5- Gallbladder Function and Bile Production
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Bile v. Bilirubin
Bile is not bilirubin but bilirubin is one of the many constituents of bile
Bilirubin is the breakdown product of hemoglobin
What’s the main blood supply to the liver?
Hepatic portal vein (75%)
Hepatic artery (25%)
What do apical and basolateral surfaces of hepatocytes (liver cells) each face?
Apical surfaces of hepatocytes face bile canaliculi
Basolateral surfaces of hepatocytes face sinusoids
What do sinusoids empty into?
Central veins → hepatic veins → IVC
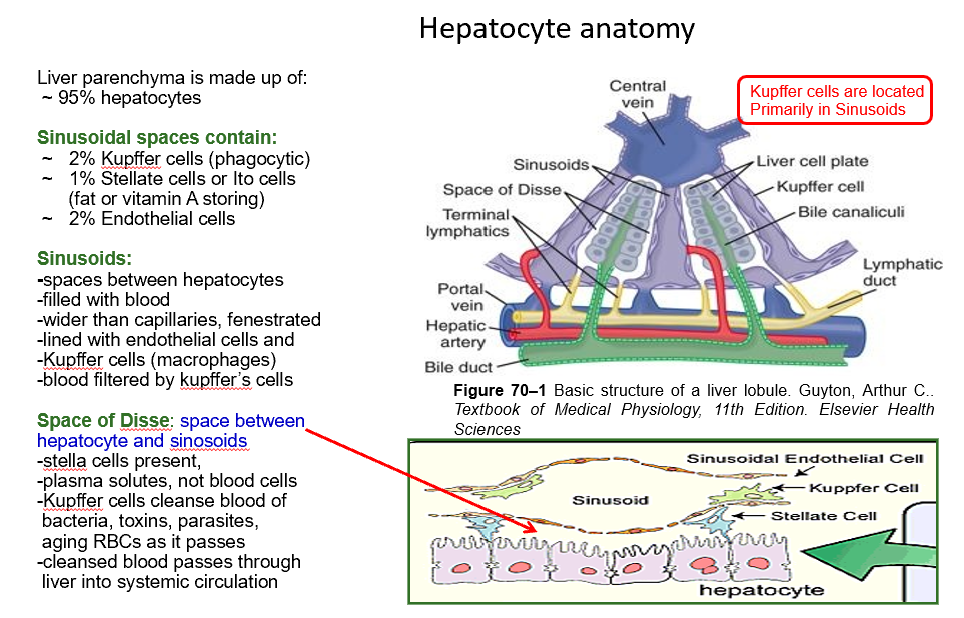
What are sinusoids lined with?
Kupffer cells
Fenestrated endothelial cells
Note: no basement membrane between endothelium and hepatocytes
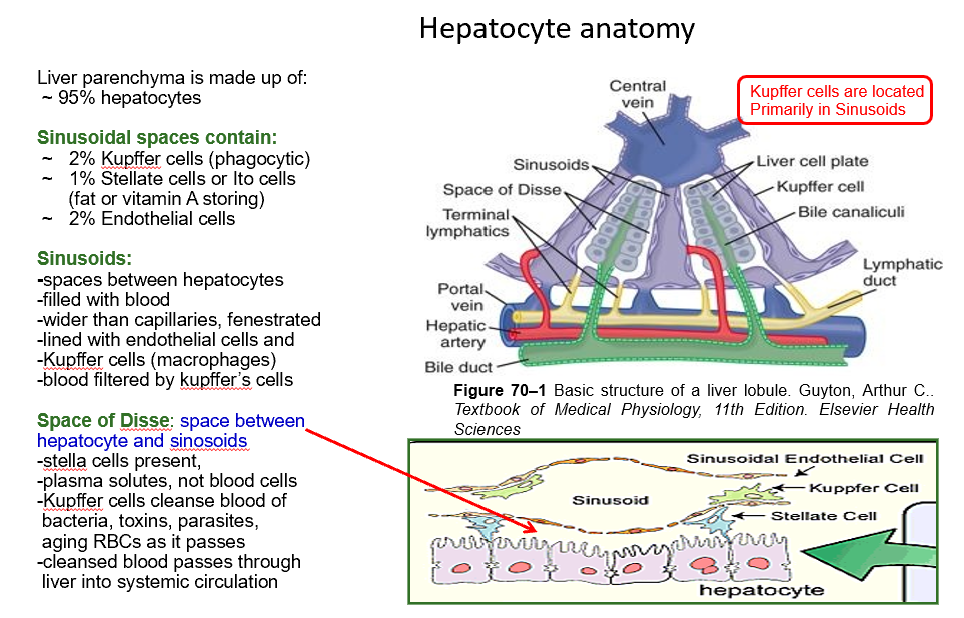
Perisinusoidal Space (Space of Disse)
Space between hepatocyte and sinusoids
Blood is cleansed and passed through
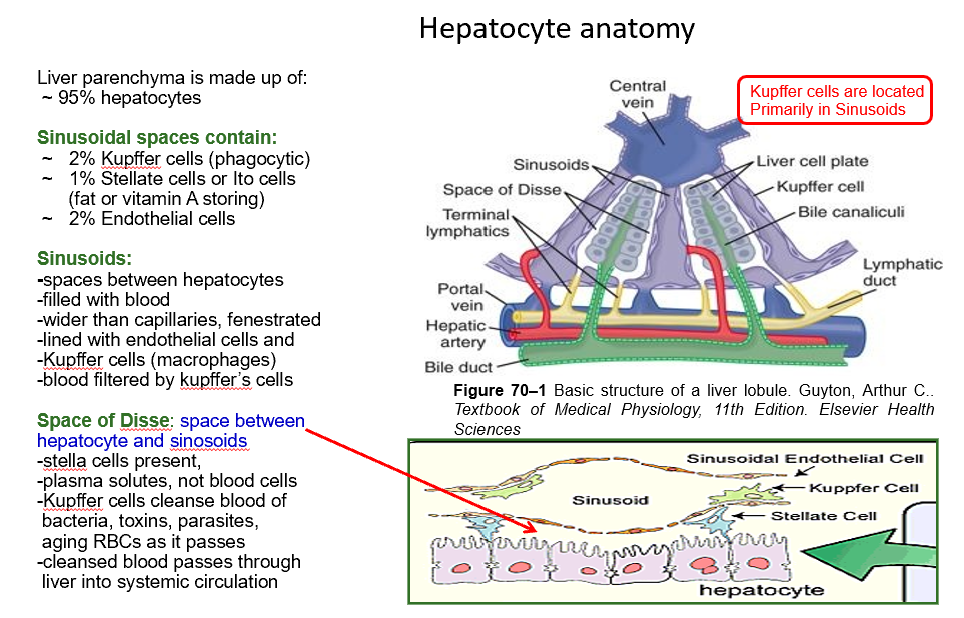
Sinusoid
Space between hepatocytes
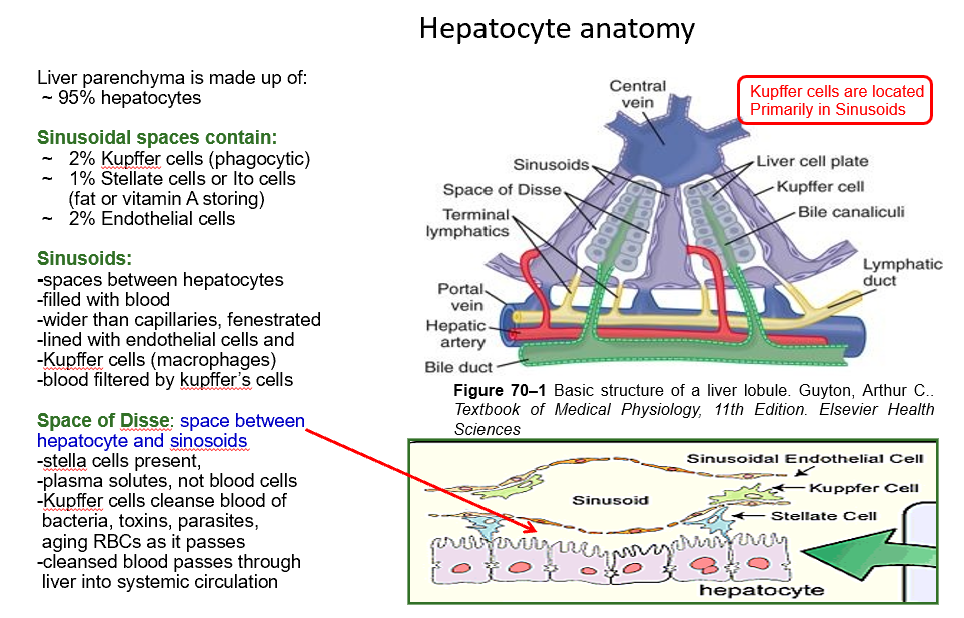
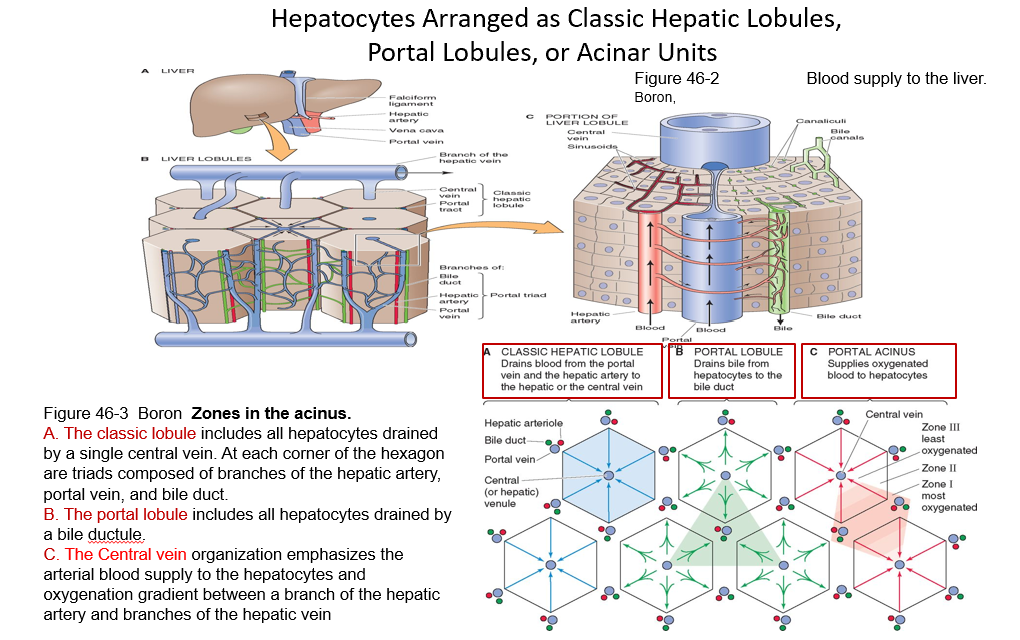
Lobules
Functional units of liver, hexagonal arrangements surrounding a central vein.
Bile Canaliculus
Bile carrying channels runs between sinusoids and within each hepatic plate.
Each hepatocyte is in contact with a sinusoid on one side and bile cannaliculus on other side.
Liver Acinus
Functional unit of hepatic parenchyma
Hepatocytes in each acinus are arranged in 3 zones
3 Elliptical Zones of Hepatocytes within Liver Acinus
Zone 1
cells are the first liver cells affected by viral hepatitis
Zone 2
Intermediate
Zone 3
Centrilobular
P450
cells are the first liver cells affected by ischemia and alcoholic hepatitis, and are most sensitive to toxic injury
What forms the common bile duct?
Common hepatic and cystic ducts
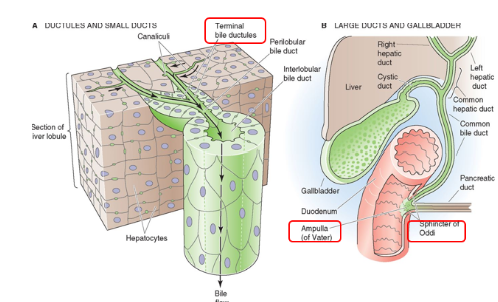
What forms the ampulla of Vater?
Common bile duct may merge with pancreatic duct
Before entering the duodenum
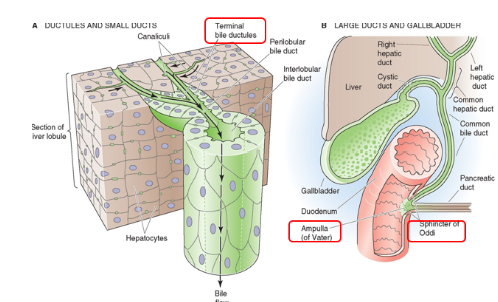
Common Sphincter/Sphincter of Oddi
Regulates flow out of common bile duct and pancreatic duct.
Prevents bile from entering duodenum
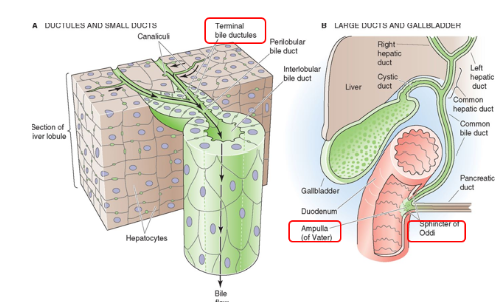
Where is bile actively diverted to between meals?
Gallbladder (from the liver)
Describe the composition of canalicular bile:
Active
Isotonic
Bile salts are actively secreted by:
The Liver
When bile salts become concentrated, they form:
Micelles
What colors bile yellow? What about brown in the stool?
Bilirubin gives a golden yellow color to bile
Stercobilin gives a brown color to the stool
Bile Composition Percentages?
Bile Acid 67%
Phospholipid 22%
Cholesterol 4%
Bilirubin 0.3%
Protein 4.5%
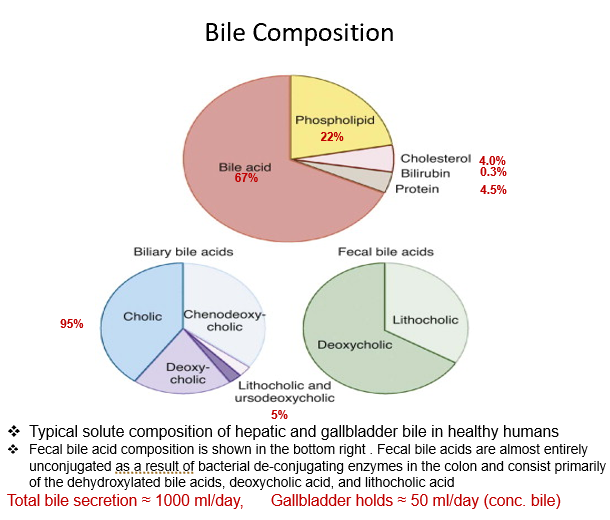
How much bile is secreted per day? How much can the gallbladder hold?
1000 ml/day
50 ml/day
4 Major Bile Components
Bile Salts
Cholesterols/Phospholipids
Bilirubin
Protein/Bicarb
Functions of bile
Emulsify lipids
Form micelles using bile salts
Neutralize pH of gastric chyme
Natural immunity
Prevent gallstone formations
When does the gallbladder deliver bile to the duodenum?
During a meal!
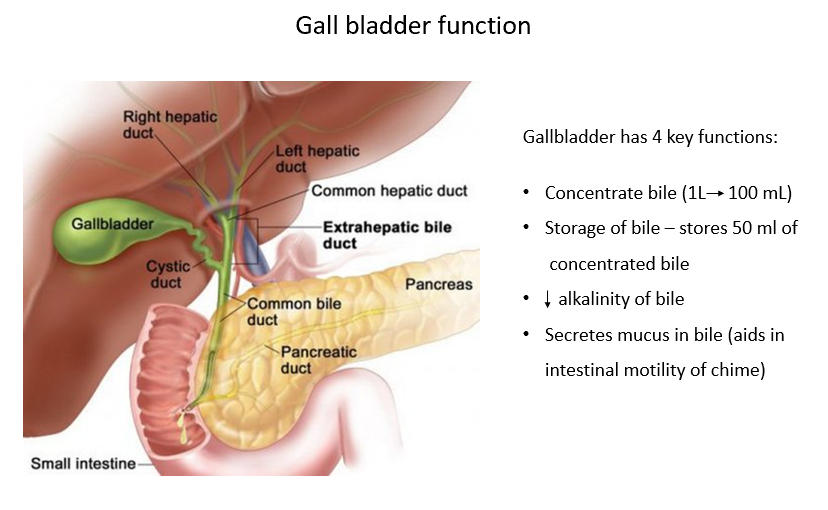
Gallbladder Functions
Concentrate bile
Store bile
Decrease alkalinity of bile
Secrete mucus in bile
Where are most bile salts reabsorbed by active transport?
Terminal Ileum
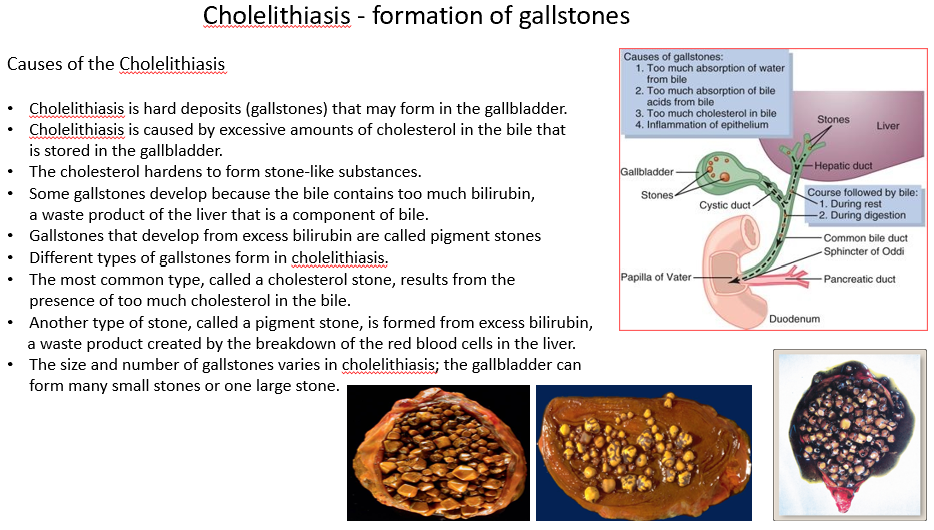
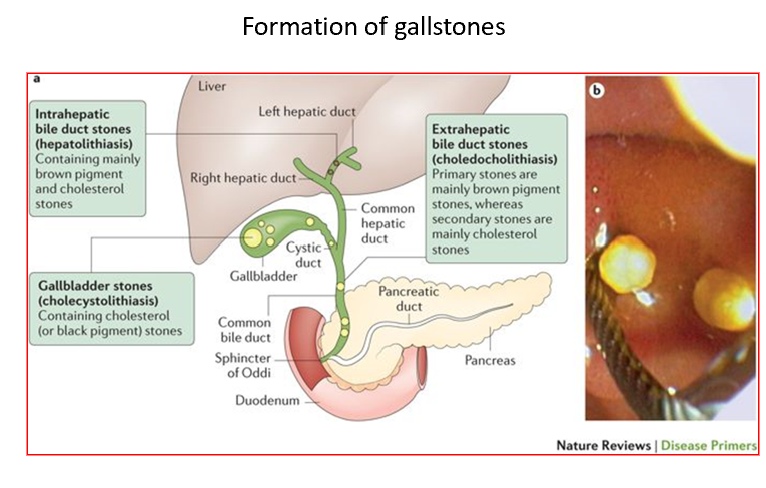
Cholelithiasis
Formation of stones (calculi) within the gallbladder or biliary duct system.
Can be caused by excess cholesterol in the bile or too much bilirubin (causes pigment stones).
Cholecystitis
Inflammation of gall bladder
Cholangitis
Inflammation of the biliary ducts
Gallstones form due to:
Abnormal bile composition
Biliary stasis
Inflammation of gallbladder
Cholestasis (cause, sx, types(2))
Bile can’t flow from liver → duodenum
Sx:
Fatigue
Pruitus (itching)
Jaundice
Pale stool
Dark Urine
2 types:
Obstructive
Metabolic (issue with bile formation)
2 Categories of Cholestatic Liver Disease
Intra-hepatic (obstruction at the level of hepatocytes/canalicular membrane)
Extra-hepatic (impediment in the biliary tree)
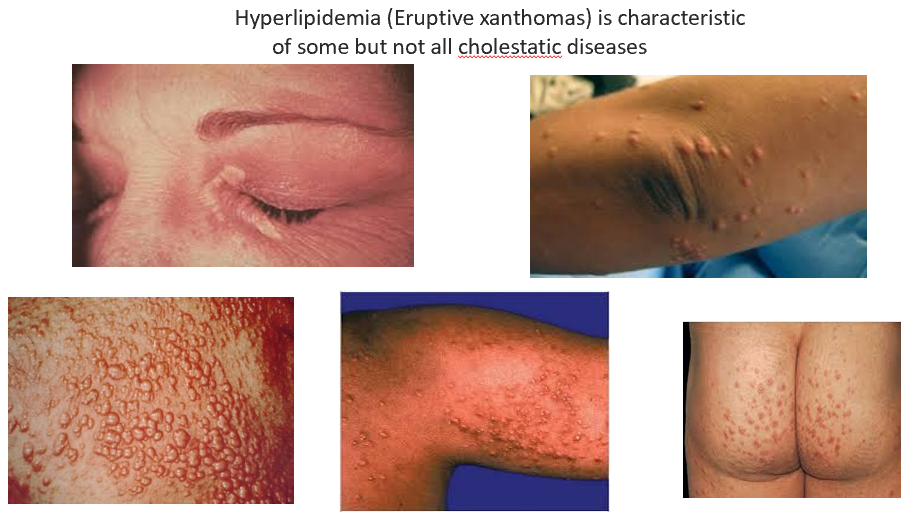
Hyperlipidemia (Eruptive xanthomas) is characteristic of some:
Cholestatic diseases
Risk factors for Cholelithiasis?
Female
Fertile
Fat
Forty
The 4 F’s!