Chapter 3: Proteins
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
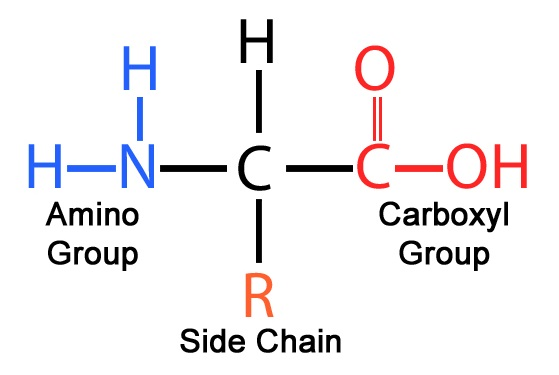
Structure of amino acid
Consists of an a-carbon atom bonded to 4 groups: H atom, amino group, carboxyl group, variable R group
Properties of amino acids
exist as zwitterions
act as buffers (can donate/ accept H+ → amphoteric)
Describe formation of a peptide bond
Amino acids are joined via peptide bonds during condensation reaction that links the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of another, with the removal of one water molecule
The sequence and direction of amino acids in a polypeptide does not matter. T/F?
F. They have a direction (N-terminus and C-terminus)
Primary structure of proteins
Number and sequence of amino acids in a single polypeptide chain, linked by peptide bonds.
Secondary structure of proteins
regular coiling and pleating of a single polypeptide chain
hydrogen bonds b/w CO and NH groups of polypeptide backbone (R groups NOT involved)
a helix and B-pleated sheets
a-helix
Single polypeptide chain wound into coiled/spiral structure
A hydrogen bond forms between the C=O group of one amino acid residue and the N-H group of another amino acid residue 4 amino acids away from the backbone of a single polypeptide
3.6 AA residues in every turn of the helix
ß-pleated sheets
2 or more segments of single polypeptide chain lying side by side linked by hydrogen bonds
Hydrogen bonds formed b/w CO grp of an AA residue of 1 region and NH group of another amino acid residue on an adjacent segment
Chains run parallel or antiparallel
Form flat sheet which becomes folded
Tertiary structure of proteins
Structure formed by further extensive folding and bending of single polypeptide chain -> compact, globular molc -> specific conformation
H bonds, ionic bonds, hydrophobic interaction, disulfide bonds formed b/w R groups of AA residues within a polypeptide
Hydrogen bond
Formed b/w electronegative (δ-, eg. O of C=O and N of NH) and electropositive (δ+, eg. H)
3˚: Formed b/w R groups of polar AAs
2˚: Formed b/w -CO and -NH groups of peptide bonds
’Weak’ individually but strong collectively
Ionic bond
Formed b/w oppositely-charged R groups of AAs
eg. B/w COO- and NH3+ (found on R groups of acidic and basic acids respectively)
Ends of polypeptide chain
Relatively strong bond but change in pH -> change [H+] (alter charges) -> disrupt ionic bonds
excess [H+] or [OH-] may affect ionisation of R-groups of charged AA (eg. Excess H+: —COO- turn into -COOH; excess —OH-: -NH3 turn into NH2)
Hydrophobic interaction
Formed b/w non-polar R groups (hydrophobic)
Interact and gather at core of protein to avoid water -> polypeptide folds so as many of hydrophobic R groups are shielded from aq environment as possible
Most hydrophobic R groups tend to point to centre
Most hydrophilic groups face outwards into aq environment -> protein soluble
Weak interactions; easily disrupted
Disulfide bond
Formed b/w 2 cysteine AA by oxidation of sulfydryl (-SH) groups (contain sulfur)
Strong covalent bond; strongest out of the 4 interactions -> stability
⬆ disulfide bond ⬆ stability of protein to heat denaturation
Quaternary structure
Association of 2 or more polypeptide chains into 1 functional protein molecule.
Maintained by all 4 types of interactions, formed between R groups of amino acid residues of different polypeptides
Constituent chains of a multimeric protein can be identical or different
Structure and function of haemoglobin (subunits)
Structure:
Quaternary structure made up of 4 subunits: 2 a-globin, 2 b-globin
Each subunit consists of:
Globin polypeptide
Haem group (prosthetic component aka non protein)
Porphyrin ring
Iron ion (Fe2+)
Function:
Fe2+ of each haem group binds reversibly to O2 -> 1 Hb molc can carry up to 4 O2 molcs -> form oxyhaemoglobin
Structure and function of Hb (R groups)
Structure
AAs with hydrophilic R groups on external surface
AAs with hydrophobic R groups buried in interior
Function
Soluble in aq environment → can take place in chemical reactions in RBCs → Transport protein
Structure and function of Hb (ixns)
Structure:
The 4 subunits held tgt by weak intermolecular ixns formed between R groups -> subunits can move wrt eo → allow change in position that influences Hb’s affinity for O2
Function:
Binding of 1 O2 molc to Hb subunit induces a conformational change in remaining 3 subunits such that their affinity for O2 increases
known as cooperative binding of O2
Structure and function of collagen (amino acids)
Structure:
Each chain consists of 1000 AAs and contain a repeating sequence, usually glycine-X-Y
X: usually proline
Y: Usually hydroxyproline
The tropocollagen molc can form a tight, compact coil as almost every 3rd AA is glycine (smallest AA)
Allows R group to fit into the restricted space in the center of the triple helix
Function
Bulky and relatively inflexible proline and hydroxyproline residues confer rigidity on the molecule.
Structure and function of collagen (H bonds)
Structure
Extensive H bonds form between amino acid residues of the 3 polypeptides
Function
Incr tensile strength due to stretching
Structure and function of collagen (staggering)
Structure
Adjacent tropocollagen molecules are arranged in a staggered manner
Function
Staggered arrangement minimizes points of weaknesses along length of fibrils
Structure and function of collagen (cross-links)
Structure:
Covalent cross-links between lysine residues at C and N ends of adjcanet tropocollagen molecules results in formation of fibrils
Function:
Incr tensile strength
Structure and function of collagen (fibres)
Bundles of fibrils unite to form long collagen fibrils → incr tensile strength