PHYL 141L Unit 3 Exam
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
spinal cord
pathway connecting the brain and the peripheral nervous system
autonomic nervous system
automatically regulates glands, internal organs, and blood vessels, pupil dilation, digestion, and blood pressure
somatic nervous system
carries sensory information and controls movement of the skeletal muscles
parasympathetic division
maintains body functions under ordinary conditions; saves energy
sympathetic division
prepares the body to react and expand energy in times of stress
sensory system (afferent)
carries messages from senses to CNS
motor system (efferent)
carries messages from CNS to muscles and glands
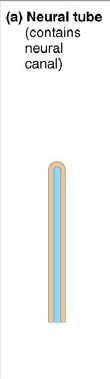
rostral
anterior side of the neural tube
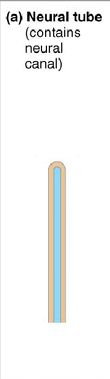
caudal
posterior side of the neural tube
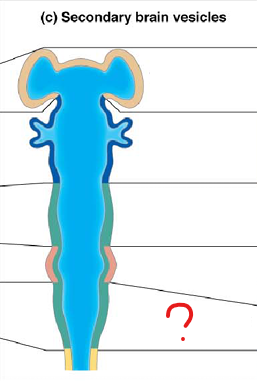
mesencephalon
midbrain
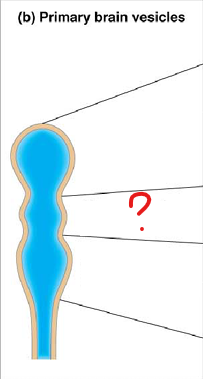
rhombencephalon
hindbrain
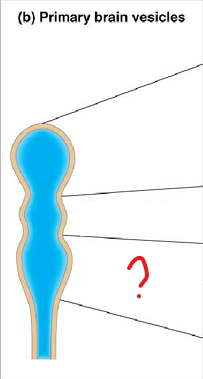
telencephalon
part of the prosencephalon (forebrain)
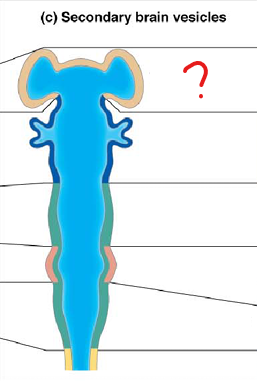
diencephalon
part of the prosencephalon (forebrain)
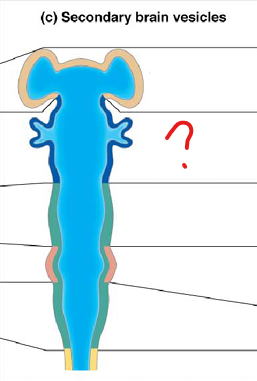
mesencephalon (secondary brain vesicle)
midbrain
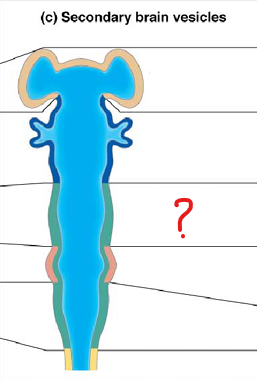
metencephalon
part of the rhombencephalon
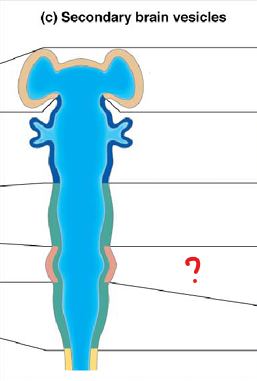
myelencephalon
part of the rhombencephalon
cerebrum
adult brain structure the telencephalon turns to
diencephalon, retina
adult brain structure the diencephalon turns to
brain stem: midbrain (midbrain)
adult brain structure the mesencephalon turns to
brain stem: pons (pons)
adult brain structure the metencephalon turns to
cerebellum
adult brain structure the metencephalon turns to (not pons)
brain stem: medulla oblongata (medulla oblongata)
adult brain structure the myelencephalon turns to
central canal
contains the spinal cord
corpus callosum
what connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres
left hemisphere
side of the brain linked to logic and analytic thinking
right hemisphere
Side of the brain that is linked with creativity and emotional processing
frontal
Personality, decision making, movement, speech product
parietal
Special awareness/relationships, somatosensory
temporal
Speech understanding, sense of smell, hearing
occipital
Vision
Insula
gustatory and sensorimotor processing, risk-reward behavior, autonomics, pain pathways, and auditory and vestibular functioning
Broca’s area
located in the left frontal lobe, this area controls speech production and articulation. It activates the muscle used to speak words
Wernicke’s area
located in the left temporal lobe, this area controls the ability to understand and select words to use when speaking. It processes the understanding of words and sends signals to Broca’s area.
diencephalon
acts as a primary relay and processing center for sensory information and autonomic control
thalamus
is considered to be a relay station that relays information between different subcortical areas and the cerebral cortex
hypothalamus
acts as the body’s control center and helps manage your body temperature, hunger and thirst, mood, sex drive, blood pressure and sleep
pineal gland
is part of the endocrine system and secretes the hormone melatonin. Its main job is to help control the circadian cycle of sleep and wakefulness
pituitary gland
(located at base blow the hypothalamus, sits in own little chamber under your brain known as the sella turcica) releases several important hormones and controls the functions of many other endocrine system glands
midbrain
the top part of the brainstem. Involved in motor control, particularly eye movements and processing of vision and hearing
pons
the middle portion of the brainstem that coordinates face and eye movements, facial sensations, hearing and balance
medulla oblongata
the bottom part of the brainstem that regulates breathing, heartbeat, blood pressure and swallowing
cerebellum
processes input from other areas of the brain, spinal cord, and sensory receptors to coordinate smooth movements of the skeletal muscular system, controls balance and other complex motor functions
gyri
ridges
sulci
Shallow grooves
fissures
Deep grooves
white matter
myelinated and unmyelinated axons, serves to transmit signals to other regions of the brain, spinal cord, and body
gray matter
short, unmyelinated neurons and cell bodies, receive information and regulate outgoing information, the most outer layer of the brain
ventricles
Fluid-filled chambers that are continuous to one another and to central canal of spinal cord
choroid plexus (composed of ependymal cells)
what membrane lines the ventricles
arachnoid mater
the middle meninx, weblike shape. Underlies the dura mater and is partially separated from the from it by the subdural space
pia mater
innermost meninx, highly vascular and clings tenaciously to the surface of the brain, following its gyri
olfactory (I)
carries afferent impulses for sense of smell (nose)
optic (II)
carries afferent impulses associated with vision (eye)
oculomotor (III)
somatic motor fibers to inferior oblique and superior, inferior, and medial rectus muscles, which direct eyeball, and to levator palpebrae muscles of the superior eyelid; parasympathetic fibers to smooth muscle controlling lens shape and pupil size (all eye muscles except those supplied by IV and VI)
trochlear (IV)
provides somatic motor fibers to superior oblique muscle that moves the eyeball (superior oblique muscle)
trigeminal (V)
major sensory nerve of face, conducts sensory impulses from skin of face and anterior scalp, from mucosae of mouth and nose, and from surface of eyes; mandibular division also contains motor fibers that innervate muscles of mastication and muscles of floor of mouth (face, sinuses, teeth, etc.)
abducens (VI)
carries somatic motor fibers to lateral rectus muscle that abducts the eyeball (external rectus muscle)
facial (VII)
supplies somatic motor fibers to muscles of facial expression and the posterior belly of the digastric muscle; parasympathetic motor fibers to lacrimal and salivary glands; carries sensory fibers from taste receptors to anterior tongue (muscles of the face)
vestibulocochlear (VIII)
vestibular branch transmits impulses associated with sense of equilibrium from vestibular apparatus and semicircular canals; cochlear branch transmits impulses associated with hearing from cochlea. Small motor component adjusts the sensitivity of the sensory receptors (inner ear)
glossopharyngeal (IX)
somatic motor fibers serve pharyngeal muscles, and parasympathetic motor fibers serve salivary glands; sensory fibers carry impulses from pharynx tonsils, posterior tongue (taste buds), and from chemoreceptors and pressure receptors of carotid artery (pharyngeal musculature)
vagus (X)
fibers carry somatic motor impulses to pharynx and larynx and sensory fibers from same structures; very large portion is composed of parasympathetic motor fibers, which supply heart and smooth muscles of abdominal visceral organs; transmit sensory impulses from viscera (heart, lungs, bronchi, gastrointestinal tract)
accessory (XI)
provides somatic motor fibers to sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles (sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles)
hypoglossal (XII)
carries somatic motor fibers to muscles of tongue (muscles of the tongue)
sensory neuron
carries the impulse from the receptor to the spinal cord
integration center
processes the information and directs the response to the motor neuron
Motor neuron
conducts the impulse from the spinal cord to an effector
Inborn (intrinsic) reflex
rapid, involuntary, predictable motor response to stimulus (maintain posture, control visceral activities, can be modified by learning and conscious effort)
Learned (acquired) reflexes
result from practice or repetition (e.g., driving skills)
somatic reflexes
activate skeletal muscle
Autonomic (visceral) reflexes
activate visceral effectors (smooth or cardiac muscle or glands)
stretch reflex
a feedback mechanism that controls muscle length by causing muscles to contract when stretched, muscle spindles detect the stretch and send the information to the central nervous system. Prevents muscles from being overstretched and injured
tendon reflex
a negative feedback mechanism that controls muscle tension. Tendon organs detect changes in muscle tension caused by contraction, not passive stretching. The tendon reflex is less sensitive than the stretch reflex, but it can override the stretch reflex when tension is high
sensory receptors
Specialized to respond to changes in the environment (stimuli)
Mechanoreceptors
respond to touch, pressure, vibration, and stretch
Thermoreceptors
sensitive to changes in temperature
photoreceptors
respond to light energy (e.g., retina)
chemoreceptors
respond to chemicals (e.g., smell, taste, changes in blood chemistry)
nociceptors
sensitive to pain-causing stimuli (e.g., extreme heat or cold, excessive pressure inflammatory chemicals)
exteroceptors
respond to stimuli arising outside the body, receptors in skin for touch, pressure, pain, and temperature, most special sense organs
interoceptors (visceroceptors)
respond to stimuli arising in internal viscera and blood vessels, sensitive to chemical changes, tissue stretch and temperature changes, sometimes cause discomfort but usually person is unaware of their workings
Proprioceptors
respond to stretch in skeletal muscles, tendons, joints, ligaments and connective tissue coverings of bones and muscles, inform brain of one’s movements
general senses
include tactile sensations (touch, pressure, stretch, vibration) temperature, pain, and muscle sense
special senses
Vision, hearing, equilibrium, smell, and taste
All are housed in complex sense organs
rods
Dim light, peripheral vision receptors
More numerous and more sensitive to light than cones
No color vision or sharp images
cones
Vision receptors for bright light
High-resolution for color vision
lateral rectus (VI)
moves eye laterally
medial rectus (III)
moves eye medially
superior rectus (III)
elevates eye and turns it medially
inferior rectus (III)
depresses eye and moves it medially
inferior oblique (III)
elevates eye and moves it laterally
superior oblique (IV)
depresses eye and moves it laterally
facial, glossopharyngeal, vagus
cranial nerves that carry taste sensation
gustatory receptors
used for sense of taste
semicircular canals and vestibule
structures involved with equilibrium (balance)
cochlea
structure involved with hearing