Digestive System
4.0(5)Studied by 97 people
Card Sorting
1/115
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:37 PM on 12/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
1
New cards
How is the Digestive system divided?
1\. Digestive organs: collectively make up the gastrointestinal (GI) tract (alimentary canal).
2\. Accessory digestive: food does not pass through their lumens, but they assist digestion
2\. Accessory digestive: food does not pass through their lumens, but they assist digestion
2
New cards
What are the Accessory organs
Teeth
Tongue
Salivary glands
Liver
Gall bladder
Pancreas
Tongue
Salivary glands
Liver
Gall bladder
Pancreas
3
New cards
What are the GI tract organs
Oral cavity
Pharynx
Esophagus
Stomach
Small intestine
Large intestine
Pharynx
Esophagus
Stomach
Small intestine
Large intestine
4
New cards
Digestive system functions
Ingestion
Propulsion
Secretion
Digestion
Absorption
Elimination
Propulsion
Secretion
Digestion
Absorption
Elimination
5
New cards
Peristalsis
ripple-like wave of muscular contraction that forces material to move further along the GI tract.
or Waves of contraction propel food along the GI tract
or Waves of contraction propel food along the GI tract
6
New cards
Segmentation
churning and mixing of material helping to disperse the material and mix it with digestive organ secretions.
or Process of moving food back & forth along the SI
or Process of moving food back & forth along the SI
7
New cards
Gingiva
Alveolar processes of the teeth are covered by the gums
8
New cards
Labial frenulum
Internal surface of the upper and lower lips are attached to the gingivae by a thin, midline mucosal fold
9
New cards
Soft palate
Posterior 1/3 palate (dense CT & muscle).
10
New cards
Hard palate
Anterior 2/3 palate (maxilla & palatines)
11
New cards
Uvula
elevates during swallowing and closes off entrance to nasopharynx
12
New cards
Tongue
manipulates and mixes food with saliva during chewing, and compresses partially digested materials into a bolus.
13
New cards
Bolus
chewed up food
14
New cards
Lingual frenulum
Inferior surface of tongue attaches to oral cavity floor
15
New cards
Saliva functions
• Moistens ingested materials to become a slick bolus.
• Moistens, cleans, lubricates oral cavity structures.
• Chemical digestion of food.
• Antibacterial action
• Dissolves food to enable taste receptor stimulation
• Moistens, cleans, lubricates oral cavity structures.
• Chemical digestion of food.
• Antibacterial action
• Dissolves food to enable taste receptor stimulation
16
New cards
Parotid glands
• Largest salivary gland.
• Near the ear.
• More serous cells
• Near the ear.
• More serous cells
17
New cards
Submandibular glands
• Under mandible.
• Produces 70 % saliva volume.
• More serous cells.
• Produces 70 % saliva volume.
• More serous cells.
18
New cards
Sublingual glands
• Under tongue.
• Produces 3-5% saliva volume.
• More mucous cells.
• Produces 3-5% saliva volume.
• More mucous cells.
19
New cards
What is the difference b/w serous cells vs. mucous cells
Serous cells produce saliva that is 97-99% water & enzymes (salivary amylase, lingual lipase), ions.
Mucous cells secrete mucin, a stringy viscous mucous solution.
Mucous cells secrete mucin, a stringy viscous mucous solution.
20
New cards
Dentition
what teeth are collectively known as
21
New cards
Tooth- crown, root, neck, dental alveoli, pulp
\
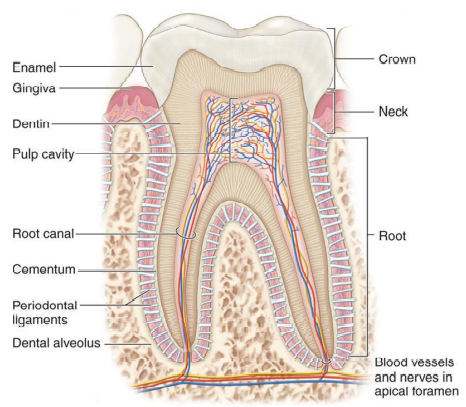
22
New cards
enamel
of the crown it a thin, brittle ceramic material (hardest substance in the body)
23
New cards
Dentin
forms the primary mass of the tooth (harder than bone, shock absorber)
surrounds the pulp cavity (CT, blood vessels, nerves = pulp).
surrounds the pulp cavity (CT, blood vessels, nerves = pulp).
24
New cards
cementum
a hard, calcified layer of tissue that covers the root of the tooth
25
New cards
Deciduous vs. permanent teeth
20 milk/baby teeth, erupt 6-30 months
32 Permanent teeth replaced by the end of adolescence. Third molars (wisdom teeth) emerge 17-25
32 Permanent teeth replaced by the end of adolescence. Third molars (wisdom teeth) emerge 17-25
26
New cards
Incisors
mostly anterior, shaped like chisels, single root. Adapted for biting or nipping off food
27
New cards
Canines
(cuspids or eye-teeth) have pointed tips for puncturing and tearing.
28
New cards
Premolars
(bicuspids) have two cusps (ridges) on the crown for crushing or grinding.
29
New cards
Molars
largest and thickest posterior teeth, have 4-5 cusps for crushing and grinding food. Upper and lower molars lock together to create tremendous crushing force
30
New cards
Pharyngeal constrictors- superior, middle, inferior
muscles form the wall of the pharynx and participate in swallowing
\- Superior 1/3 is skeletal muscle- voluntary
\- Middle 1/3 is mixed skeletal & smooth muscle
\- Inferior 1/3 is smooth muscle- involuntary
\- Superior 1/3 is skeletal muscle- voluntary
\- Middle 1/3 is mixed skeletal & smooth muscle
\- Inferior 1/3 is smooth muscle- involuntary
31
New cards
Stages of deglutition explain
oral, pharyngeal, esophageal
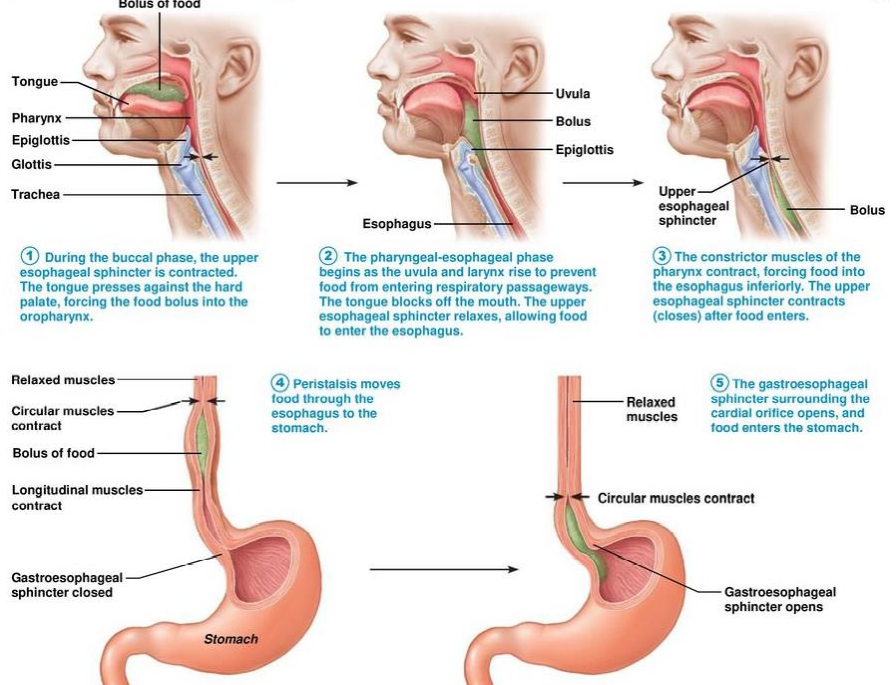
32
New cards
Buccal phase
Tongue presses against hard palate, bolus moves to oropharynx
33
New cards
Pharyngeal-esophageal phase
Pharyngeal constrictors contract, bolus moves into esophagus
34
New cards
Tunics of the GI tract
Mucosa, Submucosa, Muscularis, Adventitia
35
New cards
Mucosa
closest to the lumen; epithelium, areolar CT, smooth muscle
Epithelium + lamina propria + muscularis mucosa
Epithelium + lamina propria + muscularis mucosa
36
New cards
Lamina propria
**a complex mesh of extracellular proteins and structural molecules**
37
New cards
Muscularis mucosae
**lamina muscularis mucosae (or muscularis mucosae) is a thin layer ( lamina) of muscle of the gastrointestinal tract**
38
New cards
Submucosa
lymphatics, mucin glands, blood vessels, nerves
GI tunic under the mucosa with loose CT and vessels
GI tunic under the mucosa with loose CT and vessels
39
New cards
Meissner’s nerve plexus
Submucosal nerve plexus (inner plexus)
between submucosa and muscularis
between submucosa and muscularis
40
New cards
Muscularis externa
inner circular muscle and outer longitudinal smooth muscle
41
New cards
Auerbach’s nerve plexus
Myenteric nerve plexus (outer plexus)
between smooth muscle layers
between smooth muscle layers
42
New cards
Serosa/adventitia
loose CT with blood & lymph vessels
43
New cards
Esophagus
tube that bolus goes from oropharynx to stomach, posterior to trachea.
Approx. 25 cm long, collapsible,
Connects to stomach at gastro-esophageal junction
Approx. 25 cm long, collapsible,
Connects to stomach at gastro-esophageal junction
44
New cards
Esophageal hiatus
an opening in the diaphragm
45
New cards
Stomach
• Upper left quadrant of abdomen.
• It continues the mechanical and chemical digestion of the bolus.
• The bolus eventually is processed into a paste-like soup called chyme.
• Possesses three layers of muscle to aid in the mechanical processing of ingested materials
• It continues the mechanical and chemical digestion of the bolus.
• The bolus eventually is processed into a paste-like soup called chyme.
• Possesses three layers of muscle to aid in the mechanical processing of ingested materials
46
New cards
Chyme
what the bolus turns into in the stomach
47
New cards
Cardia
toppish region of the stomach where the cardiac sphincter is
48
New cards
Fundus
top of the stomach
49
New cards
Body
the body of the stomach aka middle
50
New cards
Pylorus
bottomish region of the stomach where the pylorus sphincter is
51
New cards
Greater & lesser curvature
big curve and small curve of stomach shape
52
New cards
Rugae
Longitudinal folds of the stomach mucosa & submucosa
53
New cards
Oblique muscle layer
Additional inner muscle layer of the stomach
54
New cards
what prevents food from coming up from your throat?
Upper esophageal sphincter
55
New cards
Cardiac (lower esophageal) sphincter
Sphincter regulating bolus passage from esophagus to stomach
56
New cards
Pyloric sphincter
Sphincter regulating chyme passage from stomach to duodenum
57
New cards
Appendix
Worm-like organ with lymphocytes & bacterial reserves
58
New cards
Ascending colon
Section of large intestine between the cecum & transverse colon
59
New cards
Bile
Green-yellow alkaline solution, bile salts & phospholipids
60
New cards
Descending colon
Large intestine region between the transverse & sigmoid colons
Travels inferiorly from splenic flexure on the left abdomen. • Adjacent to the ileum and terminates in the sigmoid colon.
Travels inferiorly from splenic flexure on the left abdomen. • Adjacent to the ileum and terminates in the sigmoid colon.
61
New cards
Duodenum
Proximal small intestine, has most plicae & villi
• C- shaped, URQ. • Entry- Pyloric sphincter of the stomach. • Exit- duodenojejunal junction. • Pancreas → major duodenal papilla permits pancreatic secretions and bile to enter. • Kick starts chemical digestion of chyme.
• C- shaped, URQ. • Entry- Pyloric sphincter of the stomach. • Exit- duodenojejunal junction. • Pancreas → major duodenal papilla permits pancreatic secretions and bile to enter. • Kick starts chemical digestion of chyme.
62
New cards
Epiploic appendages
Small fat deposits attached to haustra & taenia coli
63
New cards
Gall bladder
Small sac that holds and concentrates bile until needed
64
New cards
Haustra
Pocket-like bumps of the wall of the large intestine
65
New cards
Hemorrhoids
Dilated veins in the anus and rectum, may lead to complications
66
New cards
Hepatopancreatic ampulla
Junction point of the bile duct & pancreatic duct
67
New cards
Ileocecal valve
Sphincter regulating chyme passage from small to large intestine
68
New cards
Ileum
Distal part of small intestine with fewest villi & microvilli
distal segment • Longest portion, smallest lumen • Terminates at ileocecal valve → large intestine
distal segment • Longest portion, smallest lumen • Terminates at ileocecal valve → large intestine
69
New cards
Jejunum
Middle part of small intestine, most absorption occurs here
Both chemical digestion and nutrient absorption.
Both chemical digestion and nutrient absorption.
70
New cards
Left colic flexure
Splenic flexure; 90º bend between transverse & descending colons; under spleen
71
New cards
Mesentery
Series of peritioneal folds attaches organs to abdominal wall
72
New cards
Pancreas
Digestive secretions include digestive juices & bicarbonate
73
New cards
Pharyngeal constrictors
Three sets of muscle, contain both skeletal & smooth muscle
74
New cards
Rectal valve
Folds in the rectal wall that hold feces during flatulence
75
New cards
Right colic flexure
aka hepatic flexure; 90º bend between ascending & transverse colons; under liver
76
New cards
Sigmoid colon
S-shaped region of the colon leading to the rectum
77
New cards
Tenia coli
Unique 3-banded arrangement of colon muscularis externa
78
New cards
Transverse colon
Section of the large intestine that runs horizontally
79
New cards
Adventitia
Outer serosa tissue layer of the GI system organs
80
New cards
Emulsification
Bile acts on lipids to permit digestion and absorption
81
New cards
Endocrine pancreas
Islets of Langerhans secrete insulin & glucagon (5%)
82
New cards
Exocrine pancreas
Pancreatic acinar cells secrete digestive juices (90%)
83
New cards
Hepatic portal system
Deoxygenated blood & nutrients from SI processed in liver
84
New cards
Lacteals
Lymphatic vessels in each villus for fat absorption
85
New cards
Microvilli
Cell membrane & cytoplasm folding’s for absorption
86
New cards
Plicae (circularis)
Large folds of the small intestine mucosa and submucosa
\
The mucosal and submucosal tunics are thrown into folds called the circular folds
\
The mucosal and submucosal tunics are thrown into folds called the circular folds
87
New cards
Villi
Finger-like projections of the mucosa to increase surface area
88
New cards
Small intestine region
Duodenum
Jejunum
Ileum
Jejunum
Ileum
89
New cards
major duodenal papilla
permits pancreatic secretions and bile to enter
90
New cards
Ileocecal valve
valve that connects small intestine with large intestine
91
New cards
Large intestine
Diameter is 6.5 cm vs 2.5 cm lumen of small intestine. • Absorbs fluids and ions, compacts indigestible wastes and solidifies fecal material. • Stores and expels feces
92
New cards
Cecum
Proximal segment of the large intestine. • Blind-end sac located in LRQ. • Ileocecal valve represents junction of small & large intestines.
93
New cards
Transverse mesocolon
ligament that holds the transverse colon up
94
New cards
Sigmoid mesocolon
ligament that holds the sigmoid colon up
95
New cards
Rectum
• Muscular tube that expands to store feces prior to defecation • Rectum terminates at the anal canal.
96
New cards
Rectal valves
3 thick transverse folds of rectal wall that allow gas to pass while retaining fecal material (\~ 500 ml/day).
97
New cards
Anal canal
Distal end of large intestine
98
New cards
Anal columns
line internal surface
99
New cards
Anal sinuses
secrete mucin for lubrication during defecation
100
New cards
Internal & external anal sphincters
anal sphincters open and close the anal canal during defecation
no control over internal one but some control over external one
no control over internal one but some control over external one
Explore top notes
Unit 11: The Industrial Revolution and Imperialism. The division of the world - Point 2
Updated 1078d ago0.0(0)
Unit 11: The Industrial Revolution and Imperialism. The division of the world - Point 2
Updated 1078d ago0.0(0)