Fish Lab Exam 2
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
What specimen from Sarcopterygii do we need to know
subclass Dipnoi
Family Protopteridae
Protopterus
What specimen from Actinopterygii do we need to know
Subclass Cladistia
Order Polypteriformes
Family Polypteridae
Polypterus
Subclass Chondrostei
Order Acipenseriformes
Family Acipenseridae
Scaphirhyncus
Family Polyodontidae
Polyodon
Subclass Neopterygii
Order Amiiformes
Family Amiidae
Amia ocellicauda
Order Lepisosteiformes
Family Lepisosteidae
Lepisosteus
Atractosteus
Does Protopterus have a gular plate?
No

What caudle fin does protopterus have?
Diphycercal caudal fin

What caudle fin does Polypterus have?
Abbreviated heterocercal

What caudle fin does protopterus have?
What caudle fin does Polydon have?
Heterocercal

What caudle fin does Atractosteus have?
Abbreviated heterocercal

What caudle fin does Scaphiryncus have?
Heterocercal

What caudle fin does Lepisosteus have?
abbreviated heterocercal

What caudle fin does Hiodon alosoides have?
Heterocercal

What caudle fin does Amia ocellicauda have?
Abbreviated heterocercal

What caudle fin does Elops have?
Heterocercal

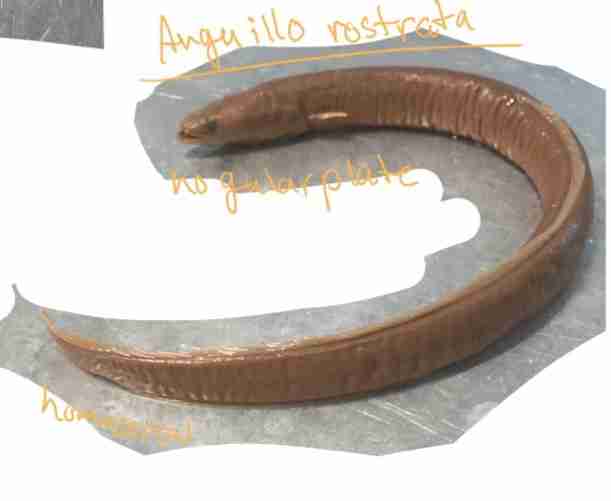
What caudle fin does Anguillo rostrata have?
Homocercal

Does Polypterus have a gular plate?
Yes

Does Polydon have a gular plate?
No

Does Atractosteus have a gular plate?
No

Does Scaphiryncus have a gular plate?
No
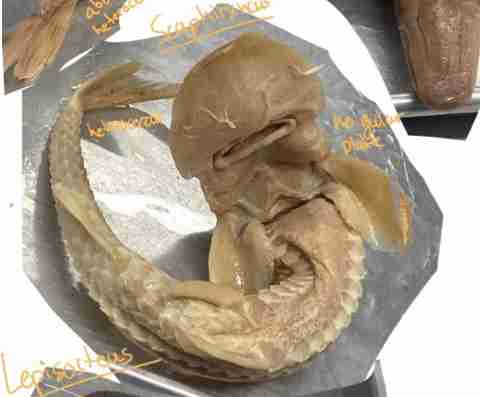
Does Lepisorteus have a gular plate?
No
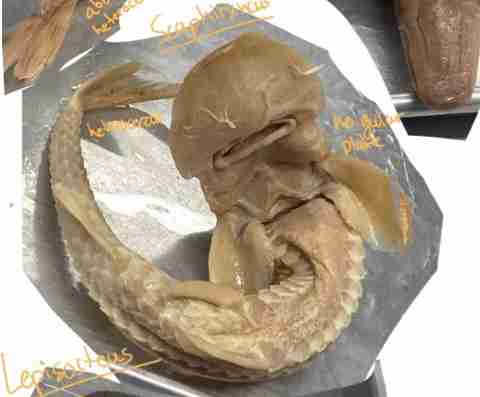
Does Hiodon alosoides have a gular plate?
No

Does Amia ocellicauda have a gular plate?
Yes

Does Elops have a gular plate?
Yes

Does Anguillo Rostrata have a gular plate?
No
What specimen from Teleostei do we need to know
Subdivision Osteoglossomorpha (Bony tounges)-tounge bite apparatus
Order Osteoglossiformes
Order Hiodontiformes
Family Hiodontidae
Hiodon alosoides
Subdivision Elopomorpha (Leptocephalus fishes)- leptocephalus larvae
OrderElopiformes
Family Elopidae
Elops
Order Anguilliformes
Family Anguillidae
Clupeomorpha
Order Clupeiformes
Family Clupeidae
Family Engraulidae
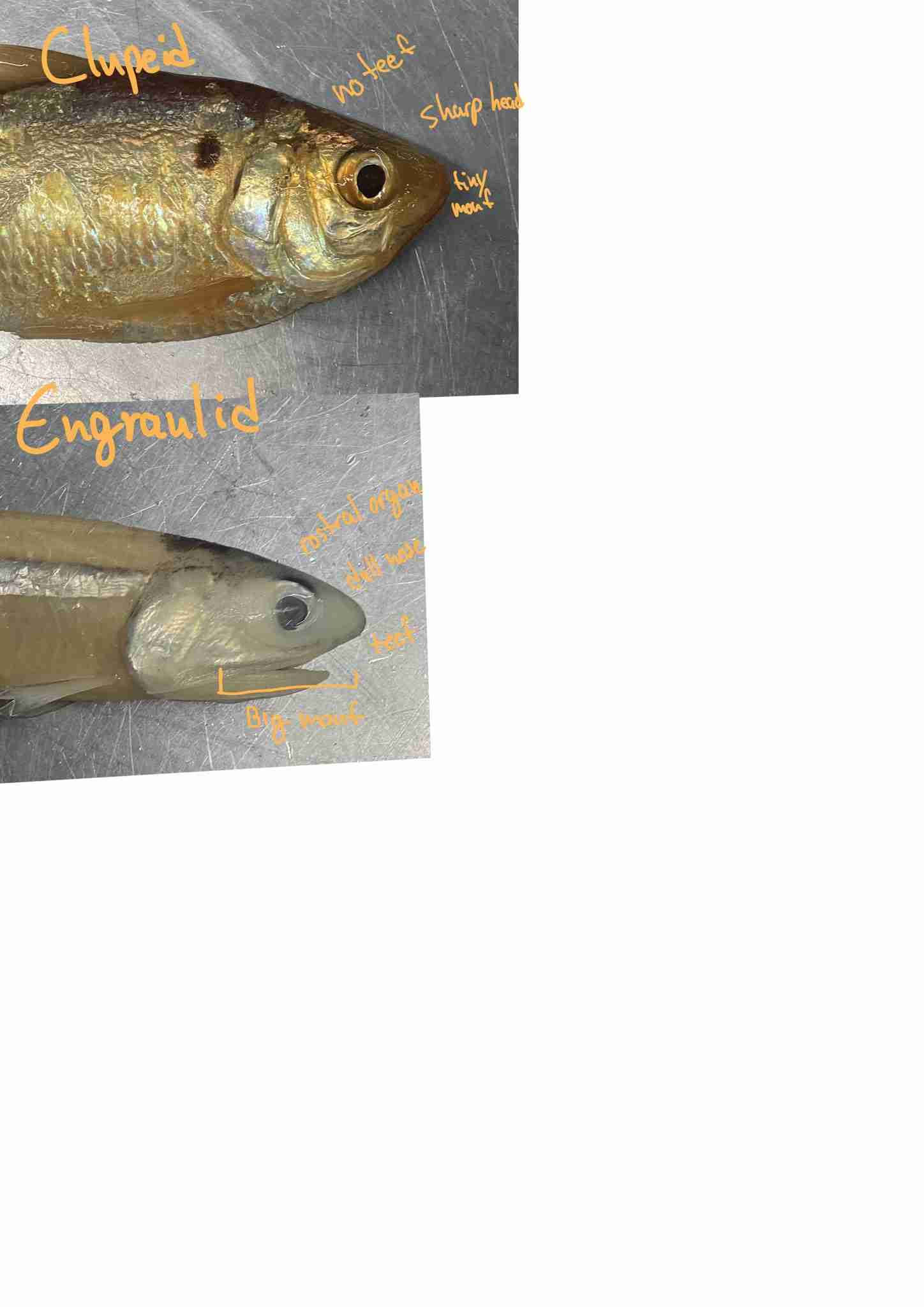
How can you distinguish between a clupeid and an engraulid
Clupeid: No teeth, Sharp head, tiny mouth
Engraulid: rostral organ, dull nose, teeth, Big mouth (extend past eyes)
What are the major character/s that distinguish the Osteoglossomorpha and Elopamorpha
Elopomorpha: Characterized by the presence of a leptocephalus larval stage.
Osteoglossmorpha: Characterized by the presence of the tongue-bite apparatus, consisting of ventral basihyal and basibranchial toothplates and dorsal parasphenoid teeth, which form a second “bite” inside of the buccal cavity
What are the difference between Cyprinid and Catostomid pharyngeal teeth.
Cyprinid: multiple rows of teeth
Catastomidae: One row of many teeth
What are the three families of catfishes found in Texas
Ariidae, Ictaluridae and Loricariidae.
What are the 4 synapomorphies of the Ostariophysi
Presence of Unculi:
Presence of Schreckstoff
Presence of mulitcellular keratinous tubercles
Separation of the swimbladder into anterior and posterior chambers
What are distinguishing characteristics of Siluriformes
1. Four pairs of barbels (maxillary, nasal and two pairs of mental barbels).
2. Maxilla toothless and rudimentary, supporting base of maxillary barbel.
3. Anteriormost soft ray of dorsal and pectoral fins modified to form “spine” (which
may or may not be associated with a venom gland).
4. Adipose fin present.
5. Scales absent.
6. Posterior chamber of swimbladder absent, anterior chamber partially or fully
encapsulated by a bony capsule, which is frequently incorporated into the back of
the skull
What are distinguishing characteristics of Cypriniformes (Families Cyprinidae and Catostomidae)
Presence of a kinethmoid bone
Absence of oral dention
Absence of upper pharyngeal tooth plates
Lower pharyngeal teeth (on ceratobranchial 5) enlarged
Pharyngeal teeth grind against modified bony plate on ventral surface of basioccipital
What are distinguishing characteristics of Characiformes
presence of an adipose fin and oral teeth in the jaws
One species of characiform, Astyanax mexicanus, is found in Texas
What are distinguishing characteristics of Gymnotiformes
complete absence of a dorsal fin and its supporting skeleton, complete absence of the pelvic fin and pelvic girdle, and the presence of electrical organs (derived from modified muscle cells) along the lateral side of the body, which allow gymnotids to produce weak electrical discharges
What is a gonopodium and what groups has it
A modification to the anal fin for reproduction. The fish equivalent of a penis
Order Cyprinodontiformes, Series Atherinomorpha
What are the defining characters of Superorder Acanthopterygii
presence of a single spinous ray along the outer edge of the pelvic fins (acanthopterygian
fishes thus possess spinous rays in the dorsal, anal and pelvic fins; it should be noted that
a number of acanthomorphs have secondarily lost spines and/or pelvic fins, e.g. members
of the Tetraodontidae)
What are the defining characters of Acanthomorpha (unranked)
The group is defined based on the presence of spinous
rays in the dorsal and anal-fins (it should be noted that many acanthomorphs have secondarily lost spinous rays). Acanthomorph fishes also possess a rostral cartilage
between the neurocranium and the upper jaw and a long ascending process on the premaxilla, which work together to enhance jaw protrusion. They also exhibit a complex
articulation between the back of the skull (occipital region) and the 1 st vertebral centrum
What are charactoristics of Order Esociformes? What are some species we have in Texas
Members of this order
are “archetypal” ambush predators, with sagittiform bodies (median fins and pelvic fins
positioned far posterior on body) and large gapes (Fig. 9.1). Esocids possess a particularly
massive mouth, with an incredible gape (interestingly the upper jaw is composed almost
entirely of premaxilla and the maxilla is small and toothless).
Three species of the Esocidae are found in Texas, one of which is not native to the state:
Esox americanus (redfin pickeral)
Esox niger (chain pickeral)
Esox lucius (northern pike) - introduced
What characteristics do Superorder Stenopterygii: Stomiiformes
have
presence of photophores (luminescent organs) which produce blue or red light, their entire bodies being either heavily pigmented or with large deposits of guanine (causes a silvery appearance) and large mouths to more easily capture prey that they come across.
What characteristics do Superorder Cyclosquamata: Aulopiformes
have
characterized by large mouths filled with teeth and the absence of a swimbladder
Superorder Scopelomorpha: Myctophiformes Characteristics
high numberof photophores distributed across their bodies
Order Lophiiformes Characteristics
a modification of the first dorsal-fin spine into a rod (illicium) and
lure (esca).
Order Percopsiformes Characteristics
jugular position of its anus
Order Atheriniformes Characteristics
are small fishes (typically silvery in appearance) with widely separated spinous and soft dorsal fins
Order Cyprinodontiformes and Family Poeciliidae
Characteristics
exhibit extreme sexual dichromatism, Livebearing
Family Fundulidae
Oviparous
How can you tell the difference between Percina and Etheostoma based off of ventral scales
Percina possess modified ctenoid scales with enlarged ctenii along their ventral surface between the anal and pelvic fins, which is the only characteristic useful for distinguishing between members of Percina and Etheostoma (which lack such scales)