28. Parasitic Eukaryotes
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Protozoa: Amoeba example
Brain eating amoeba called N. fowleri
Does N. fowleri have rRNA operons
No, each N. fowleri cell has ~4,000 copies of a 14 kb circular plasmid that harbor rRNA genes.
Protozoa: Flagellates example
T. brucei which causes African sleeping sickness and transmitted by tsetse fly
VSG switching by T. brucei
variant surface glycoprotein expression to create antigenetic variation for immune evasion
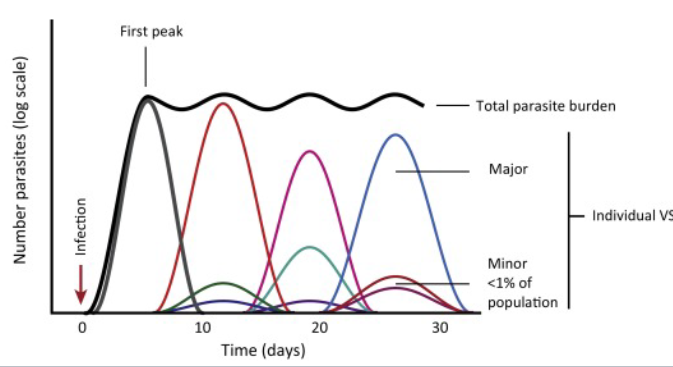
VSG switching by T. brucei pattern
Variants arise with degree of regulation because antibodies act to remove early variants, but by then later variants are already emerging
VSG switching mechanism
altering which 15 BES within the genome is active
recombination or gene conversion-mediated feeding of new
VSG sequence
Variant surface glycoprotein (VSG) switching is the major
driver of antigenic variation in Trypanosoma brucei. One
mechanism of VSG switching is what?
(1) inversion of the bloodstream expression site (BES) promoter
such that it drives transcription of a VSG gene located upstream
in the opposite orientation
(2) the mutation of RNA polymerase such that it recognizes a
different gene promoter sequence, which switches which VSG
gene is transcribed
(3) inducing transcription of a VSG gene located within one of
the densely-packed tandem arrays of VSG genes located within
one of the mini-chromosomes
(4) differential gene expression in response to levels of
extracellular iron
(5) the gene conversion-mediated feeding of new VSG sequence
information into the expressed bloodstream expression site (BES)
the gene conversion-mediated feeding of new VSG sequence
information into the expressed bloodstream expression site (BES)
Plasmodium life cycle: Schizogany
asexual reproduction by
multiple fission, producing merozoites.
The merozoites are what generate the
clinical symptoms of malaria
The first Plasmodium chloroquine-resistant isolate was recovered in 1957. In 2025, how could you determine the molecular basis of resistance?
Metagenomic analysis to compare chloroquine-resistant and -sensitive isolates
What happened when comparing chloroquine-resistant and -sensitive isolates of P. falciparum?
identified a gene on chromosome 7 as the major resistance determinant
Hookworm genomics
shed some light on the remarkable ability of these organisms to
suppress the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines
Female schistosoma
heterogametic sex with ZW chromosome
Male schistosoma
Homogametic with ZZ pair
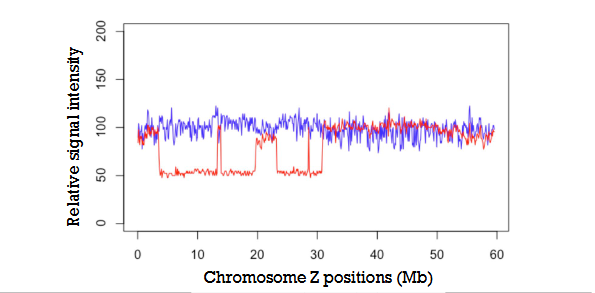
Analysis of male and female sex chromosomes in Schistosoma
suggests that there are distinct regions on the Z chromosome that differ between males and females, which could be indicative of sex-specific genetic variations or differences in chromosome structure and gene content
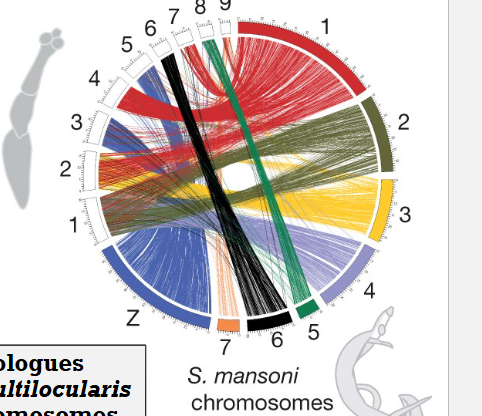
Tapeworm genome vs Flatworm distant relative
Although gene order has been lost, ancient chromosomal synteny is preserved among these parasitic flatworms
Genome data has been generated for several
species of hookworm. One insight to come
out of this data is what?
(1) insight into the mechanisms by which these
parasites can suppress production of pro-
inflammatory molecules
(2) observation that these parasites do not
express proteins on their surface, and hence no
vaccine can be developed
(3) observation that the rRNA operons of these
parasites are located on plasmids not as part of
one or more chromosomes
(4) that different hookworm species are
unrelated to each other, sharing as much
similarity to C. elegans as they do with each other
(5) that sequencing the genomes of these
multicellular eukaryotes is easy
insight into the mechanisms by which these
parasites can suppress production of pro-
inflammatory molecules