Chapter 1 - Music Fundamentals
4.0(1)Studied by 14 people
Card Sorting
1/42
Last updated 5:09 PM on 3/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
1
New cards
Aspects of sound
Properties that are fundamental to the elements of sound and music
2
New cards
Aspects of sound are
* **Pitch (Frequency)** - Wavelength
* **Dynamic (Amplitude)** - Wave height
* **Timbre (Tone color**) - Waveform
* **Articulation** - Envelope
* **Duration**
* **Dynamic (Amplitude)** - Wave height
* **Timbre (Tone color**) - Waveform
* **Articulation** - Envelope
* **Duration**
3
New cards
Pitch (Frequency)
Wavelength
4
New cards
Dynamic (Amplitude)
Wave height
5
New cards
Timbre (Tone color)
Waveform
6
New cards
Articulation
Envelope
7
New cards
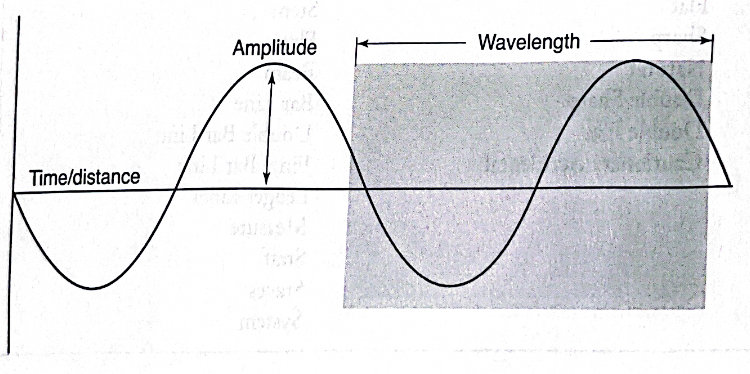
Wavelength
The distance between one wave and the next. It’s related to the frequency and the pitch.
8
New cards
Frequency
The rate of vibration measured in times per second called Hertz.
9
New cards
The higher the frequency
the higher the pitch and the shorter the wavelength.
10
New cards
Height
The size of each individual wave
11
New cards
Amplitude
The length of the wave. It determines the loudness of the sound.
12
New cards
Waveform
The shape and form of the sound wave as it moves in distance and frequency
13
New cards
Timbre
Unique qualities of sound produces by the shape of the waveform
14
New cards
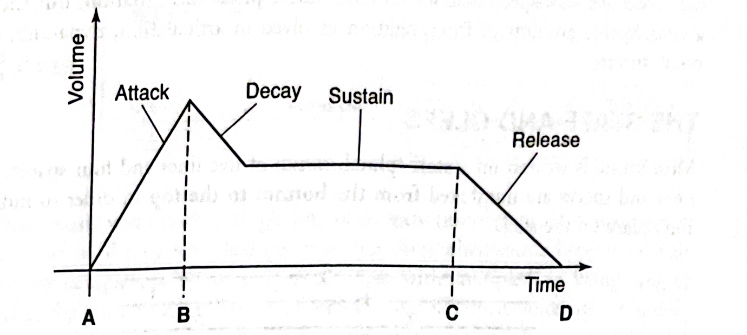
Envelope
Composed of a sounds attack, sustain, and release
15
New cards
Articulation
The manner in which we begin the note, sustain it, and end the note
16
New cards
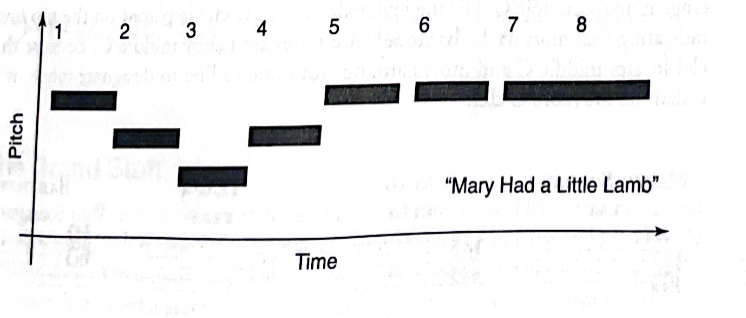
Duration
The length of time sound and silence last
17
New cards
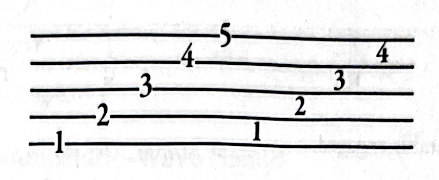
Staf (Staves)
Where most music is written. A space of five lines and four spaces.
* Lines and spaces are numbered from bottom to top.
* Lines and spaces are numbered from bottom to top.
18
New cards
Clefs
What determines the names of the lines and spaces used
* Soprano
* Mezzo soprano
* Alto
* Tenor
* Baritone
* Soprano
* Mezzo soprano
* Alto
* Tenor
* Baritone
19
New cards
C clef
Sign used for all of the previously mentioned vocal ranges

20
New cards
Movable C clef
The clef that locates middle C and moves around from line to line to designate range
21
New cards
Alto clef
When the C clef is placed on the third line of the staff
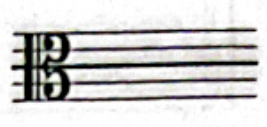
22
New cards
Tenor clef
When the C clef is placed on the fourth line of the staff

23
New cards
Treble clef
When the G clef is placed on the second line of the staff

24
New cards
Bass clef
When the F clef is placed on the fourth line of the staff

25
New cards
System
When multiple staves are connected together by bar lines, brackets, or a brace
26
New cards
Neutral clef
Used for rhythm only or for pitchless or untuned instruments such as triangle, cymbals, or tambourine
27
New cards
Ledger lines
Small lines that extend the staff while still keeping the five lines and four spaces intact
28
New cards
Half step
The smallest space or distance between notes
29
New cards
Sharp
Raises the pitch one half step above its natural pitch
30
New cards
Flat
Lowers the pitch one half step below its natural pitch
31
New cards
Enharmonic equivalent
When notes sound the same but are named differently
32
New cards
Natural
The musical symbol that cancels out a flat or a sharp
33
New cards
Double sharp
Musical symbol used to raise a pitch by two half steps
34
New cards
Double flat
Musical symbol that lowers the pitch by two half steps
35
New cards
parts of a musical note
* Head
* Stem
* Flag
* Beam
* Stem
* Flag
* Beam
36
New cards
Note head
Body of the note
37
New cards
Stem
Part of a note that is common to all note types shorter in duration than the whole note
38
New cards
Flag
Part of the note that is common to all note types shorter in duration than a quarter note
39
New cards
Music notation symbols
Bar line
Measure
Double bar line
Final bar line
Measure
Double bar line
Final bar line
40
New cards
Bar line
The vertical line that divides the staff into measures
41
New cards
Measure
The unit of space between the bar lines
42
New cards
Double bar line
Two lines that signal the end of a section of music
43
New cards
Final bar line
Indicates the end of the piece or composition