coasts pt. 1
4.8(6)
Card Sorting
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
gateway 1
Last updated 8:07 AM on 9/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
1
New cards
what is a coast
area where land meets the sea and/or ocean
\
covers area of land that is affected by waves, the tides
\
covers area of land that is affected by waves, the tides
2
New cards
how and why are coastal environments different & dynamic
* waves - main shaping force of the coast | power of waves erode landforms
* currents - large scale, continuous movement of seawater affects erosion, transportation and deposition (ETD)
* tides - daily rise and fall of the sea level | affects ETD
* geology - arrangement & composition of the rocks in the area | affects speed of erosion
* human activities - develop coastline so they affect the conditions of coastal environment | affects ETD
* types of ecosystem - communities of plants & animals interact with each other & the environment | affects ETD
* currents - large scale, continuous movement of seawater affects erosion, transportation and deposition (ETD)
* tides - daily rise and fall of the sea level | affects ETD
* geology - arrangement & composition of the rocks in the area | affects speed of erosion
* human activities - develop coastline so they affect the conditions of coastal environment | affects ETD
* types of ecosystem - communities of plants & animals interact with each other & the environment | affects ETD
3
New cards
factors that affect waves
1. wind velocity - faster wind → greater wave energy
2. wind duration - longer it blows → larger wave
3. wind distance - further the fetch → greater wave energy
4
New cards
wave energy is determined by …
wave steepness (height/length)
wave period (time taken to travel through one wavelength)
wave period (time taken to travel through one wavelength)
5
New cards
shallow water waves compared to deep water
shallow water - shorter in length, higher in height
* shallow water waves interact with the seabed
* friction slows down the speed of the wave
* its shape becomes **elliptical**
* wave height is high and length is short
* wave crest becomes steep before toppling over, breaking wave on the coast, releasing wave energy
\
deeper water - longer in length, lower in height
* do not interact with seabed
* no friction slows the wave down
* maintains its **circular shape**
* height is low and length is long
* shallow water waves interact with the seabed
* friction slows down the speed of the wave
* its shape becomes **elliptical**
* wave height is high and length is short
* wave crest becomes steep before toppling over, breaking wave on the coast, releasing wave energy
\
deeper water - longer in length, lower in height
* do not interact with seabed
* no friction slows the wave down
* maintains its **circular shape**
* height is low and length is long
6
New cards
swash
when waves break on the beach → water rushes up
moves up the beach, **carrying** sediments up
loses energy due to gravity and friction with the ground
moves up the beach, **carrying** sediments up
loses energy due to gravity and friction with the ground
7
New cards
backwash
when waves return to the sea → water rushes down
due to gravity it **carries** sediments **back towards** the sea
loses energy due to gravity and friction with the ground
due to gravity it **carries** sediments **back towards** the sea
loses energy due to gravity and friction with the ground
8
New cards
constructive waves
occur during calm weather
occur on gentle slope & sheltered coast
\
**long** wave length & **low** wave height
**low** wave frequency: 6-8mins
\
swash > backwash - strong swash carries more sediments up the coast while weak backwash carries less sediments towards sea
@@deposition dominant@@ process
\
result in @@low energy environment@@ with spilling breakers
produce @@gentle slope@@ with @@fine sediments@@
occur on gentle slope & sheltered coast
\
**long** wave length & **low** wave height
**low** wave frequency: 6-8mins
\
swash > backwash - strong swash carries more sediments up the coast while weak backwash carries less sediments towards sea
@@deposition dominant@@ process
\
result in @@low energy environment@@ with spilling breakers
produce @@gentle slope@@ with @@fine sediments@@
9
New cards
destructive waves
occur during stormy/windy weather
occur on steep slope & exposed coast
\
**short** wave length & **high**wave height
**high** wave frequency: 10-14mins
\
backwash > swash - **weak** swash carries **less** sediments up the coast while **strong** backwash carries **more** sediments towards sea
@@erosion dominant@@ process
\
result in @@high energy environment@@ with surging breakers
produce @@steep slope@@ with @@coarse sediments@@
occur on steep slope & exposed coast
\
**short** wave length & **high**wave height
**high** wave frequency: 10-14mins
\
backwash > swash - **weak** swash carries **less** sediments up the coast while **strong** backwash carries **more** sediments towards sea
@@erosion dominant@@ process
\
result in @@high energy environment@@ with surging breakers
produce @@steep slope@@ with @@coarse sediments@@
10
New cards
wave refraction
* refraction refers to the process in which waves __change direction__ when they approach a coast
* waves approach an @@uneven coast@@
* they change direction @@due to friction@@ between seawater and seabed which causes a @@change in wave speed@@
* waves @@converge on headlands@@ and @@diverge at bays@@
* when waves converge on headlands - @@increased wave height@@ and @@greater erosive energy@@ (**EROSION** dominant)
* when waves diverge at bays - @@decreased wave height@@ and @@lower erosive energy@@ (**DEPOSITION** dominant)
* @@uneven impact@@ on shoreline
* waves approach an @@uneven coast@@
* they change direction @@due to friction@@ between seawater and seabed which causes a @@change in wave speed@@
* waves @@converge on headlands@@ and @@diverge at bays@@
* when waves converge on headlands - @@increased wave height@@ and @@greater erosive energy@@ (**EROSION** dominant)
* when waves diverge at bays - @@decreased wave height@@ and @@lower erosive energy@@ (**DEPOSITION** dominant)
* @@uneven impact@@ on shoreline
11
New cards
hydraulic action
* waves strike against rock surface to @@trap air in its joints@@
* air is @@compressed by the oncoming waves@@ which exerts pressure on the joints
* over time, @@repeated compression@@ and @@pressure weaken the joints@@
* rocks shatter
\
lines of weaknesses
* air is @@compressed by the oncoming waves@@ which exerts pressure on the joints
* over time, @@repeated compression@@ and @@pressure weaken the joints@@
* rocks shatter
\
lines of weaknesses
12
New cards
abrasion
* waves break and the sediments it carried are hurled against the rock surfaces and the coast
* rock sediments @@knock and scrape@@ against the coat & rock surfaces
* over time, repeated hurling action & scraping @@weaken the surfaces@@
* surface breaks down
* @@cliff is undercut@@
\
sediment on sediment
* rock sediments @@knock and scrape@@ against the coat & rock surfaces
* over time, repeated hurling action & scraping @@weaken the surfaces@@
* surface breaks down
* @@cliff is undercut@@
\
sediment on sediment
13
New cards
attrition
* waves carry rock particles which @@rub or hit@@ against each other
* over time repeated contact @@break down and smooth@@ the surfaces of these rock particles
\
rock on rock
* over time repeated contact @@break down and smooth@@ the surfaces of these rock particles
\
rock on rock
14
New cards
solution
* seawater @@reacts chemically@@ with water soluble minerals in the coast and rock surfaces to dissolve them
* over time the rocks and surfaces @@weaken and disintegrate@@
\
dissolve
* over time the rocks and surfaces @@weaken and disintegrate@@
\
dissolve
15
New cards
longshore drift
result of both longshore currents & beach drift (transportation)
\
* waves approach coastline at an @@oblique angle@@ due to direction of prevailing wind
* creates longshore currents which flow parallel to the coast
* as waves break, @@swash carries sediments up@@ the beach at the same angle as the wave approached
* sediments are then @@brought perpendicularly down@@ the beach through backwash due to gravity
* @@zig-zag movement@@ of sediments along the beach is known as @@beach drift@@
* both longshore currents & beach drift @@transport sediments along coast for some distance@@
\
* waves approach coastline at an @@oblique angle@@ due to direction of prevailing wind
* creates longshore currents which flow parallel to the coast
* as waves break, @@swash carries sediments up@@ the beach at the same angle as the wave approached
* sediments are then @@brought perpendicularly down@@ the beach through backwash due to gravity
* @@zig-zag movement@@ of sediments along the beach is known as @@beach drift@@
* both longshore currents & beach drift @@transport sediments along coast for some distance@@
16
New cards
differences between **sheltered coast** and **exposed coast**
sheltered coast:
* calm conditions with constructive waves
* strong swash - more materials being pushed up
* weak backwash - less materials carried down
* finer materials deposited further inland
* coarser materials nearer the sea
\
exposed coast:
* strong wind with destructive waves
* weak swash - less materials being pushed up
* strong backwash - more materials carried down the beach
* coarser materials deposited further inland
* finer materials nearer the sea
* calm conditions with constructive waves
* strong swash - more materials being pushed up
* weak backwash - less materials carried down
* finer materials deposited further inland
* coarser materials nearer the sea
\
exposed coast:
* strong wind with destructive waves
* weak swash - less materials being pushed up
* strong backwash - more materials carried down the beach
* coarser materials deposited further inland
* finer materials nearer the sea
17
New cards
types of landforms
erosional
1. cliffs and wave-cut platforms
2. headlands and bays
3. caves, arches, stacks, stumps
\
depositional
1. beaches
2. spits and tombolos
1. cliffs and wave-cut platforms
2. headlands and bays
3. caves, arches, stacks, stumps
\
depositional
1. beaches
2. spits and tombolos
18
New cards
factors affecting coastal erosion
1. types of waves
1. destructive waves
2. structure of rocks
1. lines of weaknesses
2. soft rocks
3. composition of rocks
1. easily soluble minerals
4. position of coast
1. open and unprotected by natural/man-made structures
19
New cards
factors affecting coastal deposition
1. types of waves
1. constructive waves
2. supply of sediments
1. large quantity of sediments from coastal erosion and transportation
2. weak energy of waves leading to low carrying capacity of waves
3. gradient of slope
1. the more gentle the slope, the more wave energy spread out and reduced due to friction and gravity leading to constructive waves
4. position of coast
1. protected/sheltered by natural/man-made structures
20
New cards
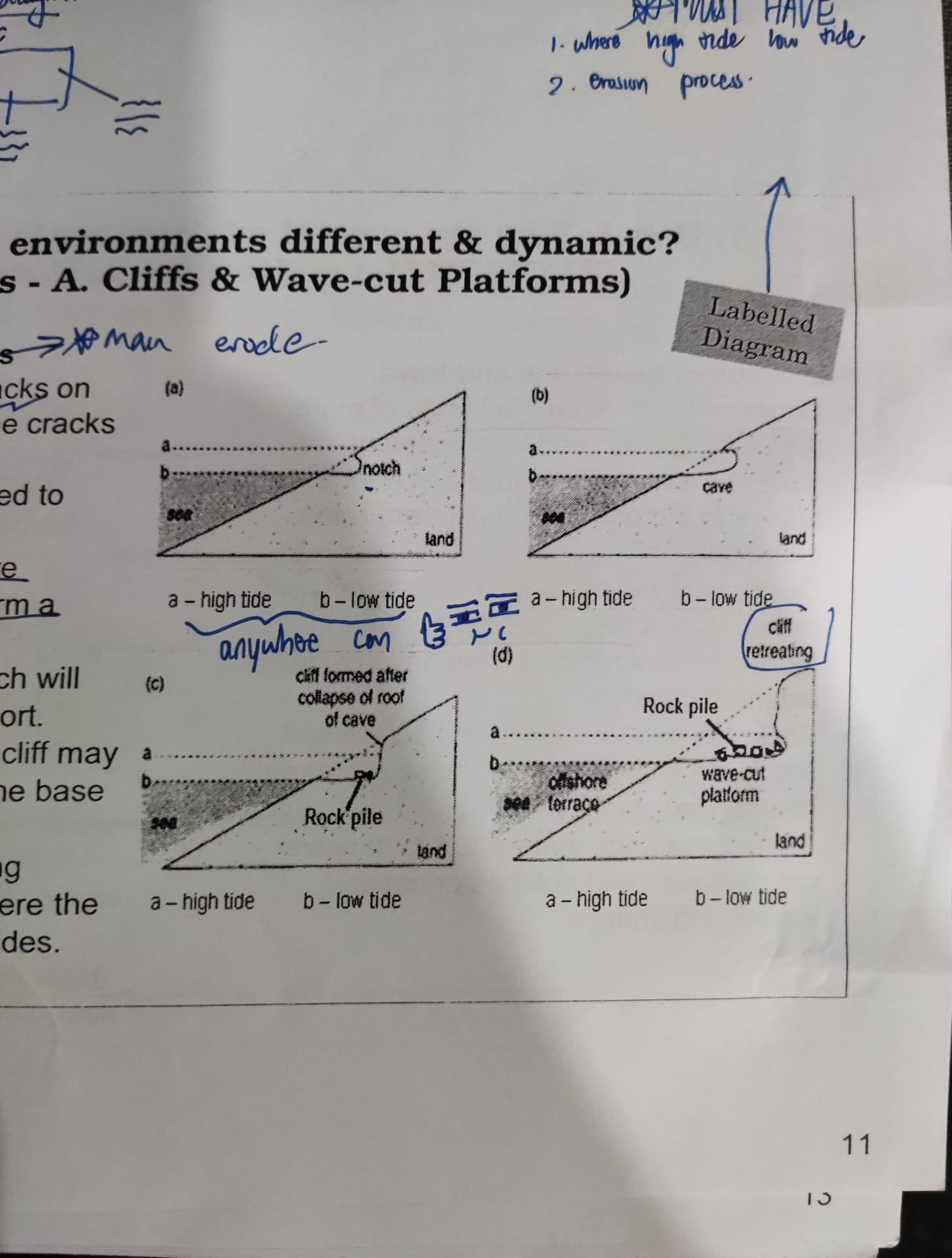
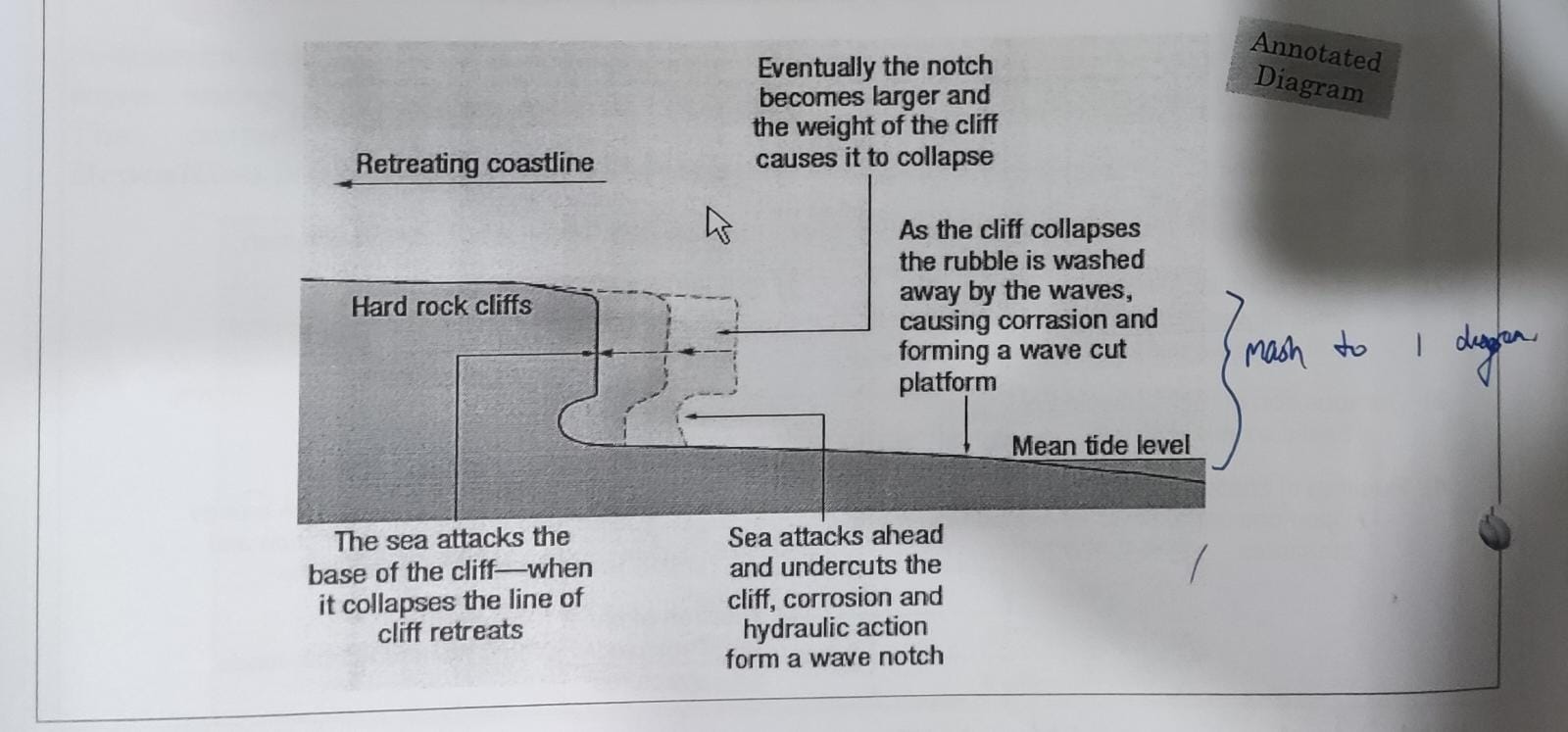
cliffs & wave-cut platforms (labelled diagram)
* @@hydraulic action and abrasion@@ erode cracks on the rock surfaces, gradually enlarging cracks to form a notch
* this @@notch is further eroded@@ and deepened to @@produce a cave@@
* as the process continues, @@roof of the cave collapses due to a lack of support@@ and form a @@steep cliff@@
* over time, an @@overhanging cliff forms@@ which will also in turn collapse due to a lack of support
* the materials deposited at the foot of the cliff may be @@carried by waves@@ and thrown against the base of the cliff to @@cause more erosion@@
* the cliff @@retreats inland@@ and a @@gently sloping wave-cut platform appears@@ at the base where the cliff used to be and is @@submerged at high tides@@
* this @@notch is further eroded@@ and deepened to @@produce a cave@@
* as the process continues, @@roof of the cave collapses due to a lack of support@@ and form a @@steep cliff@@
* over time, an @@overhanging cliff forms@@ which will also in turn collapse due to a lack of support
* the materials deposited at the foot of the cliff may be @@carried by waves@@ and thrown against the base of the cliff to @@cause more erosion@@
* the cliff @@retreats inland@@ and a @@gently sloping wave-cut platform appears@@ at the base where the cliff used to be and is @@submerged at high tides@@
21
New cards
cliff & wave-cut platforms (annotated diagram)
22
New cards
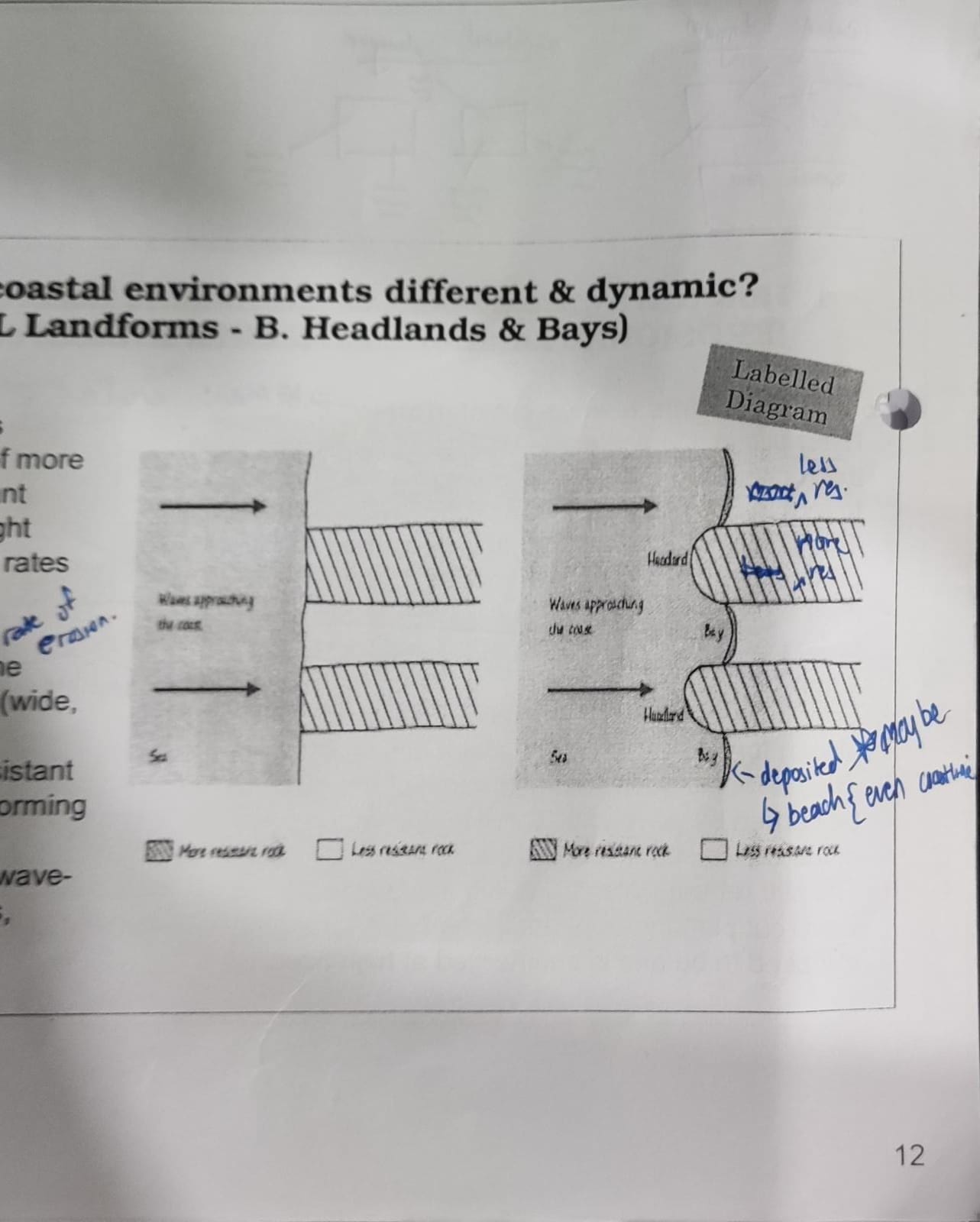
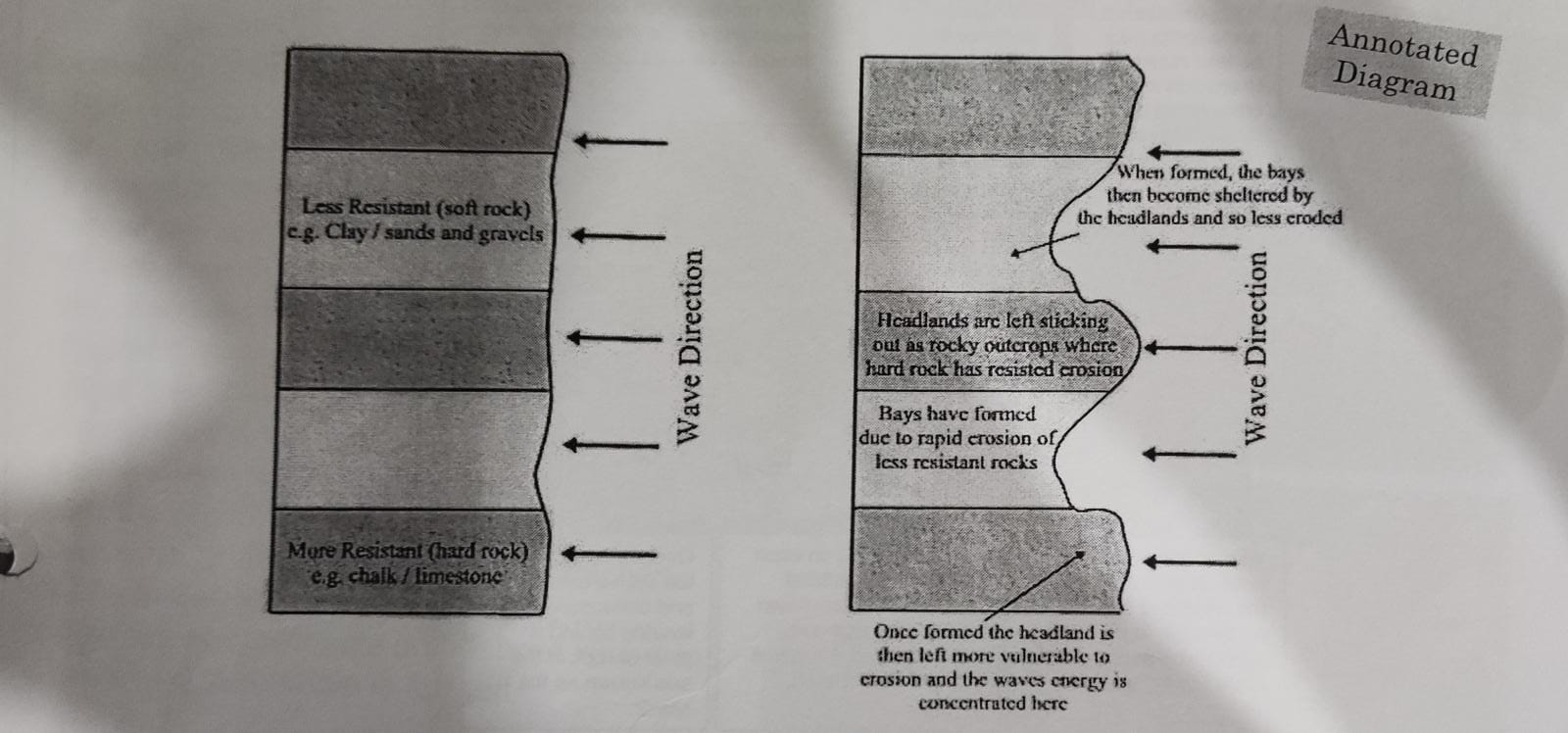
headlands and bays (labelled diagram)
* coastlines with @@alternate bands@@ of more resistant and less resistant rock layers arranged at right angles to the coast have @@different rates of erosion@@
* destructive waves @@erode the less resistant rocks more quickly@@ than the more resistant rocks to @@form bays@@
* while the @@harder rocks is more resistant@@ and is left @@protruding@@ into the sea @@forming headlands@@
* at the headlands there @@often form wave-cut platforms@@ and notches or caves, stacks and stumps
* destructive waves @@erode the less resistant rocks more quickly@@ than the more resistant rocks to @@form bays@@
* while the @@harder rocks is more resistant@@ and is left @@protruding@@ into the sea @@forming headlands@@
* at the headlands there @@often form wave-cut platforms@@ and notches or caves, stacks and stumps
23
New cards
headlands and bays (annotated diagram)
24
New cards
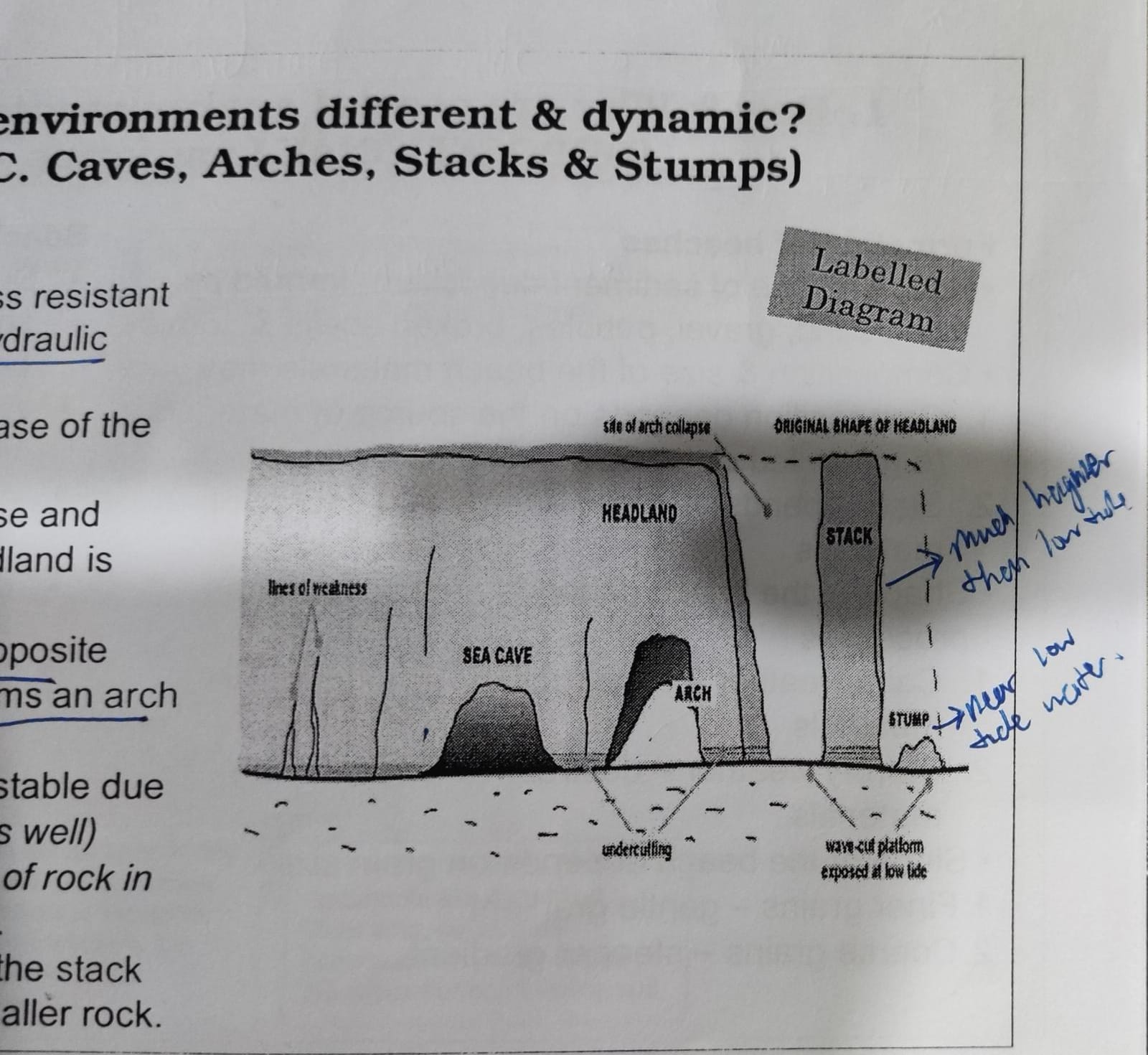
caves, arches, stacks & stumps (labelled diagram)
* within headlands, some rocks may be @@less resistant to erosion@@ thus @@eroded more quickly@@ by hydraulic action and abrasion
* waves @@enlarge lines of weaknesses@@ at the base of the headland to @@form a notch@@
* the @@continuous action of erosion@@ at the base and undercutting it @@forms a cave when the headland is hollowed@@
* @@wave refraction@@ causes @@two caves at the opposite sides@@ of the headland to be @@aligned and forms an arch@@
* over time the @@roof of the arch becomes unstable@@ due to further @@erosion and gravity,@@ causing its @@collapse to form a stack@@
* continued wave erosion and weathering of the stack will @@break the rock down to form stump@@ - smaller rock
* waves @@enlarge lines of weaknesses@@ at the base of the headland to @@form a notch@@
* the @@continuous action of erosion@@ at the base and undercutting it @@forms a cave when the headland is hollowed@@
* @@wave refraction@@ causes @@two caves at the opposite sides@@ of the headland to be @@aligned and forms an arch@@
* over time the @@roof of the arch becomes unstable@@ due to further @@erosion and gravity,@@ causing its @@collapse to form a stack@@
* continued wave erosion and weathering of the stack will @@break the rock down to form stump@@ - smaller rock
25
New cards
caves, arches, stacks & stumps (annotated diagram)

26
New cards
formation of beaches
beach - zone of sediment deposition, formed by loose sand, gravel, pebbles, broken shells & corals
\
composition & size of the beach materials may vary
1. composition depends on source of materials
2. size depends on wave energy and source of materials
\
shape of the beach depends on coastal processes
1. calm weather - constructive waves deposit materials
2. stormy weather - destructive waves erode material
\
slope of the beach depends on grain size
1. finer grains - gentle gradient
2. coarse grains - steeper gradient
\
composition & size of the beach materials may vary
1. composition depends on source of materials
2. size depends on wave energy and source of materials
\
shape of the beach depends on coastal processes
1. calm weather - constructive waves deposit materials
2. stormy weather - destructive waves erode material
\
slope of the beach depends on grain size
1. finer grains - gentle gradient
2. coarse grains - steeper gradient
27
New cards
beaches at the bays\`
* due to wave refraction, waves @@approach the shallow sea in front of the headland first@@ before reaching the adjacent bays
* as wave energy tends to @@concentrate at the headland@@, @@erosion@@ occurs there
* along the bays, @@waves are diverged@@, thus energy is @@spread out and weakened@@
* @@deposition of sediments occurs@@ along the bays and over time, @@forming a sandy beach@@
* as wave energy tends to @@concentrate at the headland@@, @@erosion@@ occurs there
* along the bays, @@waves are diverged@@, thus energy is @@spread out and weakened@@
* @@deposition of sediments occurs@@ along the bays and over time, @@forming a sandy beach@@
28
New cards
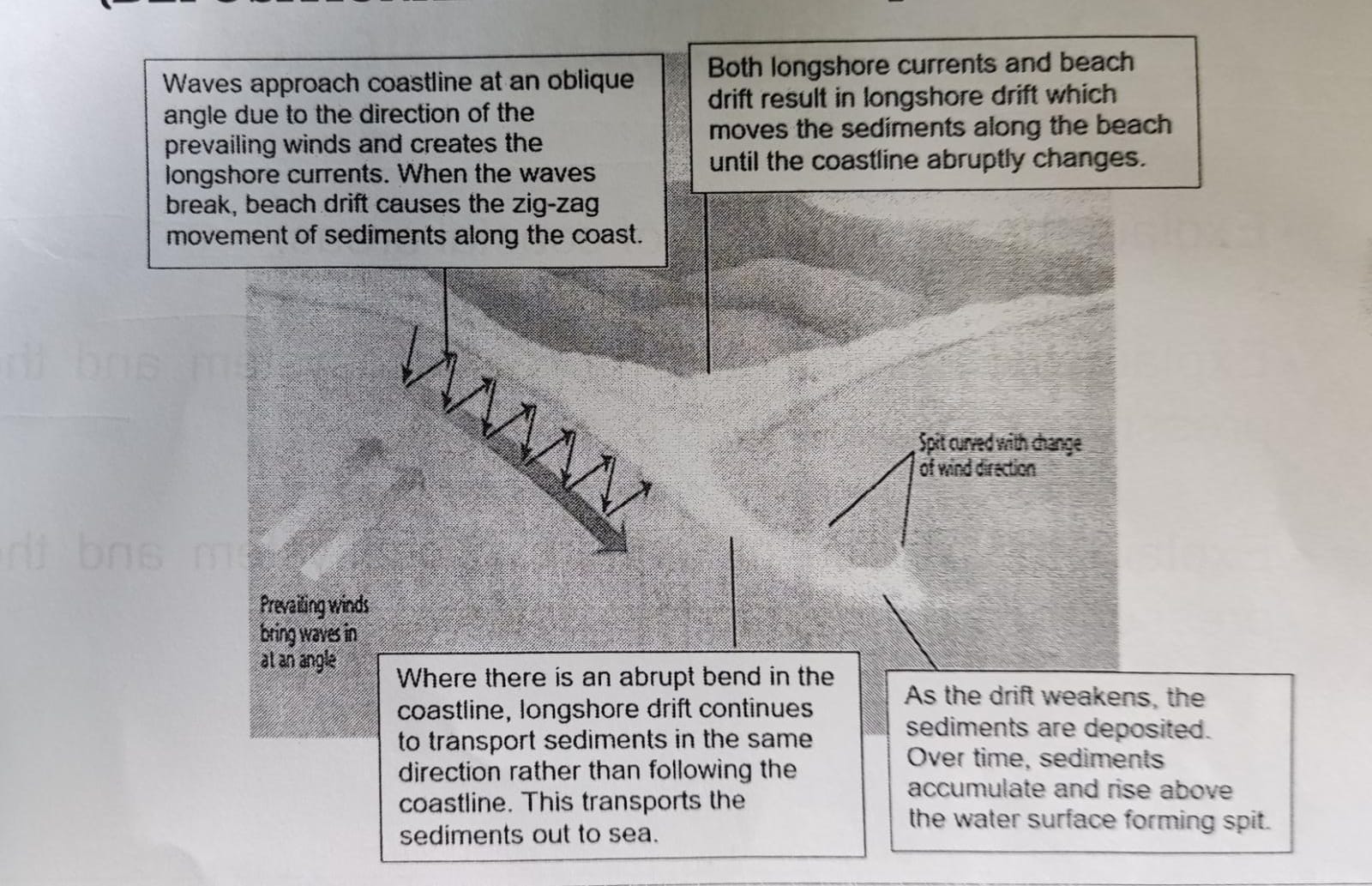
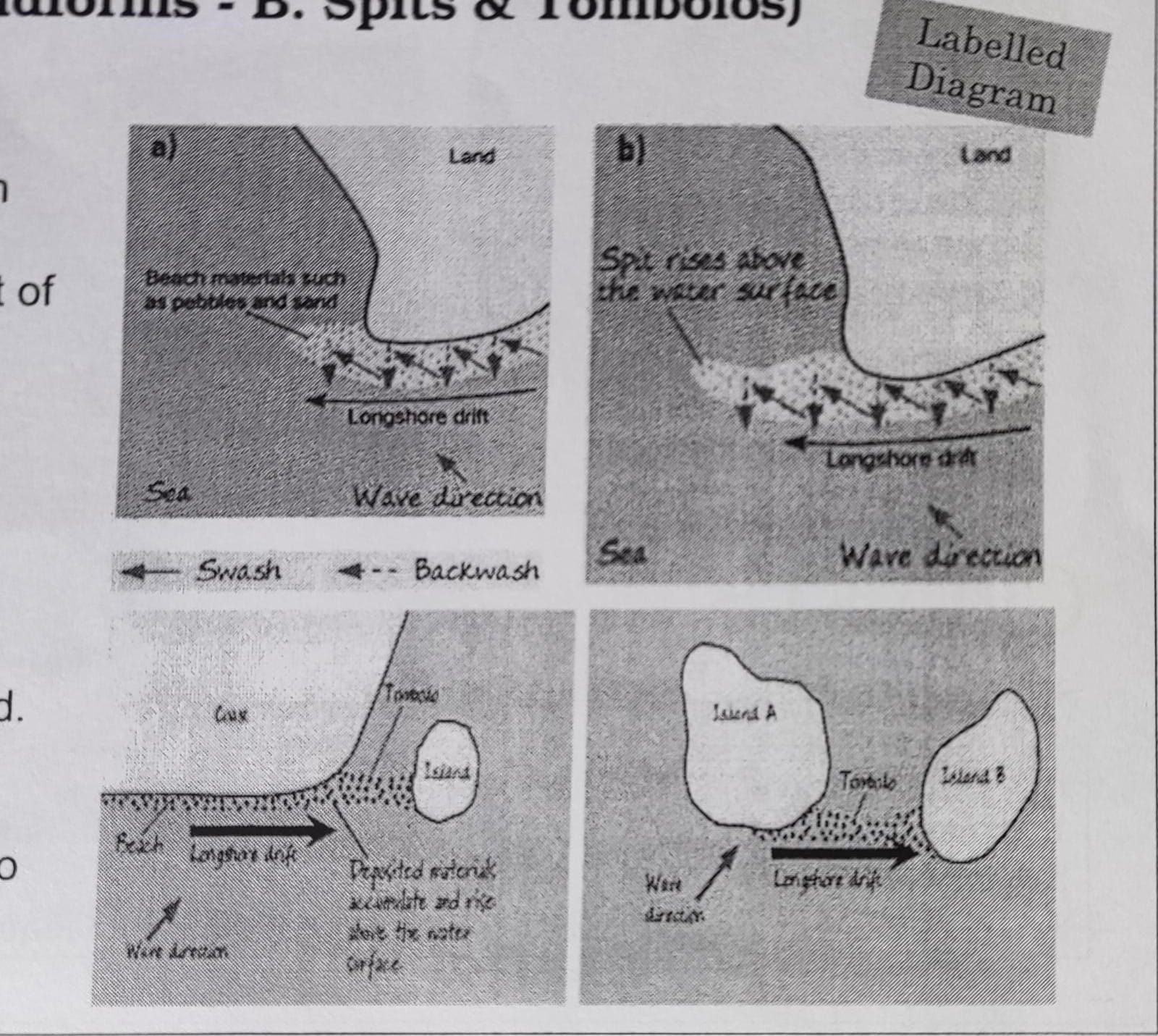
spits and tombolos (labelled diagram)
spit - long, narrow ridge of sediments with one end attached to the land
\
* @@formed by longshore drift@@ which is a result of longshore currents & beach drift
* where there is an @@abrupt bend in the coastline@@, @@longshore drift continues to transport sediments in the same direction@@ rather than following the coastline → this @@transports the sediments out to the sea@@
* as the @@strength of the drift weakens away@@ from the coast, the sediments are @@deposited@@
* over time, sediments @@accumulate and rise@@ above the water surface @@forming spit@@
* when the spit @@connects an offshore island@@ to a mainland, a @@tombolo is formed@@
\
* @@formed by longshore drift@@ which is a result of longshore currents & beach drift
* where there is an @@abrupt bend in the coastline@@, @@longshore drift continues to transport sediments in the same direction@@ rather than following the coastline → this @@transports the sediments out to the sea@@
* as the @@strength of the drift weakens away@@ from the coast, the sediments are @@deposited@@
* over time, sediments @@accumulate and rise@@ above the water surface @@forming spit@@
* when the spit @@connects an offshore island@@ to a mainland, a @@tombolo is formed@@
29
New cards
spits and tombolos (annotated diagram)