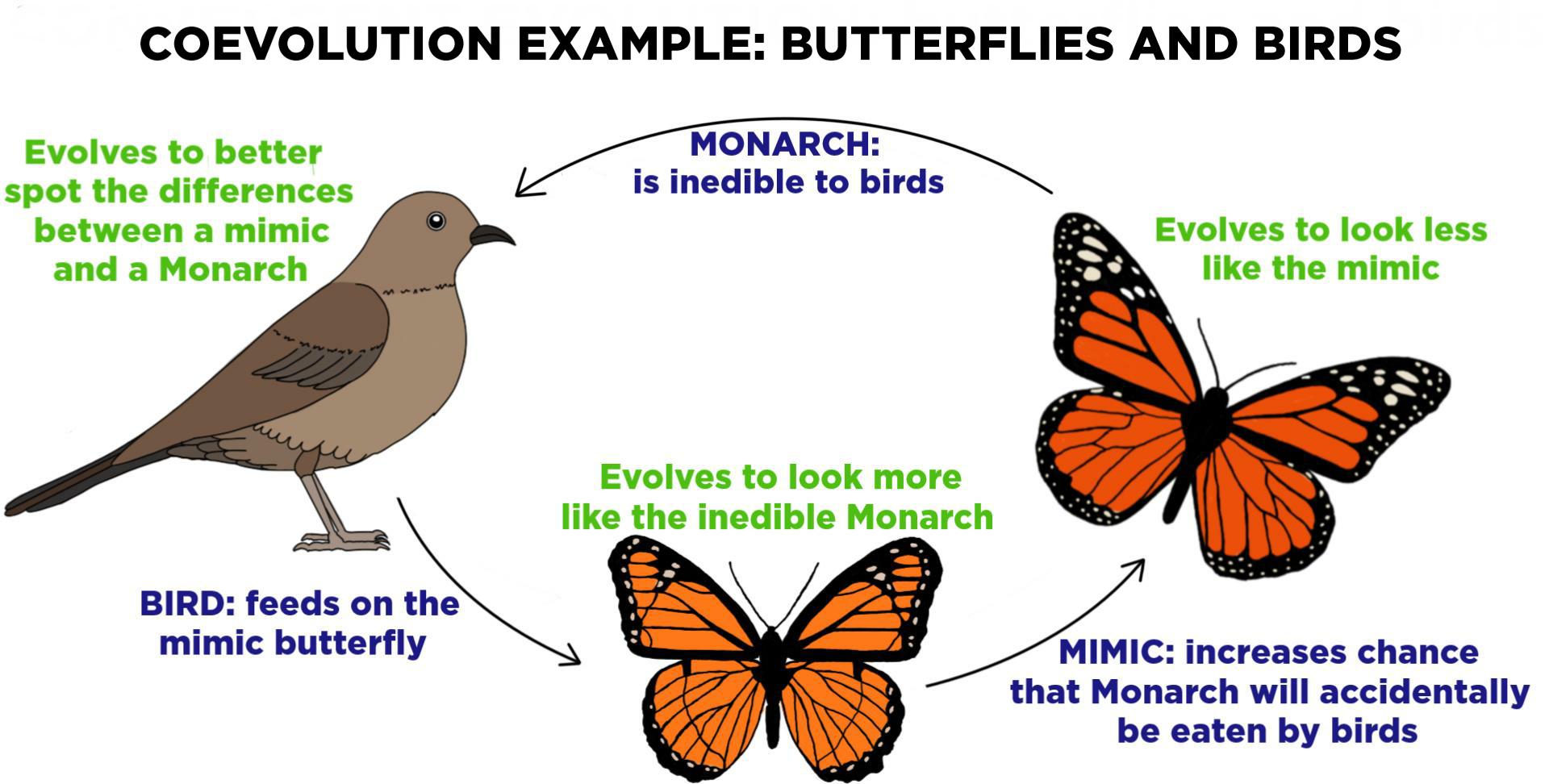
Coevolution
evolution of species that evolved together and often because of each other
(ex. host/pathogen coevolution)
Cohesive (multicellular adhesion)
cells split via mitosis and join together
(ex. animals, plants, some fungi and seaweeds)
Aggregative (multicellular adhesion)
separate organisms join together
(ex. amoebas, slime molds)
The mammary glands in mammals evolved from…
sweat glands
(This basically means that milk is highly nutritious sweat!)
The chemical gadusol, which is known to aid in UV protection, was first spread to vertebrates via ___________ from protists.
horizontal gene transfer
Convergent evolution
evolution of similar traits that happened independently from one another
(ex. compound eyes of humans and octopi)
Host / pathogen coevolution leads to a balance between _____ and ______.
fecundity, virulence
Monkeys are primates (with/without) tails.
with
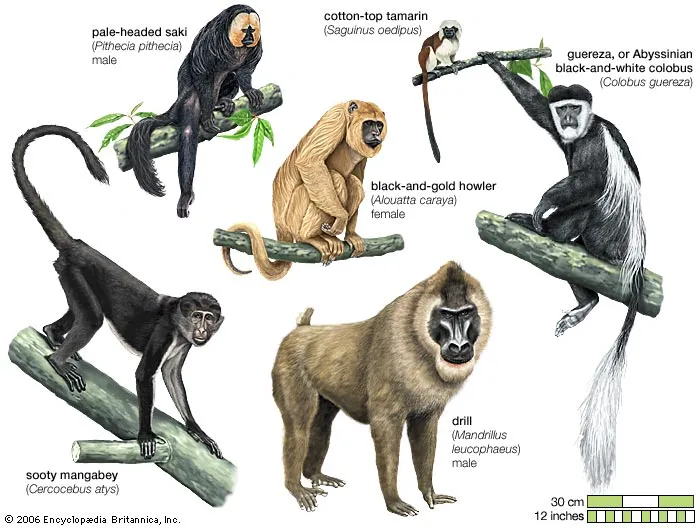

Apes are primates (with/without) tails.
without

How and when did trichromatic vision evolve?
Via duplication of the green-sensitive opsin gene into a mutant red-sensitive opsin gene
Present in apes, but not monkeys
Hominids
group consisting of all modern and extinct Great Apes (includes humans)
(Think of these like the distant cousins of humans.)
Hominins
group consisting of modern humans, extinct human species, and our immediate ancestors
(Think of these like our more closely related cousins.)
Where and when did Homo sapiens originate?
Africa, 200KYA
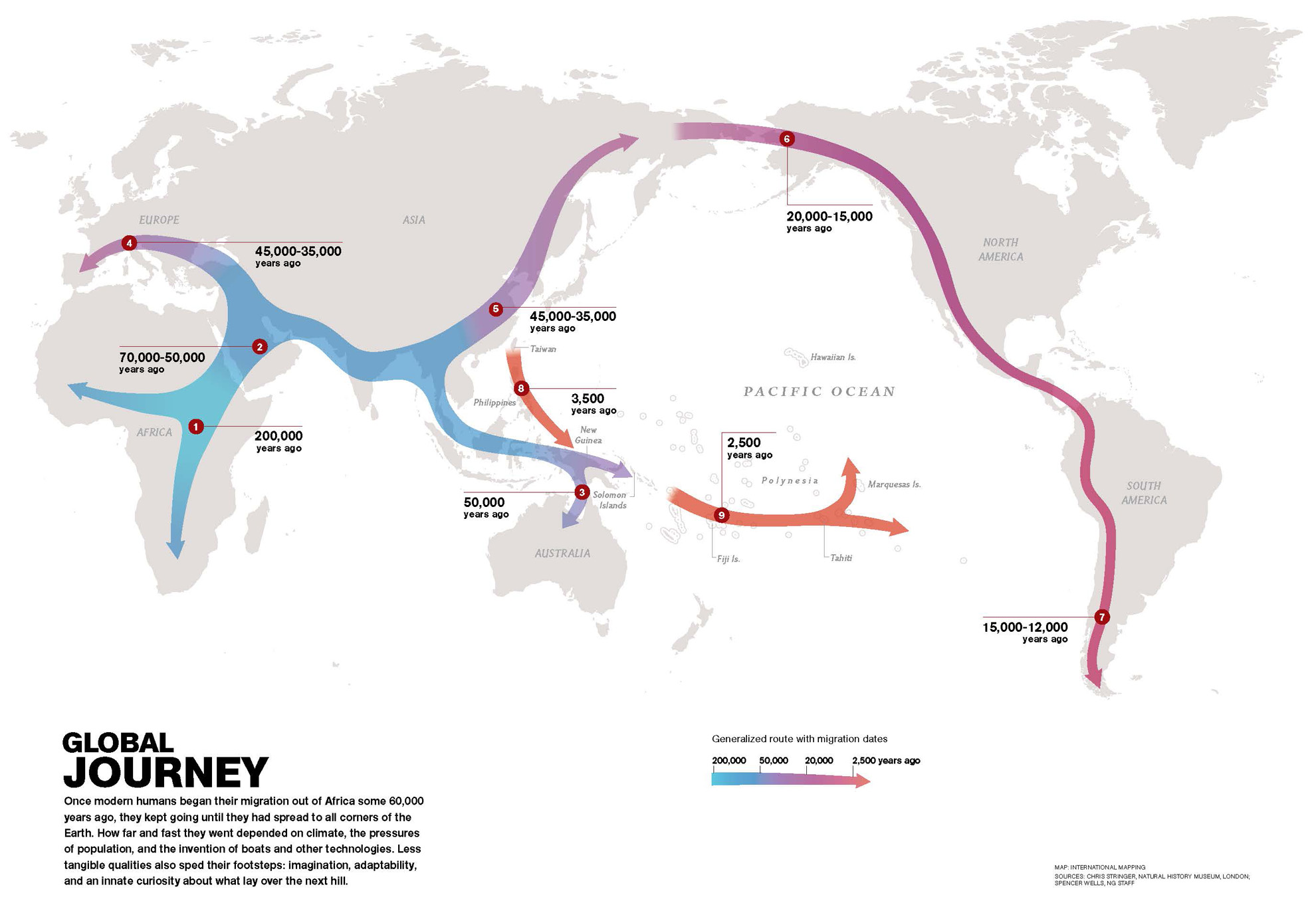
From Africa, Homo sapiens travelled to…
Middle East, ~60KYA
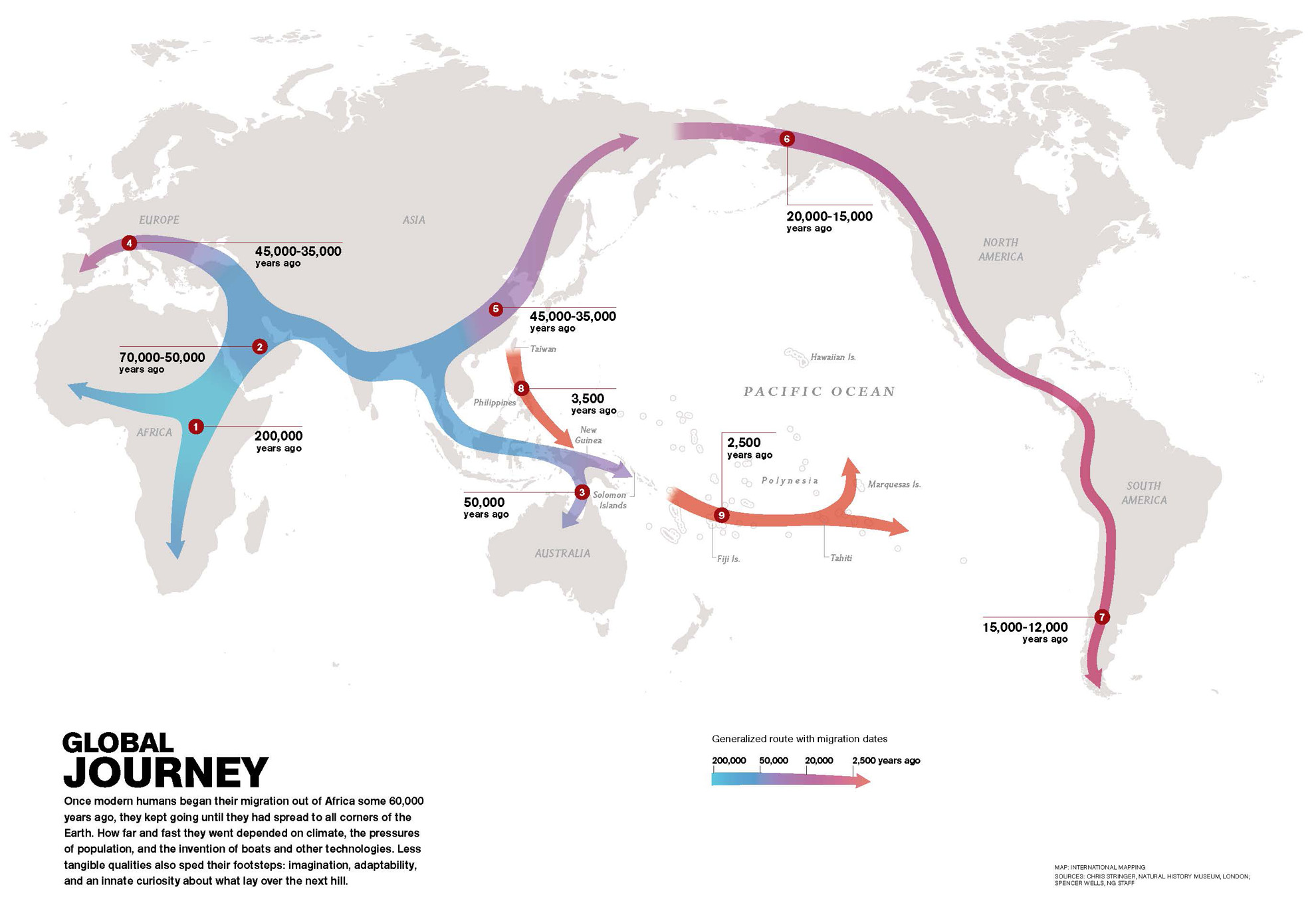
Homo sapiens travelled from the Middle East to… (hint: 3 locales)
Australia, 50KYA
Asia, 45KYA
Europe, 40KYA
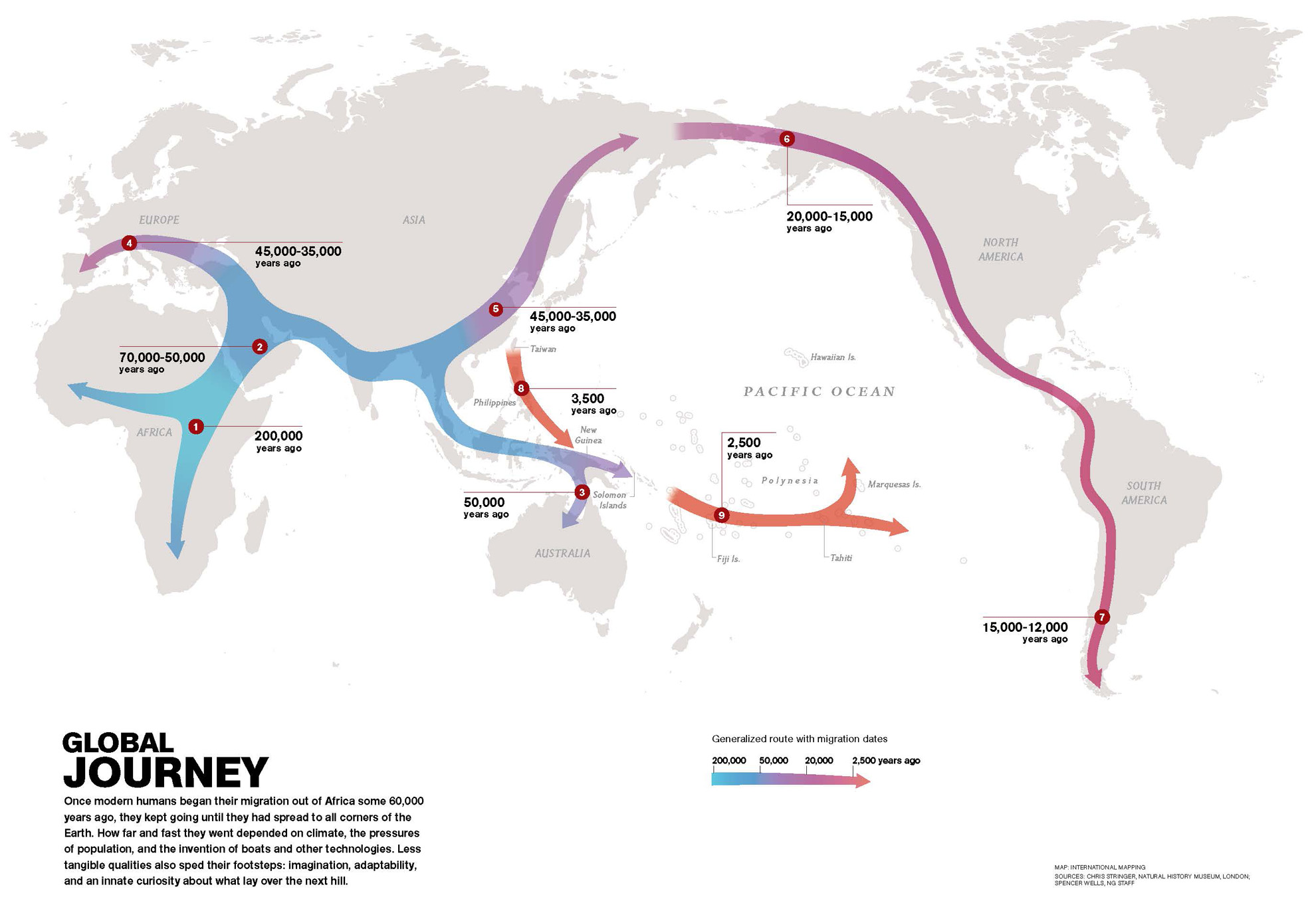
From East Asia, Homo sapiens travelled to… (hint: 2 locales)
North America, 20KYA → South America, 15KYA
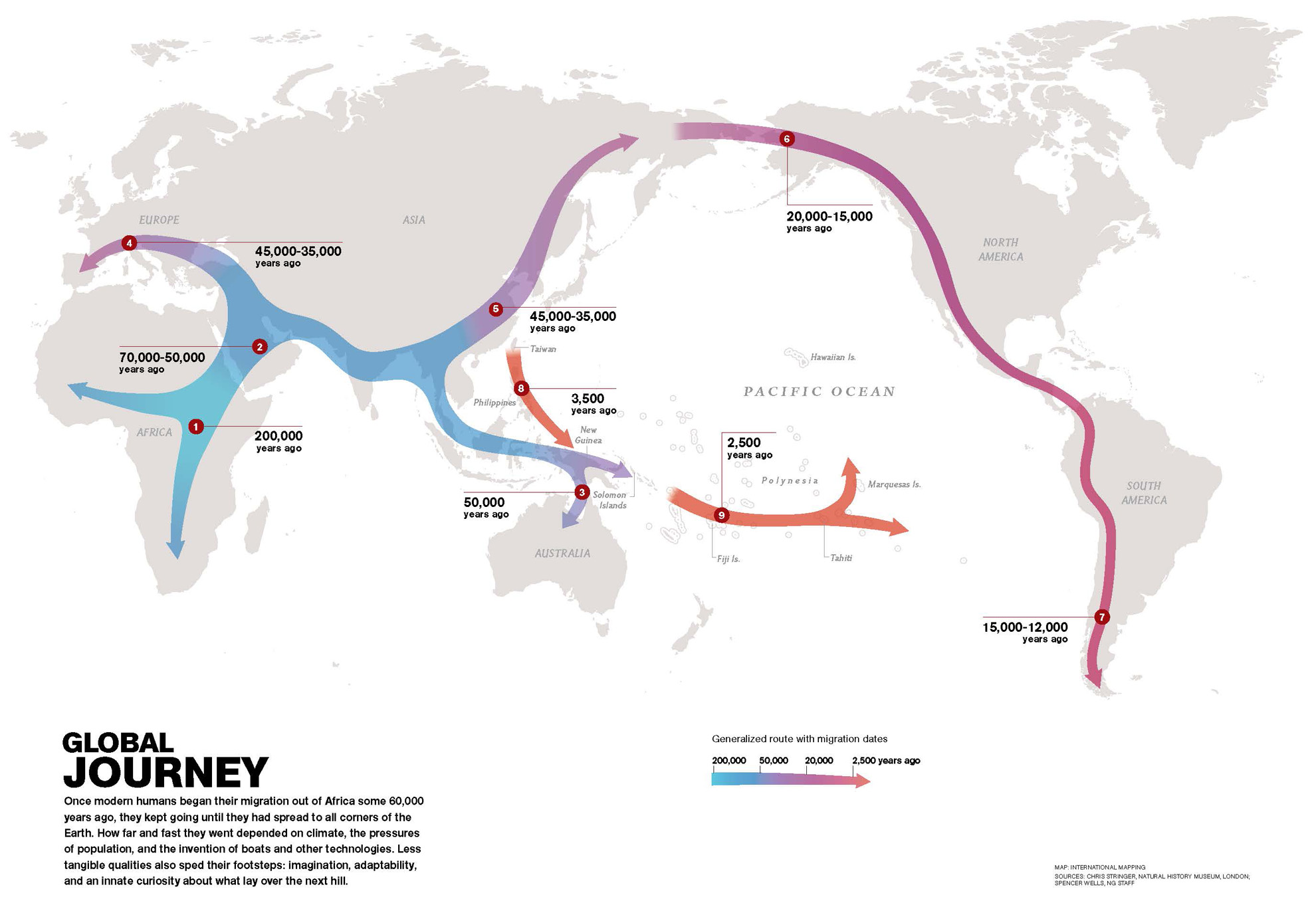
Homo sapiens travelled from East Asia by water to… (hint: 2 locales)
New Guinea, 3500YA
Polynesia, 2500YA
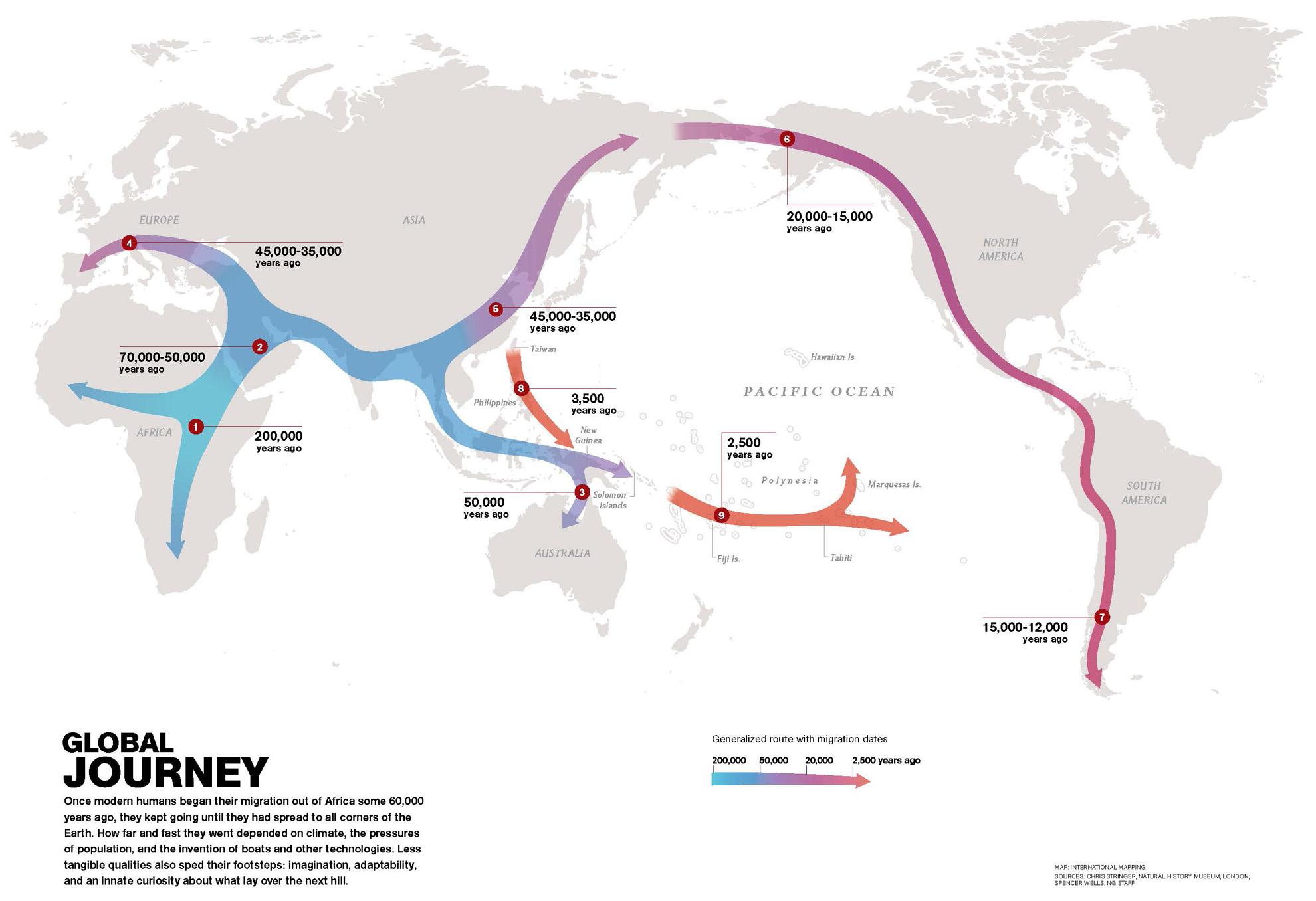
Homo sapiens travelled from the Polynesian islands to…
Hawaii, 1500YA
The last place on Earth to be settled by Homo sapiens / humans was…
New Zealand, 700YA
What are some ways that humans across the globe have adapted to their environments?
Body shape (ex. larger bodies conserve more heat)
Skin pigment in response to UV intensity (higher towards the equator)
Salt retention rates
High altitude adaptations (ex. higher hemoglobin levels in the blood = higher blood oxygen)
In terms of skin pigment, how does folic acid and vitamin D come into play?
It’s all about finding balance.
Folic acid breaks down under UV light, but we need UV light to make vitamin D.
(Note: There are some exceptions, as vitamin D can also be gained through diet and especially meat.)
How did lighter skin tones evolve?
Living further away from the equator (less UV light = less need for protection)
Switching to a more plant-based diet (plants are lower in vitamin D than meat)