Lecture 2 - Cardiovascular system
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/45
Last updated 3:51 PM on 5/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
1
New cards
Describe the size, shape and location of the heart
- Size
> Closed fist
- Shape
> Apex is a blunt rounded point of cone
> Base is flat part at opposite of end of cone
- Location
> Thoracic cavity, mediastinum
> Closed fist
- Shape
> Apex is a blunt rounded point of cone
> Base is flat part at opposite of end of cone
- Location
> Thoracic cavity, mediastinum
2
New cards
Describe what pericardium is and what it does
- Membrane that surrounds the heart
- Keeps the heart in place and limits its motion
- Prevents it from over expanding and acts as an anchor
- Keeps the heart in place and limits its motion
- Prevents it from over expanding and acts as an anchor
3
New cards
What are the two layers of the pericardium called?
1. Outer layer
fibrous pericardium
2. Inner layer
serous pericardium
fibrous pericardium
2. Inner layer
serous pericardium
4
New cards
Name and describe the two layers of the serous pericardium?
1. Parietal layer
Lines the fibrous pericardium
2. Visceral layer
Covers the heart surface
- The two are continuous and have a pericardial cavity in between that reduces friction as the heart beats
Lines the fibrous pericardium
2. Visceral layer
Covers the heart surface
- The two are continuous and have a pericardial cavity in between that reduces friction as the heart beats
5
New cards
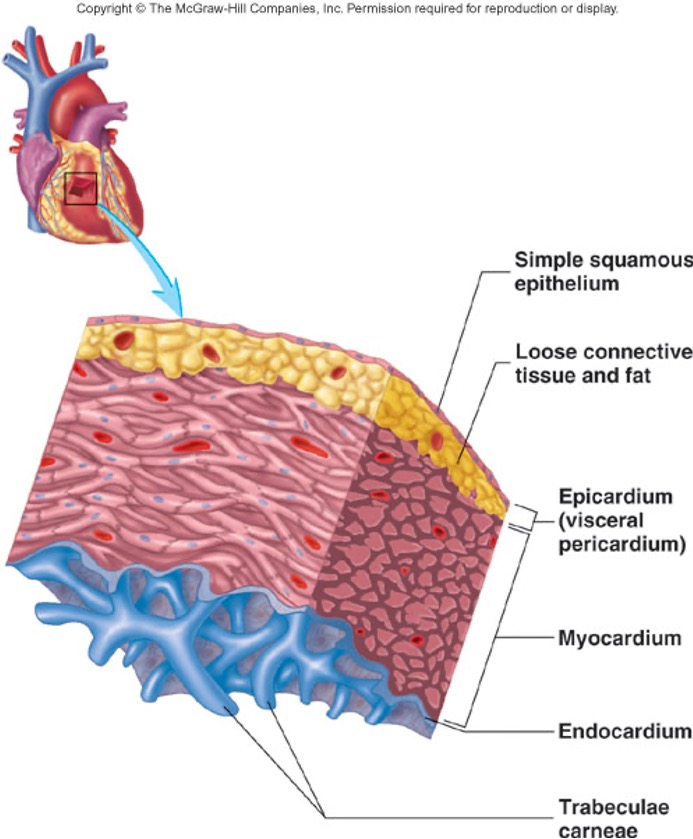
Name and describe the three layers of the heart
1. Epicardium
Smooth outer surface of heart
2. Myocardium
Composed of cardiac muscle cell, responsible for heart contracting
3. Endocardium
Smooth inner surface of heart chambers
Smooth outer surface of heart
2. Myocardium
Composed of cardiac muscle cell, responsible for heart contracting
3. Endocardium
Smooth inner surface of heart chambers
6
New cards
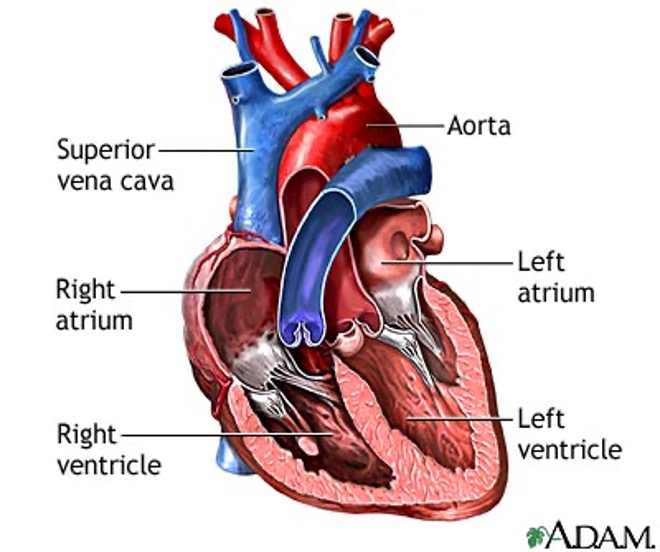
Name and describe the four chambers of the heart and the two septums
1. Right atrium
Receives deoxygenated blood from the superior and inferior vena cava and the coronary sinus
2. Left atrium
Receives oxygenated blood from pulmonary veins
3. Right ventricle
Pumps deoxygenated blood to pulmonary trunk/artery
4. Left ventricle
Pumps oxygenated blood to aorta
5. Inter-atrial septum
Wall between the atria
6. Inter-ventricular septum
Wall between the two ventricles
Receives deoxygenated blood from the superior and inferior vena cava and the coronary sinus
2. Left atrium
Receives oxygenated blood from pulmonary veins
3. Right ventricle
Pumps deoxygenated blood to pulmonary trunk/artery
4. Left ventricle
Pumps oxygenated blood to aorta
5. Inter-atrial septum
Wall between the atria
6. Inter-ventricular septum
Wall between the two ventricles
7
New cards
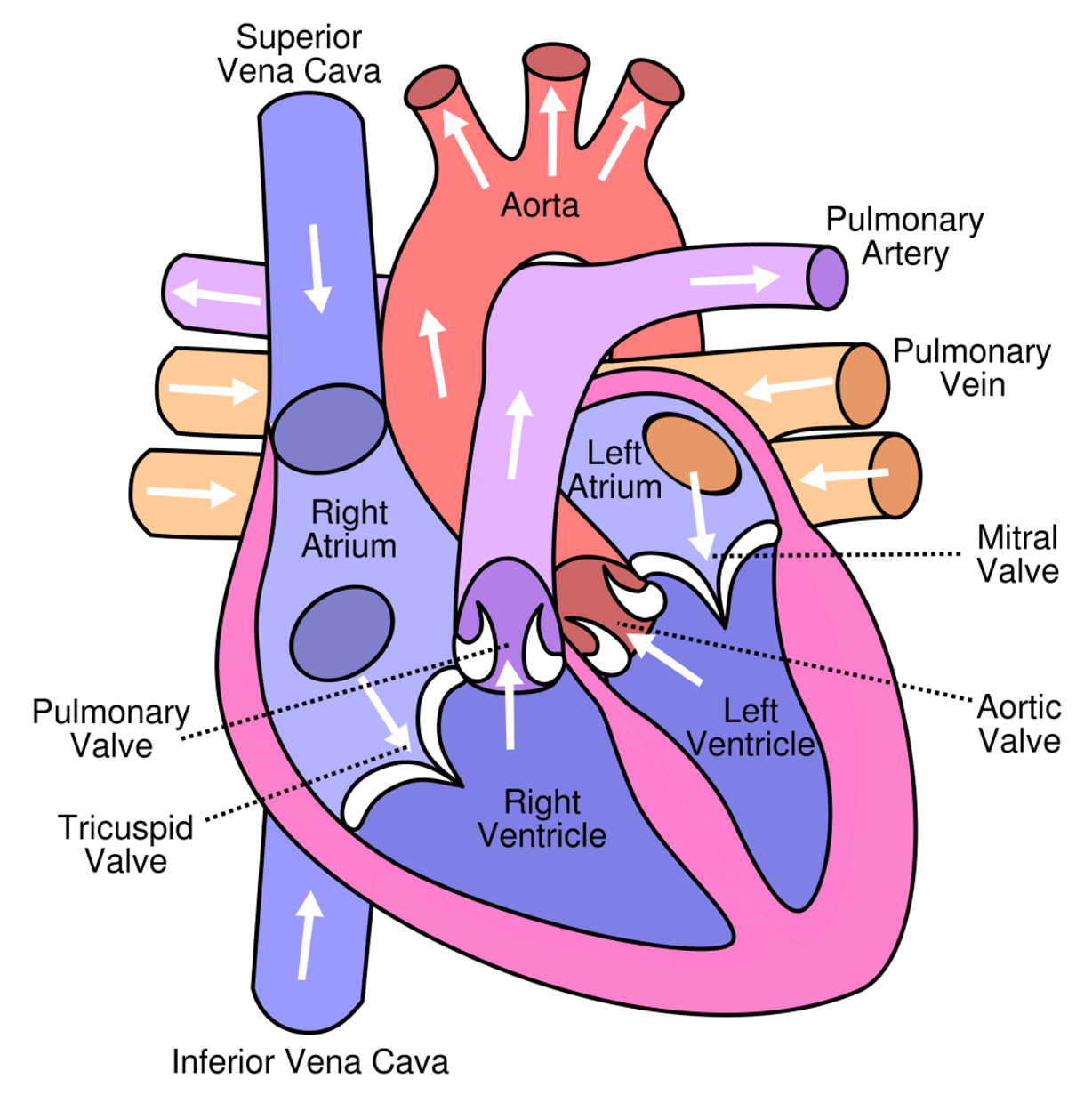
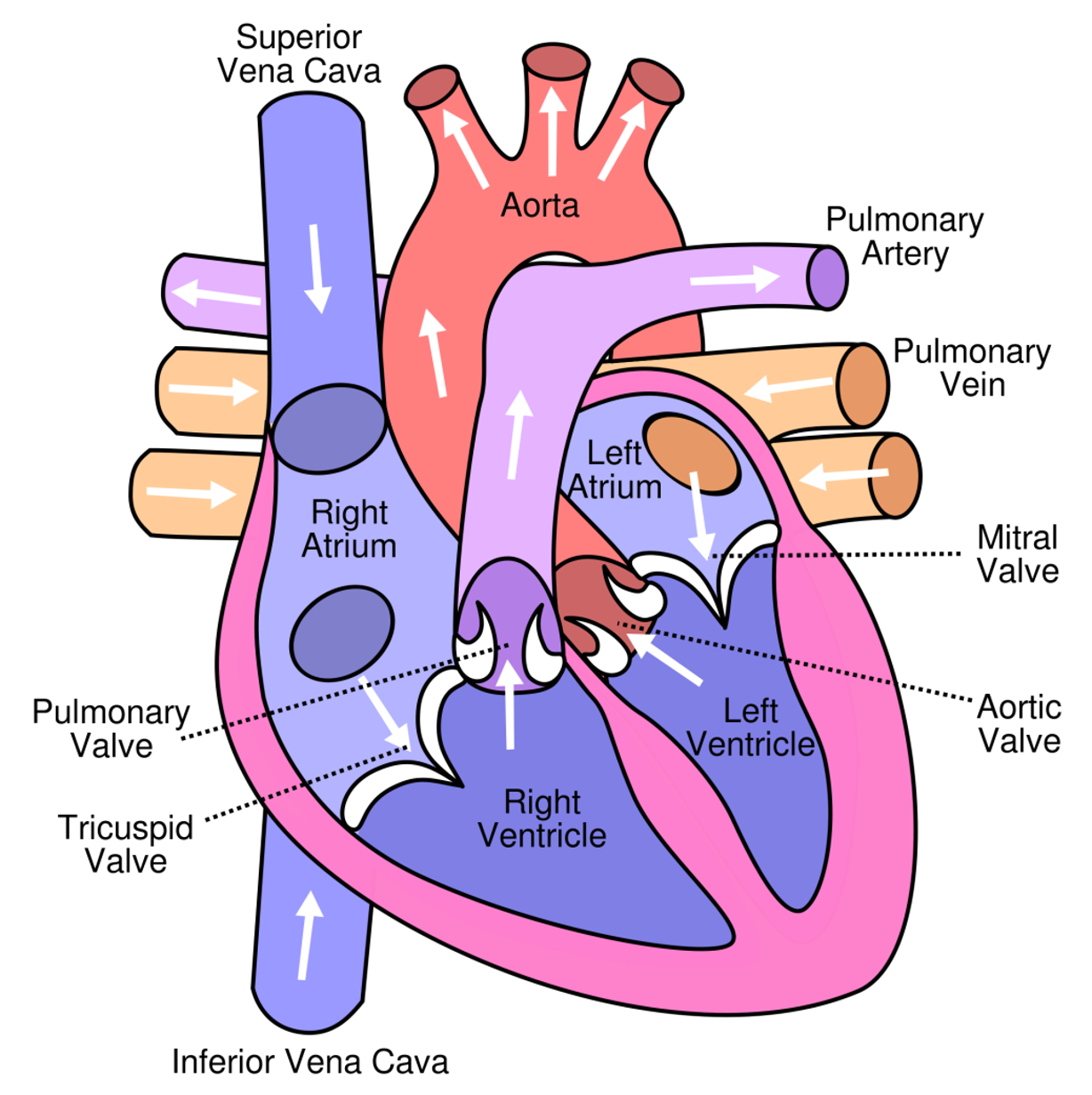
What is the primary function of heart valves?
Prevents back flow of blood
8
New cards
Where do the atrioventricular (AV) valves lie?
Between atria and ventricles are the tricuspid valve on the right side of the heart and bicuspid valve on the left
9
New cards
What are the valves attached to?
Each valve has leaf like cusps that are attached to cone shaped papillary muscles by tendons
10
New cards
What and where are the two semilunar valves?
1. Aortic valve - base of the aorta
2. Pulmonary valve - base of the pulmonary trunk
2. Pulmonary valve - base of the pulmonary trunk
11
New cards
Outline the route of blood flow within the body
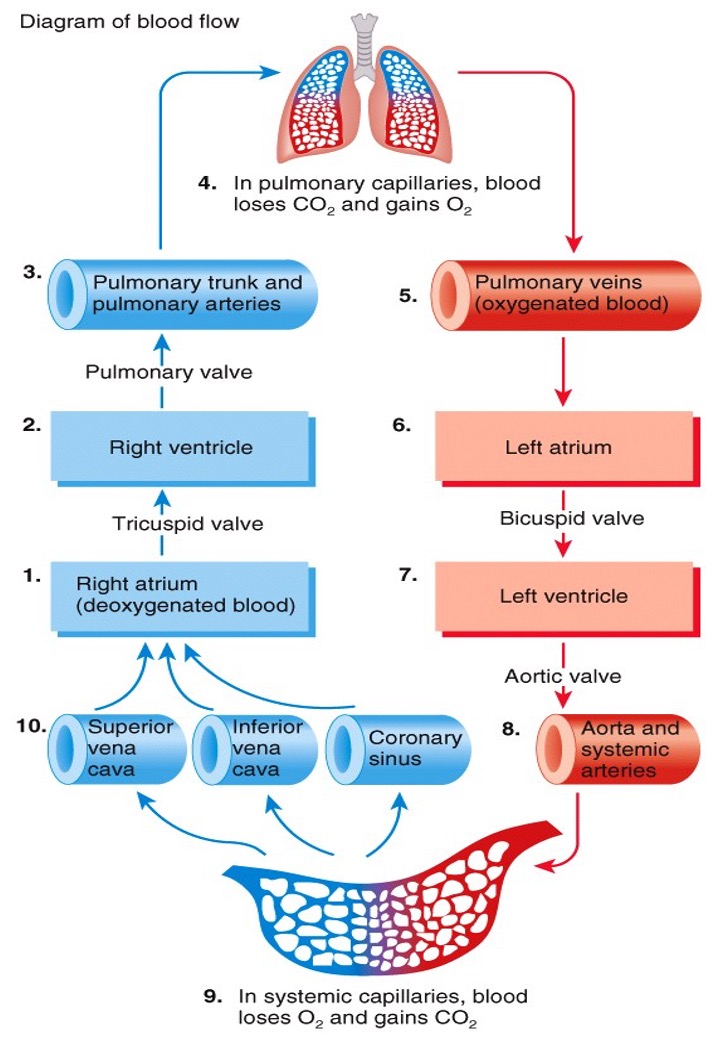
12
New cards
What are the three parts of the body's circulatory system?
1. Pulmonary
2. Coronary
3. Systemic
2. Coronary
3. Systemic
13
New cards
Describe systemic circulation
- The left side of the heart is the pump for the systemic circulation
- It pumps oxygenated blood from the lungs out into the vessels of the body
- It pumps oxygenated blood from the lungs out into the vessels of the body
14
New cards
Describe pulmonary circulation
- The right side of the heart is the pump for the pulmonary circulation
- It receives deoxygenated blood from the body and sends it to the lungs for oxygenation
- It receives deoxygenated blood from the body and sends it to the lungs for oxygenation
15
New cards
What is the blood volume distribution?
Pulmonary circulation - 18%
Coronary - 12%
Systemic - 70%
Coronary - 12%
Systemic - 70%
16
New cards
Describe coronary circulation
Provides blood flow to the myocardium
17
New cards
coronary artery disease
18
New cards
How is the myocardium specialised?
- Has intercalated discs with gap junctions to allow muscle action potentials to conduct from one muscle fibre to its neighbours
19
New cards
Describe what is meant by autorythmic cells
- Cells can spontaneously depolarise and generate action potentials
- Cells act as a pacemaker to set the rhythm for the entire heart
- Form their own conduction system
- Cells act as a pacemaker to set the rhythm for the entire heart
- Form their own conduction system
20
New cards
How do cardiac muscle cells contract?
- Action potential initiated in the conduction system is propagated across the sarcolemma of cardiac muscle cells
- Thin filaments and sarcomeres shorten within cardiac muscle cells
- Thin filaments and sarcomeres shorten within cardiac muscle cells
21
New cards
What does the conduction system do?
Heart regulates the rate and strength of contraction through an intrinsic conduction system, modified by external sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways
22
New cards
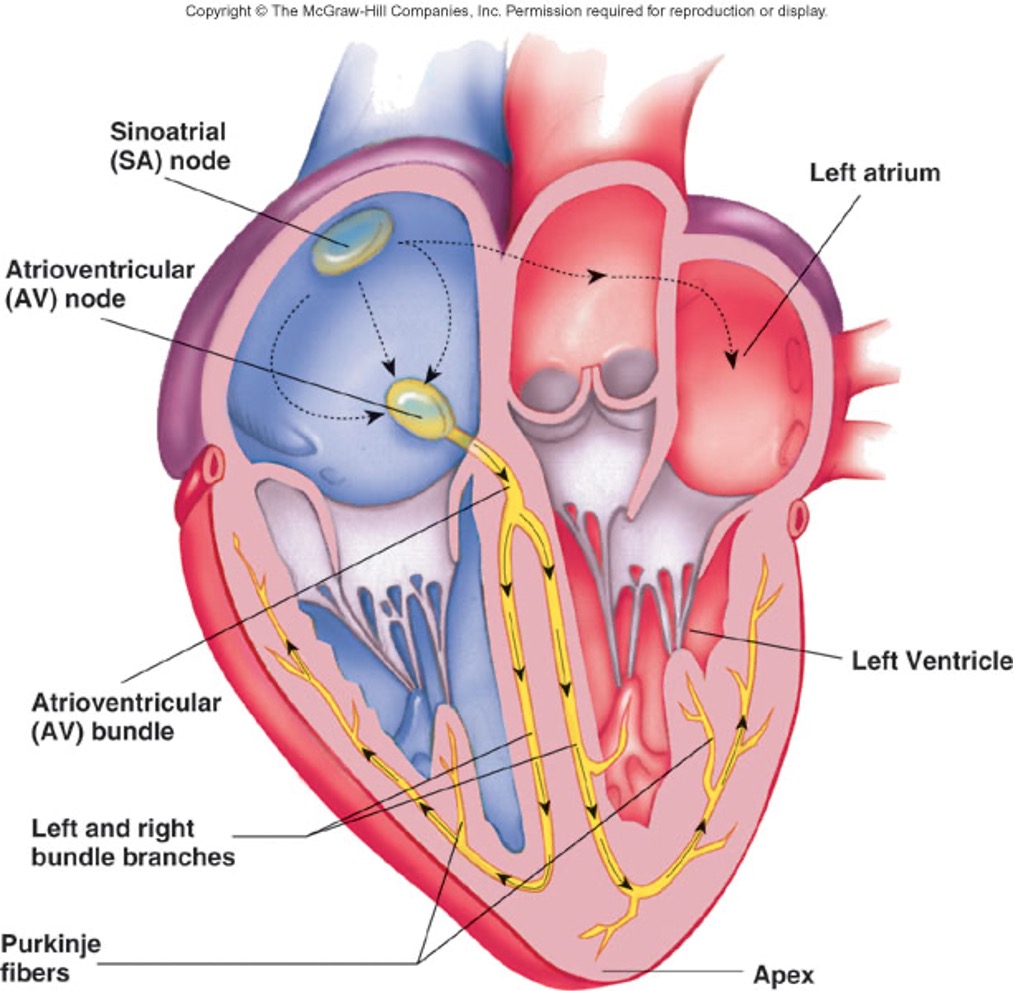
Describe the function of the SA node in relation to the conduction system
- mass of auto-rhythmic cells in the right atrial wall near the entrance of the superior vena cava
- generates impulses about 100x per minute and sets pace for entire heart
- generates impulses about 100x per minute and sets pace for entire heart
23
New cards
Describe the function of the AV node in relation to the conduction system
- mass of auto-rhythmic cells located in the inferior portion of the inter-atrial septum above the tricuspid valve
- each impulse is delayed briefly here, allowing atria to contract before ventricles
- each impulse is delayed briefly here, allowing atria to contract before ventricles
24
New cards
Describe the function of the bundle of His in relation to the conduction system
- Auto-rhythmic cells located in the inter-ventricular septum
- Only electrical connection between atria and ventricles
- Only electrical connection between atria and ventricles
25
New cards
Describe the function of the Purkinje fibres in relation to the conduction system
- Run through the inter-ventricular septum, penetrate the heart apex, then turn upwards through the ventricular myocardium triggering ventricular contraction and pushes blood through the semilunar valves.
26
New cards
Define ECG
- Electrocardiogram
- A recording device for the heart's electrical events during each cardiac cycle
- A recording device for the heart's electrical events during each cardiac cycle
27
New cards
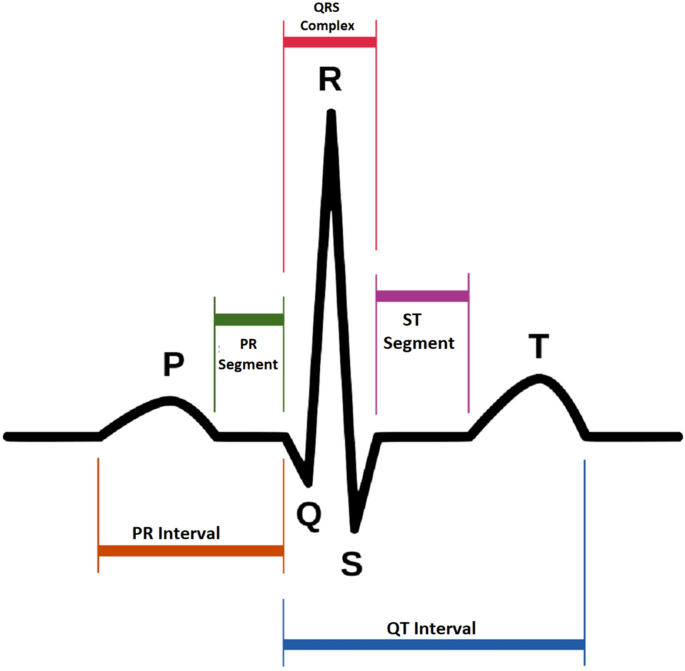
What does the P wave represent on the ECG?
- Depolarisation of atrial myocardium
- Signals onset of atrial contraction
- Signals onset of atrial contraction
28
New cards
What does the QRS complex represent on the ECG?
- Ventricular depolarisation and signals onset of ventricular contraction
- Repolarisation of atria simultaneously
- Repolarisation of atria simultaneously
29
New cards
What does the T wave represent on the ECG?
- Repolarisation of ventricles
- Precedes ventricular relaxation
- Precedes ventricular relaxation
30
New cards
What does the PQ interval represent on the ECG?
- Atria contract and begin to relax
- Ventricles begin to contract
- Ventricles begin to contract
31
New cards
What does the QT interval represent on the ECG?
- Ventricles contract and begin to relax
32
New cards
Label the waves on an ECG
33
New cards
What is the cardiac cycle made up of?
- Sequence of events that make up a heartbeat
- Consists of systole and diastole of both atria, rapidly followed by systole and diastole of both ventricles
- Consists of systole and diastole of both atria, rapidly followed by systole and diastole of both ventricles
34
New cards
How long does a complete cardiac cycle take?
75 beats/min = 0.8 secs
35
New cards
Define auscultation
Act of listening to heart sounds within the body
36
New cards
What is the 'lub' and 'dup' caused by?
- 'Lub' - blood turbulence associated with tricuspid and bicuspid valves closing
- 'Dup' - blood turbulence associated with pulmonary and aortic valves closing
- 'Dup' - blood turbulence associated with pulmonary and aortic valves closing
37
New cards
Define cardiac output?
- Amount of blood pumped out by each ventricle in one minute
- Volume of blood ejected from the left ventricle into the aorta each minute
- heart rate x stroke volume
- Volume of blood ejected from the left ventricle into the aorta each minute
- heart rate x stroke volume
38
New cards
Define stroke volume
- Volume of blood pumped out by a ventricle with each contraction/heart beat
- Usually 70ml
- Usually 70ml
39
New cards
What is stroke volume affected by?
- Venous return
- Force of contraction of heart regulated by
> hormones sympathetic
> nervous system
- Force of contraction of heart regulated by
> hormones sympathetic
> nervous system
40
New cards
Define heart rate
Number of times the heart beats in one minute
41
New cards
What is the heart rate regulated by?
- Parasympathetic nervous system - acts on SA node to decrease heart rate
- Sympathetic nervous system - acts on SA node to increase heart rate
- Hormones, age, exercise, body temperature
- Sympathetic nervous system - acts on SA node to increase heart rate
- Hormones, age, exercise, body temperature
42
New cards
Define tachycardia
Heart rate greater than 100bpm
43
New cards
Define bradycardia
Heart rate slower than 60bpm
44
New cards
Define venous return
Amount of blood which returns to the heart
45
New cards
What is venous return regulated by?
- Blood volume - increases with exercise and decreases in event of a haemorrhage
- Skeletal muscle and respiratory pumps - muscles contracting around blood vessels aid venous return to the heart
- Skeletal muscle and respiratory pumps - muscles contracting around blood vessels aid venous return to the heart
46
New cards
State the formula for mean arterial pressure?
(1/3 x Systolic BP) + (2/3 x Diastole BP)