ALL of Cells 3.2 Aqa
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Describe the structure of the nucleus
Nuclear membrane- that is a double membrane
Nuclear pores
Nucleoplasm -jelly like
Chromosomes- associated with histones
Nucleolus - smaller sphere inside, site of rRNA production and ribosomes.
Describe the function of the Nucleus
Site of DNA replication and transcription
Making mRNA
Contains the genetic code for each cell.
Describe the structure of the Endoplasmic reticulum (both smooth and rough)
Both have folded membranes called cisternae
Rough has membrane bound ribosomes on the cisternae
What is the function of RER?
Protein synthesis
What is the function of SER?
Synthesis and storage of lipids and carbohydrates
Describe the structure of the Golgi Apparatus
Folded membranes called cisternae
Secretory vesicles that are pinched off from the cisternae
What are the many functions of the Golgi Apparatus?
Add carbohydrates to a proteins to form a glycoproteins
Produce secretory enzymes
Secrete carbohydrates
Transport, modify and store lipids
Form lysosomes
Create vesicles which transport productsM where the vesicles fuse with the cell membrane and the products are released outside.
Describe the structure of lysosomes
Sacks of lysozymes, digestive and hydrolytic enzymes
What is the function of lysosomes?
Digest worn out organelles so the materials are reused.
Exocytosis-destroy outside material
Autolysis- destroy dead cells
Fuse-with a phagosome to form a phagolysosome And
Hydrolyse pathogens
Describe the structure of the mitochondria
Double membrane
Inner membrane has a large surface area and called CRISTAE (do not confuse with cisternae)
Matrix - fluid in the inner membrane
Have their own Circular DNA
Have their own 70s ribosomes
What is the function of the mitochondria
Site of aerobic respiration
Site of ATP production
Has their own mitochondrial DNA to code for enzymes needed in respiration
Describe the structure of the ribosome
Made up of 2 sub units Of protein and rRNA
What is the function of the ribosome?
Protein synthesis
What are the two types of ribosomes in eukaryotic cells and where do you find them?
80s- large ribosomes- found in eukaryotic cells
70s- small ribosomes- found in prokaryotic cells, mitochondria and chloroplasts
Describe the structure of the vacuole
Fluid filled and surrounded by single membrane called the tonoplast
What is the function of the Vacuole?
Provide the plant cell turgidity, which provides support
Temporarily store sugars and amino acids
Contain pigments which colour petals, which attract pollinators
Describe the structure of a chloroplast
Surrounded by a double membrane
thylakoids-fluid filled sacs, contain photosynthetic pigments which stack up to form granum
Grana- Granum (plural)
Lamella/Lamellae (plural)- membrane channels that connect the grana
Fluid filled stroma - contains enzymes, sugars, 70s ribosomes and its own chloroplast DNA
Starch grains - glucose store
What is the function of chloroplasts? (2 marks)
The site of photosynthesis
Light dependant reaction in the thylakoid membrane
Light independent reaction in the stroma
What is the structure of the cell wall in plants and fungi?
Plants- cellulose
Fungi-chitin
What is the function of the cell wall?
Provide structural strength to the cell
What is the structure of the cell membrane?
Phospholipid bilayer that’s embedded with proteins, cholesterol, carbohydrates
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Controls what enters and exits the cell
Describe the structure of prokaryotic cells
Plasma membrane,
cell wall of murein,
slime capsule,
flagellum/flagella (plural)- for movement
Plasmids- carry extra genes for survival
Circular DNA
70s ribosomes
Cytoplasm
Much smaller
What are the differences between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells are…
Much smaller
Have no membrane bound organelle
Smaller 70s ribosomes
Circular DNA that is not associated with histones, no nucleus
Cell wall is made of murein
They also contain plasmids, a slime capsule and one or more flagella
What are viruses described as?
Non-living- no metabolic reactions or movement
Acellular- not made of cells and no cell membrane
Describe the structure of viruses
RNA or DNA
Capsid- contains the genetic material and any enzymes
Attachment proteins- to attach to the cell receptors on a host cell
May have a lipid envelope- which they take from the host cell
Smaller than bacteria
What are the the three types of microscopes?
Optical
Scanning electron
Transmission electron
Define magnification
How many times larger the image is compared to the object
Define resolution
The minimum distance between two objects, which can still be viewed as separate. And is determined by the wavelength
What are the differences between the Optical microscope and Electron microscopes?
Light- A beam of light is condensed to crate an image
Electron- a beam of electron is condensed to create an image. Electromagnets are used to condense the beam
Light- poor resolution
Electron- high resolution, because electrons have a shorter wavelength
Light- low magnification
Electron-high magnification
Light- Coloured images
Electron- black and white images
Light- Can view living samples
Electron- Samples must be dead
Light- Easy to use
Electron-need to be used in a vacuum and very expensive
describe the TEM (Transmission Electron Microscopes)
Need very thin specimens
2D image
An electron gun produces a beam of electrons that pass through the specimen
Denser parts absorb more electrons and appear darker
Describe the SEM (Scanning Electron Microscope)
Thick specimens can be used
Electrons are beamed on the surface and reflected
3D image
What is the formula for magnification?
Magnification= Image size/Actual size
How do you calibrate an Eye piece graticule?
Use a stage micrometer
Line up the stage micrometer and eye piece graticule when looking down the lens
Count how many divisions on the eyepiece graticule fit ONE division of the micrometer
Each division on the micrometer is 10 micrometers, calculate what One division is on the eye piece graticule at the current magnification.
A student used an eyepiece graticule, and observed that 20 micrometers measure 2.35 divisions on the graticule
Calculate the diameter of the nucleus if the nucleus measures 1.4 graticule divisions (2 marks)
(20/2.35)x 1.4= 11.91 micrometers
What solution do cells need to be out in before cell fractionation? And explain why (2 marks)
Cold- reduce enzyme activity
Isotonic- to maintain the water potential of the cells, so cells do not shrivel or burst
Buffered- maintain pH levels, otherwise the organelles can be damaged
Describe the process of cell fractionation
Homogenisation
Organelles are released as the Cells are broken open by a homogeniser
Creating a homogenate
Filtration
Remove debris
Ultra centrifugation
The filtrate is spun in a centrifuge causing the heaviest organelles to form a pellet at the bottom
Which can be removed
This is repeated at increasingly higher speeds until the desired organelles form a pellet
What is the order of organelles from heaviest to lightest?
Nuclei
Chloroplasts
Mitochondria
Lysosomes
Endoplasmic reticulum
Ribosomes
How many times do you need to centrifuge to isolate the mitochondria?
The third spin
How do Eukaryotic, Prokaryotic and Viruses replicate?
Eukaryotic- mitosis and meiosis
Prokaryotic- binary fission
Viruses- replicate in host cells and using the cell’s machinery
Describe the process of Binary fission (3 marks)
The circular DNA and plasmids are replicated
The cytoplasm splits to creat 2 daughter cells
Each daughter cell has one copy of the circular DNA but a varying number plasmids
What are the 4 stages in the cell cycle?
G1- Interphase- growth
S-phase - Interphase- DNA replication, Organelles double and cell grows bigger
G2- Interphase-preparation for mitosis
M-phase- mitosis and cytokinesis
Which is the longest stage in the cell cycle?
Interphase- when the organelles double, DNA replicates and the cell grows bigger
Explain what happens in Prophase
The chromosome condense, becoming visible when stained
Centrioles move to opposite poles
What happens in Metaphase
Chromosomes line up along the equator,
Spindle fibres attach to the centromeres of the chromosomes
What happens in Anaphase?
Spindle fibres retract and the Centromere splits
pulling the chromatids to opposite poles
What happens in Telophase and Cytokinesis?
Spindle fibres disintegrate and the chromosomes start to condense again
Nucleus starts to reform, cytoplasm splits forming 2 identical daughter cells
What is the formula for the mitosis index?
Mitosis index= number of cells IN mitosis/total number of cells IN view
How does disruption in mitosis cause cancer?
Disruption in the control of mitosis can result in uncontrolled cell division
Which can result in tumour cells (malignant or benign)
Why is the cell meme range described as the fluid mosaic model?
Due to the unsaturated fatty acid chains in the phospholipids allowing the phospholipid bilayer being able to move
And the arrangement of proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins and glycolipids that are embedded in it.
Why is the cell membrane described as partially permeable?
Small lipid soluble non-polar substances can pass through the phospholipid bilayer through simple diffusion
Large, water soluble, polar molecules cannot
What is the role of cholesterol in the cell membrane?
Restricts the lateral movement of phospholipids, making it less fluid at high temperature
This it’s important as it stop substance from leaking out.
Describe Simple diffusion
The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
Until equilibrium is reaches
No ATP
Must be small, lipid soluble and non-polar molecules
Describe facilitated diffusion
Passive process
Large, water soluble, polar molecules
Channel proteins and Carrier proteins
What are channel proteins
Tubes that are filled with water allowing water soluble ions to pass through
What are carrier proteins?
Can change its shape and its affinity to bind to a molecule
What is Osmosis?
The net movement of water molecules from an area of high water potential to an area of low water potential
across a partially permeable membrane
What is water potential?
It is the pressure created by water molecules and is measured in kPa
What value of water potential does pure water have?
0 kPa
What does isotonic solution mean?
The water potential of the solution is the same as the water potential of the cell
Animal cells are normal
Plant cells are flaccid
What does a hypotonic solution mean?
The water potential is higher in the solution than the water potential in the cell
Therefore can cause the animal cells to burst (cytolysis)
Plant cells to become turgid
What does a hypertonic solution mean?
The water potential of the solution is lower than the water potential in the cell
Animal cells become shrivelled
Plant cells become Plasmolysed
What is active transport?
The movement of substances from low to high concentrations
Requires ATP and carrier proteins
Describe the process of active transport by the sodium potassium pump (6 marks)
3 Na+ ions bind the the carrier proteins binding site. ATP attaches to the carrier protein
As ATP is hydrolysed it release energy
Causing the carrier protein to invert and lower its affinity for sodium
So the Sodium ions to be released on the other side
2 K+ ions bind to the carrier protein
Causing the carrier protein to revert back and increase its affinity for sodium
Releasing the potassium ions and the inorganic phosphate
Describe the process of co-transport of sodium ions and glucose in the ileum
Sodium ions Na+ are actively transported out of the epithelial cell into the blood by the sodium potassium pump.
The movement of Na+ provides energy for glucose to move against its conc. gradient
Reducing the conc. of Na+ in the epithelial cell and establishing a conc. gradient.
So Sodium and glucose bind to the co-transporter
The binding of both and the energy from the diffusion causes the co-transporter to invert which moves both of them across the cell membrane
Releasing both Sodium and glucose in the cell.
How do lymphocytes identify pathogens and self-cells?
Cells have proteins on the cell membrane which are complementary to the cell receptors on the lymphocyte.
What are the three cells which can trigger an immune response?
Pathogens-(bacteria, viruses and fungi)
Foreign cells
Cancer cells
Toxins
Definition of an Antigen (2 marks)
Antigens are foreign proteins that trigger an immune response by the lymphocytes
They are located on the surface of cells
What is Antigen variability?
When the pathogen’s DNA mutates frequently, and the gene which codes for the antigen mutates.
Causing the shape of the antigen to change
This causes any previous immunity to no longer be effective as the memory cells have the memory of the OLD antigen shape
What are the 2 types of macrophages?
Phagocytes- non-specific
Lymphocytes- specific
Describe the process of phagocytosis and what kind of response is it?
Non-specific
Any foreign cell will trigger phagocytosis
Receptors attach to the chemicals or antigens on the pathogen
The phagocyte changes shape and moves around and engulfs the pathogen
Once engulfed the pathogen is contained in a phagosome vesicles
The Phagosome fuses with a lysosome forming a phagolysosome. Releasing the lysozymes which hydrolyse and breakdown the pathogen. And any useful substances are re used by the phagocyte
How can a phagocyte become a Antigen presenting cell after phagocytosis?
The antigens from the hydrolysed pathogen are the presented on the cell surface to signal the presence of the pathogen to the lymphocytes
What are T lymphocytes?
T Lymphocytes which are white blood cells
Involved in the specific immune response and the cell mediated response
Where are lymphocyte made in? What about T cells?
All lymphocytes are made in the bone marrow
But T lymphocytes mature in the thymus
Describe the cell mediated response
Helper T cells have receptors on their cell surface which attach to the antigens on an APC
Once attached it activates the helper T cells to divide by mitosis
To replicate and make a large number of T helper cell clones
Which can differentiate into T helper cells (ones that activate B lymphocytes and ones that stimulate macrophages to perform phagocytosis)
cytotoxic T cells
How do cytotoxic T cells destroy abnormal or infected cells?
They release a protein called perforin
Which embeds in the cell surface membrane which makes a hole
So that any substances can enter and leave the cell
Causing cell death
What type of infection is cell death the most common immune response?
Viral infections, because viruses infect body cells
What are B Lymphocytes? And how are they activated?
B cells are white blood cells involved in the specific immune response.
Antigens in the blood collide with the complimentary antibody on a B cell, the B cell takes an antigen by endocytosis, and the presents it on a cell surface membrane.
A t helper cell will cause the B-cell to mature and differentiate into plasma cells and memory B cells
What do plasma cells do?
Secrete antibodies
What can B memory cells do? And how do they provide active immunity?
They can quickly divide by mitosis and differentiate into lots of plasma cells
This results in a large number of antibodies being produced rapidly, destroying the pathogen before symptoms can occur.
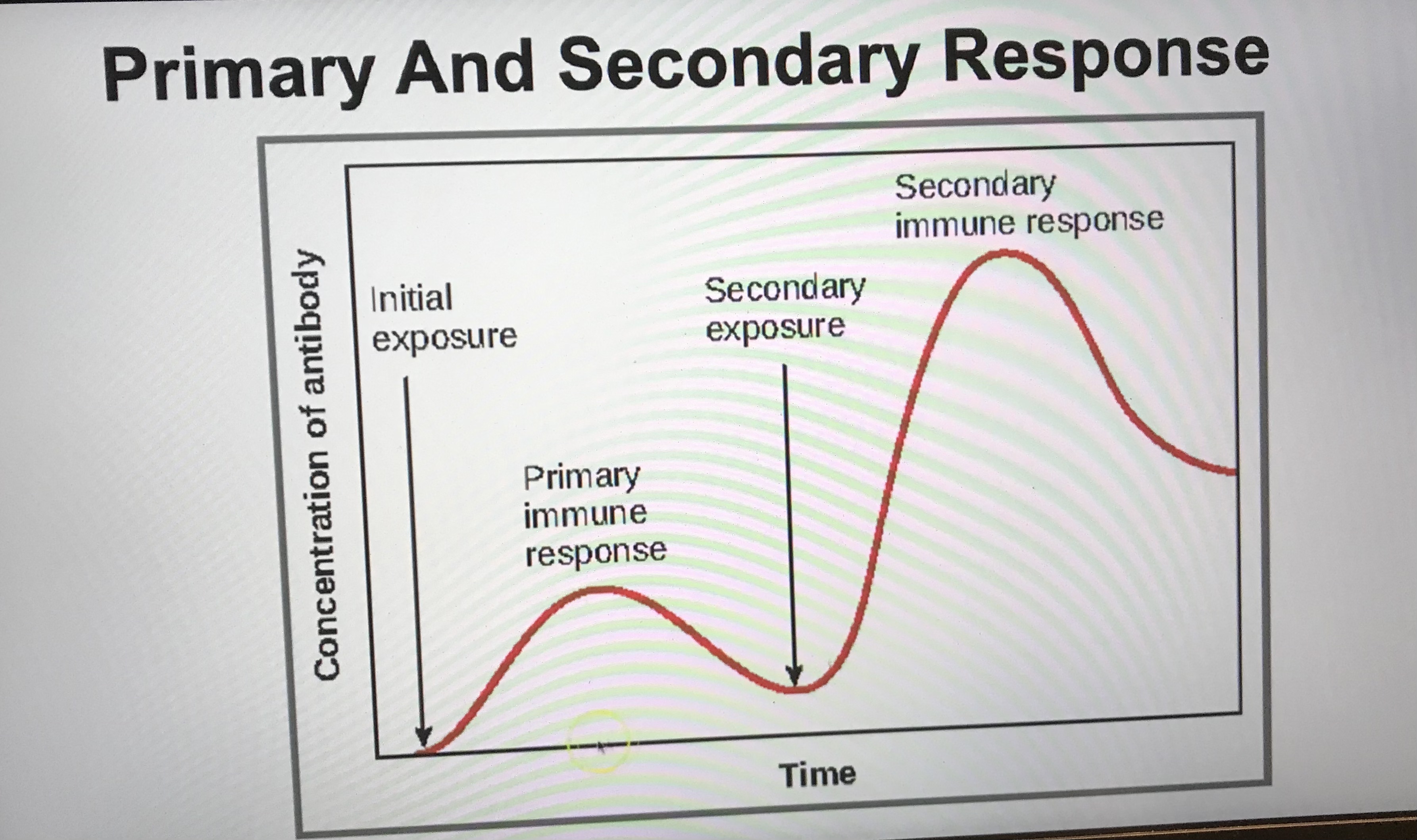
Explain the curves in the graph
The first exposure to the pathogen
Takes a longer period of time for the b cells to collide with the antigen, clonal expansion and differentiation.Takes longer to make antibodies, lower rate of antibody production
The second exposure
Memory b cells can divide rapidly and differentiate into plasma cells. Large quantity of antibodies and high rate of antibody production.
Draw and describe the structure of an antibody
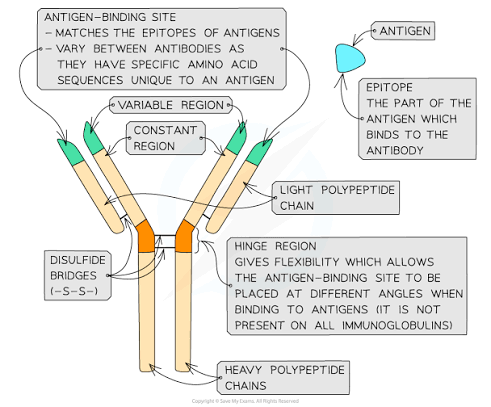
Explain how the structure of an antibody relates to its function (2 marks)
Antibodies have strong disulphide bridges and hinge regions which give it flexibility.
Allowing the binding sites to bind to multiple antigens and agglutinate.
Describe differences and similarities of passive immunity and active immunity
Passive immunity
Where someone receives antibodies
Short term immunity
Active immunity
antibodies are created by your immune system due to exposure to a pathogen or antigen.
Long term immunity
Give an example of passive and active immunity
Passive- antibodies in the mothers breast milk being past down to the baby
Active- vaccines provide artificial active immunity, where a small amount of dead or inert version of the pathogen is given. The antigens activate the B cells to undergo clonal expansion and differentiation.
So when there is an exposure to the real pathogen the memory b cells can rapidly divide and differentiate into plasma cells and make large quantities of antibodies
Describe herd immunity and which people are vulnerable?
When a large numbers of the population are vaccinated, and the pathogen cannot spread among the population
protecting those who are vulnerable.
Such as elderly people, people with immunodeficiencies, cancer patients, immunocomprimised patients,
What type of virus is HIV and describe its structure
It’s a retrovirus
Lipid envelope- taken from host cell
Capsid- which contains reverse transcriptase enzymes and RNA for viral replication
Attachment proteins- to enable the virus to attach to the helper T cells
Describe the process in which HIV replicates in helper T cells (6 marks)
HIV is transported in the blood until it attaches to a CD4 protein on a T helper cell
HIV fuses with the membrane releasing the capsid inside which releases the RNA and reverse transcriptase
Reverse transciptase copies the RNA into a DNA copy
Which combines with the host DNA in the nucleus
Here mRNA is transcribed by ribosomes and undergoes protein synthesis using th whist cells machinery ti the create new viral proteins
Which are assembled to form new viral particles
Which then bud off from the cell membrane or are released when the cell bursts
State 3 symptoms of AIDS
Weight loss
Fever
chronic infections
How does AIDS occur?
When HIV has destroyed many T helper cells and the immune system is weaker, making the body more susceptible to infection and disease.
How does HIV viruses weaken the immune system?
They decrease the number of T-helper cells
Therefore less b cells are stimulated to differentiate into plasma cells to produce antibodies against infections
Increased chance of infections
Less cytotoxic t cells are stimulated to kill and destroy infected cells, cancer cells or foreign cells through apoptosis, increased risk of cancer.
How do monoclonal antibodies differ from regularly antibodies?
They are single type of antibody that has been isolated and cloned.
Describe the process of direct monoclonal antibody therapy in cancer treatments
Where the monoclonal antibodies binding site is complementary to the antigens on cancer cells and not normal cells
This prevents chemicals from binding to cancer cells which enable uncontrolled cell division
Therefore preventing the cancer cells from growing
Describe Indirect monoclonal antibody therapy in targeted cancer medication
When a cancer drug is attached to the monoclonal antibodies, and the drugs are delivered directly to cancer cells and kill them.
Less harmful side effects
Give 4 examples that monoclonal antibodies can be used in
Direct monoclonal antibody therapy
Indirect monoclonal antibody therapy
Testing for pregnancy
Testing for Covid 19
What does ELISA stand for?
Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay
What does the indirect and direct ELISA test detect for?
Indirect- detects for antibodies
Direct- detects for antigens
Describe the process of the indirect ELISA (used to measure antibodies)
Add the patients sample in to an antigen coated well
Then Wash it to remove any unbound antibodies
Then add a secondary antibody which has enzymes attached to it
Then wash to remove any unbound antibodies
Add the complementary substrate, which will form an enzyme substrate complex and cause a colour change
measure the colour
Describe the process of a direct ELISA test (used to measure antigens)
Add the patients sample in to an antibody coated well
Then Wash it to remove any unbound antigens
Then add a secondary antibody which has enzymes attached to it
Then wash to remove any unbound antibodies
Add the complementary substrate, which will form an enzyme substrate complex and cause a colour change
measure the colour
What is another name of a direct ELISA test.
Sandwhich ELISA