GEO Chapter 14
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
River
The trunk stream or an entire river system
Stream
General term not related to size; interchangeable with river. A mixture of water and solids
Functions of a River
Drainage of precipitation in the landscape
Erosion (dislodging, dissolving, or removal of material)
Transportation (the movement of material)
Deposition (when materials are laid down by water) (alluvium)
Base level
The lowest point a stream reaches during its flow, below which it cannot recede.
Ultimate base level
The ocean
Local base level
A temporary base level limiting the erosion of local streams
Processes to create fluvial landforms
Erosive action of flowing water
Deposition of alluvial material
Drainage basin
An area of land where runoff collects and moves through the same area. Separated by ridges that divide precipitation into different basins
Watershed
A word used specifically to refer to the catchment area of a drainage basin
Internal drainage
Never reaches the ocean or other river systems
Drainage patterns
The ways drainage flows in a particular landscape
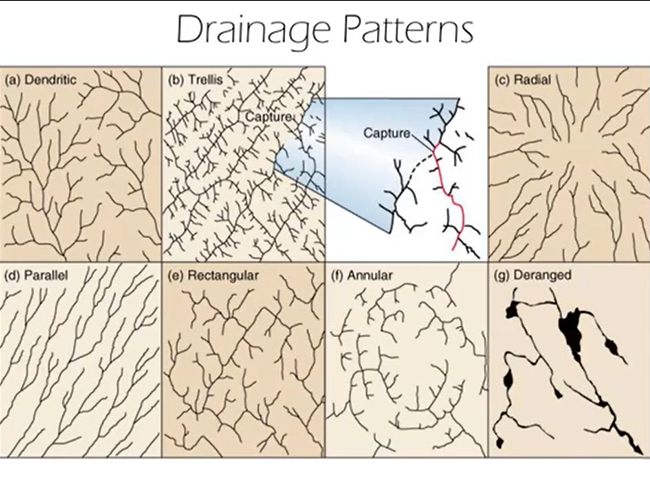
Dendritic drainage pattern
Tree-like. Indicates typical landscape conditions and mature drainage developed
Trellis drainage pattern
Major rivers running parallel to each other. Indicates presence of anticlines and synclinal valleys
Radial drainage pattern
Forms at the top of a high peak. Consists of rivers running down from a high point, forming a “radial” look
Parallel drainage pattern
Long tree-like streams that run parallel to each other. Occurs where there is a slope and unconsolidated materials such that the water ends up easily eroding the materials and shedding off of the slopes effectively.
Rectangular drainage pattern
Consists of near 90 degree turns. Occurs when bedrock is present at the surface, and the river follows the bedrock’s joints/fractures.
Annual drainage pattern
Circular, somewhat similar to the radial pattern, but much more circular or “clock-like".” Occurs where a dome is present.
Deranged drainage pattern
Consists of a series of ponds, marshes, and bogs that are poorly connected. Occurs in a newer landscape where the drainage pattern has had less time to develop
Discharge
A stream’s rate of flow. Equal to width X depth X velocity
Velocity
Determines a stream’s rate of erosion or deposition. Represents the energy a stream’s flow has.
Competency
The ability of a stream to move particles of a given size
Capacity
The amount of material a stream can move
Solution
A stream’s movement of materials via the dissolved load derived from chemical weathering of materials
Suspended load
A stream’s movement of material via fine grained materials held aloft in water
Bed load
A stream’s movement of material via coarse material dragged along the streambed
Fluvial transport
The movement of material through streams
Aggradation
The deposition of sediments in a stream. Associated with slower velocities (decreasing capacity and competency)
Degradation
The removal of sediments and rock from a stream. Associated with faster velocities (increasing capacity and competency)
Types of stream channels
Straight
Braided (several interconnecting channels)
Meandering (single winding channel)
Undercut bank
A degradation feature on the outside of a river bend
Point bar
An aggradation feature on the inside of a river bend
Oxbow Lake
A horseshoe shaped lake that forms when a wide meander from the main stem of a river is cut off from the main stream
Meander scar
Spots where water from a meandering river used to flow but no longer does
Yazoo tributary
A stream running through the backwater area of a large meandering stream
Head
The origin point of a river, where the elevation is highest
Steeper gradient
The steep, rapid decline in water immediately from the head of the river
Longitudinal stream profile
The gradual “midpoint” decrease in elevation in a river
Gentler gradient
The slower decline in stream elevation that occurs near the mouth of a river
Mouth
The lowest point of a river, where a stream ends
Nickpoint
Points in a river where resistant strata cause rapids or waterfalls
Alluvial Terrace
A step-like, relatively level landform of sediment that was once an active floodplain but is now elevated above the current river
Delta
A usually triangular landform, created by the deposition of the sediments that are carried by the waters of a river, where the river merges with a body of slow-moving water or with a body of stagnant water
Flood
When high water levels overflow the natural banks and levees of a river. Rated statistically by their probability of reoccurrence based on past experience (questionable accuracy due to limited observation time)
Methods to measure stream flow rates
Staff gauge (depth), stilling well (volume), suspended current meter (velocity)
Urban flooding
The tendency for urban areas to experience increasing numbers of small scale floods because of decreased water absorption of urban building materials