Practical Exam Material
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Aseptic technique
quadrant streaking- loop goes through bunsen burner and then streak 1-2 times and then repeat process 4 times- goal is to perform pure colonies
during this make sure to wear proper PPE
keep lids OFF the bench
minimizing contamination
Liquid culture
Transferring pure colony into broth by reflaming loop
also lids NOT on bench top!
CLOSE THE TIP BOX
Chunking- scapel to cut out agor. flame it first
don’t leave plate open
do not put loop down or keep it in air
resterilize loop immediately after
NEMATODES
keep bunsen burner on at all times while the lids are off the plates
sterilize the worm pick before and after touching each worm
Labeling samples
THREE THINGS GIRL DON’T FORGET
initials, the date, and the name of the sample
Proper Use of Lab Equipment
Balance: make sure to tare to 0 and then weight and then close
analytical balance: it has a screen on it make sure to close it- for SMALL ass measurements (0.01 mg)
incubator
provides a controlled environment for cell or microbial culture, maintaining specific temperature, humidity, and gas levels

shaking incubator
agitate or shake cell cultures

fridge freezer
used to store samples at low temperatures, capable of freezing items as well as refrigeration.
spectrophotometer
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/0/03/Spectrophotometer_Model_1.JPG measures the amount of light that a sample absorbsIt is commonly used to determine the concentration of solutes in a solution.
NEEDS a blank
click the number you wanna measure (1,2,3,4,5)
Nanodrop
know how to read a nanodrop
SHOWS ABSORBANTS at various wavelengths (concentration and measurement of your impurity)
260/280 ratio of dna to protein
> 1.8 RATIO OF DNA
aim for > 20 ng/mL
microcentrifuge
for the actual tube it needs to be the same amount of liquid
make sure they are 7 apart
across from each other (orientation)
micropipettes
fair game may be asked to pipette, choosing one, closing the tip box
go down to the first to pick up liquid, second to expel it
serological pipettes
accurately measuring and transferring liquid volumes, typically from less than 1 ml to up to 50 ml
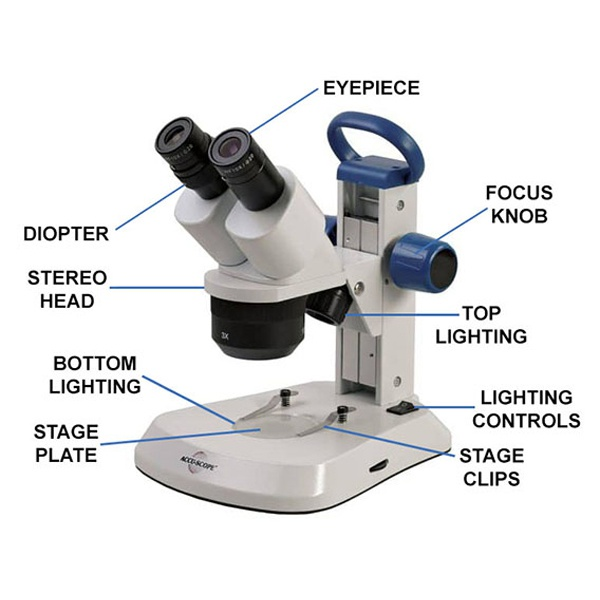
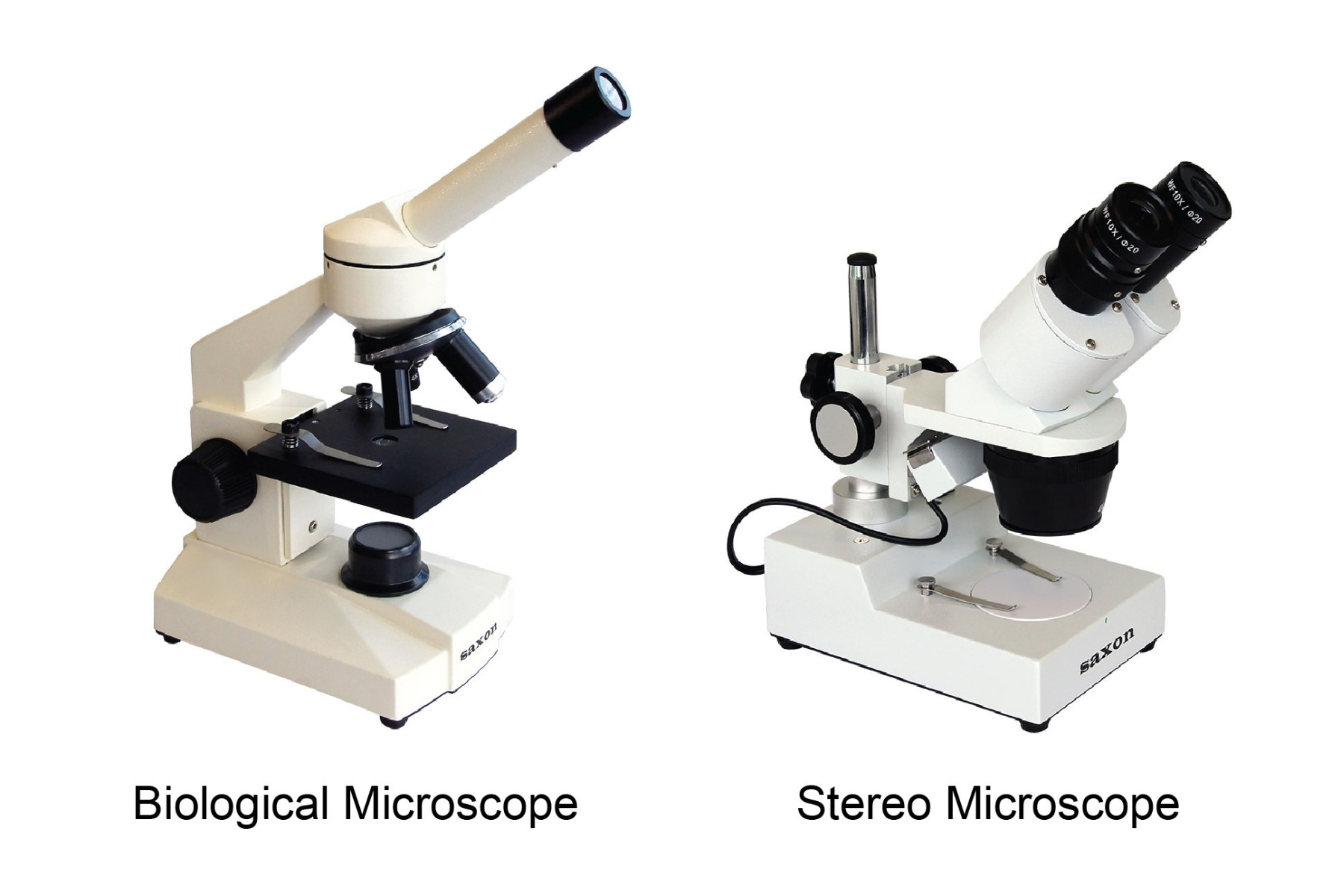
stereoscopic microscope
3D view of a sample, typically used for dissection or examining surface details.

compound microscope
Compound microscopes are used for observing very small, transparent specimens at high magnification (40x-1000x).
inner large one- coerce
outer one - fine
thermocycler
PCR
DNA sequencing, cloning, generation of probes, quantification of DNA and RNA, studying patterns of gene expression, detection of sequence-tagged sites, and many more techniques.

op50
PINKKKKK basillcus
circular
e.coli
NO SPORES
G-
= worm food
4A4-
PURPLE, bacillus
squares
Bt
G+
purple
firms spores
toxic- not worm food they will die
Explain the purpose of quadrant streaking
a technique used to obtain pure cultures on agar medium
Describe the purpose of pure colonies
study the properties of the species/ strain
Compare and contrast a male and hermaphrodite
hermaphrodites are capable of self fertilization and mating with males, they have XX chromosomes. much larger
males can mate with hermaphrodites, X0 gonads, small and have a tail fin
Describe how nematodes are cultured in the lab
they are cutlured in agar rows containing petri dishes on the lawn of the bacteria E. coli
purpose of light microscopy
to visualize and study small structures and samples by creating a magnified image of how they interact with visible light
Gram Staining
to differentiate between two typs of bacteria (G-) (G+)
stains the peptidoglycan within the cell wall
List the components needed for a successful reaction in the correct order used in the protocol, and describe their functions
cells are fixed to slide surface
crystal violet is added (covers entire slide)
this sits and is washed off
its function is to stain the cells
IODINE- added and covers the whole slide
this sits and then is washed off
function is to bind stain the G+ cells, helps increase stain retention
wash off with ethanol
functions as a solvent and will completely wash outdie of thin peptidoglycan
add safranin
functions in staining the G- cells, staining the bacteria that has been decolorized
GRAM STAINING : Interpret and analyze data obtained through this method (Did you get the expected staining pattern? If not, what might be the reason?
G+ cells= DARK PURPLE
G- cells= pink/ reddish
if no color= a step was skipped or heat wasn’t applied to sample before it was stained
if G+ is pink then= over decolorization with ethanol
if G- is dark purple= under decolorization with ethaol (Wasn’t fully washed)
DNA Purification
purpose: to amplify a specific gene
PCR water (volume of the reaction- thing that the reaction takes place in)
Template- result of the dna protocol
BEF 1 and BER 1 (FORWARD AND REVERSE)- goal to stick to strands
dNTPs = ATCG- nucleotides to synthesize new DNA
Rx buffer- buffer
PFU = polymerase enzyme- MUST BE LAST!!!!
Whole procedure done on ICE ICE ICE!!
GEL ELECTROPHORESIS: Interpret and analyze data obtained through this method (Did you get the expected staining pattern? If not, what might be the reason?
expected product is a single clear band that appears as the expected size compared to DNA ladder
band in negative color= contamination
faint band= low concentration of DNA
smear instead of sharp band= degraded dna, overloaded the sample
gel electrophoresis: purpose
to separate and visualize DNA based on their size and charge
Demonstrate how to correctly set up a gel and gel apparatus
precast or handmade gel
samples loaded into wells of gel
need to be mixed with loading dye so you can visualize
cover the gel with TAE buffer
always run to red
DNA is negatively charged
Nematodes
N2 is wild type for c. elegans
XX vs. X0
Go through 4 larval stages
L1 and L2 will go into dauer stage, very skinny, go into status
C. elegans are free living, not parasitic